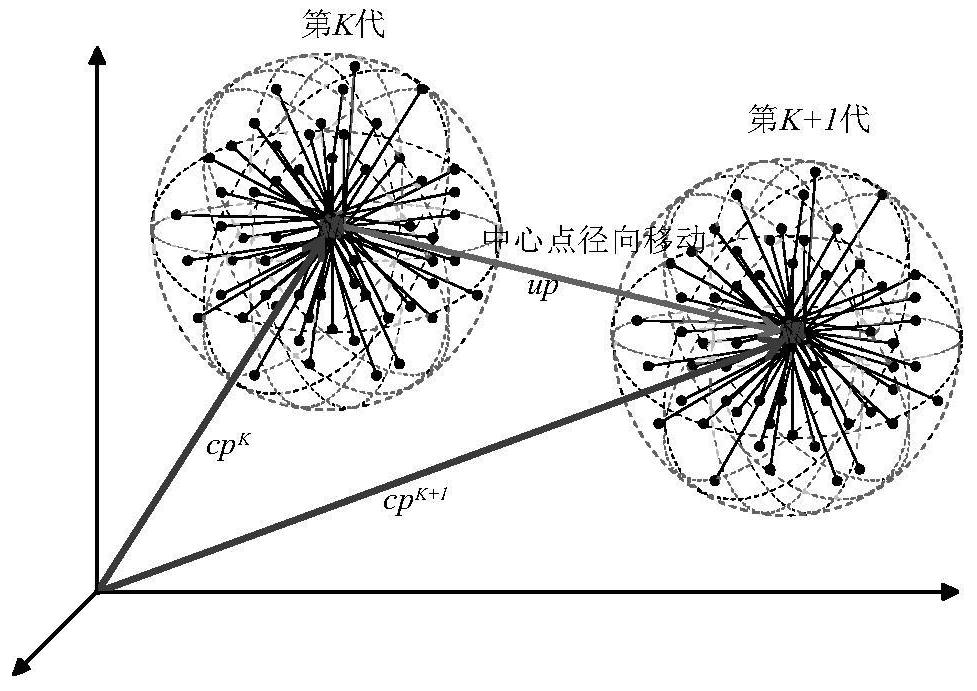
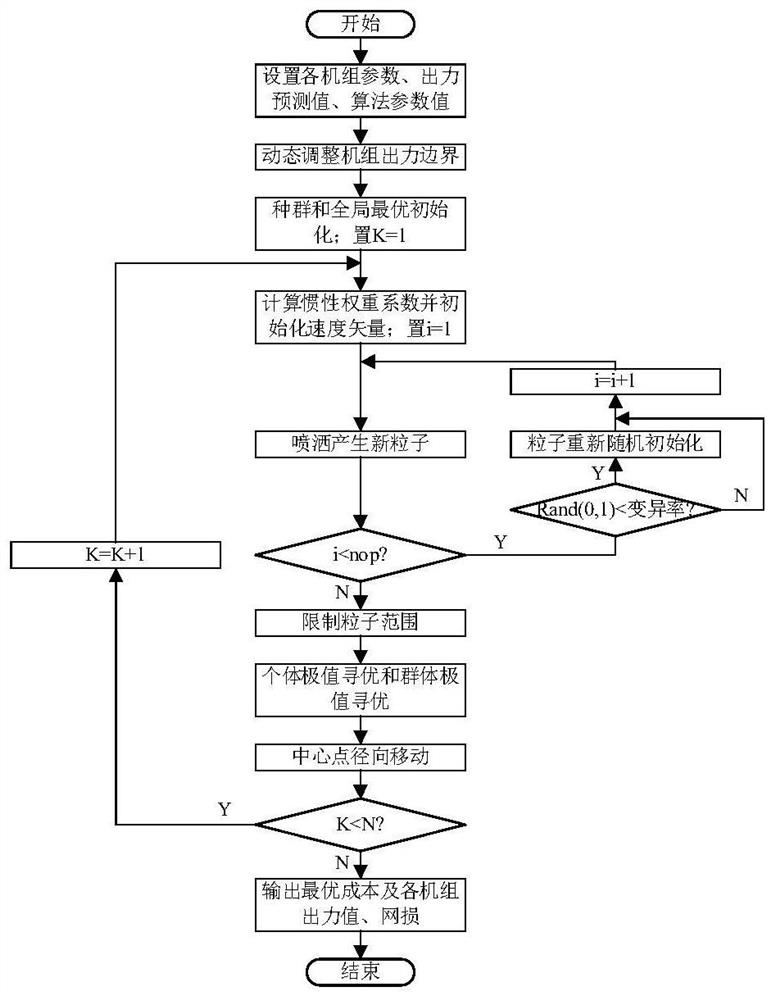
Economic dispatch method of power system with wind farm based on improved radial movement algorithm
A technology for economic scheduling and power systems, applied in wind power generation, single-network parallel feeding arrangements, etc., can solve problems such as time-consuming, complex algorithms, and easy to fall into local optimal solutions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0110] Taking a 6-unit IEEE 30-node power system with two wind farms as an example, the model considers all items in formula (1), does not consider network loss and backup constraints, and the algorithm parameters take the value C 1 =0.7, C 2 =0.8, nop=50, N=200, calculate the unit output, total unit output (P / MW) and total consumption cost (C / USD·h -1 ), and compared with the results of QPSO and GABC algorithms proposed in related literature.
[0111] (1) First consider the case of no wind power, set nod=6, use IRMO to solve the model, the results are shown in Table 1.
[0112] Table 1 The optimization results of each algorithm under different loads without wind power model
[0113]
[0114]
[0115] It can be seen from Table 1 that under the load of 1200MW, the results obtained by QPSO, GABC algorithm and IRMO are 29555.72USD, 29147.00USD and 29109.64USD respectively. In contrast, the cost of IRMO is 445.39USD less than that of QPSO, and 37.36USD less than that of GA...
Embodiment 2
[0121] Taking the 10-unit system as an example, consider formulas (2), (3) and (6) in the model, consider network loss and backup constraints, dispatch period H=24h, and time interval is 1h. The total output power of the grid-connected wind farm is 100MW, a total of 50 wind turbines, and the system load forecast value P D , wind power prediction value w av See Table 3, and see Table 4 for the values of algorithm-related parameters.
[0122] Table 3 Wind power and load forecast values in each time period
[0123]
[0124] Table 4 Algorithm parameter value table
[0125]
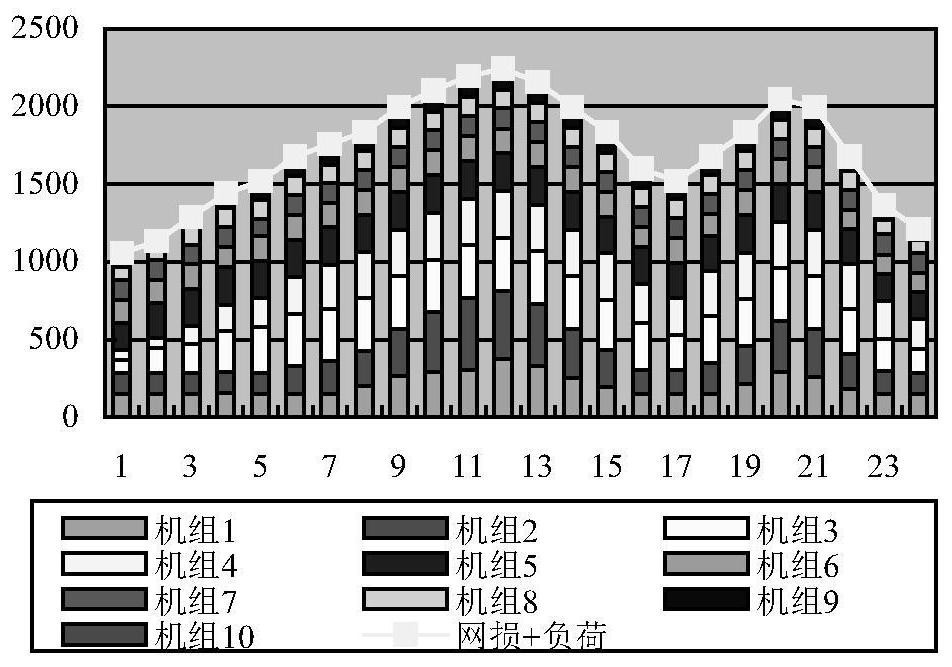
[0126] (1) First consider the case of no wind power, and use IRMO to solve the DED model. The obtained unit output, network loss and cost in each period of 24h are shown in Table 5, and the total is represented by T. The total cost of 24h system consumption is 2476739USD, and the power borne by each unit is as follows: image 3 shown. It can be seen that this scheduling combination satisfies the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com