Method for evaluating onset risk of coronary heart disease by using value of apolipoprotein E-containing high-density lipoprotein
A high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein technology, applied in the field of risk assessment of coronary heart disease, can solve problems such as not established
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
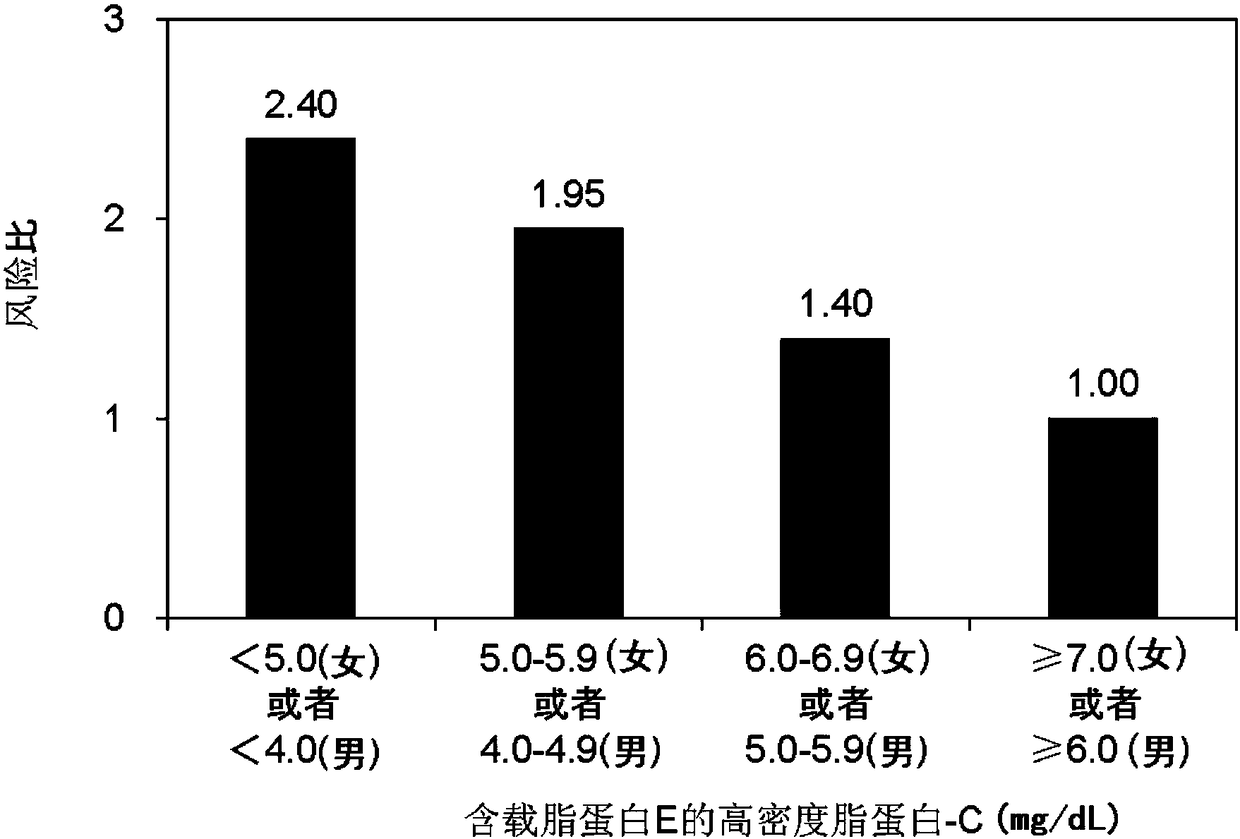
[0092] To evaluate the association between apolipoprotein E-containing high-density lipoprotein-C and the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) using the test samples stored in the cardiovascular disease risk factor cohort study in multiple provinces and cities in China. Specifically, at the time of baseline blood collection, the above-mentioned items were measured for 5,417 CHD-free patients. Then, based on the results of the 6.45-year follow-up of the subjects of the cohort study, the incidence of CHD during the investigation period was verified to verify the correlation with the measurement items.
[0093] The determination of high-density lipoprotein-C containing apolipoprotein E uses the following method: In the first step, cholesterol in lipoproteins other than high-density lipoprotein containing apoE is treated with cholesterol esterase, cholesterol oxidase, and peroxidation Hydrogenase elimination; step 2, use cholesterol esterase, cholesterol oxidase, peroxidase to mea...
Embodiment 2
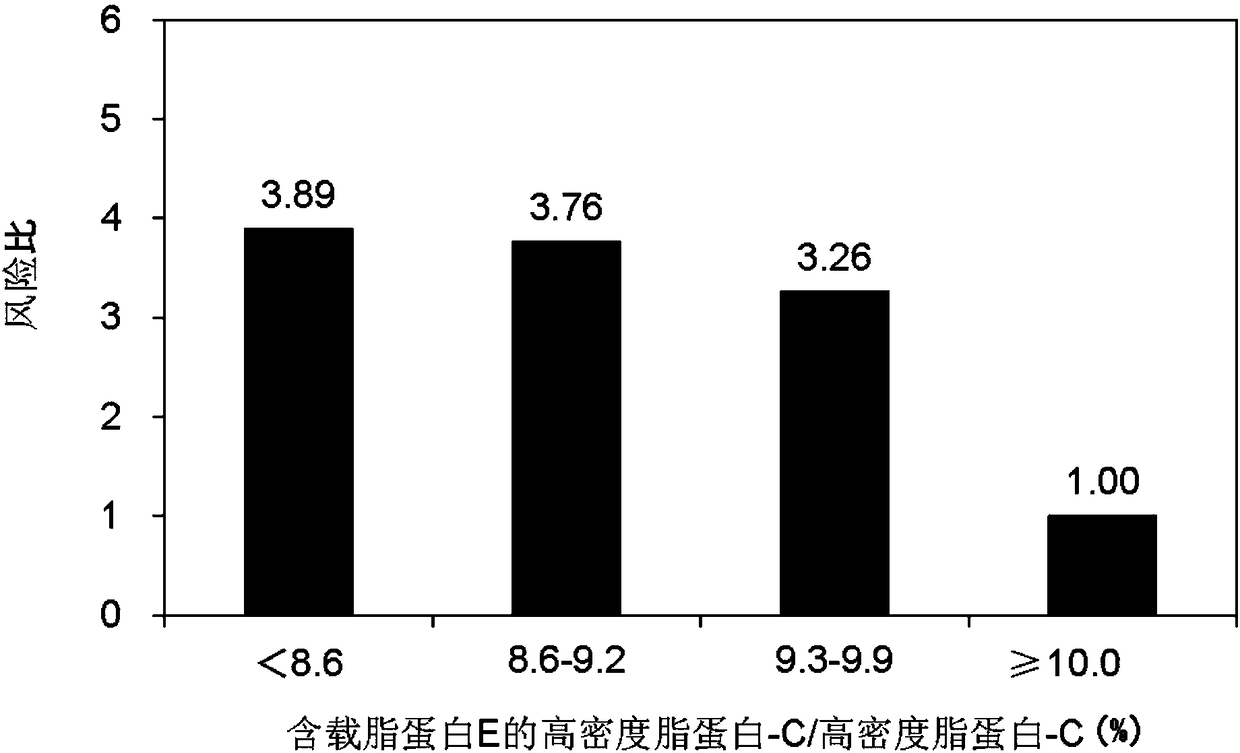
[0098]Using the same cohort study test samples as in Example 1, the correlation between the ratio of apolipoprotein E-containing high-density lipoprotein-C and high-density lipoprotein-C and the risk of CHD was analyzed.
[0099] High-density lipoprotein-C containing apolipoprotein E was measured using the same method as in Example 1, and high-density lipoprotein-C was measured using HDL-EX "Seiken" (manufactured by DENKA SEIKEN Co., Ltd.).
[0100] The ratio of apolipoprotein E-containing HDL-C to HDL-C was divided into the following four groups: less than 8.6%, 8.6-9.2%, 9.3-9.9%, and more than 10.0%, using Cox proportional regression The model compares the hazard ratios of each group with respect to the group containing HDL-C / HDL-C containing 10.0% or more of apolipoprotein E.
[0101] show the result in figure 2 .
[0102] Such as figure 2 As shown, as the ratio of apoE-containing HDL-C / HDL-C becomes smaller, the hazard ratio increases and the risk of CHD increases. ...
Embodiment 3
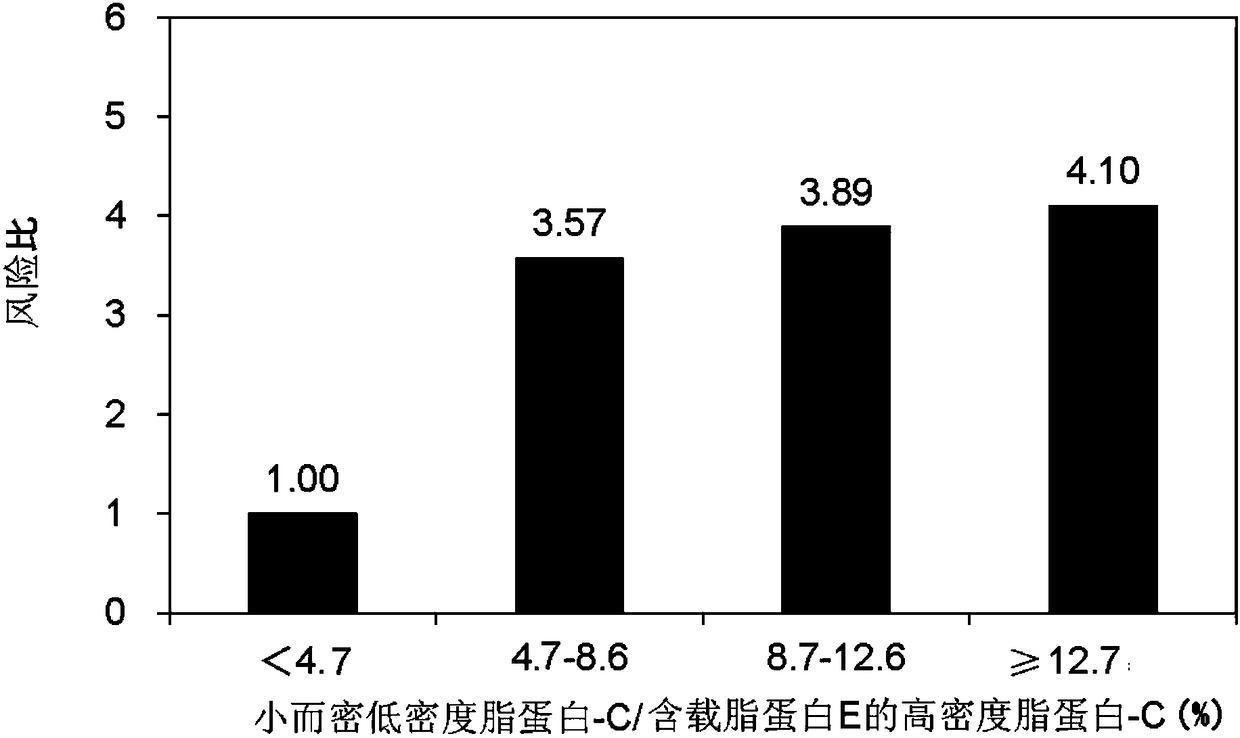
[0104] Using the same cohort study test samples as in Example 1, the correlation between the ratio of small and dense low-density lipoprotein-C to high-density lipoprotein-C containing apolipoprotein E and the risk of CHD was analyzed.
[0105] High-density lipoprotein-C containing apolipoprotein E was measured using the same method as in Example 1, and small dense low-density lipoprotein-C was measured using Small Dense LDL-EX "Seiken" (DENKA SEIKEN Co., Ltd. system).
[0106] The ratio of small, dense LDL-C to HDL-C containing apoE was divided into the following four groups: less than 4.7%, 4.7-8.6%, 8.7-12.6%, and more than 12.7%, using Cox proportional regression models comparing hazard ratios for each group relative to the small dense LDL-C / HDL-C with apoE less than 4.7% group.
[0107] show the result in image 3 .
[0108] Such as image 3 As shown, as the ratio of small dense LDL-C / HDL-C containing apoE increases, the hazard ratio increases and the risk of CHD incr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com