Non-recursive SC decoding partial sum determination method and device
A deterministic, non-recursive technology, applied in the field of channel coding, which can solve the problems of long operation time, large storage space, and many recursive function calls.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
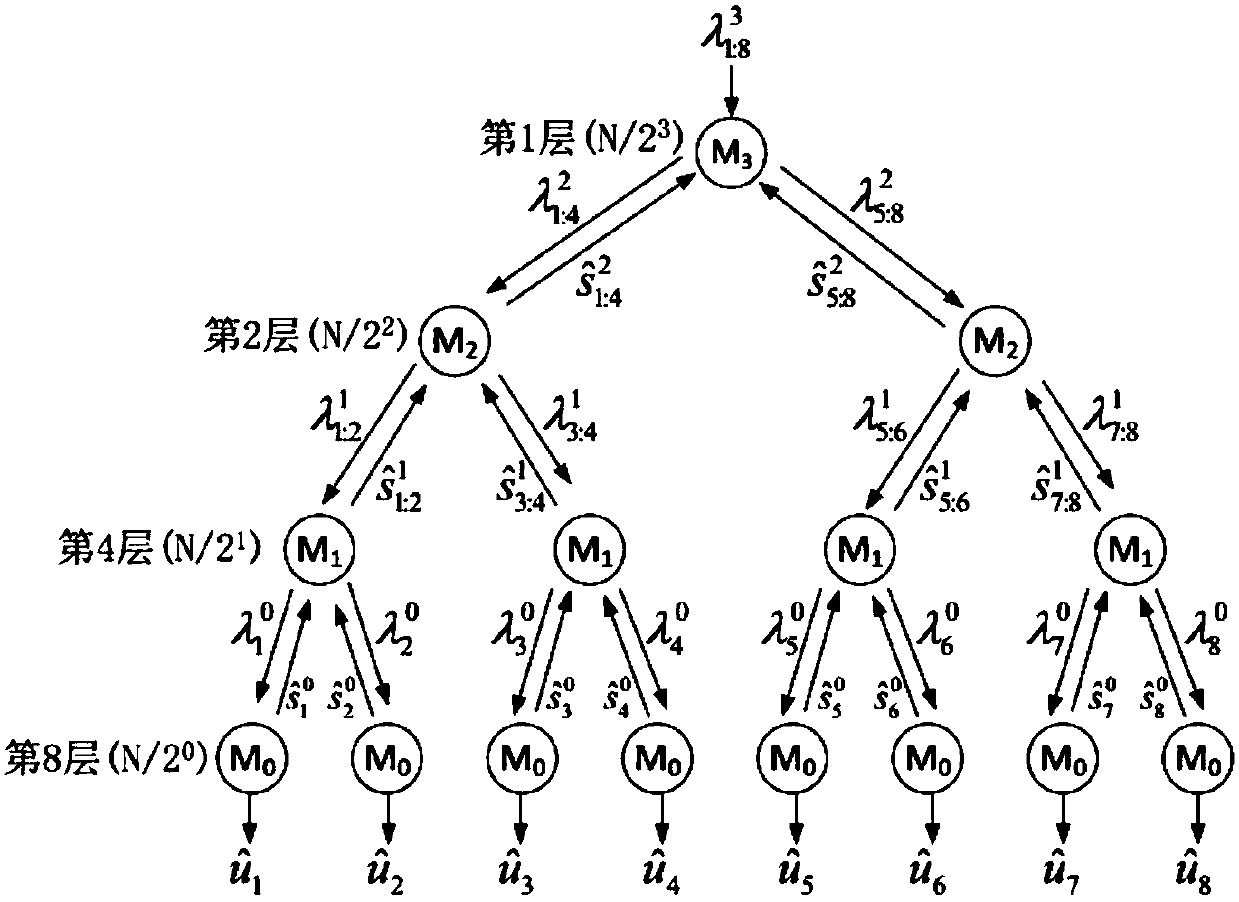
[0057] Specific Embodiment 1: This embodiment provides a non-recursive SC decoding part and a determination method. Before the method transmits information, the communication parties first need to determine the desired channel transmission code rate, and then the communication parties need to select according to the channel selection method. Pick NR out of N polarized channels such that the channel W N The reliability of is as high as possible. Finally, the two parties need to agree on the bit value filled in the frozen bit;
[0058] The sender encodes the polar code to encoded as Afterwards, it is sent to the receiver N times through the channel W, and the bit string received by the receiver is assumed to be This process can also be viewed as combining channels W N The above input message is The output message is The transmission process; the receiver needs to And quadruple information (N, K, I, u Ic ),estimate value, denoted as Composite channel W N Consist...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0071] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is:
[0072] estimate The specific method is:
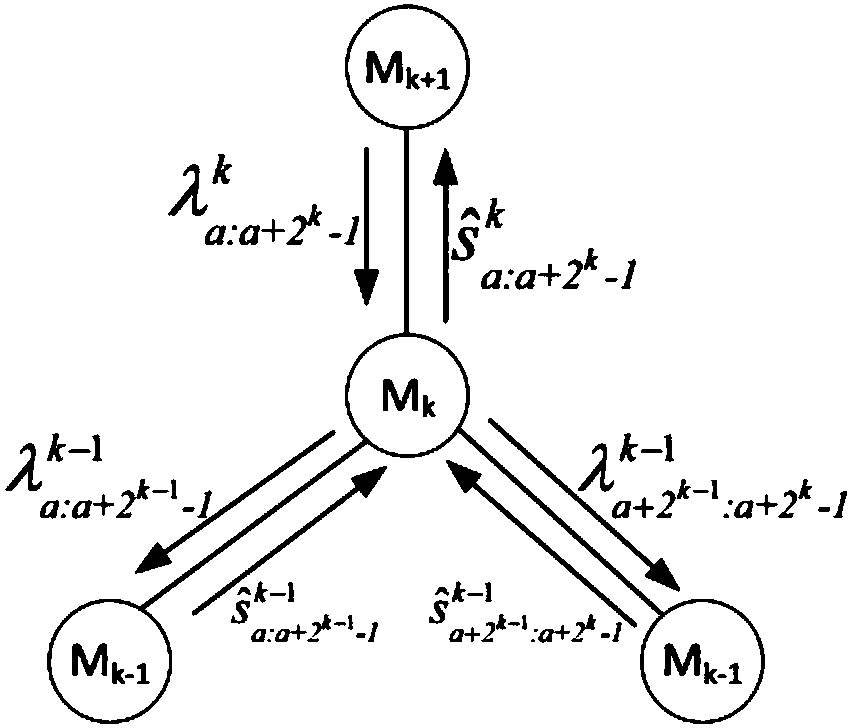
[0073] when calculating , sequentially calculate f 2 , f 4 ,..., f N ;
[0074] when calculating , calculate in turn where f j Indicates that the likelihood ratio of the jth layer is calculated using the formula f The formula f is specifically:
[0075]
[0076]
[0077] g j Indicates that the likelihood ratio of the jth layer is calculated using the formula g The formula g is specifically:
[0078]
[0079] g(a,b,s)=a 1-2s b
[0080] k i to estimate The maximum recursion depth for time-likelihood ratio calculation; 2≤i≤N.
[0081] That is, there are many ways to obtain the likelihood ratio, and the likelihood ratio calculation method in this embodiment can be used. The advantage of this embodiment is that the calculation of the likelihood ratio also uses a non-recursive meth...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0083] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is:
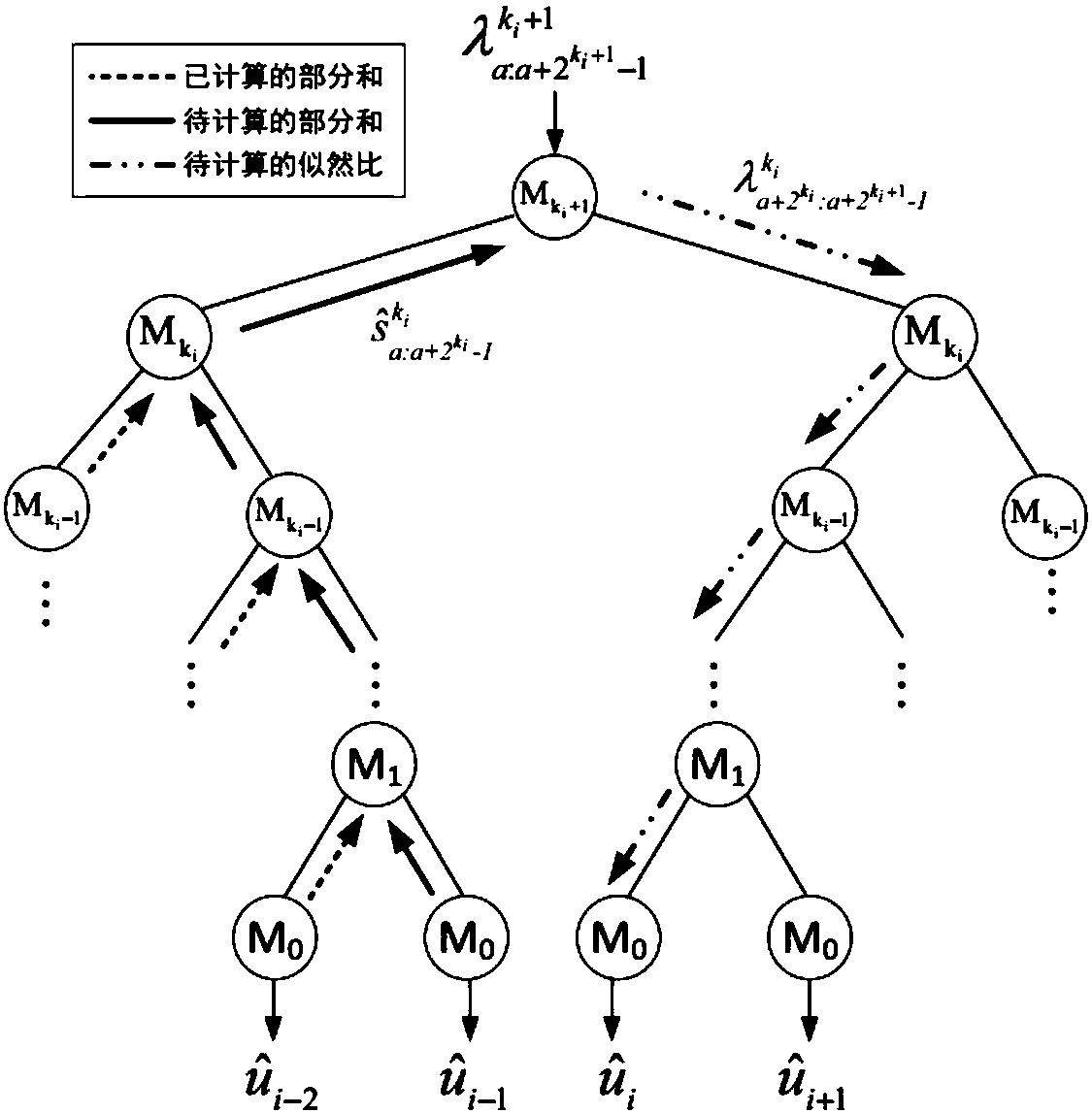
[0084] When the calculation of M k When the left child node part of the node is summed, the left child node part sum should be stored in M k part and In the storage space, when the calculation of M k When the partial sum of the right child node, the M k The partial sum of the right child is stored in M k In the storage space of the left child node, when passing M k Left child node partial sum and M k The right child node part and the calculated M k part of and when, will Stored in the storage space of the right child node.
[0085] Specifically, in order to reduce the space complexity, we use time-division multiplex storage for likelihood ratios and partial sums in the non-recursive SC decoding algorithm. For the likelihood ratio, because only the likelihood ratio of one node is input or output each time, there will be no access conflict in the time-di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com