Distributed group robot cooperative clustering algorithm based on improved gene regulation network
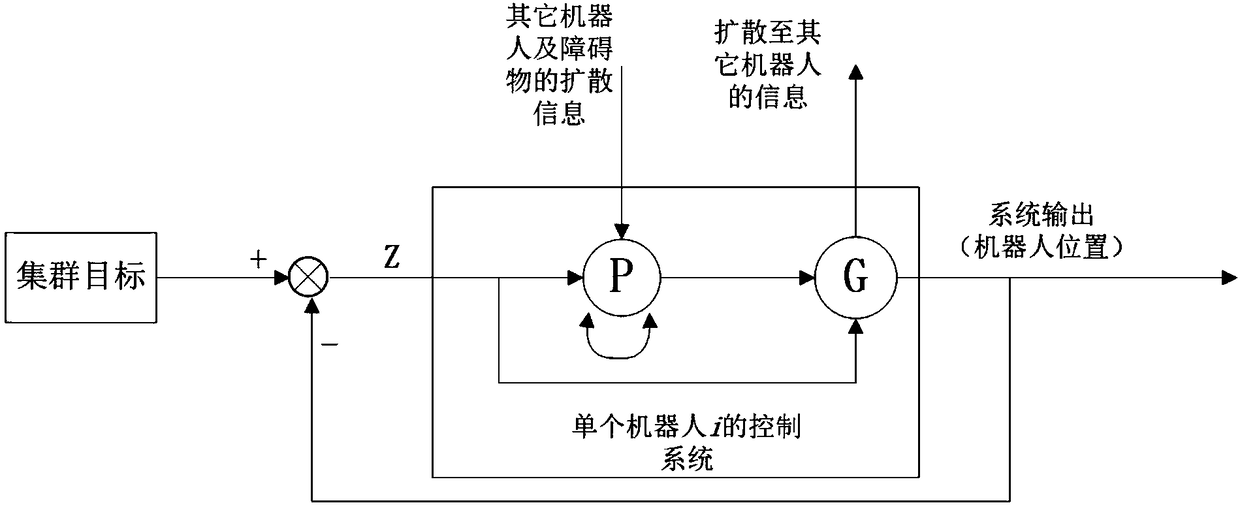
A gene regulation network and swarm robot technology, applied in the field of distributed swarm robot collaborative cluster control, can solve problems such as robot control communication burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0130] According to the above model, set the total number of robots in the system to n=50, and the cluster formation distance d 1 = 1, the sensing range between robots r = 1.2, d 1 = 1.2, the distance range d of robot i’s obstacle avoidance response to surrounding robots and obstacles 2 =0.95, the value of δ is 0.01, and the Tr equation of the robot’s trajectory is as follows:
[0131]
[0132] For the NSGA II algorithm, the population size is set to 100, the crossover rate is 0.9, the SBX crossover distribution index is 20, the mutation probability is 0.2, the variation distribution index is 20, and the number of generations is set to 50 generations. Parameter range, a, l, m, c, k range from 1 to 100, b range from 1000 to 3000. Finally, the parameters obtained after NSGA II optimization are as follows:
[0133] Table 1 Model parameter values
[0134] a
[0135] The model is simulated by Matlab. In the experiment, a circular obstacle with the coordinates of the...
Embodiment 2
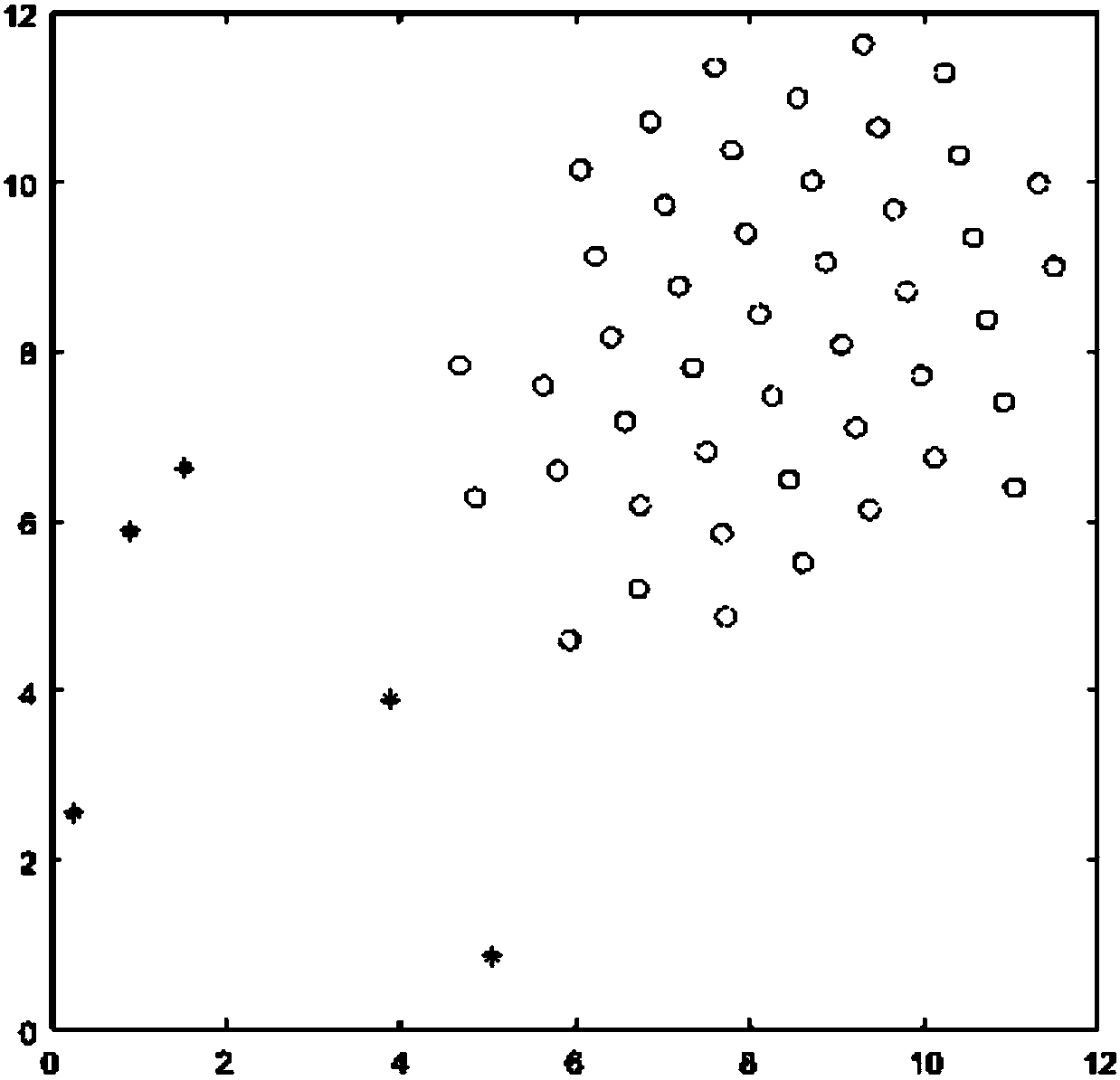
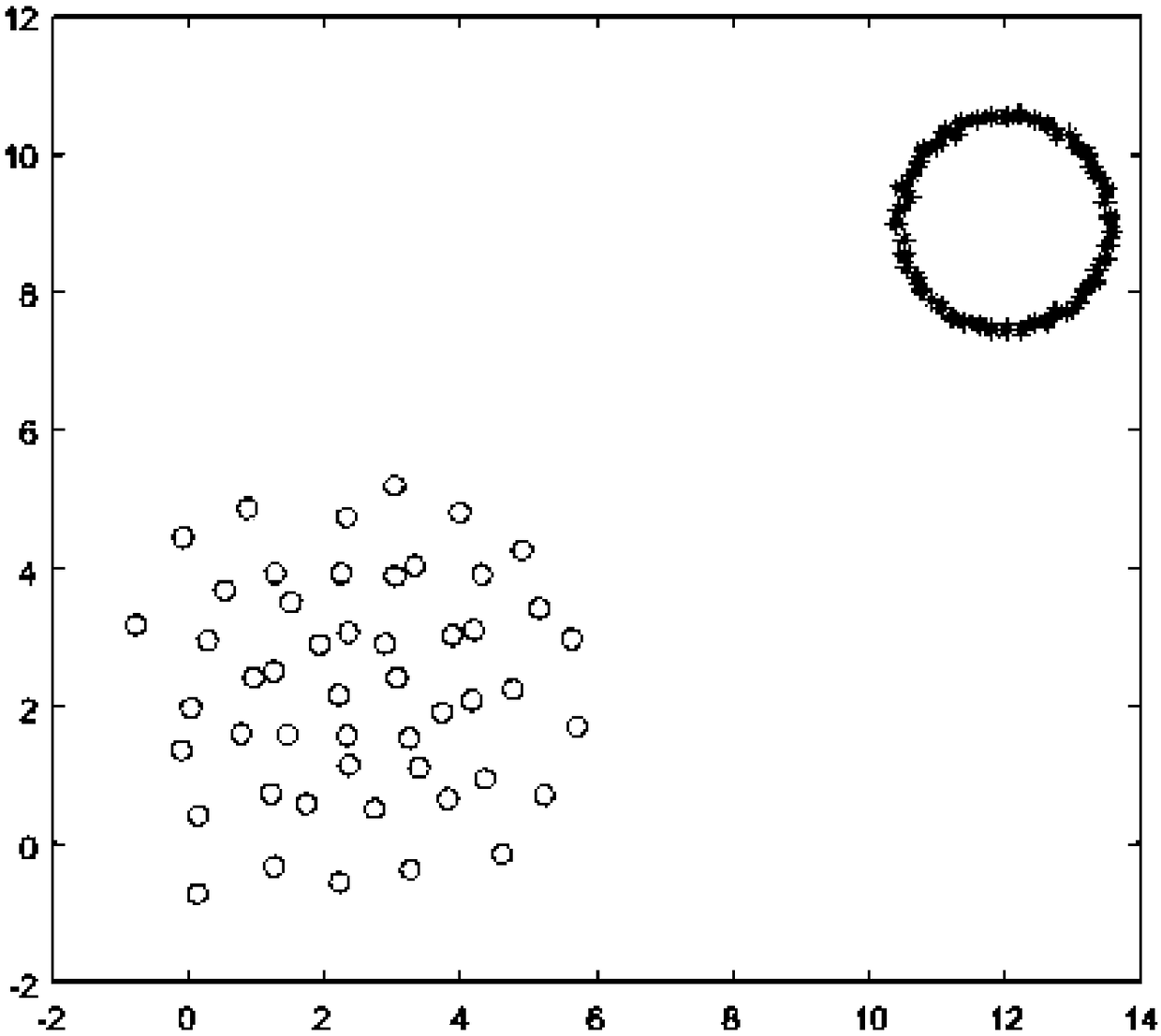
[0137] According to the above-mentioned model, some robots may fail to stop working during the traveling process. The situation is simulated by Matlab. The parameter setting is the same as that of Example 1, and the trajectory setting is also the same as that of Example 1. For example, Figure 9 As shown, start the normal cluster of robots. During the running process, 5 robots are randomly selected to make them stop moving, such as Figure 10 As shown, the symbol changes from "o" to "*" after the faulty robot stops moving. Figure 11 to Figure 13 It is shown that the rest of the robots can still self-organize and rebuild into a rhombus grid for clustering without collision, and the system has good robustness.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com