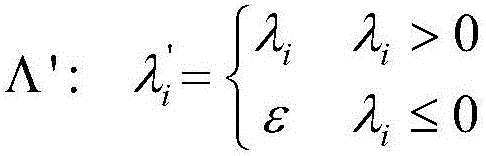Improved Latin hypercube sampling method suitable for non-positive correlation control
A Latin hypercube and correlation technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems that non-positive definite matrices cannot be obtained, the cumulative distribution function of input variables is difficult to obtain accurately or is unknown, and achieve calculation Fast speed, small error, and the effect of expanding the scope of application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] The present invention provides an implementation case of the improved Latin hypercube sampling method suitable for non-positive definite correlation control:
[0059] The determination of cumulative distribution function and discrete data matrix in step S1 includes:
[0060] Connect distributed power to 5 nodes of PG&E69 node system. Taking photovoltaics as an example, the photovoltaic model adopts the beta distribution model, the selection of shape parameters is: α=0.9, β=0.85, and the capacity is 100kVA. Determine the cumulative distribution function of the input variable as The correlation coefficient matrix between 5 photovoltaic output power samples is P 5 .
[0061] In step S2, when the distribution function is known, sampling by importance sampling method includes:
[0062] Sampling principle The value of the kth variable a is: when x=x ka hour, Z k (x ka )have the maximum value in .
[0063] In step S3, based on the positive definite spectrum deco...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com