Flexible force tactile sensor based on transparent biomaterial, sensitive element and preparation method thereof
A tactile sensor and biomaterial technology, applied in the field of sensing, can solve problems such as low service life, low flexibility, and low precision, and achieve the effects of saving time and cost, reducing water evaporation, and reducing impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The preparation of embodiment 1 sensitive element
[0039] 1) Preparation of PDMS
[0040] 1> Mix PDMS and curing agent (Sylgard 184silicone elastomer, Dow Corning) in proportion (10:1), place in a centrifugal mixer, and stir at 1500RPM for 10 minutes to make it evenly mixed.
[0041] 2> Pour the stirred PDMS into the plastic spinner mold and rotate at 150RPM for 3 minutes to spread it evenly.
[0042] 3>Place the evenly spread PDMS on the heating table and heat it at 50°C for 2 hours to form it.
[0043] 2) Preparation of hydrogel colloid
[0044]1>Add 0.4g Sodium alginate and 0.2g Ethylenediamine tetra acetic acid calcium Disodium salt hydrate to 10ml of deionized water, put it in a centrifugal mixer, and stir at a speed of 1000RPM 10 minutes to mix well.
[0045] 2>Add 0.2g of glucono δ-lactone to the well-mixed colloid, place it in a centrifugal mixer, and stir at a speed of 1000RPM for 2 minutes to make it evenly mixed.
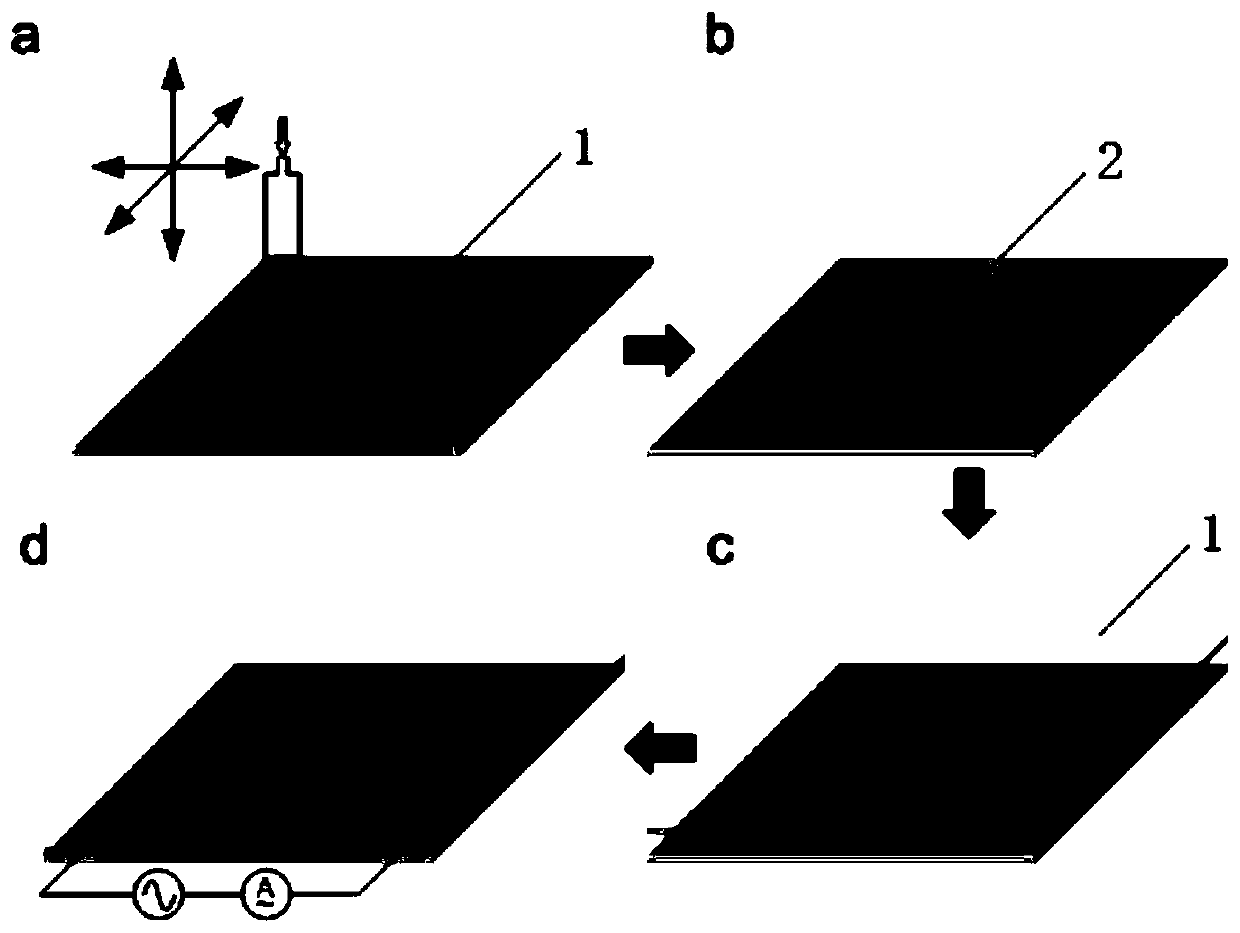
[0046] 3) PDMS-hydrogel-PDMS structure...
Embodiment 2
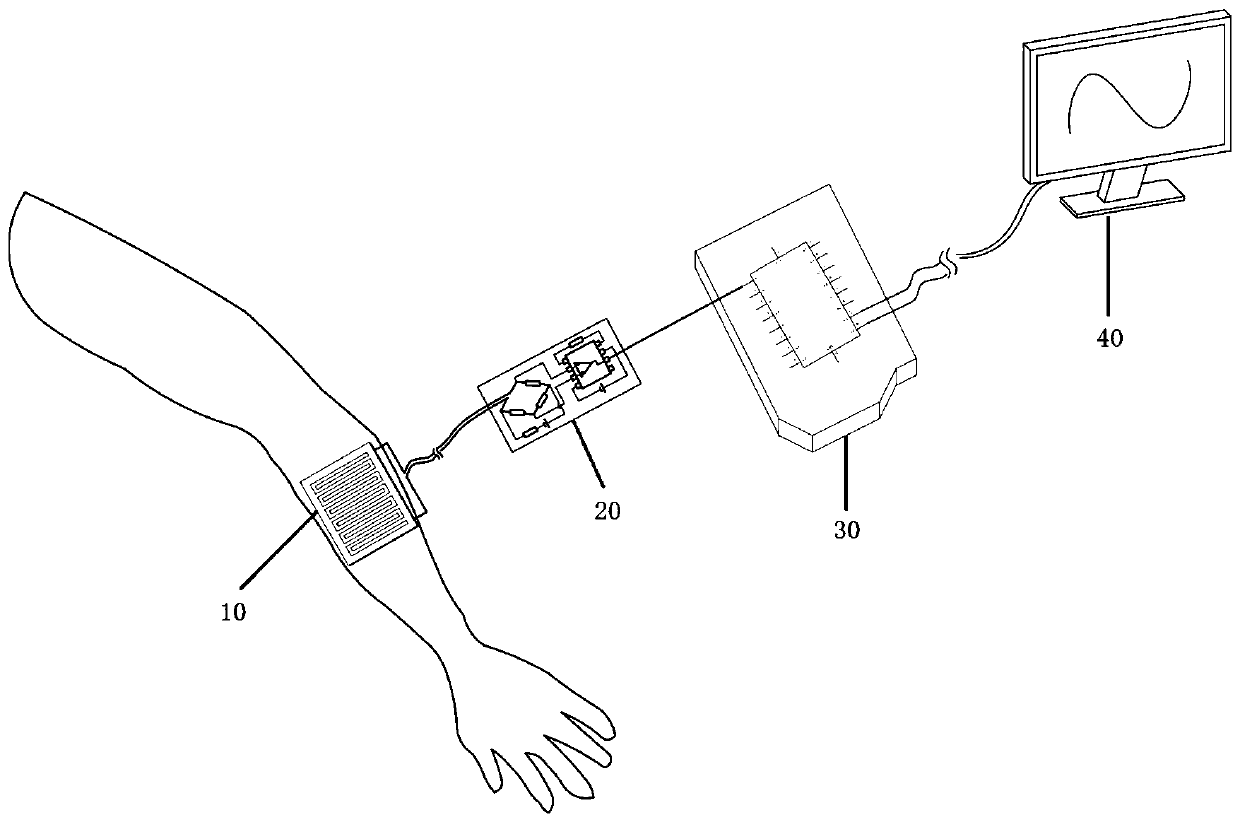
[0053] Embodiment 2 The sensor is applied to the human arm
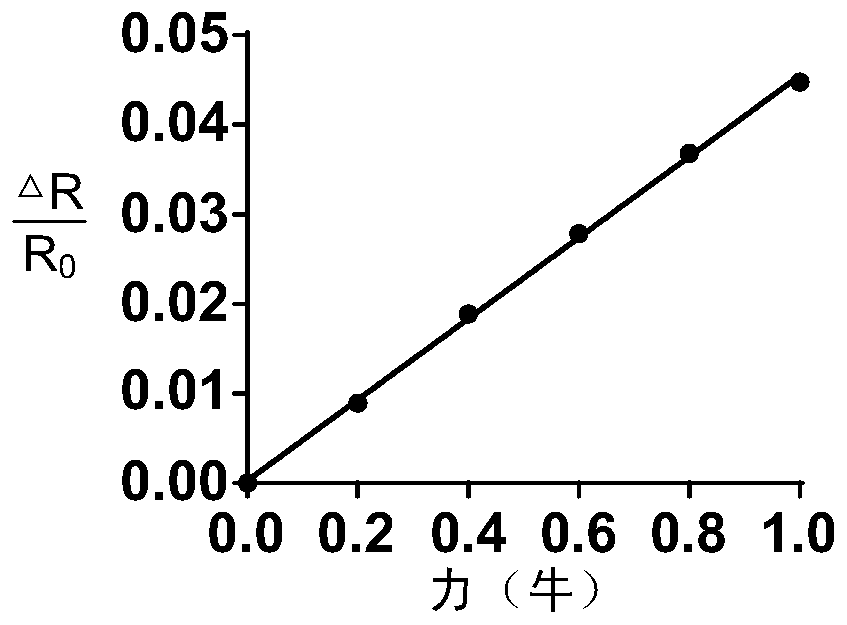
[0054] Such as image 3 As shown, the flexible force tactile sensor based on transparent biomaterials described in the present invention is installed on the human arm, the sensitive element 10 is attached to the arm, and a wired bridge measurement circuit 20, an AD conversion circuit 30 and a display 40 are used in sequence. . The sensor shown in the figure is in the bridge circuit. The pressure change of the sensor causes the resistance value to change, which causes the output voltage of the bridge circuit to change. After being amplified by the amplifier, the voltage signal is recorded by the single-chip microcomputer.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Embodiment 3 The sensor is applied to the fingertip of a person
[0056] Figure 4 The sensor is demonstrated to enable wireless tactile measurements. The principle of the flexible sensor can also be used to achieve tactile measurement in a small area through high-precision three-dimensional printing, such as fingertips. At the same time, using wireless transceiver technology, the sensor can realize wireless signal transmission. The single-chip microcomputer records the resistance value of the sensor changed by the force through the bridge, and transmits it through the wireless module; the host computer receives, displays and records the tactile signal through the wireless module.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com