Crane period anti-swing control method
A control method and crane technology, applied in the directions of load hanging components, transportation and packaging, can solve the problems of high cost and complex anti-sway control system, and achieve the effects of low cost, anti-sway control and easy engineering realization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
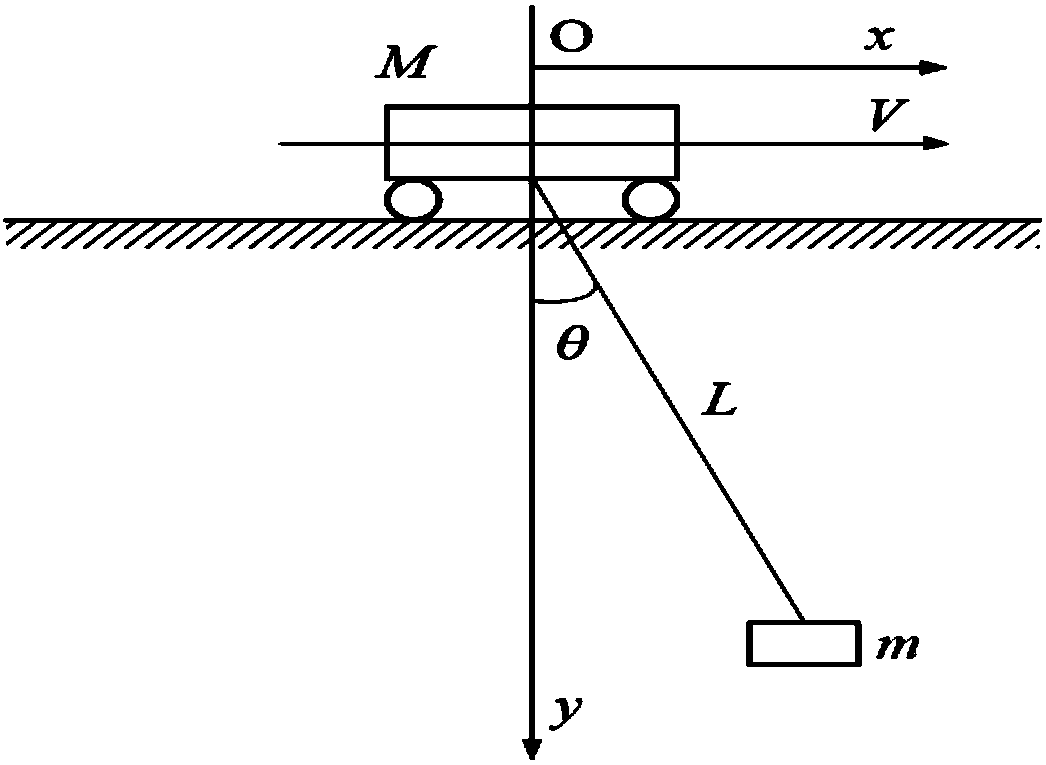
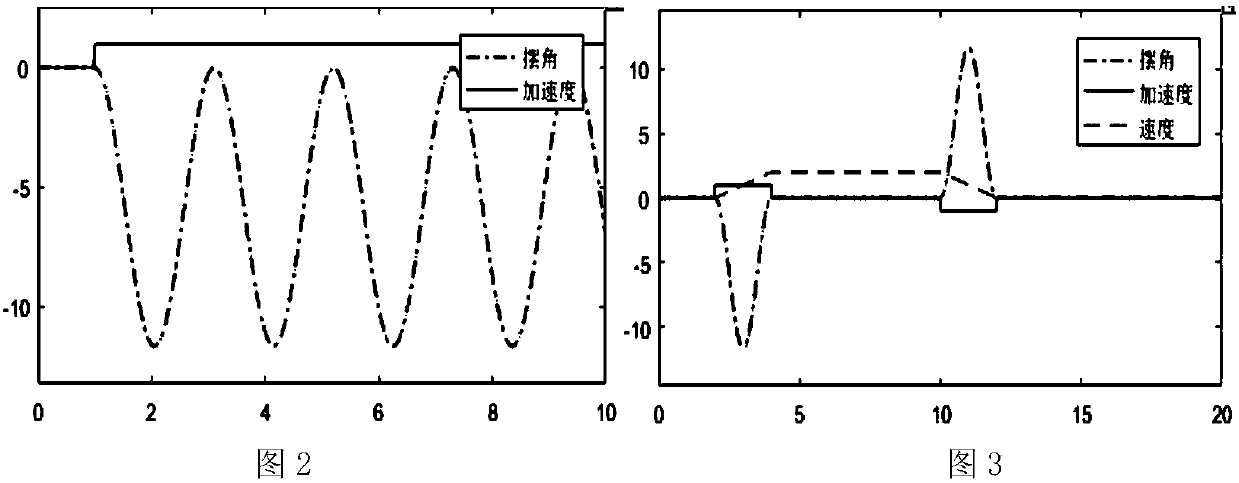
[0035] like figure 1 , 3 , 4 shown.
[0036] A crane cycle anti-sway control method, the key of which is to divide the hoisting process of the crane into a constant acceleration process, a constant speed process, and a constant deceleration process, and the load swing angle is zero during the constant speed process and stop; a as input, the acceleration time is one or an integer number of periods nT, T is the swing period, n is a natural number, acceleration a=garctan(θ max / 2), to meet the maximum allowable swing angle θ max Constraint conditions; in the process of constant speed, the trolley with V 匀 = naT hoisting at a constant speed; the constant deceleration process is the inverse process of the constant acceleration process, that is, the trolley takes the acceleration-a as input, and the duration is the same as the acceleration time, for example figure 1 shown.
[0037] Take the car movement as an example. refer to image 3 , Figure 4 , give the trolley a consta...
Embodiment 2
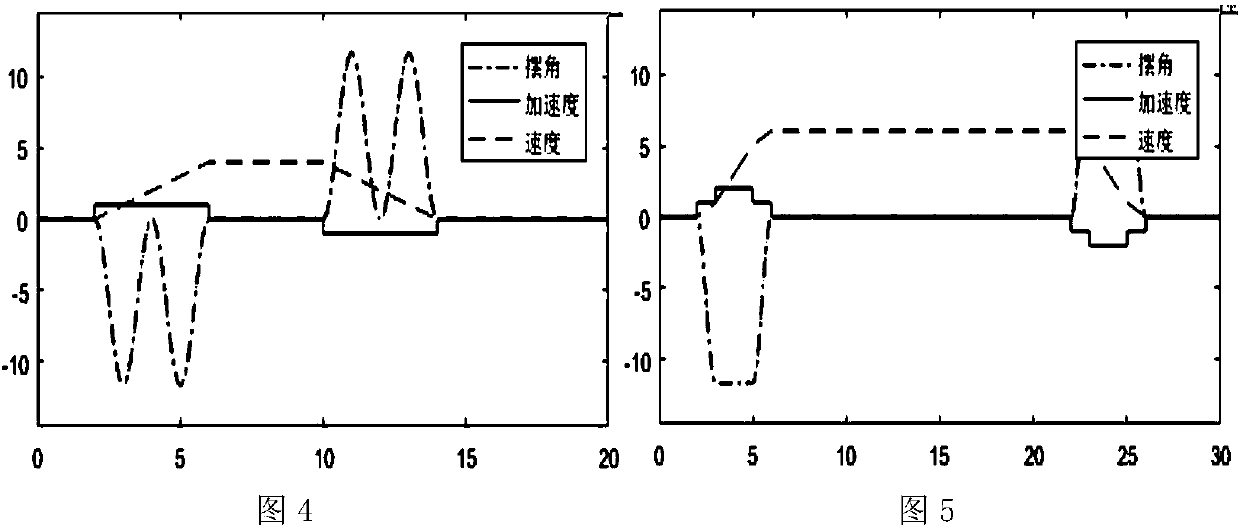
[0040] like figure 1 , 5 shown.
[0041]A crane cycle anti-sway control method, the key of which is to divide the hoisting process of the crane into an acceleration process, a constant speed process, and a deceleration process. The expected constant speed value plans the specific control process; the acceleration process can be divided into T 1 , T 2 , T 3 Three stages: where T 1 Phase and T 3 The stage car input is symmetrical, and the acceleration and duration are the same, that is, a 1 =a 3 ,T 1 =T 3 =T / 2, T is the swing period; acceleration a 1 =garctan(θ max / 2), to meet the maximum allowable swing angle θ max constraints; T 2 Stage acceleration a 2 =garctanθ max , at this time there is a 2 = 2a 1 / (1-a 1 2 / g 2 ), the duration is adjusted according to the desired constant speed; the deceleration process is the inverse process of the acceleration process, such as figure 1 shown.
[0042] refer to Figure 5 , the whole lifting process still includes ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com