A new energy vehicle charging pile wire
A technology for new energy vehicles and charging piles, which is applied to power cables, circuits, and electrical components with shielding layers/conductive layers to achieve strong conductivity, low resistivity, and reduced charging time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
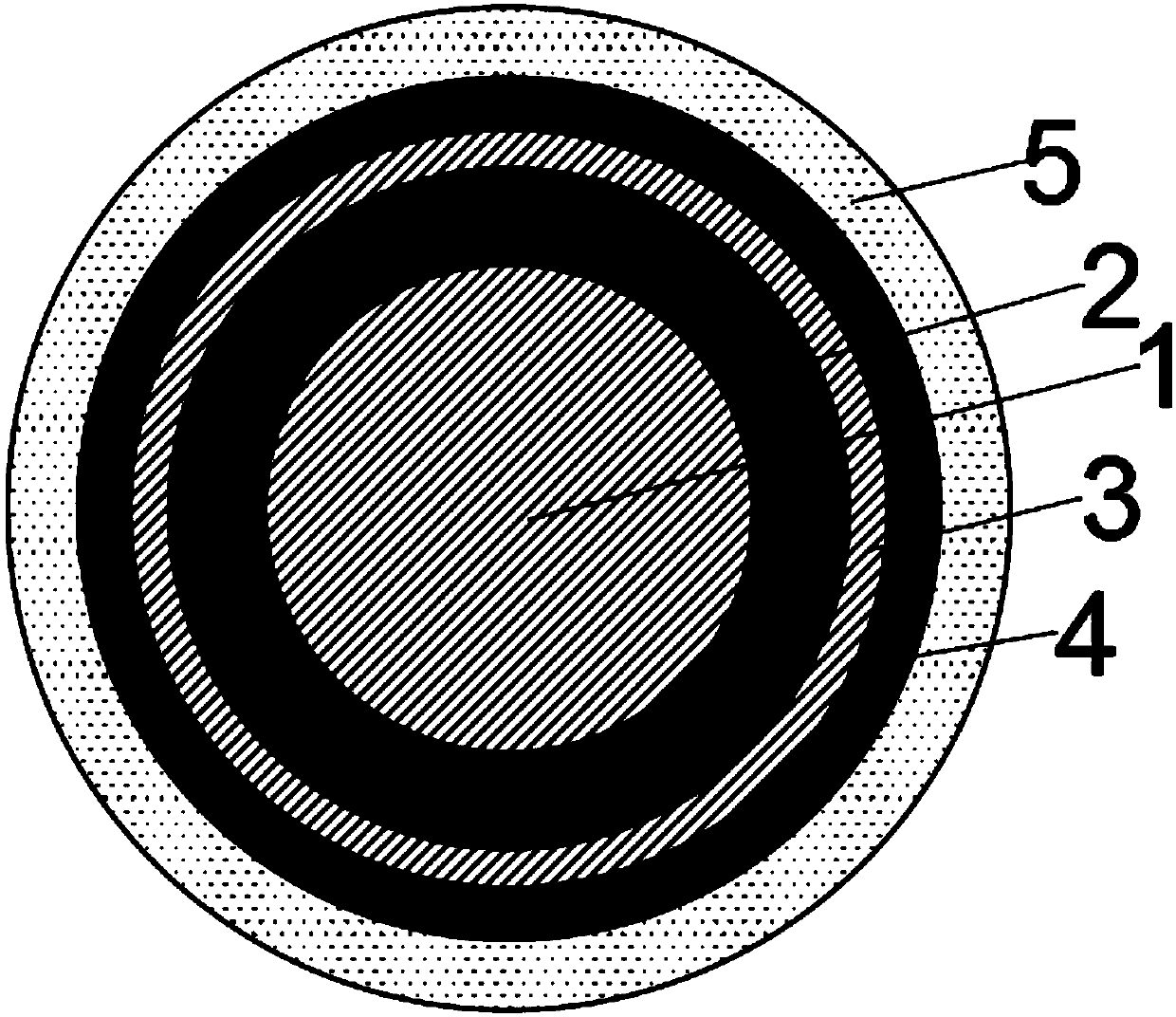
[0043] A new energy vehicle charging pile wire, comprising graphene 1, a silver-copper alloy 2 disposed on the outer layer of the graphene 1, a shielding layer 3 disposed on the silver-copper alloy 2, and a shielding layer 3 disposed on the outside of the shielding layer 3 The insulating layer 4 of the first layer and the protective layer 5 arranged on the outer layer of the insulating layer 4;
[0044] The silver-copper alloy 2 is made of the following materials by weight: 44% silver, 55% copper, 0.02% iron, 0.1% nickel, 0.6% aluminum, 0.15% silicon, 0.1% magnesium and 0.03% boron;
[0045] The cross-sectional area of the silver-copper alloy 2 is 0.5 times the cross-sectional area of the graphene 1;
[0046] The thickness of the shielding layer 3 is 0.1mm;
[0047] The thickness of the insulating layer 4 is 0.3mm;
[0048] The thickness of the protective layer 5 is 1 mm.
[0049] Specifically, the shielding layer 3 is tinned copper material.
[0050] Specifically, the...
Embodiment 2
[0052] A new energy vehicle charging pile wire, comprising graphene 1, a silver-copper alloy 2 disposed on the outer layer of the graphene 1, a shielding layer 3 disposed on the silver-copper alloy 2, and a shielding layer 3 disposed on the outside of the shielding layer 3 The insulating layer 4 of the first layer and the protective layer 5 arranged on the outer layer of the insulating layer 4;
[0053] The silver-copper alloy 2 is made of the following materials by weight: 46% silver, 53% copper, 0.02% iron, 0.1% nickel, 0.6% aluminum, 0.15% silicon, 0.1% magnesium and 0.03% boron;
[0054] The cross-sectional area of the silver-copper alloy 2 is 0.5 times the cross-sectional area of the graphene 1;
[0055] The thickness of the shielding layer 3 is 0.1mm;
[0056] The thickness of the insulating layer 4 is 0.3mm;
[0057] The thickness of the protective layer 5 is 1 mm.
[0058] Specifically, the shielding layer 3 is tinned copper material.
[0059] Specifically, the...
Embodiment 3
[0061] A new energy vehicle charging pile wire, comprising graphene 1, a silver-copper alloy 2 disposed on the outer layer of the graphene 1, a shielding layer 3 disposed on the silver-copper alloy 2, and a shielding layer 3 disposed on the outside of the shielding layer 3 The insulating layer 4 of the first layer and the protective layer 5 arranged on the outer layer of the insulating layer 4;
[0062] The silver-copper alloy 2 is made of the following materials by weight: 47% silver, 52% copper, 0.02% iron, 0.1% nickel, 0.6% aluminum, 0.15% silicon, 0.1% magnesium and 0.03% boron;
[0063] The cross-sectional area of the silver-copper alloy 2 is 0.6 times the cross-sectional area of the graphene 1;
[0064] The thickness of the shielding layer 3 is 0.3mm;
[0065] The thickness of the insulating layer 4 is 0.5mm;
[0066] The protective layer 5 has a thickness of 3 mm.
[0067] Specifically, the shielding layer 3 is tinned copper material.
[0068] Specifically, the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com