Device for photonic generation of arbitrary microwave signals having linear frequency modulation
A microwave signal and photonic device technology, applied in nonlinear optics, laser components, lasers, etc., can solve the problems of unacceptable high signal reproducibility, not to mention phase stability, no frequency stability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
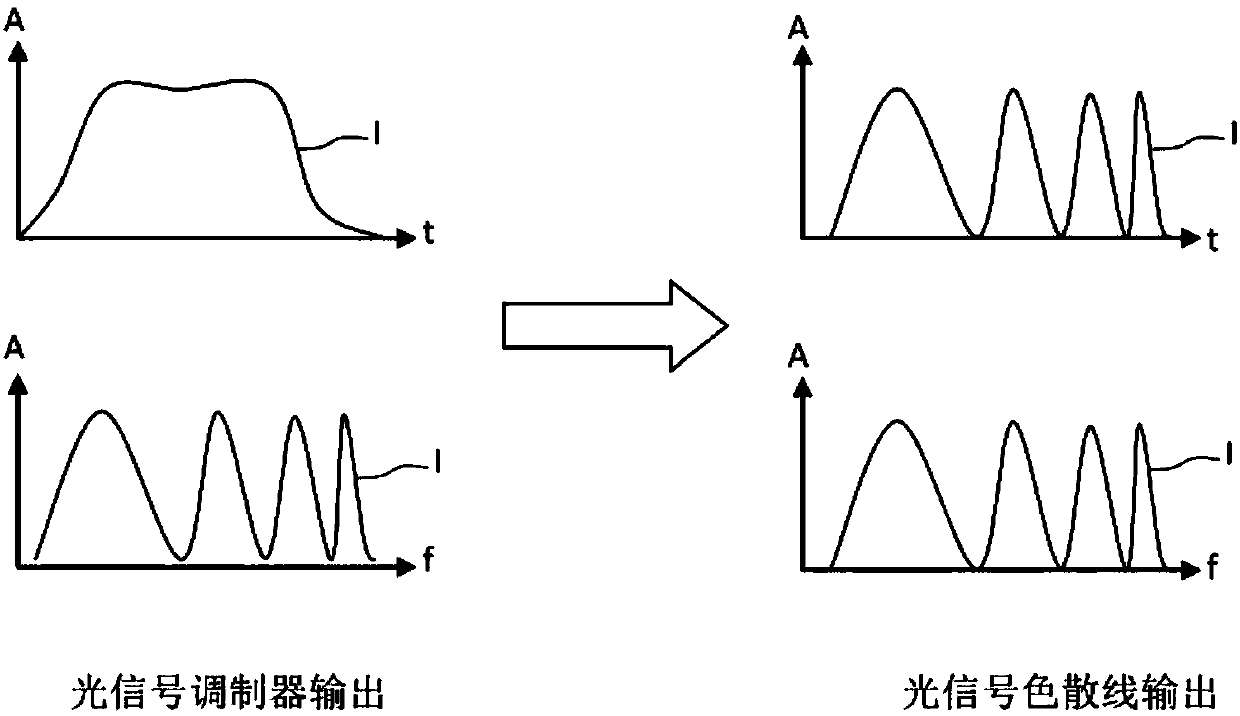
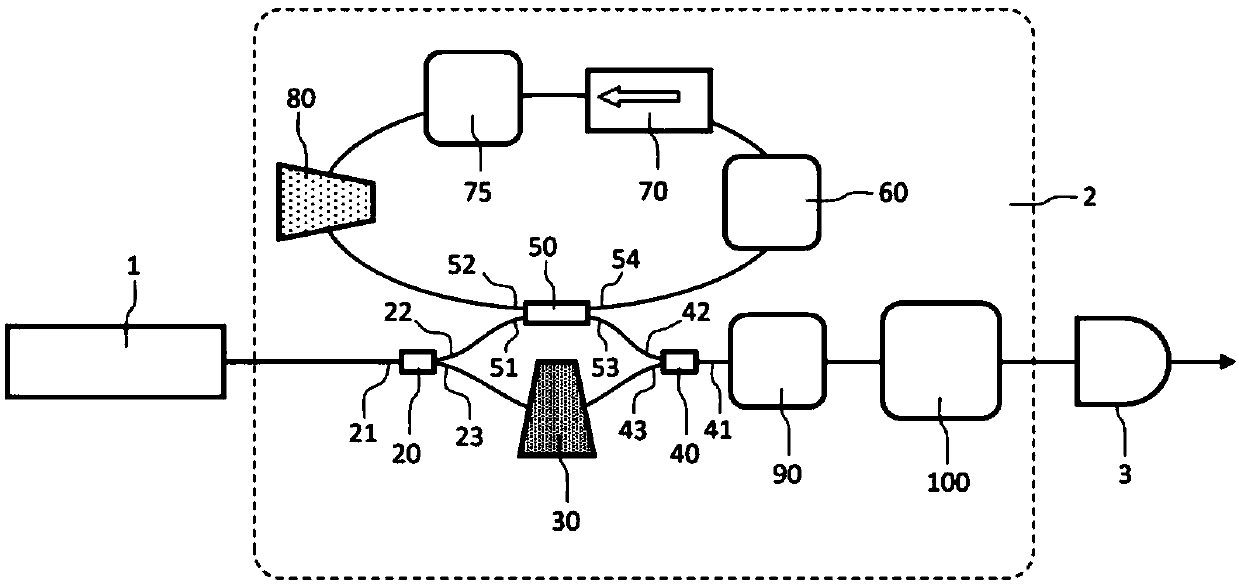
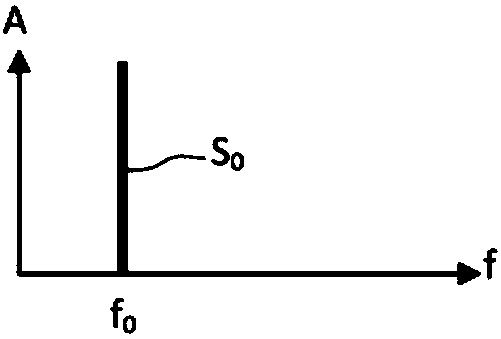
[0047] Photonic devices for generating microwave signals according to the present invention can be implemented in "fibre-based" or "integrated optics" configurations, frequency-shifting loops comprising optical fibers or waveguides; or in "free-space" configurations with discrete optical components, It is implemented in a frequency-shifting loop fabricated with precisely aligned mirrors. The expression "free space configuration" is understood to mean a configuration in which the light beam propagates completely or partly through free space.
[0048] exist figure 2 A schematic diagram of a "fibre-based" version of a photonic device for generating chirped arbitrary microwave signals according to the present invention is shown in . This version is detailed below. However, it is pointed out every time there is a clear difference between the fiber-based version and the free-space version.
[0049] figure 2 The photon-generating devices include, in order:
[0050] - laser, wh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com