Data sending method and device
A data sending method and data technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as insufficient reassembly buffer and packet loss at the receiving side
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
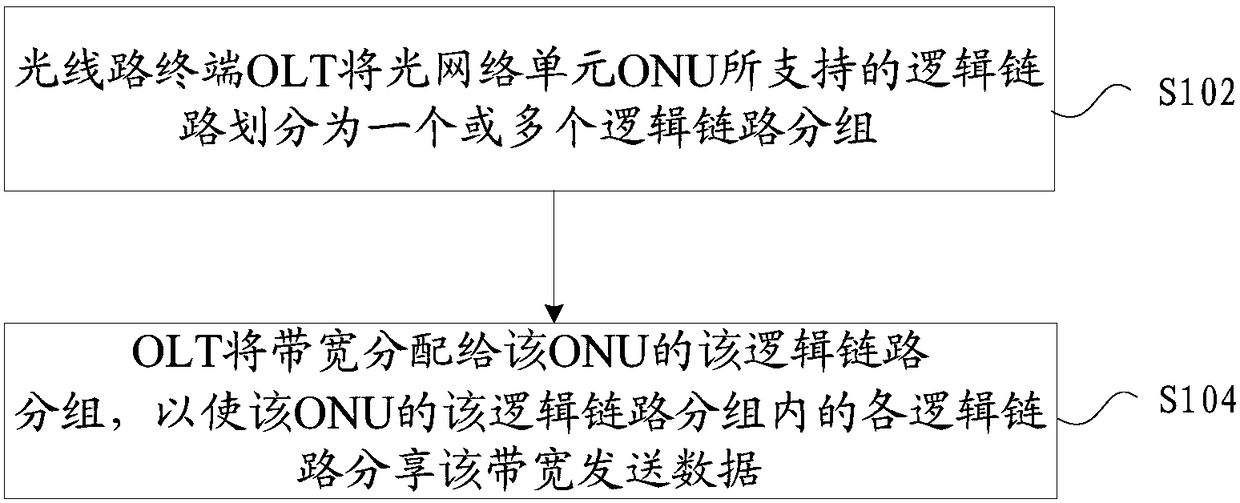
[0075] In this embodiment, a method for sending data is provided, figure 1 is a flow chart of data transmission according to an embodiment of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, the process includes the following steps:
[0076] Step S102, the optical line terminal OLT divides the logical links supported by the optical network unit ONU into one or more logical link groups;
[0077] In step S104, the OLT allocates bandwidth to the logical link group of the ONU, so that each logical link in the logical link group of the ONU shares the bandwidth to send data.
[0078] Optionally, the execution order of the above step S102 and step S104 can be interchanged, that is, step S104 can be executed first, and then S102 can be executed.
[0079] Optionally, the application scenarios of the above data sending method include but are not limited to: in a passive optical network system, in this application scenario, the optical line terminal OLT divides the logical link suppor...
Embodiment 1
[0104]In the passive optical network system, each ONU supports an uplink fragmentable data flow, and the size of the OLT reassembly buffer is in accordance with the requirements of the passive optical network (NGEPON (Next Generation EPON, Next Generation Passive Optical Network), NG-PON2) system. Design the maximum number of ONUs that can be supported, for example, the maximum packet length multiplied by the maximum number of ONUs is the reassembly cache. In the operation of the passive optical network system, all logical links in each ONU are set as a logical link grouping, as an upstream bandwidth container, the OLT allocates the upstream bandwidth to the logical link grouping of the ONU, and the logical link grouping of each ONU The link group uses the uplink bandwidth according to the local policy, and sends uplink data on each logical link (LLID, XGEM-Port (10Gigabit Passive Optical Network Encapsulation Method Port, 10GPON encapsulation port)).
[0105] Take NGEPON as a...
Embodiment 2
[0121] The OLT supports each ONU to support more than one fragmentable data stream link N, and the number of fragmentable data streams supported by each ONU is fixed, such as N=2, or N=3, etc., the logical link (LLID) of the OLT to the ONU , XGEM-Port) are grouped into logical link groups, and the OLT allocates bandwidth to the logical link groups of the ONU.
[0122] Take NGEPON as an example:
[0123] 1. The OLT's reassembly cache is designed according to the number of fragmentable data streams that each ONU can support;
[0124] 2. When the NGEPON system is started, the OLT obtains the reassembly cache and the maximum supported packet length, and divides the reassembly cache by the maximum packet length to obtain the maximum number of fragmentable data streams that can be supported, which is greater than or equal to all ONUs that can support fragmentation The sum of the number of data streams;
[0125] 3. The OLT groups the logical link LLIDs of each ONU to form several l...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com