Method for varying vehicle engine braking torque using discretionary active fuel management
A technology of active fuel management and engine cylinder, applied in engine control, machine/engine, fuel injection control, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The following description is merely exemplary in nature and is not intended to limit the disclosure, application or uses.
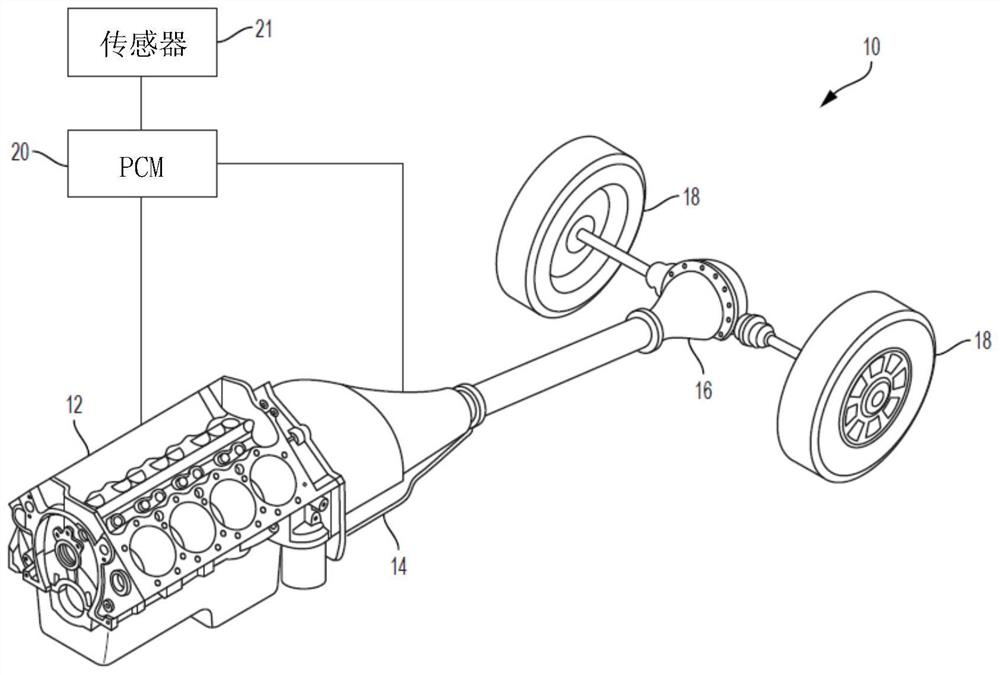
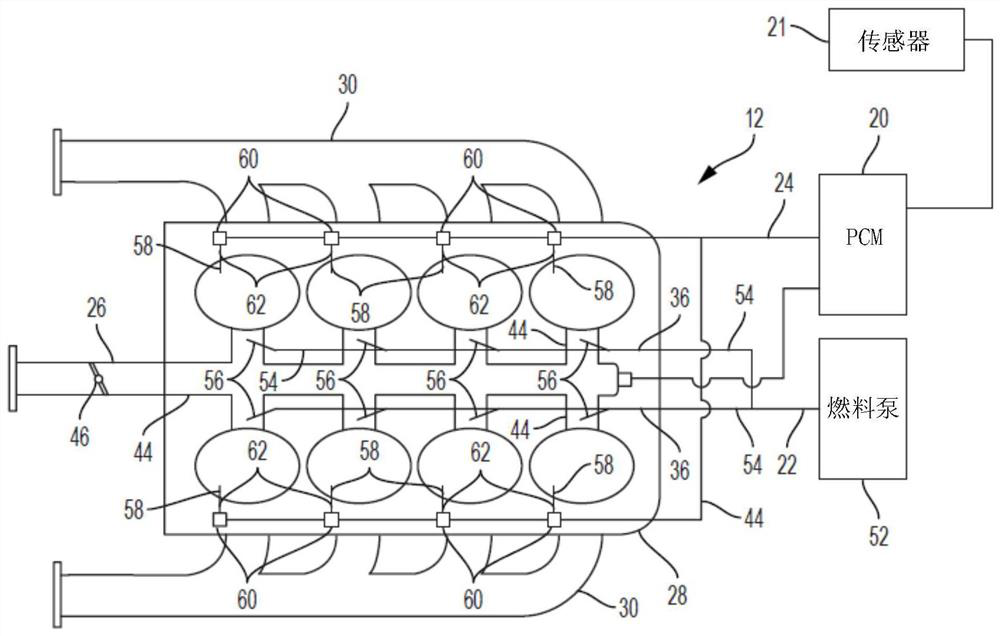
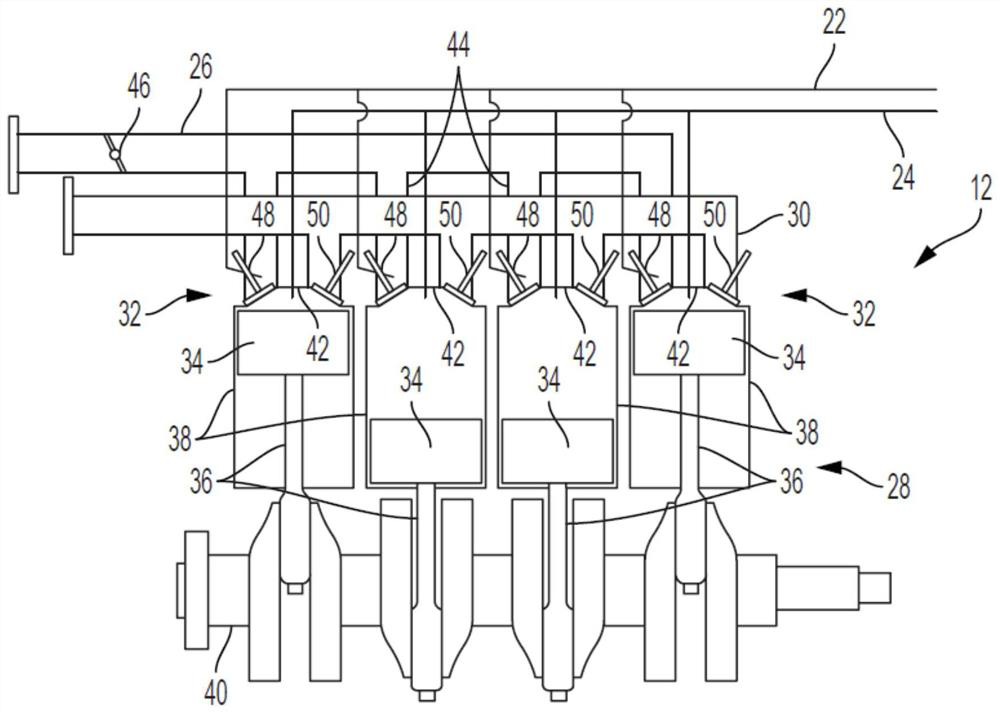
[0021] refer to figure 1 , an exemplary powertrain is generally indicated by the reference numeral 10 . The powertrain 10 includes an engine 12 , a transmission 14 , a driveshaft and rear differential 16 , drive wheels 18 and a powertrain control module (PCM) 20 . Sensors 21 are in communication with PCM 20 and may include, for example, an accelerator position sensor sensing instantaneous position of an accelerator pedal (not shown), a brake pedal (also not shown) position sensor sensing brake pedal position, and the like. Sensor 21 may then provide this information to PCM 20 .
[0022] The PCM 20 may calculate a driver commanded engine torque based on vehicle speed and accelerator pedal position. The PCM 20 may also use the instantaneous position of the accelerator pedal (from the accelerator pedal position sensor) to calculate the rate of acce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com