Ultra low loss optical fiber replacement scheduling method and system in backbone network
A scheduling method and backbone network technology, applied in the direction of transmission system, digital transmission system, multiplexing system selection device, etc., can solve the problems affecting the optimization effect of network operators, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] In this embodiment, the ultra-low-loss optical fiber replacement scheduling method in the backbone network is called the MG strategy, which specifically includes:
[0102] S1 respectively calculates the gain of each optical fiber link after replacement, that is, calculates the number of frequency slots FS reduced after the replacement of each optical fiber link and multiplies the remaining time until all the remaining optical fiber links are replaced;
[0103] S2 selects one of the optical fiber links with the highest gain after replacement of the optical fiber link for replacement;
[0104] S1 to S2 are repeated until all fiber links that need to be replaced are replaced.
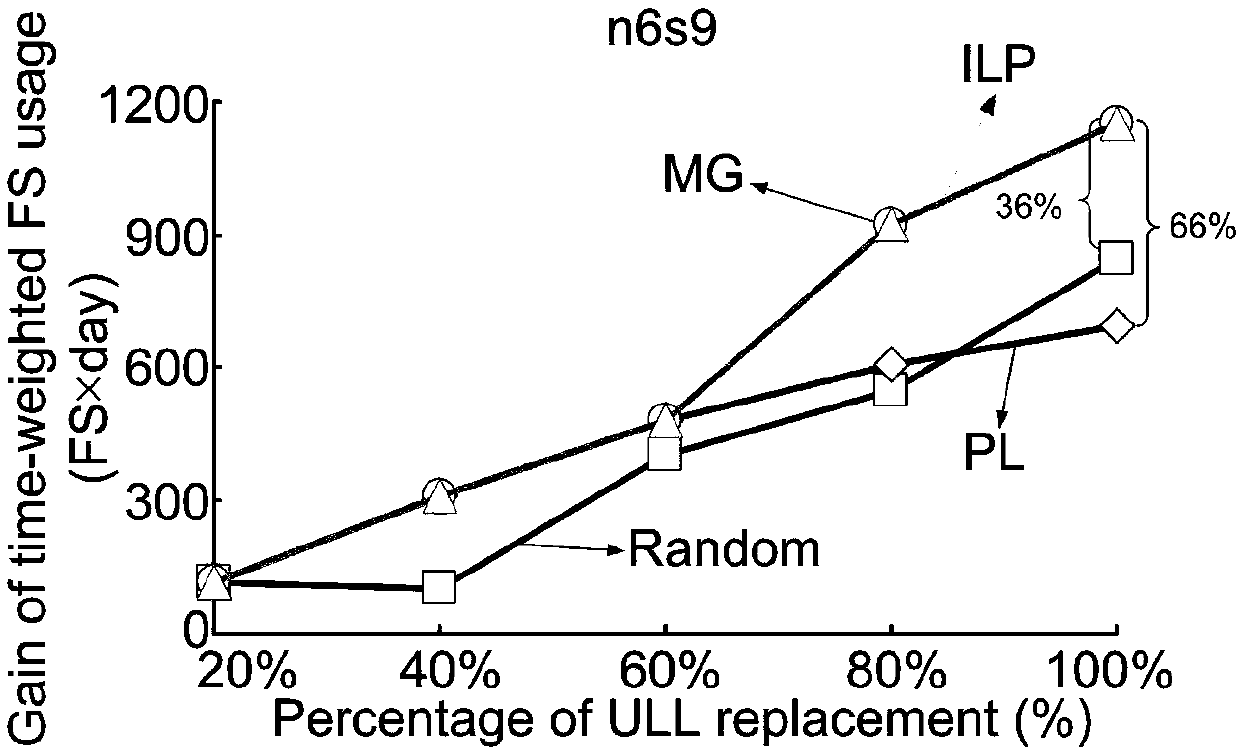
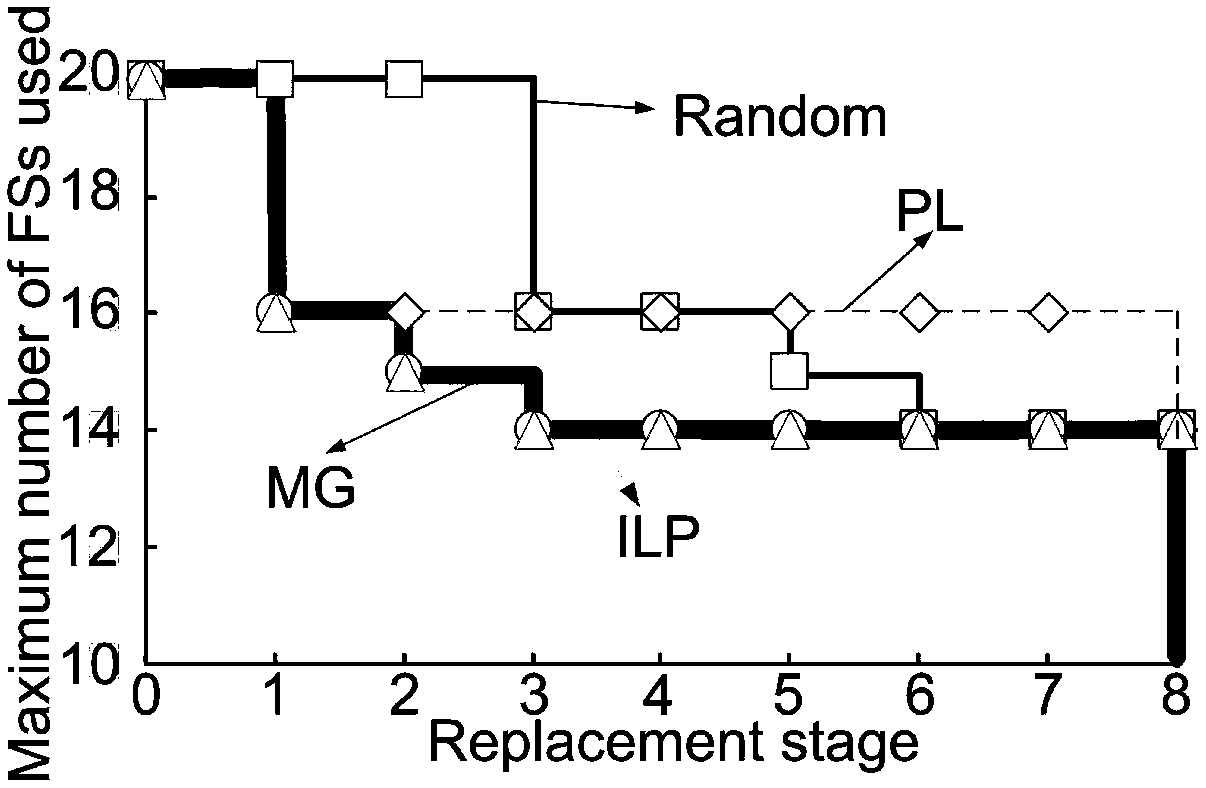
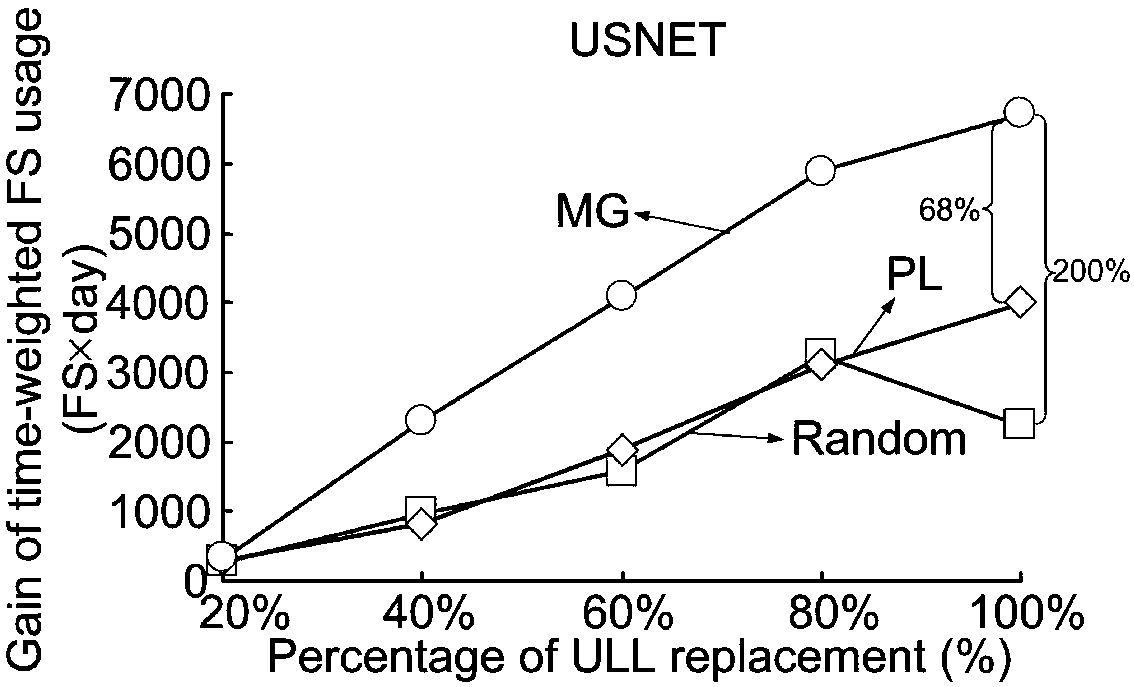
[0105] In this embodiment, two test networks are taken as examples, namely the n6s9 network with 6 nodes and 9 links and the USNET with 24 nodes and 43 links. In each fiber link, there are at most 320 FSs, each FS has a bandwidth of 12.5-GHz spectrum. In each optical fiber link, optical amplifiers...
Embodiment 2
[0110] The ultra-low-loss optical fiber replacement scheduling method in the backbone network of this embodiment is applicable to small-scale networks with a small amount of computation, and the specific methods include:
[0111] Construct the linear programming model ILP, take the topology of the optical fiber link with replacement as input, and run the linear programming model ILP with the goal of maximizing the gain of the optical fiber link replacement process, where the gain formula of the replacement process is: ∑ k∈1..P C k-1 ·T k ; The constraints of the linear programming model ILP are:
[0112] Constraint 1 ensures that the maximum number of frequency slots FS used in the entire network is greater than the last frequency slot FS occupied by any optical channel, the expression:
[0113] Constraint 2 is guaranteed to meet the optical channel service request between each node pair after each fiber link is replaced, the expression:
[0114]Constraints 3 and 4 ensu...
Embodiment 3
[0154] The ultra-low loss optical fiber replacement dispatching system in the backbone network of this embodiment includes:
[0155] The gain calculation unit is used to calculate the gains after the replacement of each fiber link before selecting the current replacement link, that is, calculate the number of frequency slots FS reduced after the replacement of each fiber link and multiply it until the rest of the fiber links are completed. replace the remaining time;
[0156] The replacement link selection unit is used to select one of the optical fiber links with the highest gain after the replacement of the optical fiber link to complete the current optical fiber link replacement according to the result of the gain calculation unit;
[0157] The gain calculation unit and the replacement link selection unit operate repeatedly until all the optical fiber links that need to be replaced are completely replaced.
[0158] In this embodiment, a linear programming model ILP is also...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com