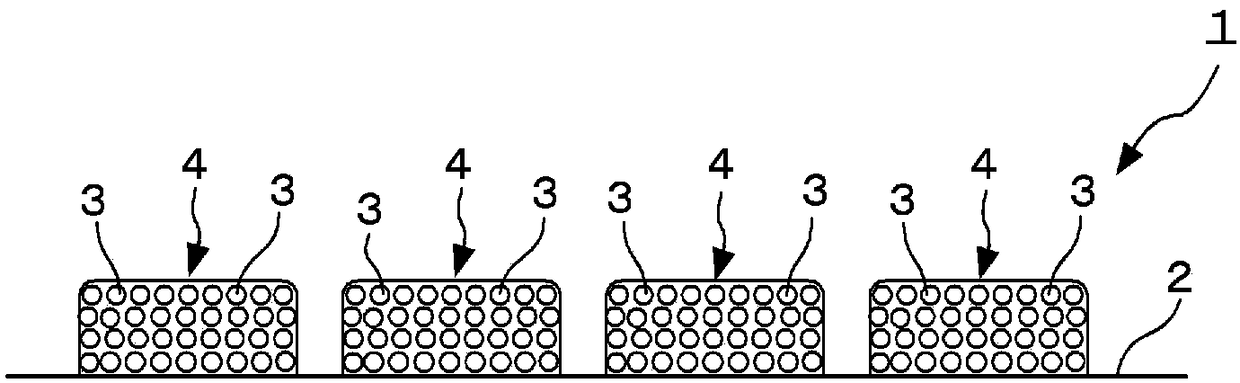
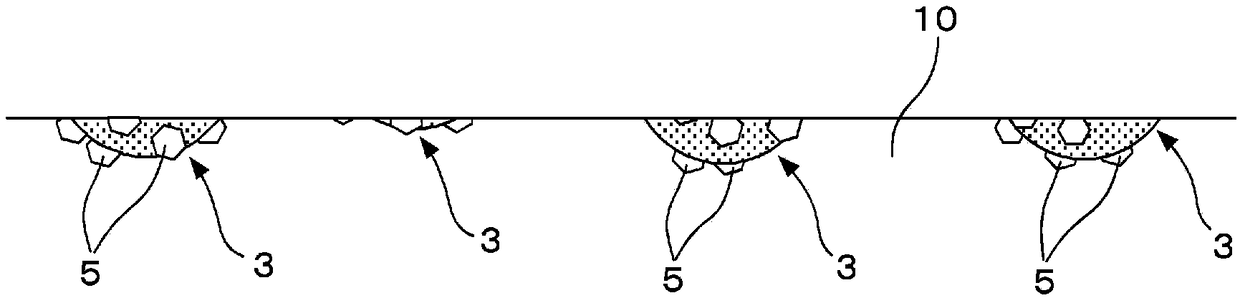
Method for manufacturing glass substrate for magnetic disk and method for manufacturing magnetic disk
一种磨削工具、玻璃基板的技术,应用在制造工具、适用于磨削工件平面的机床、研磨工具等方向,能够解决加工变质层变深、削减加工成本、低弹性等问题,达到可靠性高的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
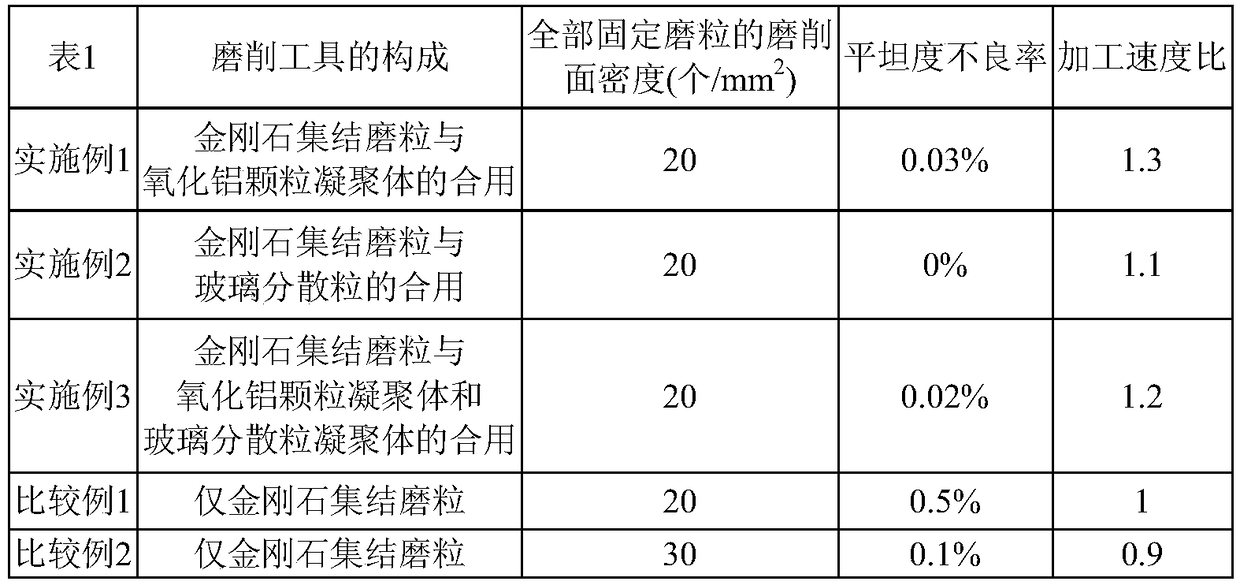
[0102] After the following (1) substrate preparation, (2) shape processing, (3) end surface grinding, (4) main surface grinding, (5) main surface grinding (first grinding), (6) chemical strengthening, (7) ) Main surface grinding (2nd grinding) The glass substrate for magnetic discs of this Example was manufactured.
[0103] (1) Substrate preparation
[0104] A large plate glass made of aluminosilicate glass with a thickness of 1 mm produced by the float method was prepared, and was cut into small pieces of a square of 70 mm×70 mm using a diamond cutter. Next, it was machined into a disc shape with an outer diameter of 65 mm and an inner diameter of 20 mm using a diamond tool. As this aluminosilicate glass, SiO containing 62% by weight to 75% by weight is used. 2 , 5.5% to 15% by weight of ZrO 2 , 5% to 15% by weight of Al 2 o 3 , 4% to 10% by weight of Li 2 O, 4% to 12% by weight of Na 2 O chemically strengthenable glass.
[0105] The surface of the obtained substrate ...
Embodiment 2
[0120] In the grinding process of the main surface of Example 1, the following diamond polishing pad is used. The diamond polishing pad is equipped with: an aggregated abrasive grain formed by fixing two or more diamond abrasive grains through glass; two or more diamond abrasive grains formed by glass Dispersed grains; and a resin that combines two or more of the aggregated abrasive grains and dispersed grains, wherein the average particle diameter of diamond abrasive grains is about 4.0 μm, the average particle diameter of diamond aggregated abrasive grains is 40 μm, and the average diameter of glass dispersed grains Grinding was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the average particle size was 4.0 μm, the maximum particle size of the glass aggregates was 45 μm, and the ratio of diamond aggregated abrasive grains to glass aggregates was 1:0.5 and dispersed in the resin. Processing and production of glass substrates for magnetic disks.
Embodiment 3
[0122] In the grinding process of the main surface of Example 1, the following diamond polishing pad is used. The diamond polishing pad has: an aggregated abrasive grain formed by fixing two or more diamond abrasive grains through glass; An aggregate of particles fixed by glass; an aggregate of two or more dispersed particles formed by glass; and a resin that combines two or more of the aggregated abrasive grains, the aggregate of alumina particles, and the aggregate of glass dispersed particles, which The average particle size of diamond abrasive grains is about 4.0 μm, the average particle size of alumina particles is about 1 μm to 4.0 μm, the average particle size of glass particles is about 1 μm to 4.0 μm, and the maximum diameter of alumina aggregates and glass aggregates The particle size is 45 μm, and these diamond aggregated abrasive grains, alumina aggregates and glass aggregates are dispersed in the resin in a ratio of 1:0.5:0.5, and are ground in the same manner as i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com