Methods and compositions useful in generating non canonical CD8+ T cell responses
A cell and cytomegalovirus technology, applied in the field of CD8+ immune response, can solve the problems of virus disappearance, CD4 not observed, and SIV-specific antibody response not occurring
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0155] Example 1. Induction of MHC-E-restricted CD8 by rhesus cytomegalovirus vaccine vector lacking UL128 and UL130 but containing UL40 and US28 genes + T cells.
[0156] It was previously demonstrated that RhCMV / SIV vectors drive alternative SIV-specific CD8 + T cell responses, which are quite different from typical responses produced by conventional vaccine formats, and even from SIV infection itself (Hansen, S.G. et al., Science 340, 1237874 (2013), which is incorporated herein by reference).
[0157] Although RhCMV / SIV-induced CD8 + T cell responses are MHC-II restricted CD8 + T cell populations are present predominantly, but remaining CD8 restricted + The molecules of T cells (those inhibited by the pan-MHC-I blocking antibody W6 / 32) remain unknown.
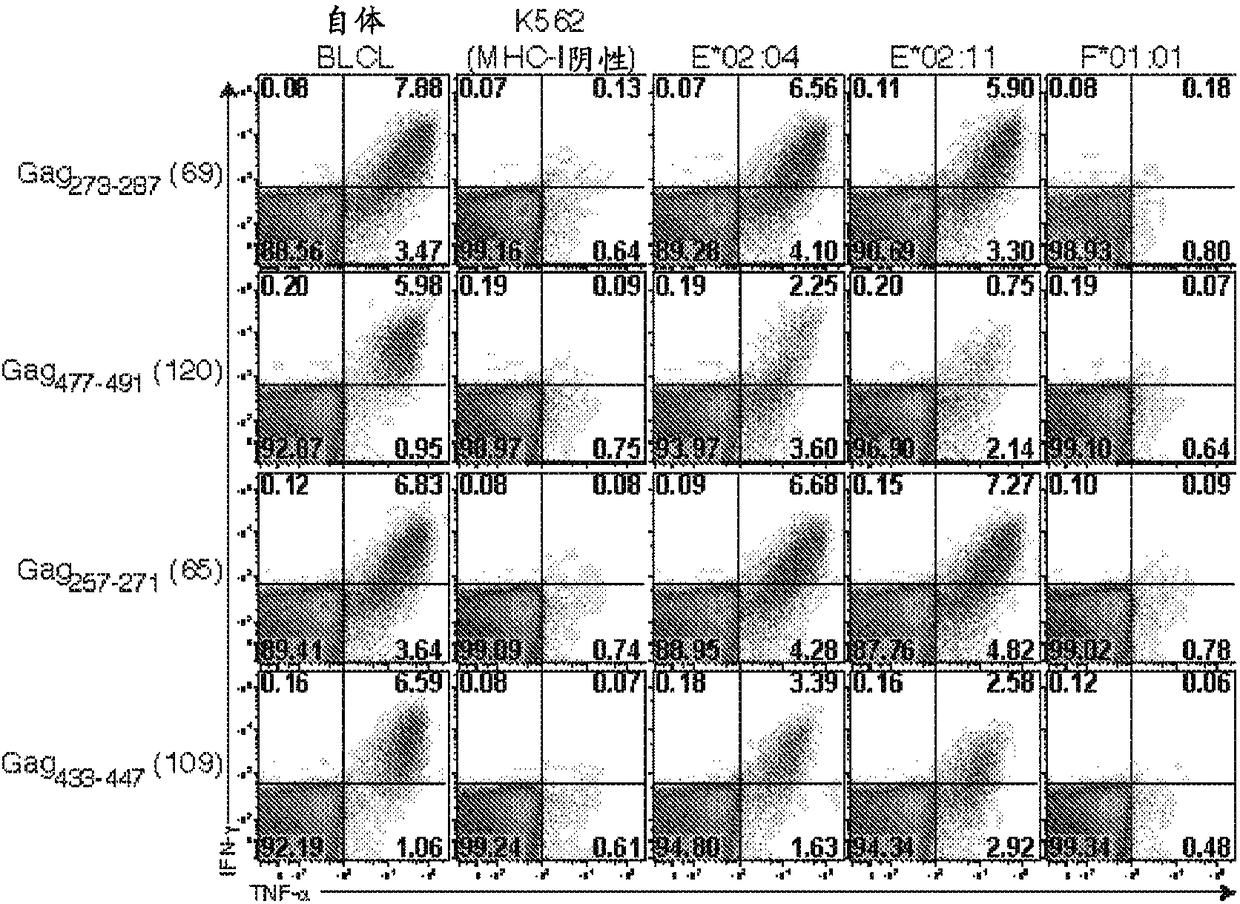
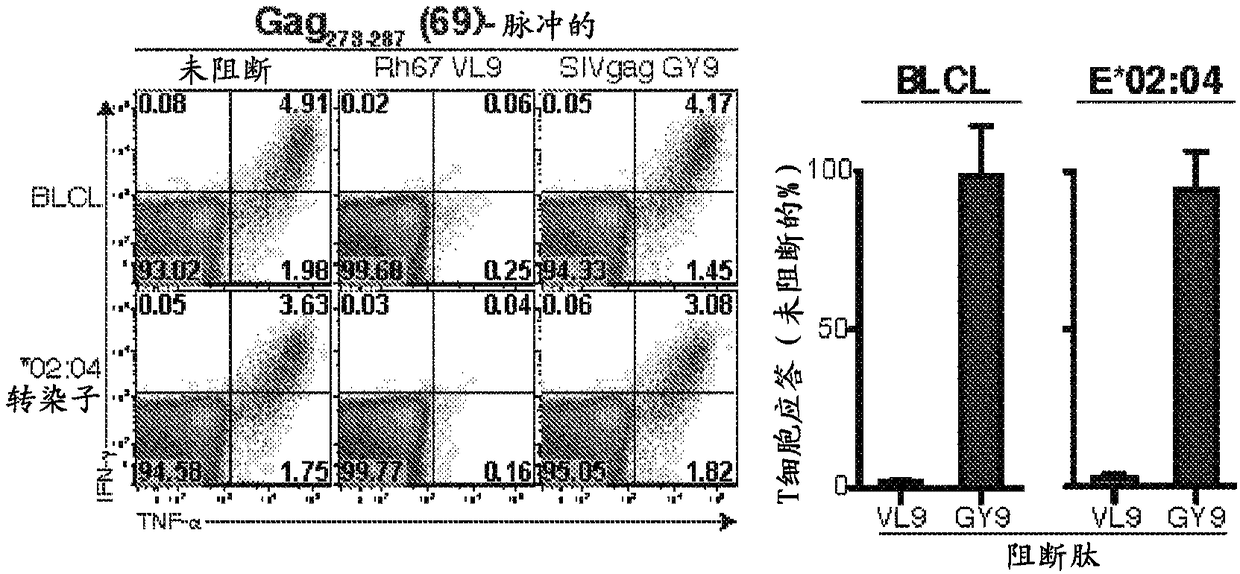
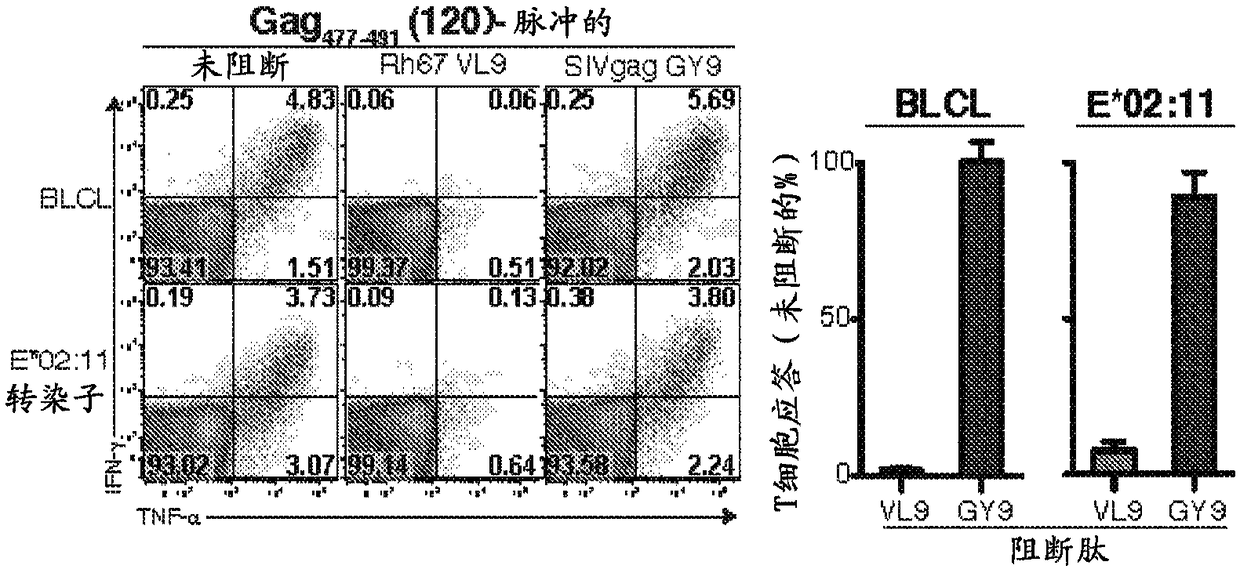
[0158]In particular, administration of 68-1 RhCMV / gag vectors resulted in targeting of SIVmac239Gag in rhesus macaques vaccinated with each RhCMV / gag vector 273-287 (Gag 15-mer #69) and Gag 477-491 (Gag 15-mer #1...
Embodiment 2
[0184] Example 2 - Target peptide specific CD8 in the context of MHC-E + production of T cells
[0185] T cell receptors that recognize target peptides from antigens in the case of classically polymorphic MHC-Ia molecules can be used to transfect autologous T cells for immunotherapy of diseases such as cancer or infectious diseases. A major obstacle to this approach is the diversity of MHC-Ia in the population, which limits the use of a given TCR to MHC-Ia-matched patients. By generating target peptides that recognize antigen-derived peptides (e.g., peptides from tumor antigens and peptides from pathogens) in the context of non-classical, non-polymorphic MHC-E molecules, MHC matching becomes obsolete and the resulting TCR Can be used on all patients.
[0186] CD8 recognizing MHC-E / peptide complexes in nature + T cells are rare, and there are currently no reliable methods to generate such T cells against target antigens such as tumor antigens, antigens from pathogens, tiss...
Embodiment 3
[0187] Example 3 - Broadly targeted CD8 restricted by major histocompatibility complex E + T cell response
[0188] Major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-E is a highly conserved, ubiquitous, non-canonical MHC-Ib molecule with limited polymorphisms that is involved in NK cell reactivity primarily through interaction with NKG2 / CD94 receptors adjustment. Here, among all protein antigens tested, rhesus macaques sensitized with Rh157.5 / .4 gene-deleted RhCMV vectors uniquely shifted MHC-E function to present highly diverse peptide epitopes to CD8α / β + T cells, about 4 different epitopes per 100 amino acids. Since MHC-E is upregulated on HIV / SIV and other persistent virally infected cells to evade NK cell activity, MHC-E restricts CD8 + The ability of T cell responses to exploit the potential of pathogen immune evasion to adapt may make these unconventional responses very effective.
[0189] Adaptive cellular immunity against intracellular pathogens is the recognition of CD8 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com