Patents
Literature
579results about "Bidirectional transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
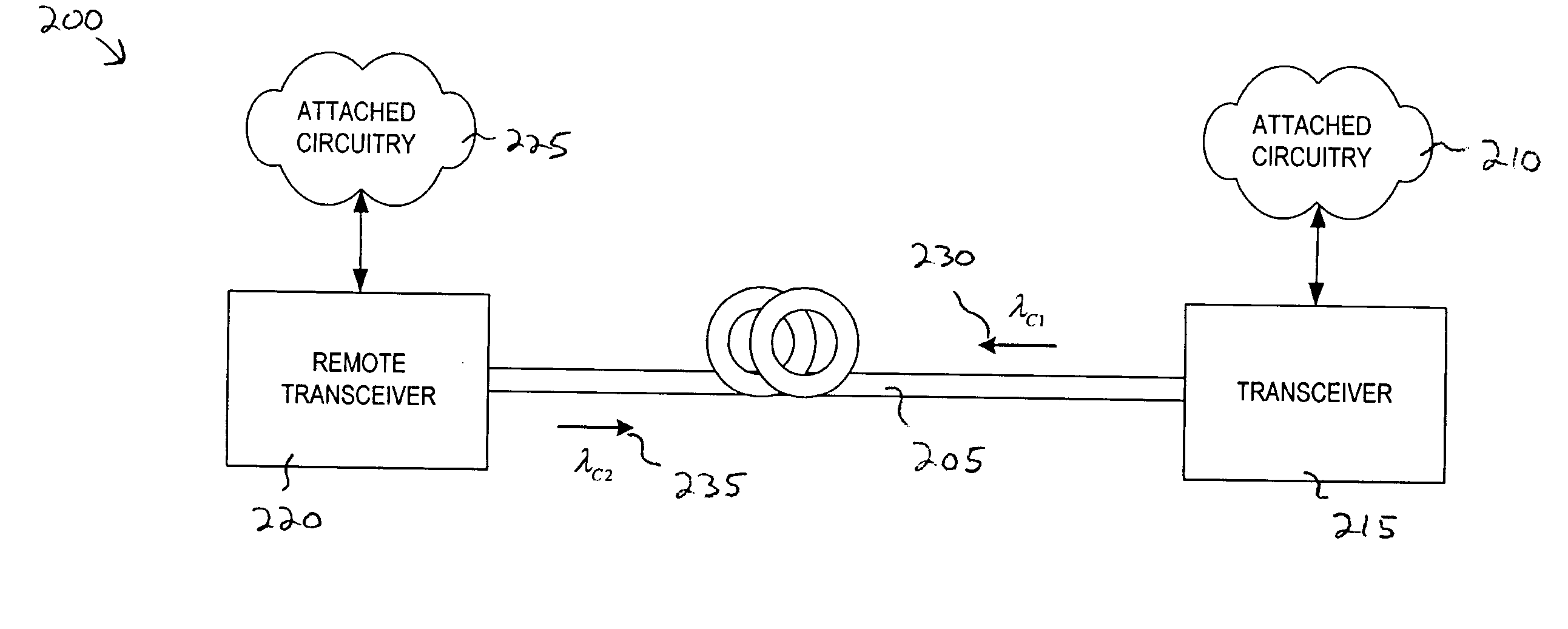
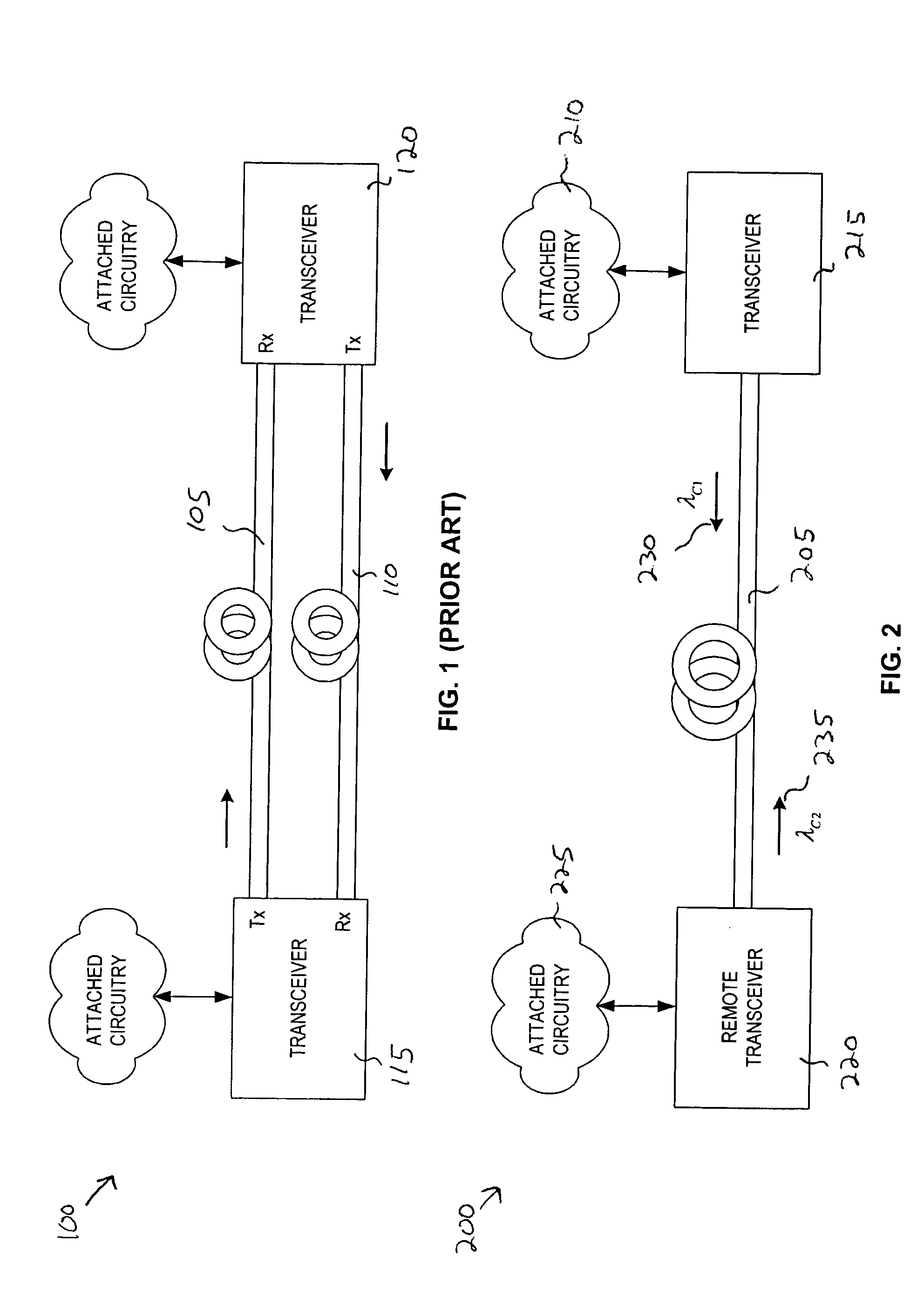
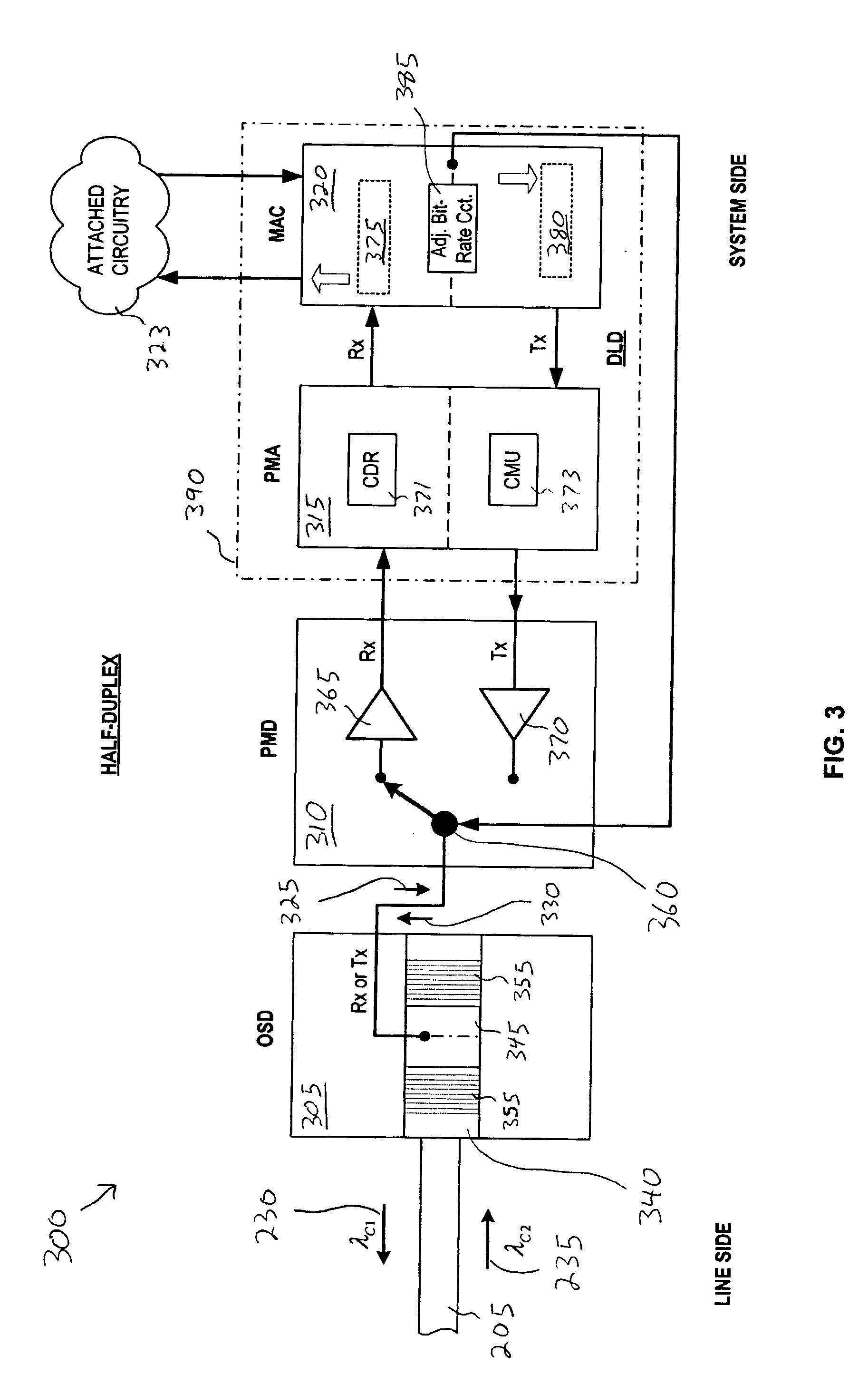
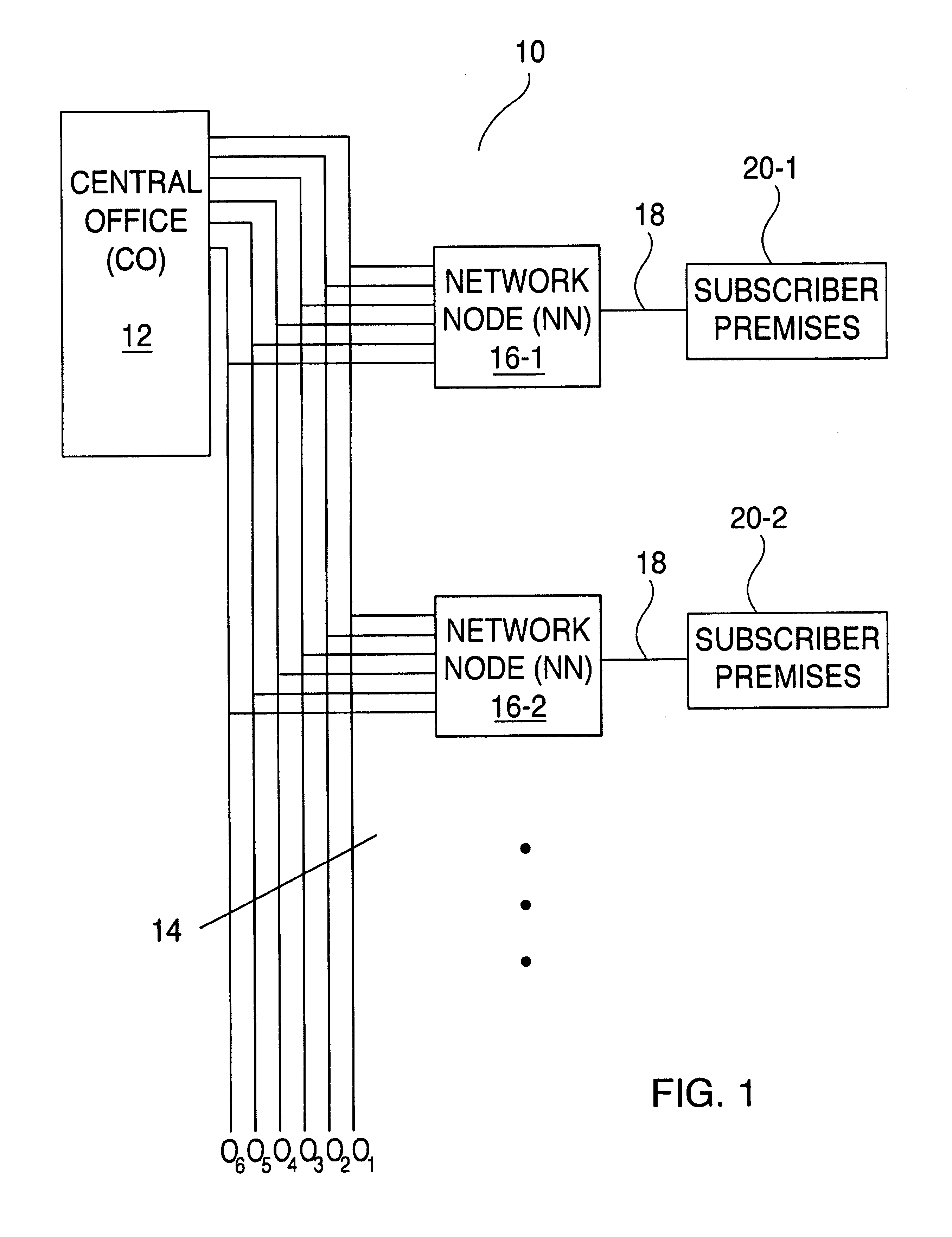
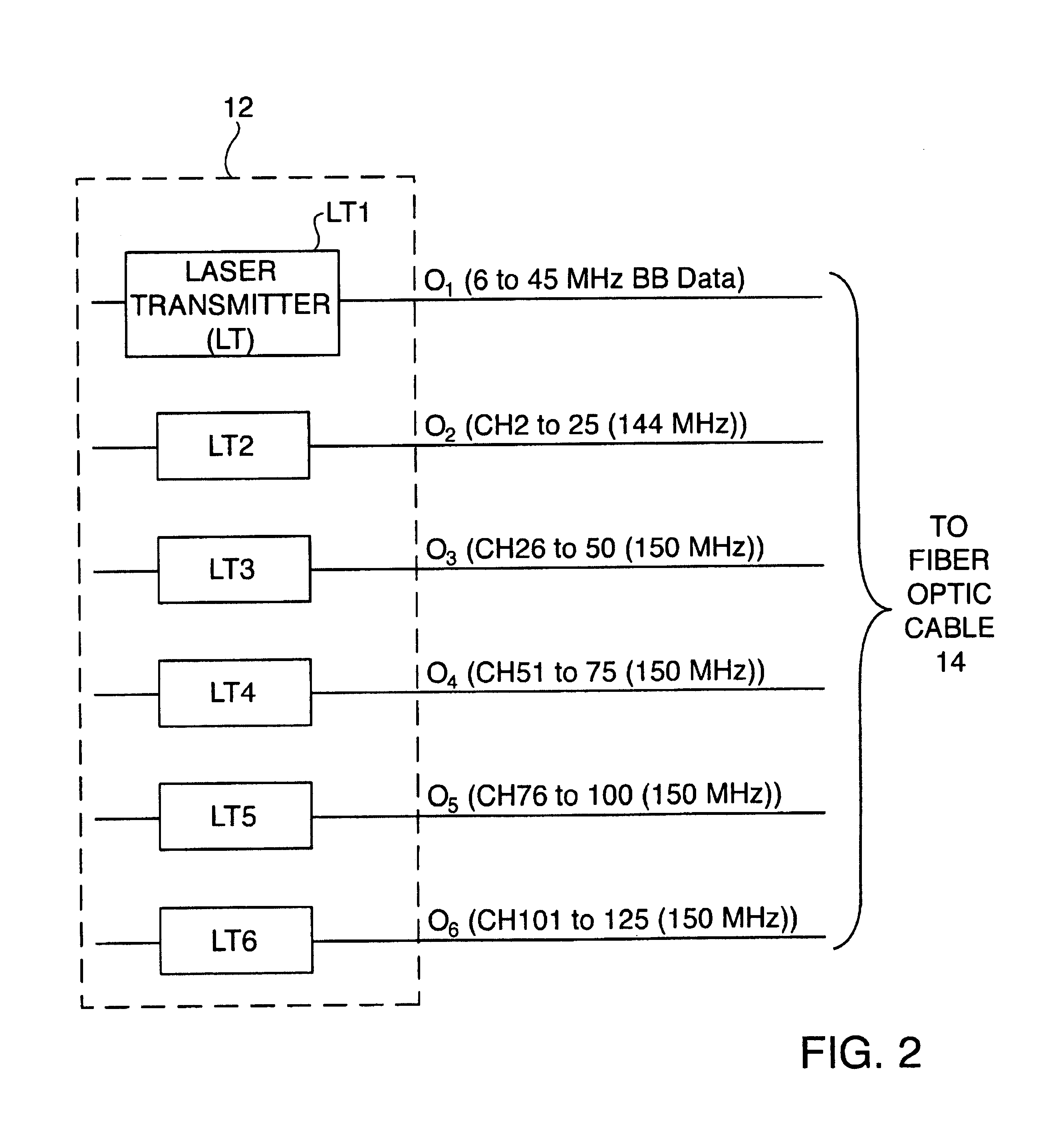
System and Method for Optical Layer Management in Optical Modules and Remote Control of Optical Modules
ActiveUS20120275784A1Low costMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsTransceiverNetwork connection
A system and method for managing the optical layer network data communications of an optical fiber data network by an optical transceiver module is disclosed. The management of the optical layer network data communications comprising data link layer functions or layer 2 functions in an OSI model. Benefits include reduction in reduced cost of network deployments from consolidation of network equipment, such as switches, and reduction in power consumed as well as enabling point-to-multipoint network connections from previously only point-to-point network connection.
Owner:SOTO ALEXANDER I +1
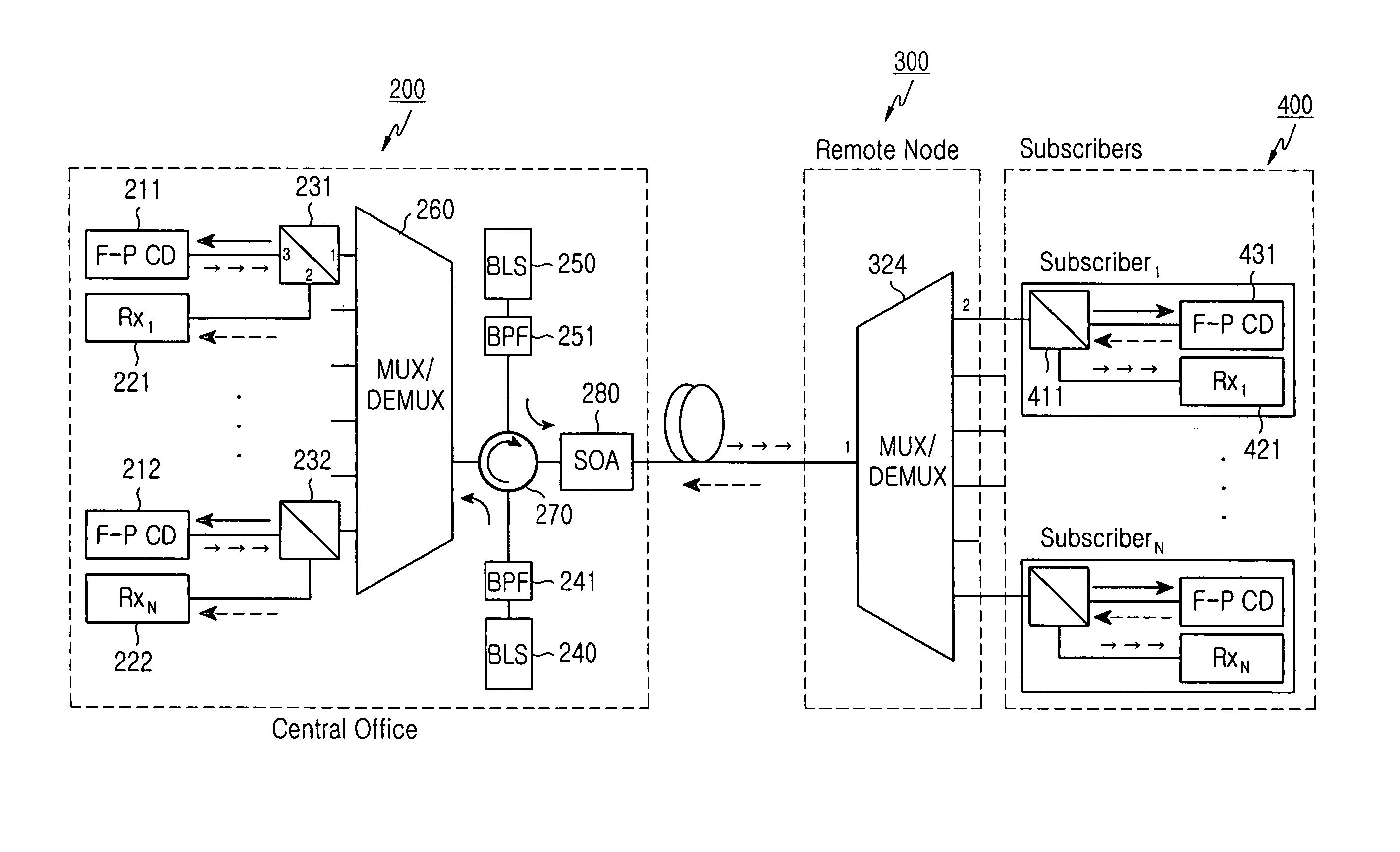
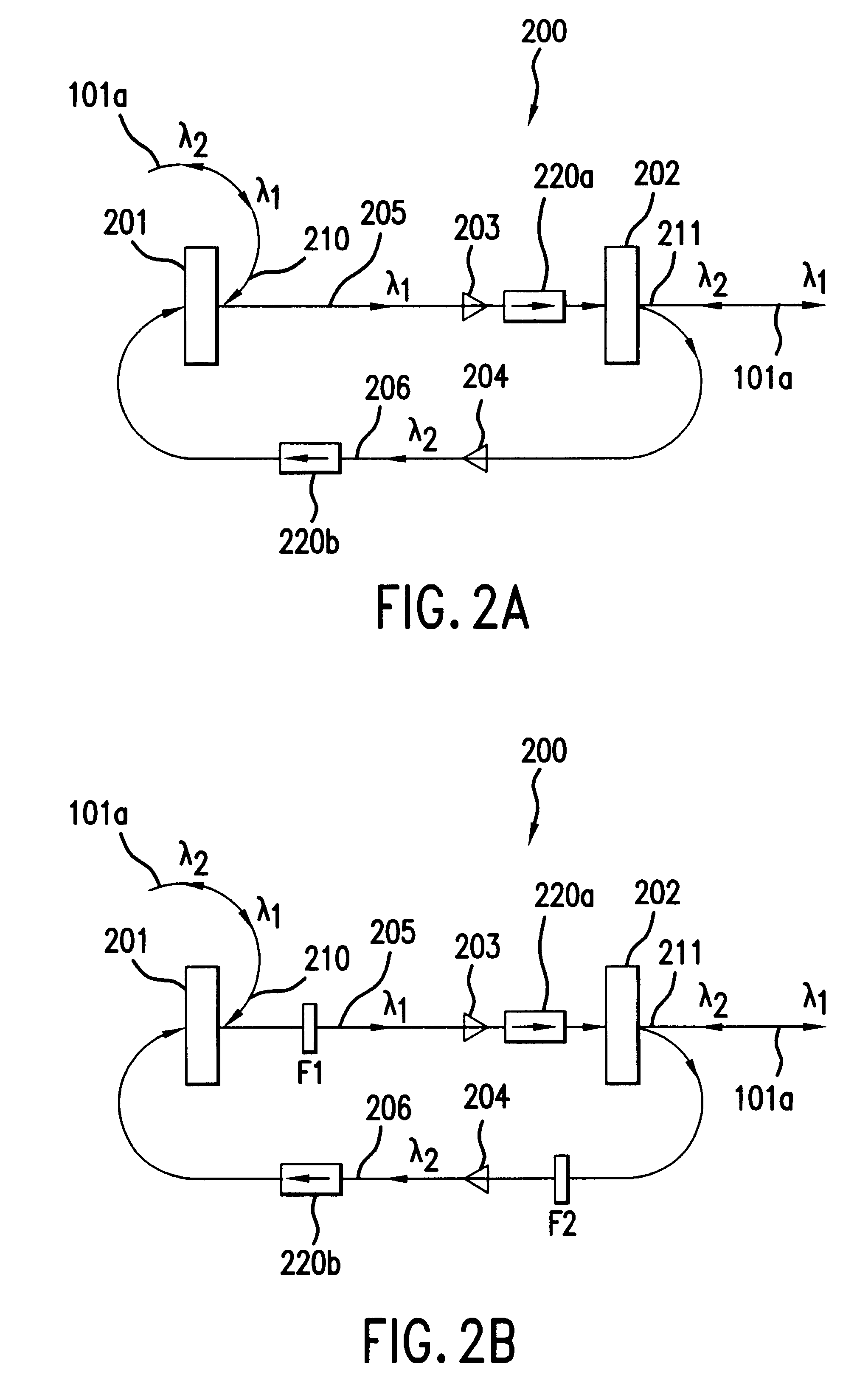
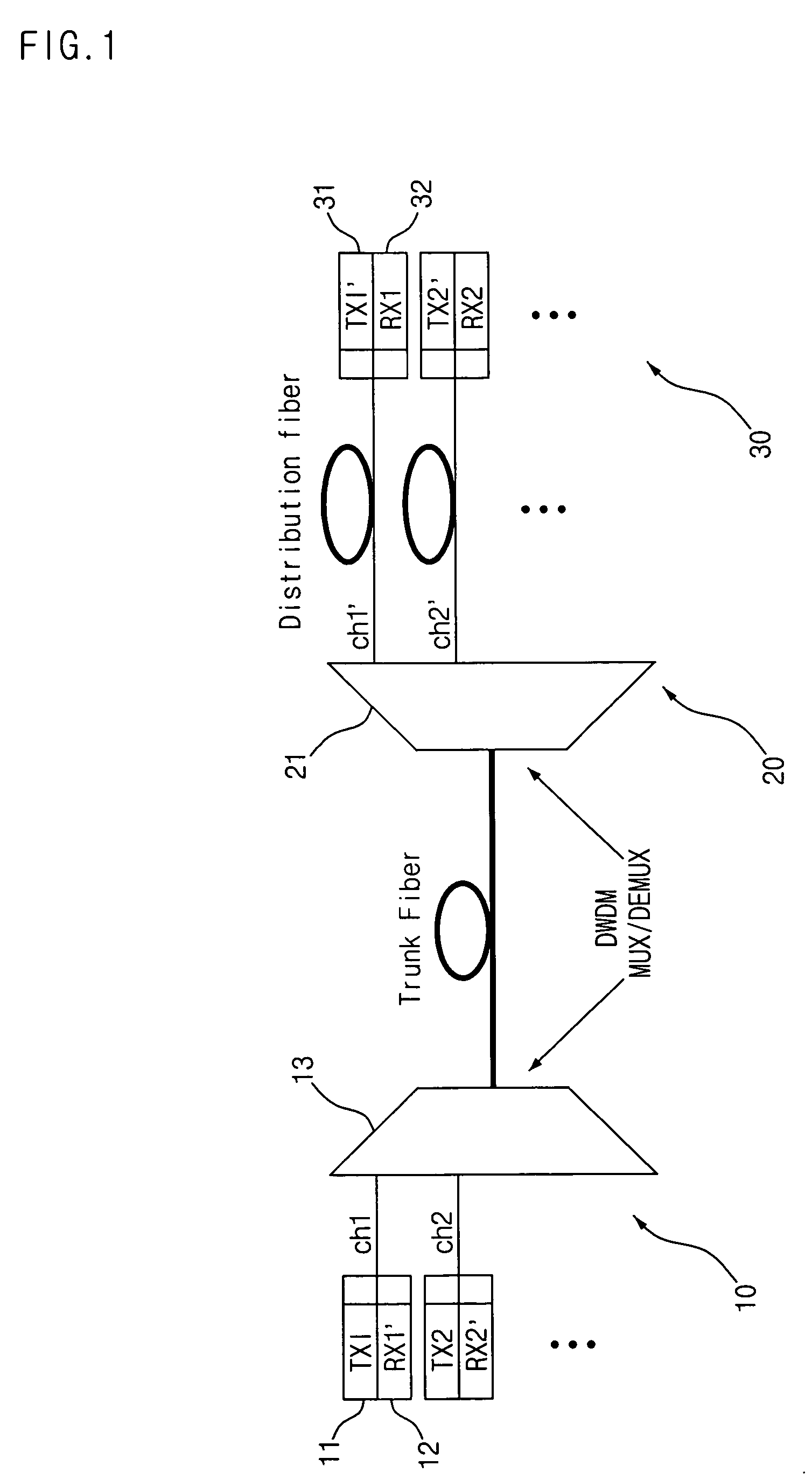
Method for decreasing and compensating the transmission loss at a wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network and an apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20030142978A1Decreasing and compensating optical lossLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveTransmission loss
The present invention relates to a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network. In particular, it relates to a technology for minimizing the optical loss at a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network based on wavelength-locked light source Thereby it improves the transmission quality and increases the transmission distance. A 4-port optical path setting device of the present invention increases the amount of light injected into an optical transmitter and thereby improves the wavelength-locking characteristic of a light source. In addition, it can decrease the optical transmission loss in an optical transmission path, and by an optical amplifier being inserted therein; it can also compensate the optical loss in an optical transmission path. In the present invention, a 4-port optical path setting device having the characteristics described above and a method for fault recovery without an additional optical loss are presented.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Transceiver system on a card for simultaneously transmitting and receiving information at a rate equal to or greater than approximately one terabit per second
An optical transceiver system is provided that comprises multiple parallel transceiver modules that are mounted on a card. The transceiver card is small in terms of spatial dimensions, has very good heat dissipation characteristics, and is capable of simultaneously transmitting and receiving data at a rate equal to or greater than approximately one Tb per second (1 Tb / s). A plurality of the transceiver systems may be interconnected to achieve a communications hub system having even higher bandwidths. In addition, the transceiver system may be configured such that each card has a routing controller mounted thereon for performing router functions. The router functions include, for example: causing signals received by one transceiver module on the card to be routed to and transmitted by another of the transceiver modules; causing signals received by one transceiver module on the card to be retransmitted by the same transceiver module over one of it's optical transmit channels; and causing signals received by one transceiver module on the card to be routed to and transmitted by a transceiver module on a different card.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Remotely deployed optical fiber circulator
ActiveUS20040113104A1ConstructionsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFiberOptical circulator
Fiber-optic-based systems and methods for monitoring physical parameters using a remotely deployed circulator are disclosed. In a preferred embodiment the circulator is remotely deployed with respect to an optical source / detector and coupled thereto by two dedicated fiber optical cables: a forward line for passing light from the source through the circulator to fiber-optic-based sensors, and a return line for passing light reflected from the sensors through the circulator back to the detector. By using separate forward and return lines in conjunction with the circulator, backscattering phenomenon experienced on the forward line will not interfere with the reflected light signals coming from the sensors. The circulator, and hence the sensors, may therefore be remotely deployed from the source / detector present at a monitoring station, greatly expanding distances which optical sensing systems can span.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
Remotely deployed optical fiber circulator
InactiveUS6933491B2Increase distanceEasy to deployMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorConstructionsFiberOptical circulator
Fiber-optic-based systems and methods for monitoring physical parameters using a remotely deployed circulator are disclosed. In a preferred embodiment the circulator is remotely deployed with respect to an optical source / detector and coupled thereto by two dedicated fiber optical cables: a forward line for passing light from the source through the circulator to fiber-optic-based sensors, and a return line for passing light reflected from the sensors through the circulator back to the detector. By using separate forward and return lines in conjunction with the circulator, backscattering phenomenon experienced on the forward line will not interfere with the reflected light signals coming from the sensors. The circulator, and hence the sensors, may therefore be remotely deployed from the source / detector present at a monitoring station, greatly expanding distances which optical sensing systems can span.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
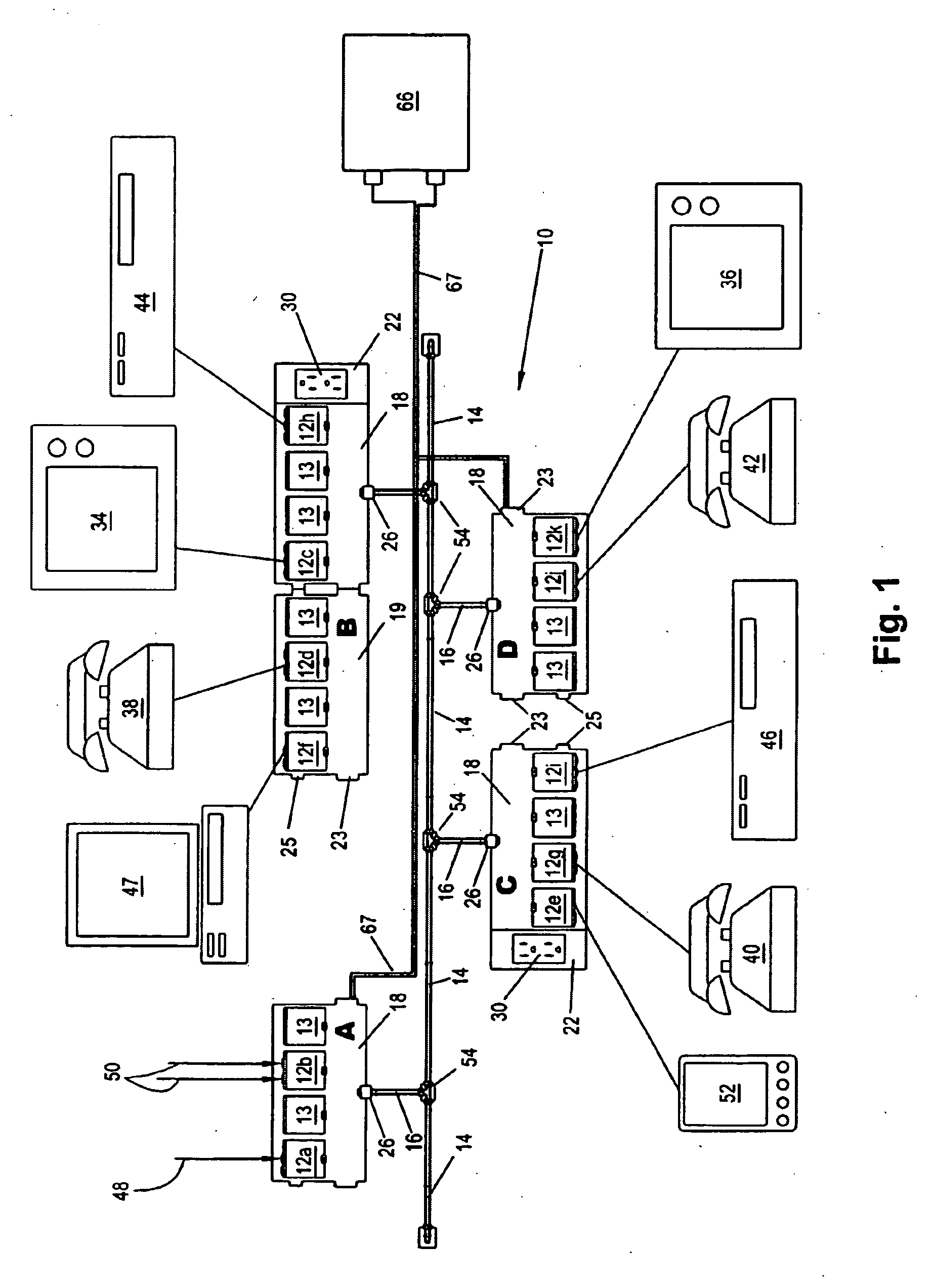
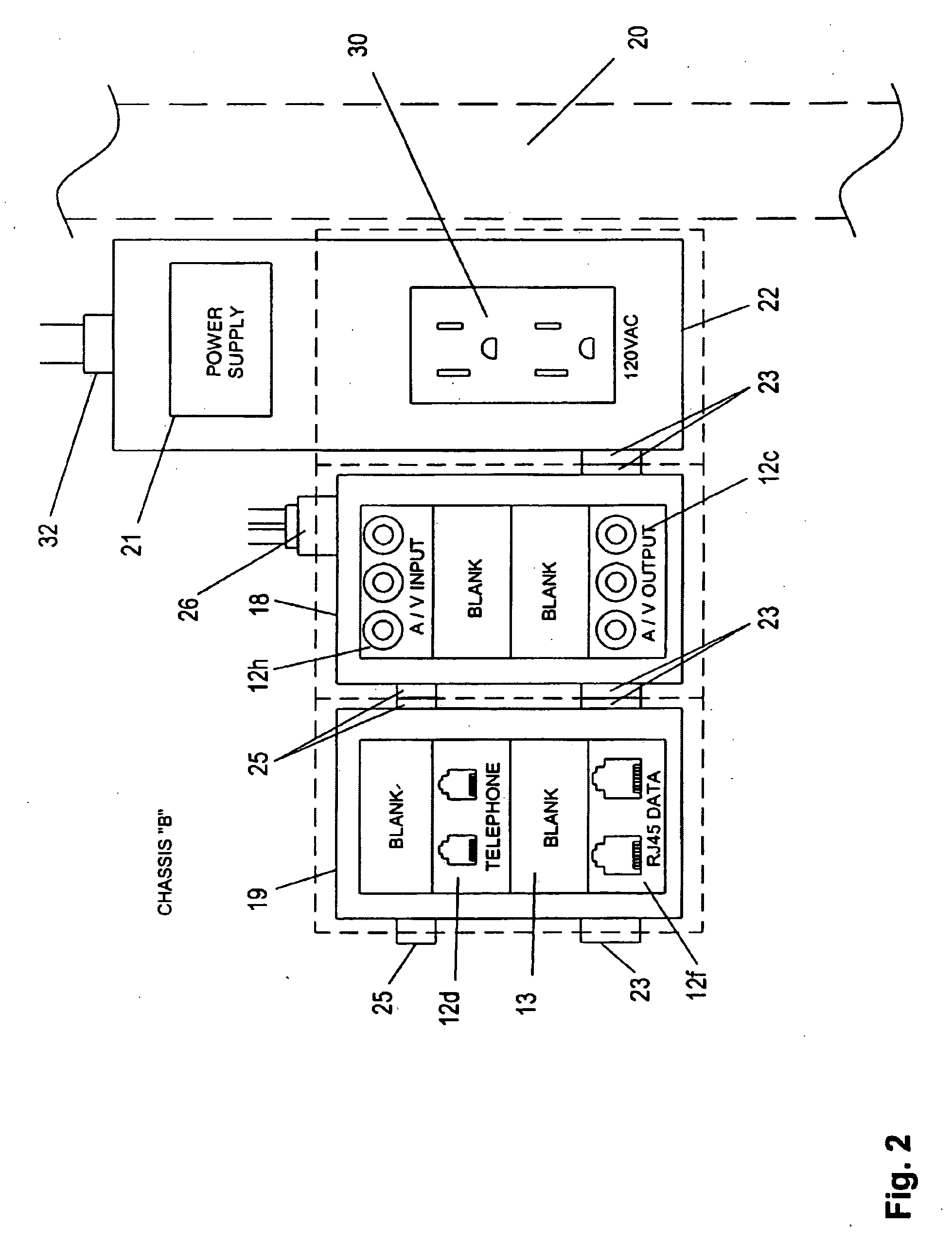
Intelligent modular multimedia data distribution system
A modular multimedia data distribution system includes a plurality of modules interconnected by fiber optic cables wherein data can be sent directly from one module to another. Each module is provided with connections for connecting the module to a media device. The system also includes a plurality of chassis, each chassis having one or more slots for interchangeably receiving the modules. Each of the slots includes connections for powering the modules and connecting the modules to a common fiber optic network. One or more of the modules may be capable of receiving signals from media devices, converting received signals into data, and sending data to at least one other module. Furthermore, one or more of the modules may also be capable of receiving data from other modules, converting received data into signals, and sending signals to a media device.
Owner:INFINITE MEDIA SOLUTIONS
Margin-based optimization systems and methods in optical networks for capacity boosting
ActiveUS20150333824A1Increase capacityReduce marginTransmission monitoringOptical multiplexLength waveOptimization system
Systems and methods of optimizing capacity of an optical network include identifying a first wavelength with an associated target capacity; determining that the first wavelength has insufficient capability to operate at the associated target capacity; and adjusting one or more wavelengths to increase capability of the first wavelength such that the first wavelength can operate at the associated target capacity.
Owner:CIENA
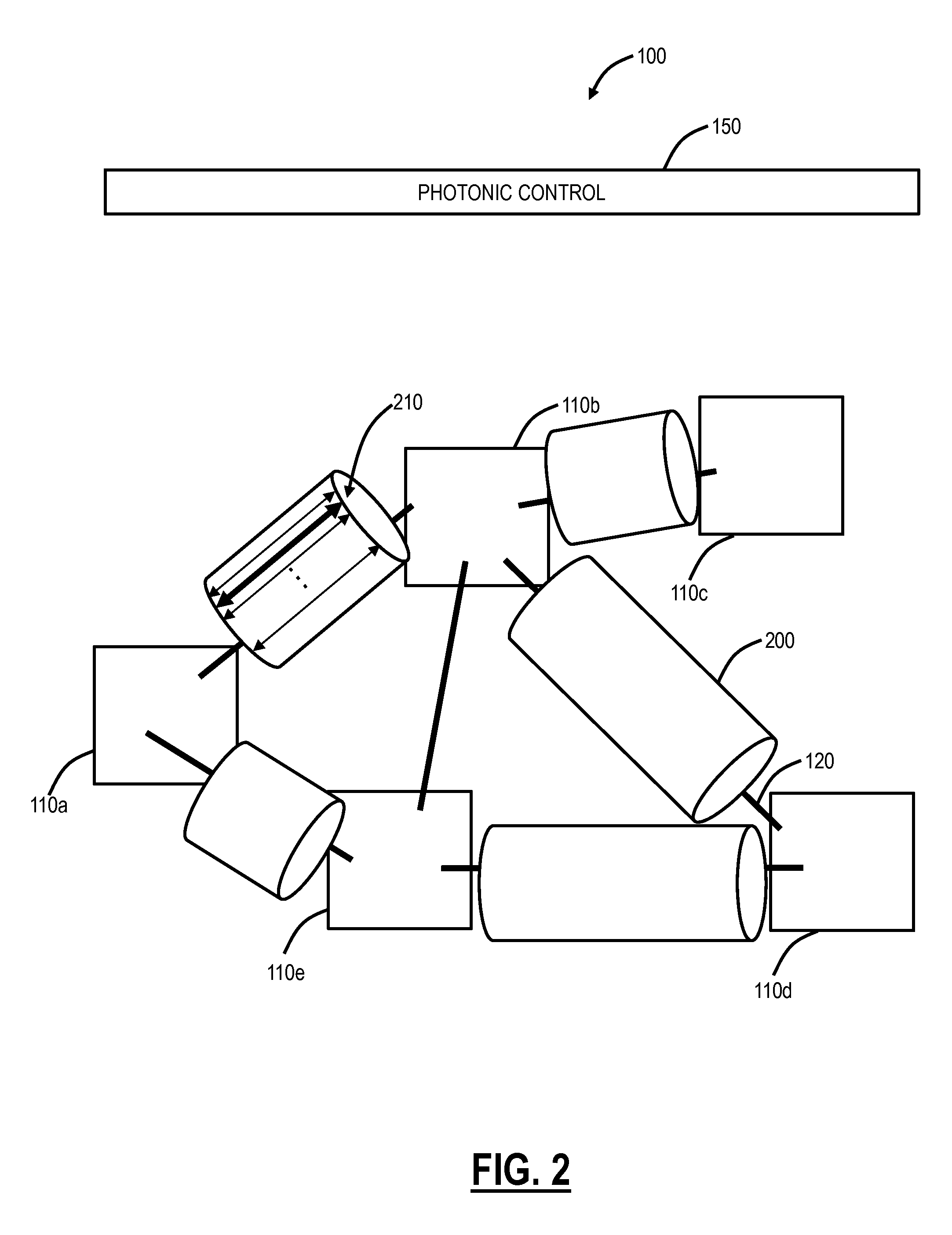
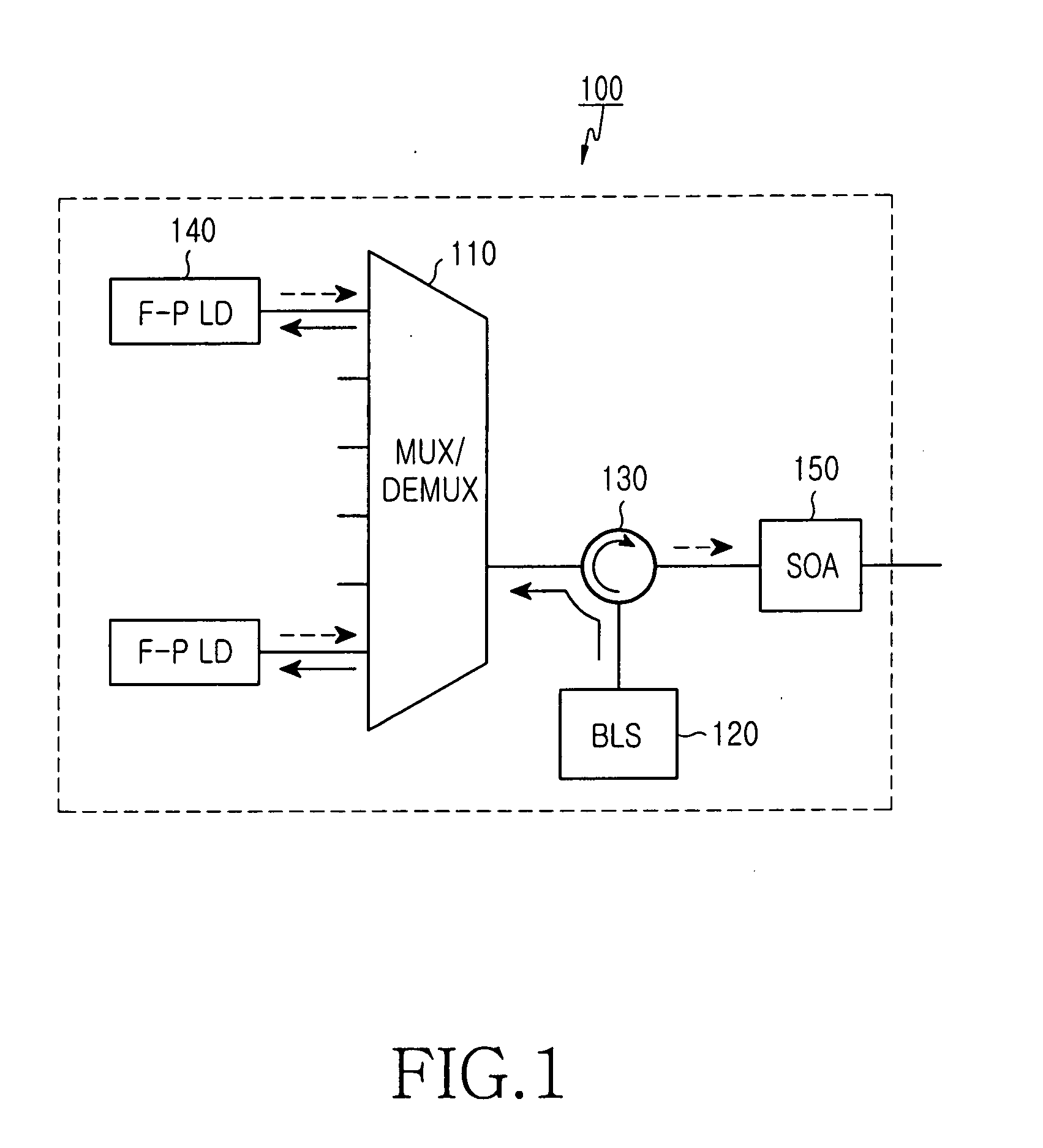
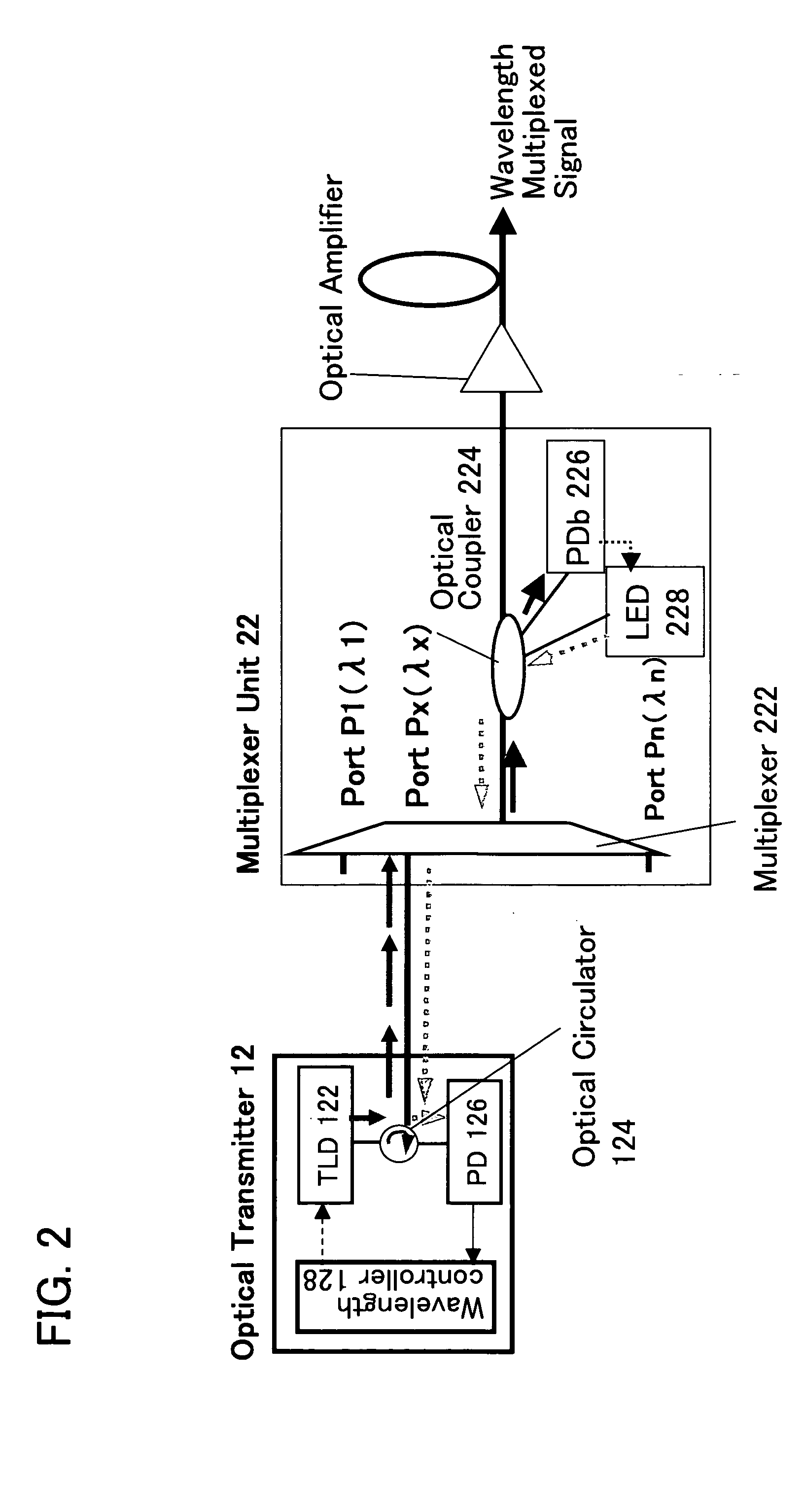
Multi-wavelength optical transmitter and bi-directional wavelength division multiplexing system using the same
InactiveUS20050041971A1Stable distanceStable transmission speedLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMulti wavelengthTransmitter
A multi-wavelength optical transmitter which multiplexes a plurality of channels having different wavelengths into an optical signal for output includes lasers for generating mode-locked channels by corresponding incoherent light received in the lasers. The transmitter also has a semiconductor optical amplifier for amplifying, while in a gain saturation state, the optical signal multiplexed by the multiplexer / demultiplexer. Light from a broadband light source is directed by a circulator to the multiplexer / demultiplexer for demultiplexing among the lasers. Light back from the lasers is multiplexed and then directed by the circulator and amplified by a semiconductor optical amplifier for output external to the transmitter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for communicating a clock signal over an optical link
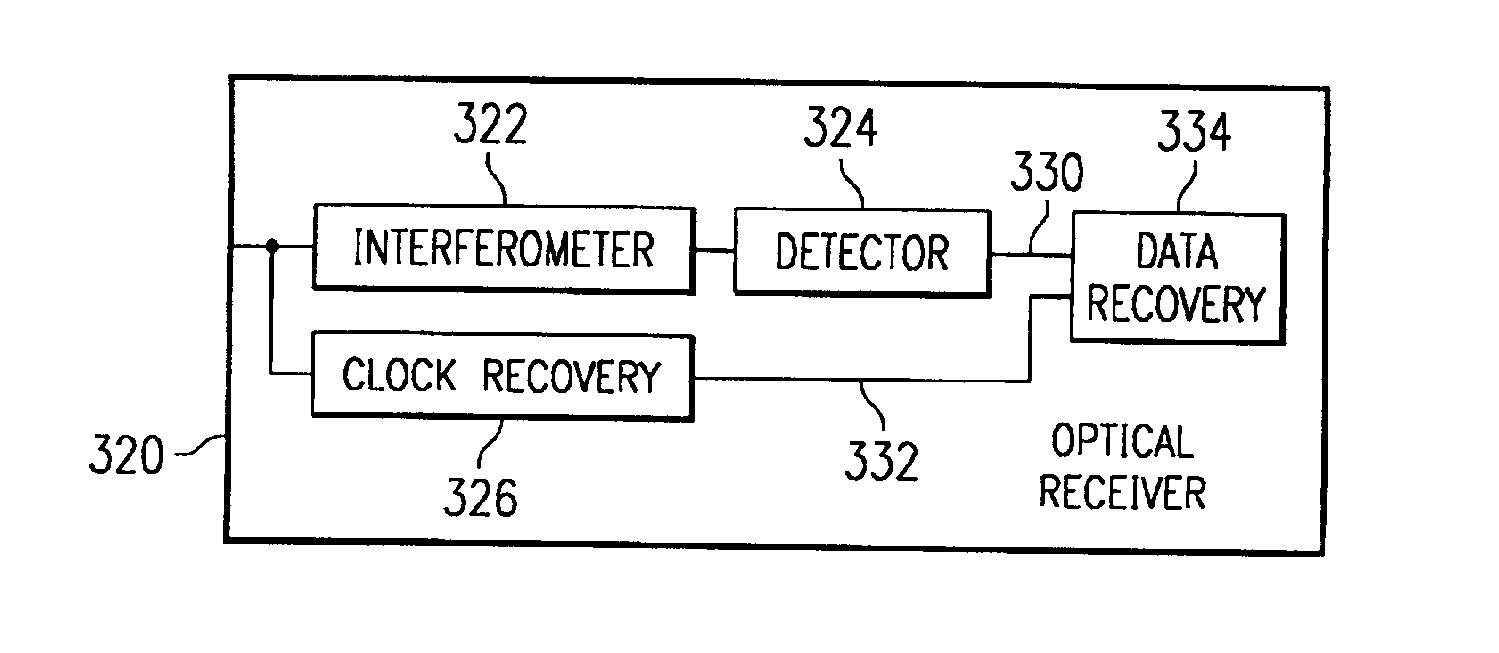
InactiveUS6941078B1Reduces and eliminated problemReduces and eliminated and disadvantageTime-division optical multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansData signalIntensity modulation
A method and system for communicating a clock signal over an optical link includes receiving a multimodulated optical information signal including non-intensity modulation for a data signal and intensity modulation for a clock signal. The clock signal is recovered based on the intensity modulation of the multimodulated optical information signal. The non-intensity modulation for the data signal is converted to intensity modulation for the data signal. The data signal is recovered from the intensity modulation for the data signal using the clock signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and system for providing protection in an optical communication network
InactiveUS20040114925A1Laser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemSignal quality
A method and system for providing tandem protection in a communication system. Path protection is provided using at least two redundant communication paths and selecting the communication path having a higher signal quality. Interface protection is provided through a protection transceiver. The interface protection may be delayed while the path protection attempts to restore communication.
Owner:CIENA
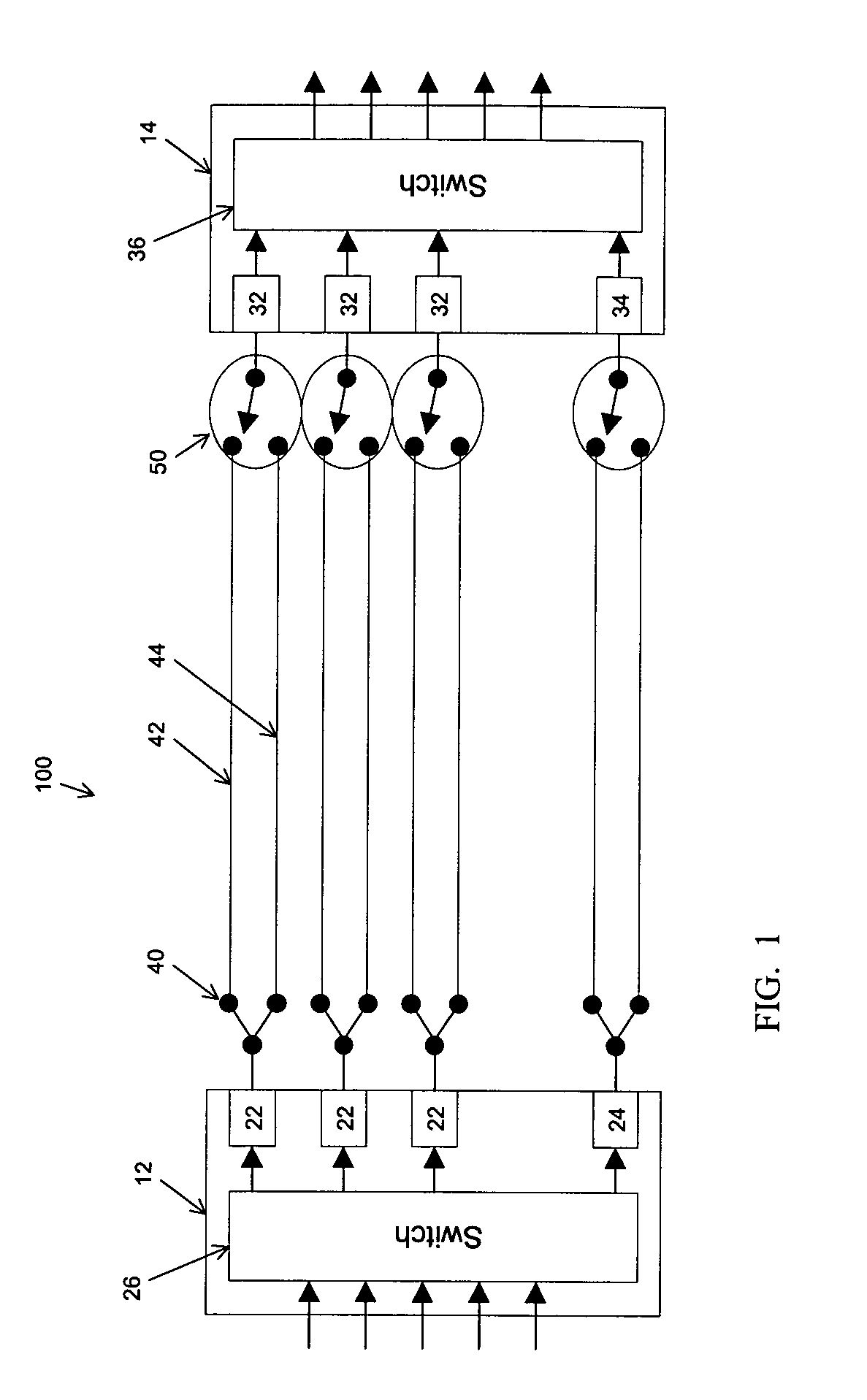
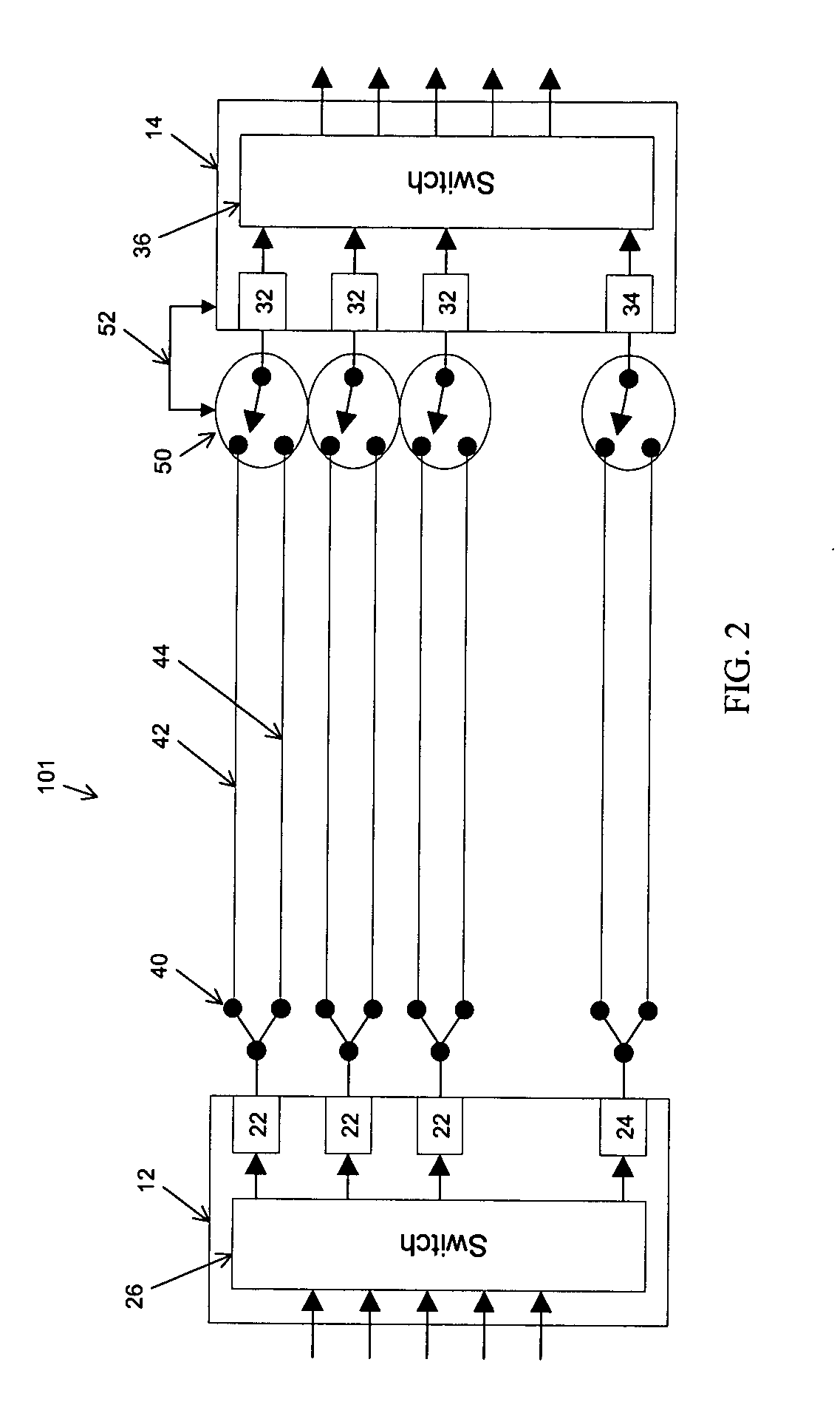
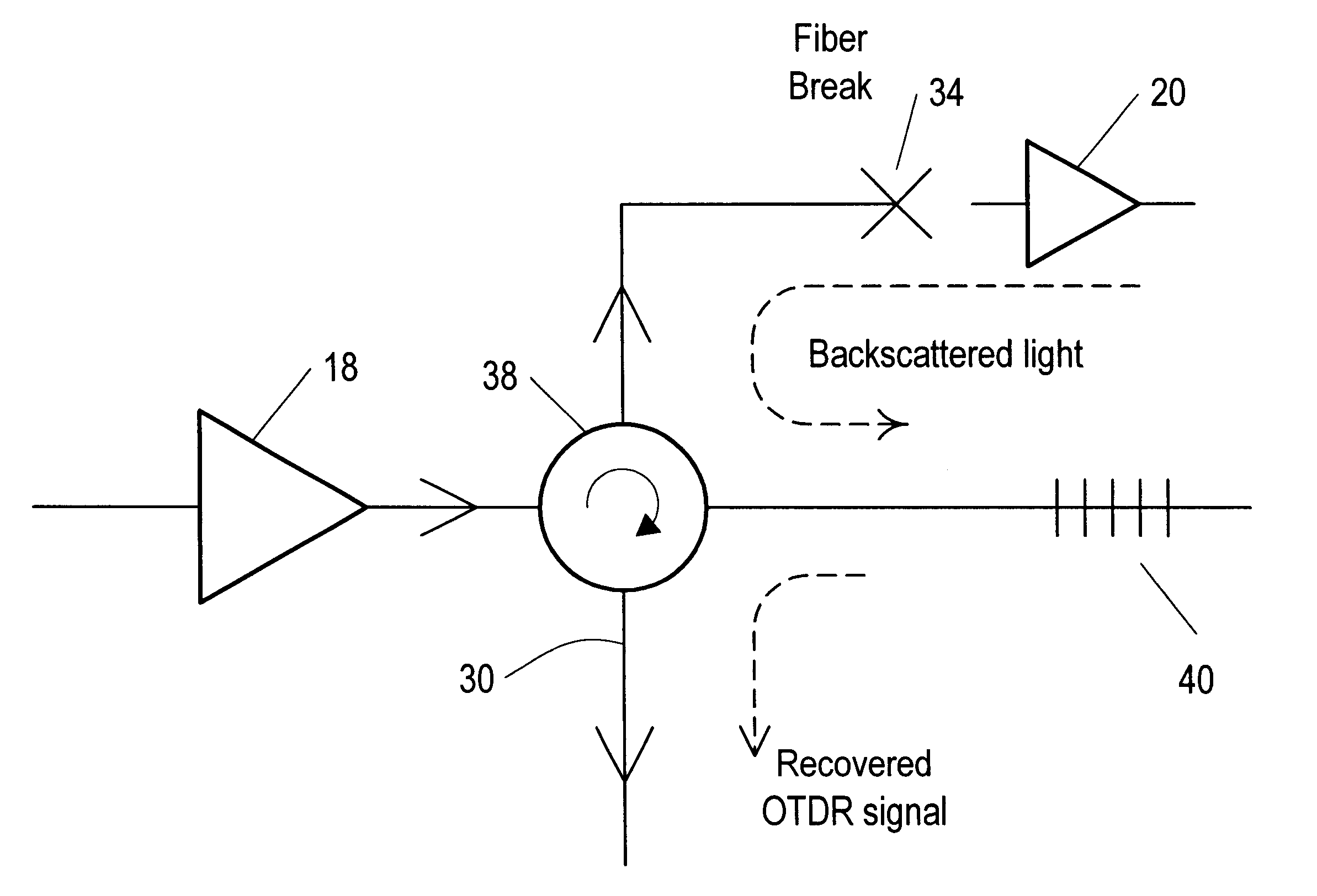
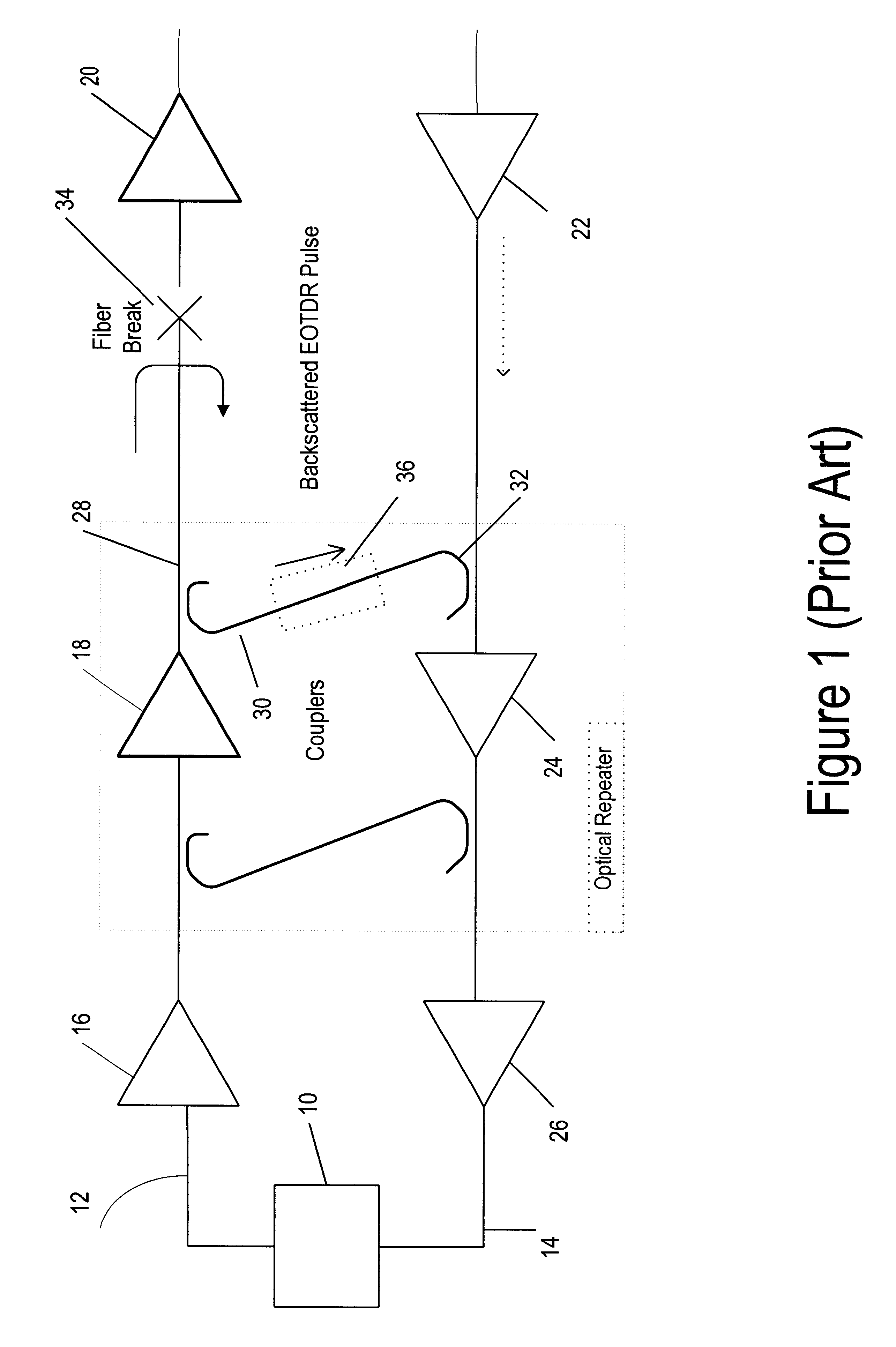
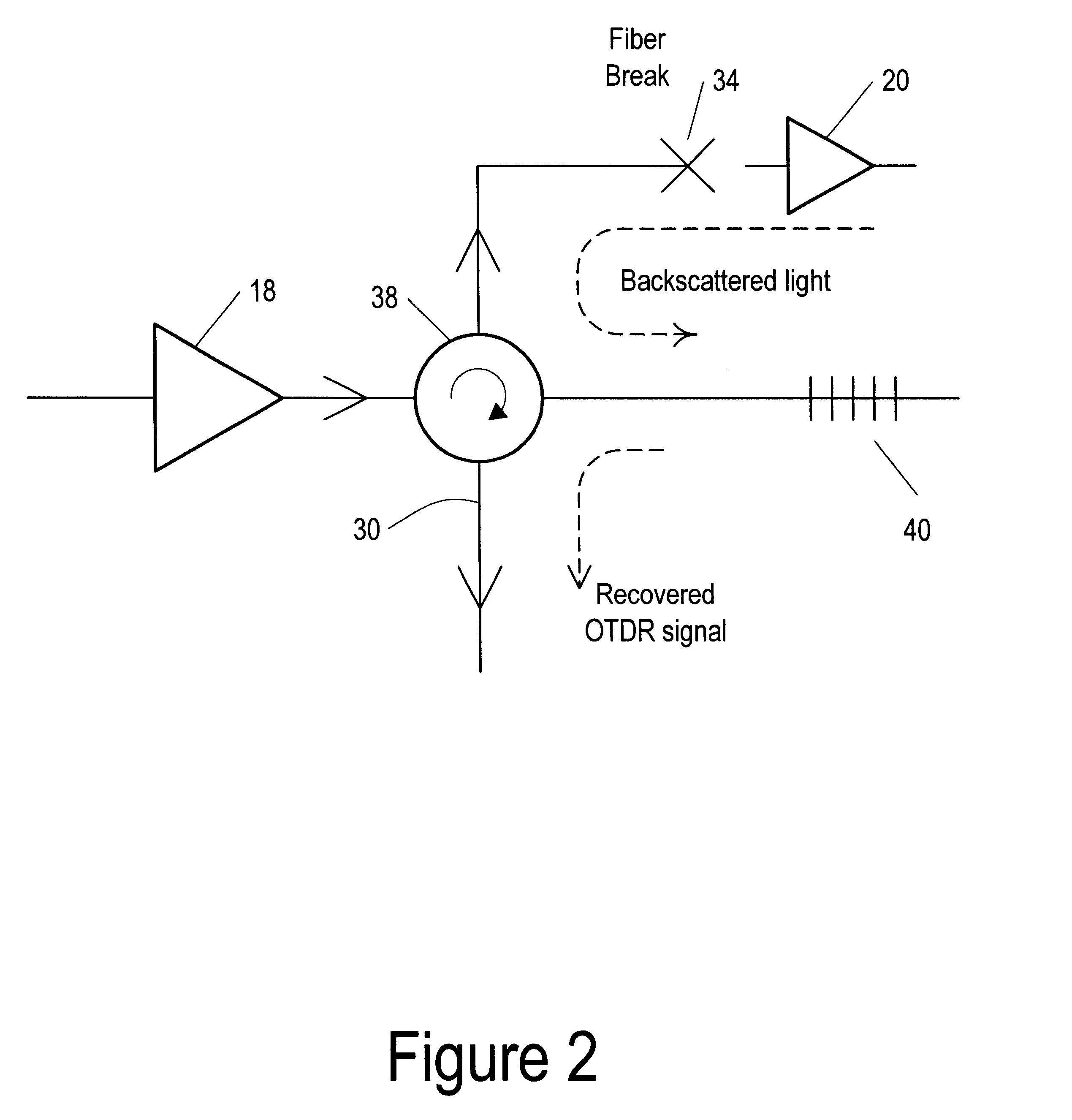
Optical signal transmission network with fiber-break detection
InactiveUS6301036B1Inhibit transferTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsFiberTraffic signal
A bi-directional optical signal transmission network comprises an outbound (12) and an inbound (14) fibre each including an optical amplifier / repeater (18 / 24). An optical coupling (30, 38, 40) communicates between one of the fibres (12) to the output side of the amplifier / repeater (18) and the other fibre (14). The coupling includes a filter (40) which is arranged to permit transfer of a test signal wavelength between the outbound (12) and the inbound (14) fibre but which prevents transfer of unwanted traffic signal.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Terminal detection authentication process, device and operation administrative system in passive optical network
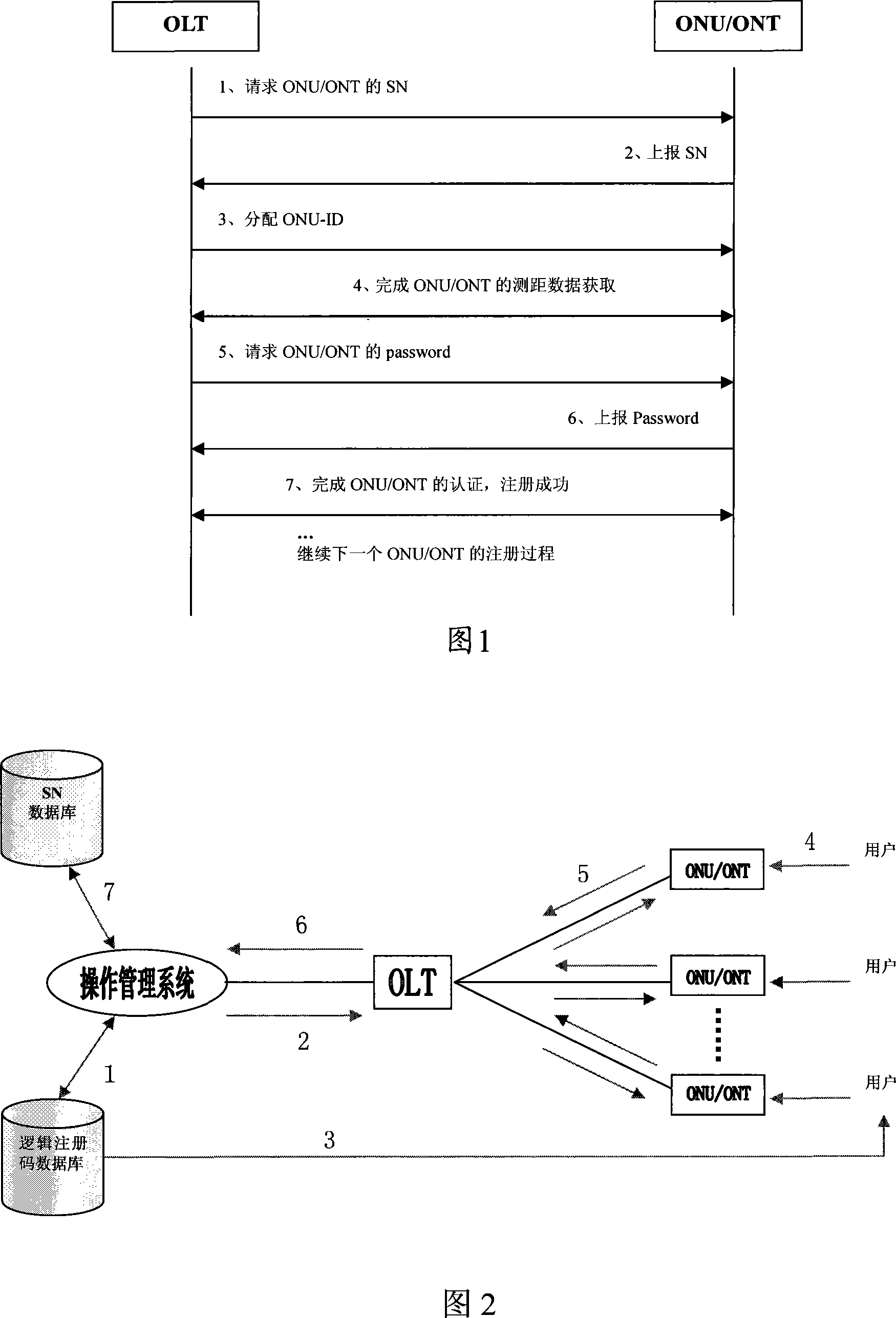
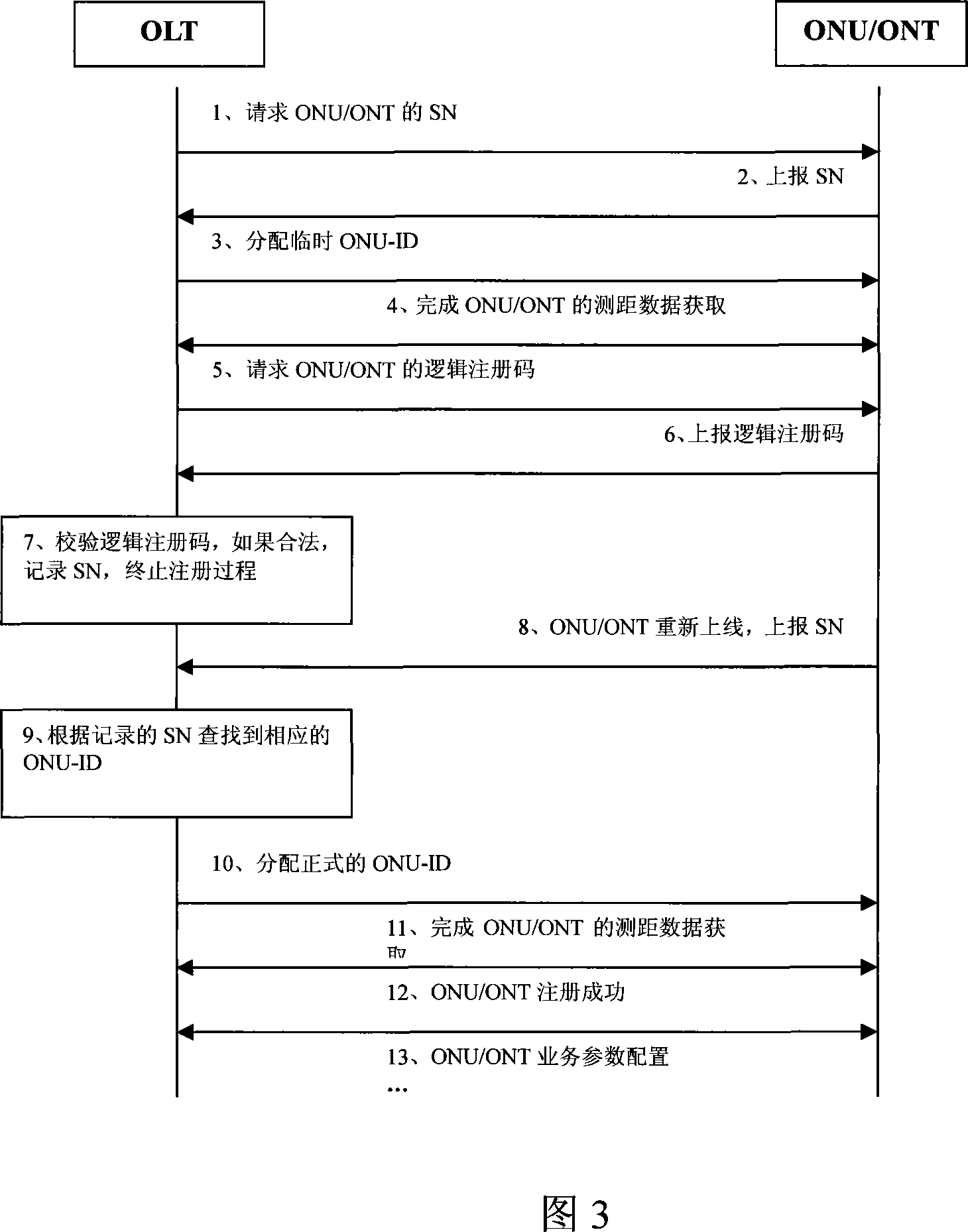
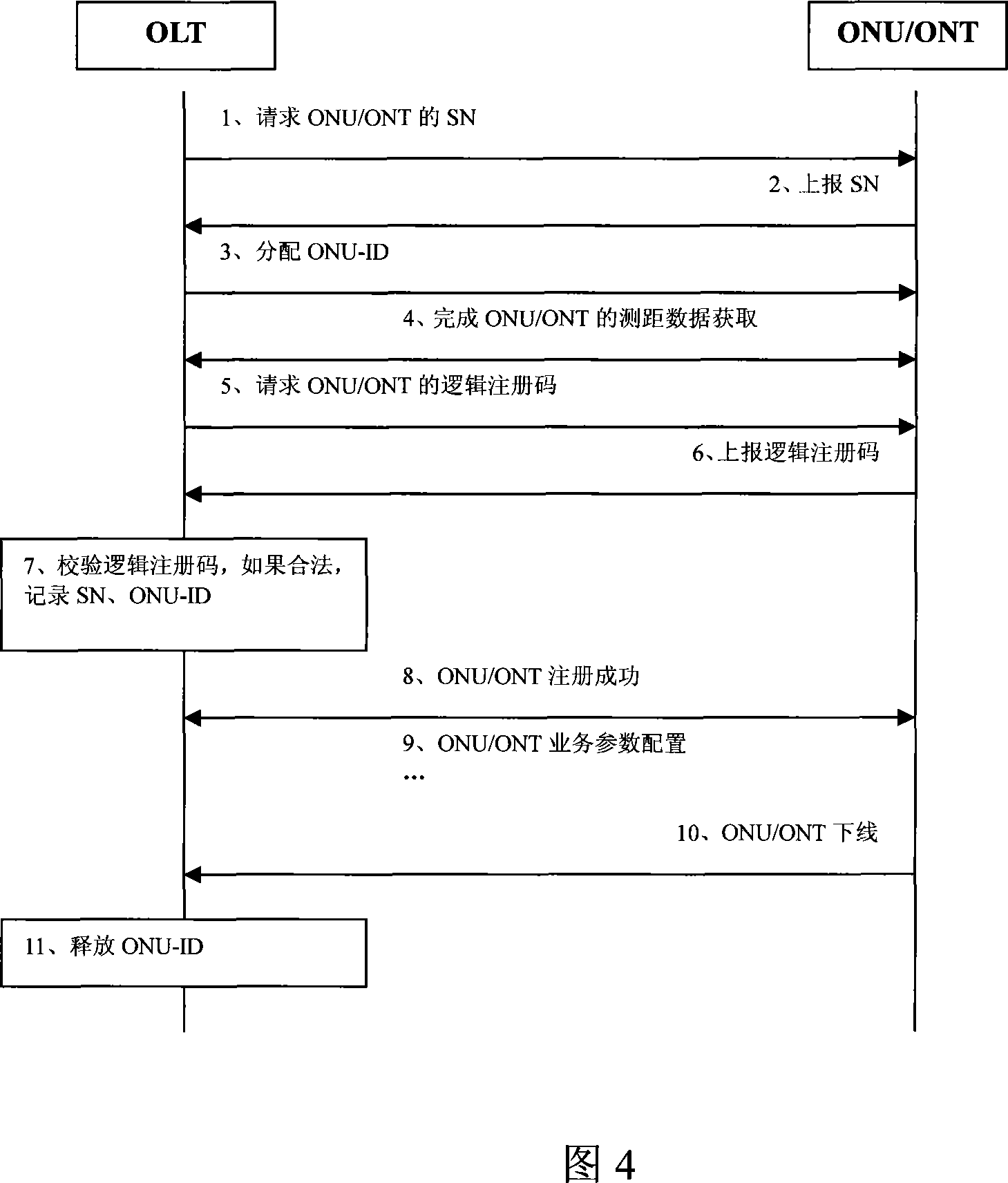
ActiveCN101083589AReduce maintenance costsIncrease flexibilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareMaintainability
The invention relates to terminal detecting certifying method, device and operational management system in passive optical network. The method includes the following steps: the terminal has logic poll code; the local terminal will confirm the received logic poll code matches with stored one to check it is legal; recording the legal terminal sequence code as terminal mark. The invention can reduce maintenance cost, increase detecting certifying flexibility and maintainability.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Optical transceiver over single communication link
InactiveUS20050069327A1Coupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmittersTelecommunications linkEngineering
A method, apparatus, and system for optical communications. An optical transmit signal is generated in response to an electrical transmit signal. The optical transmit signal is coupled into a single communication link for transmission there over. An optical receive signal is received from the single communication link, and in response an electrical receive signal is generated.
Owner:INTEL CORP
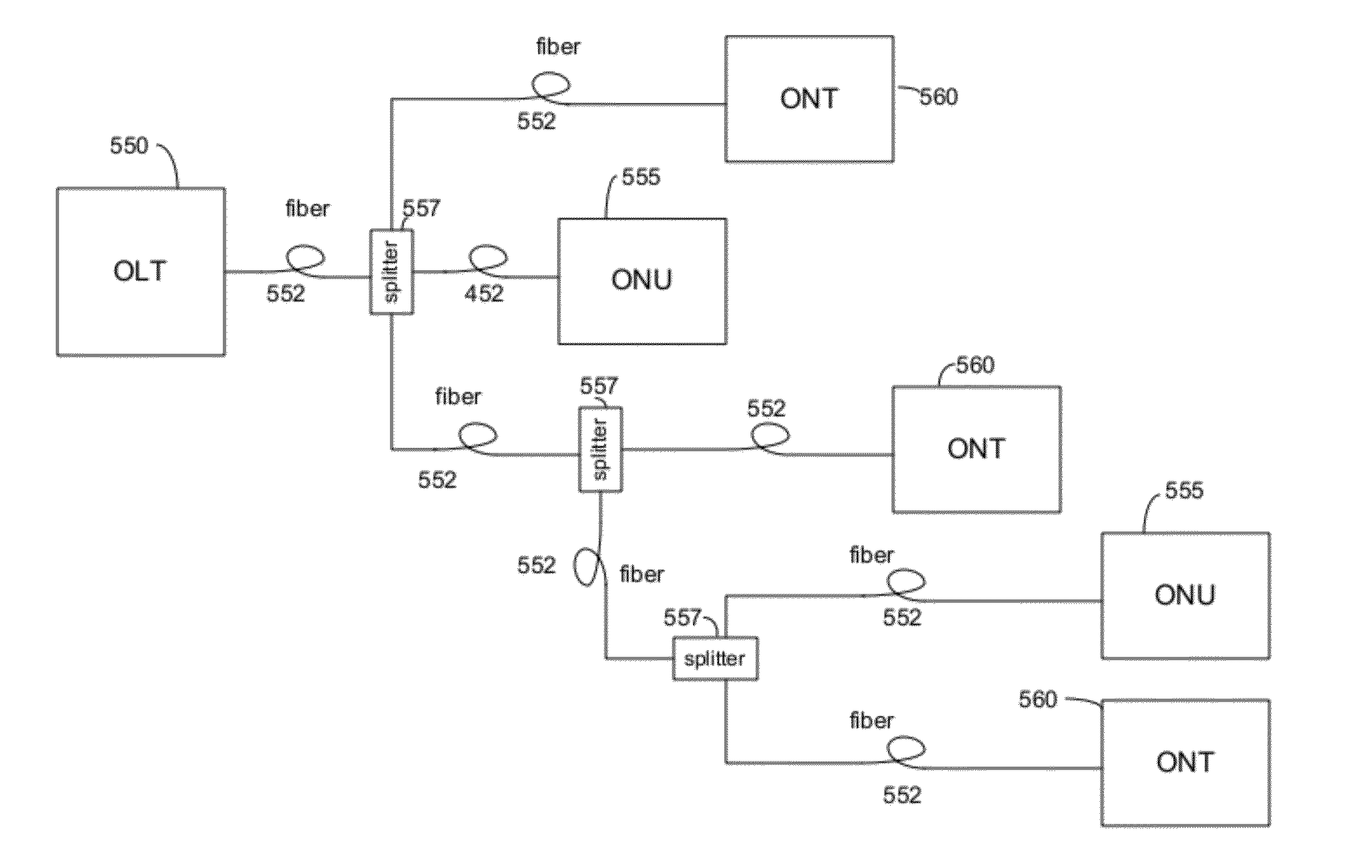
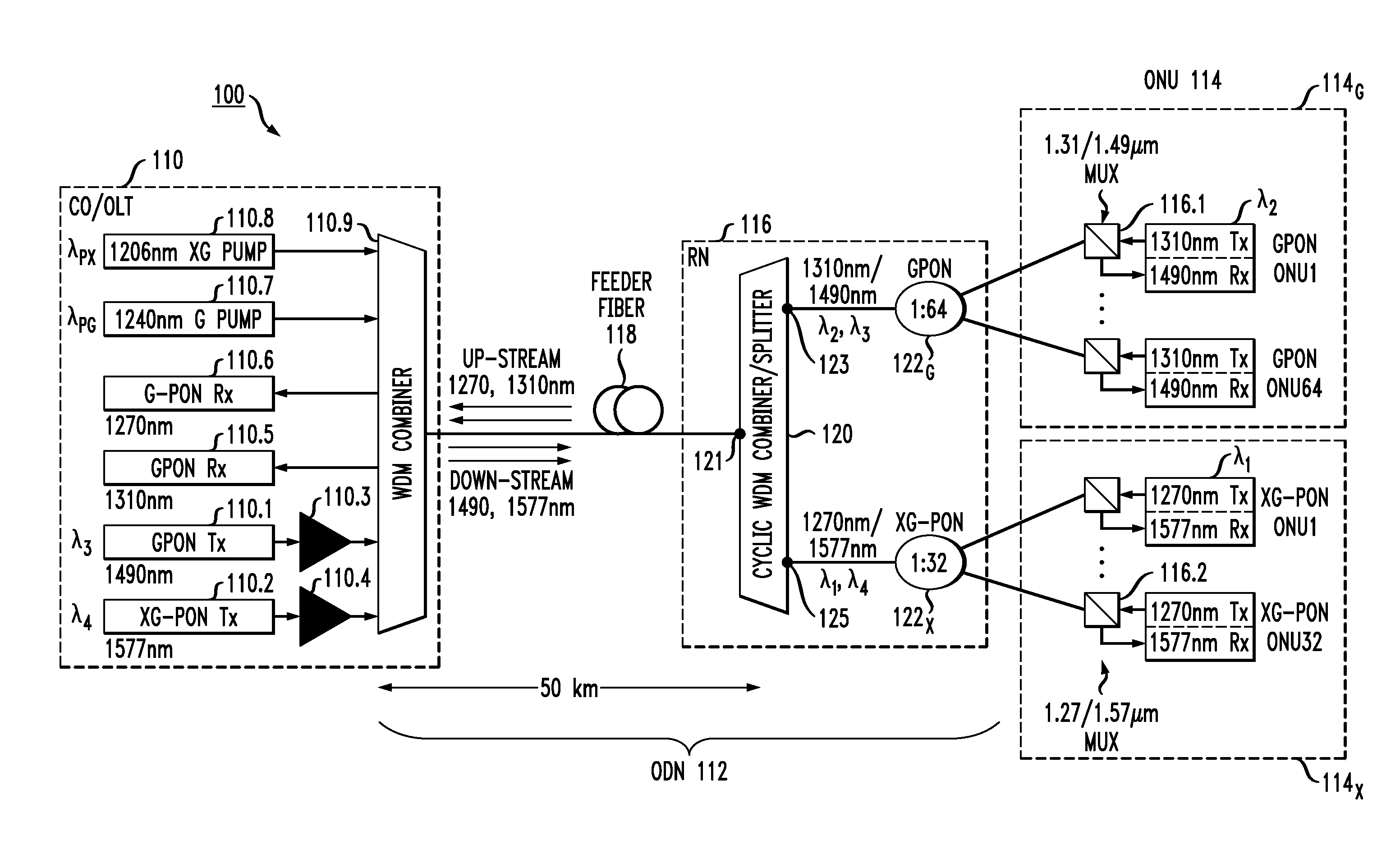
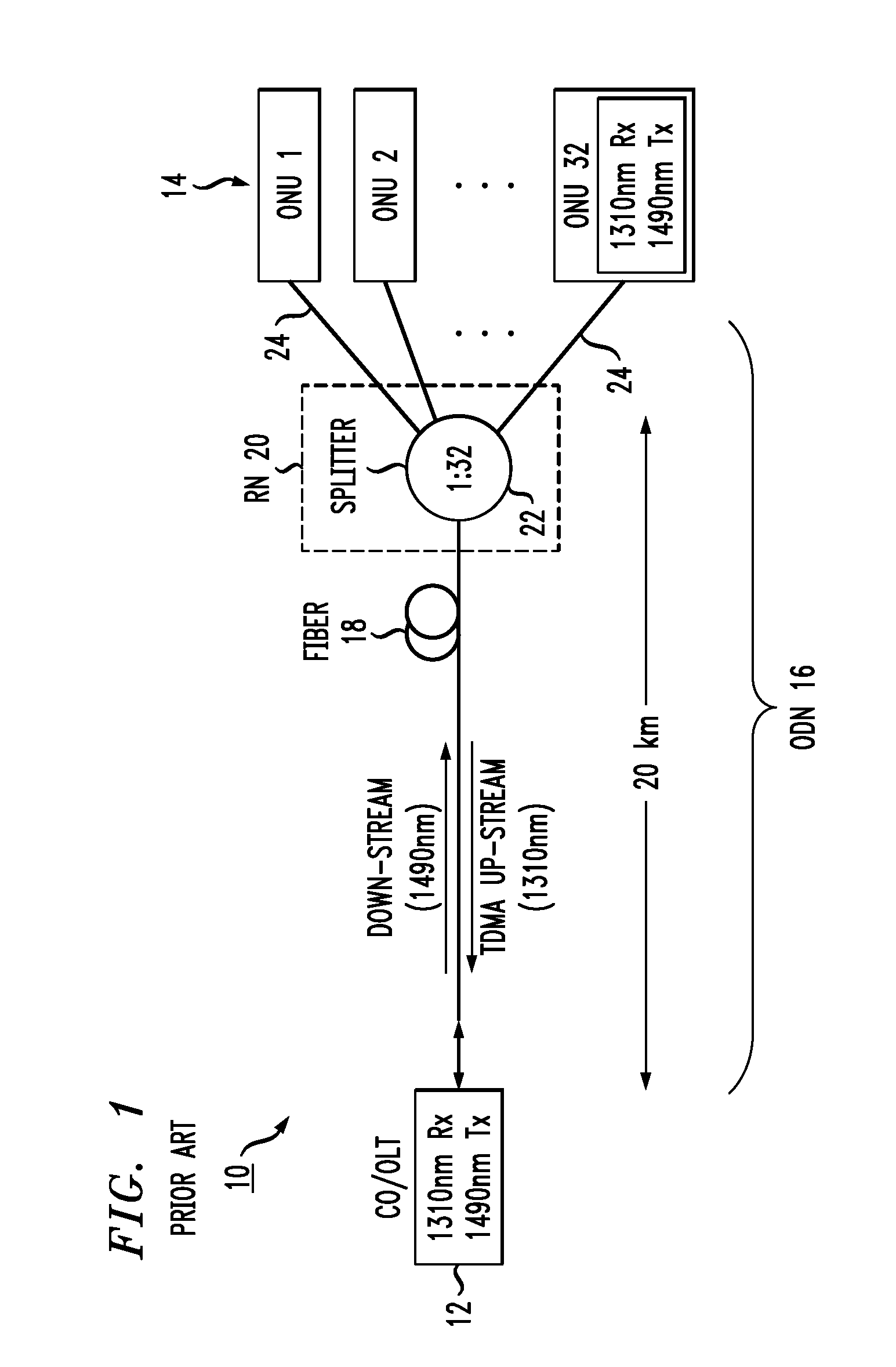
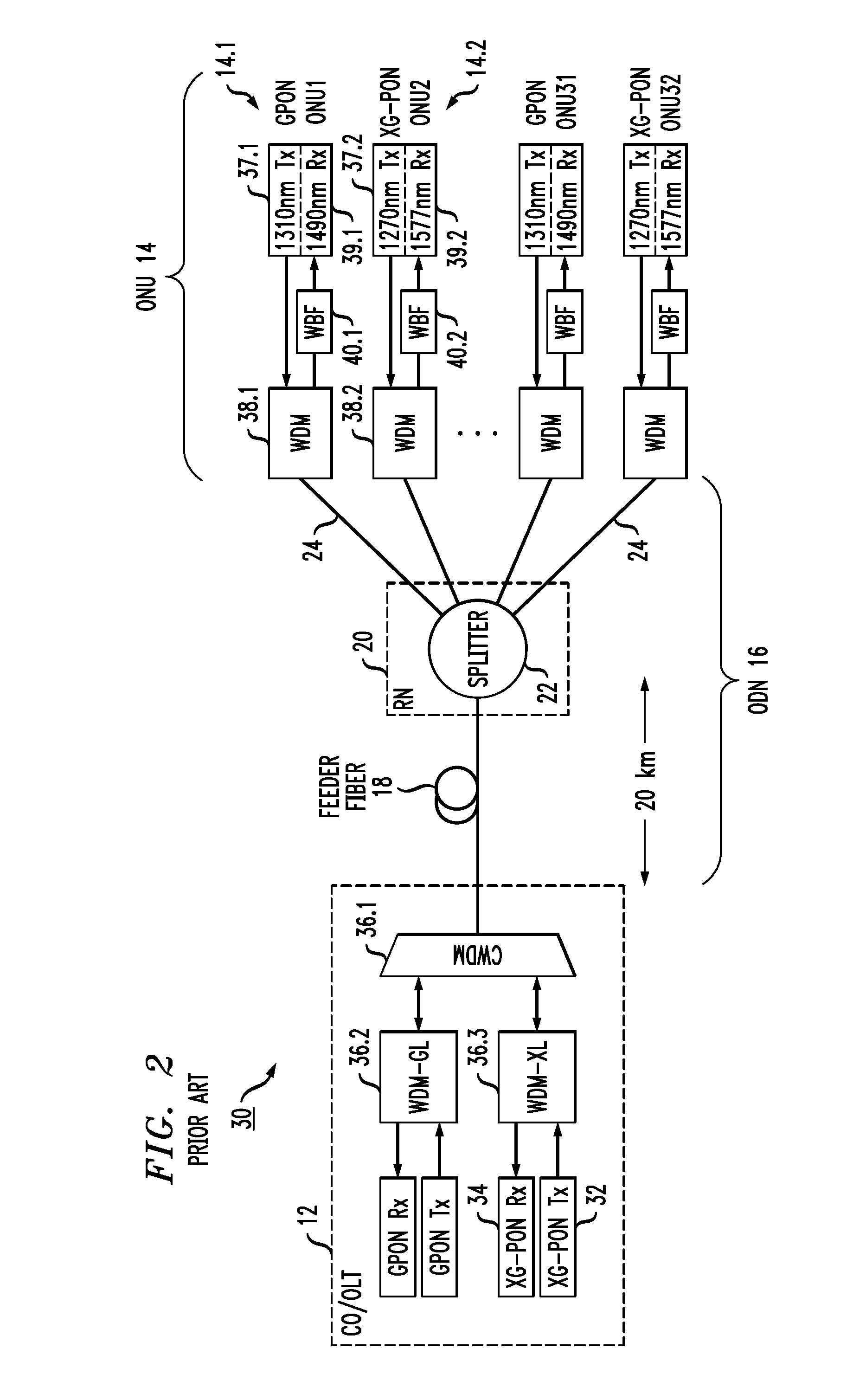
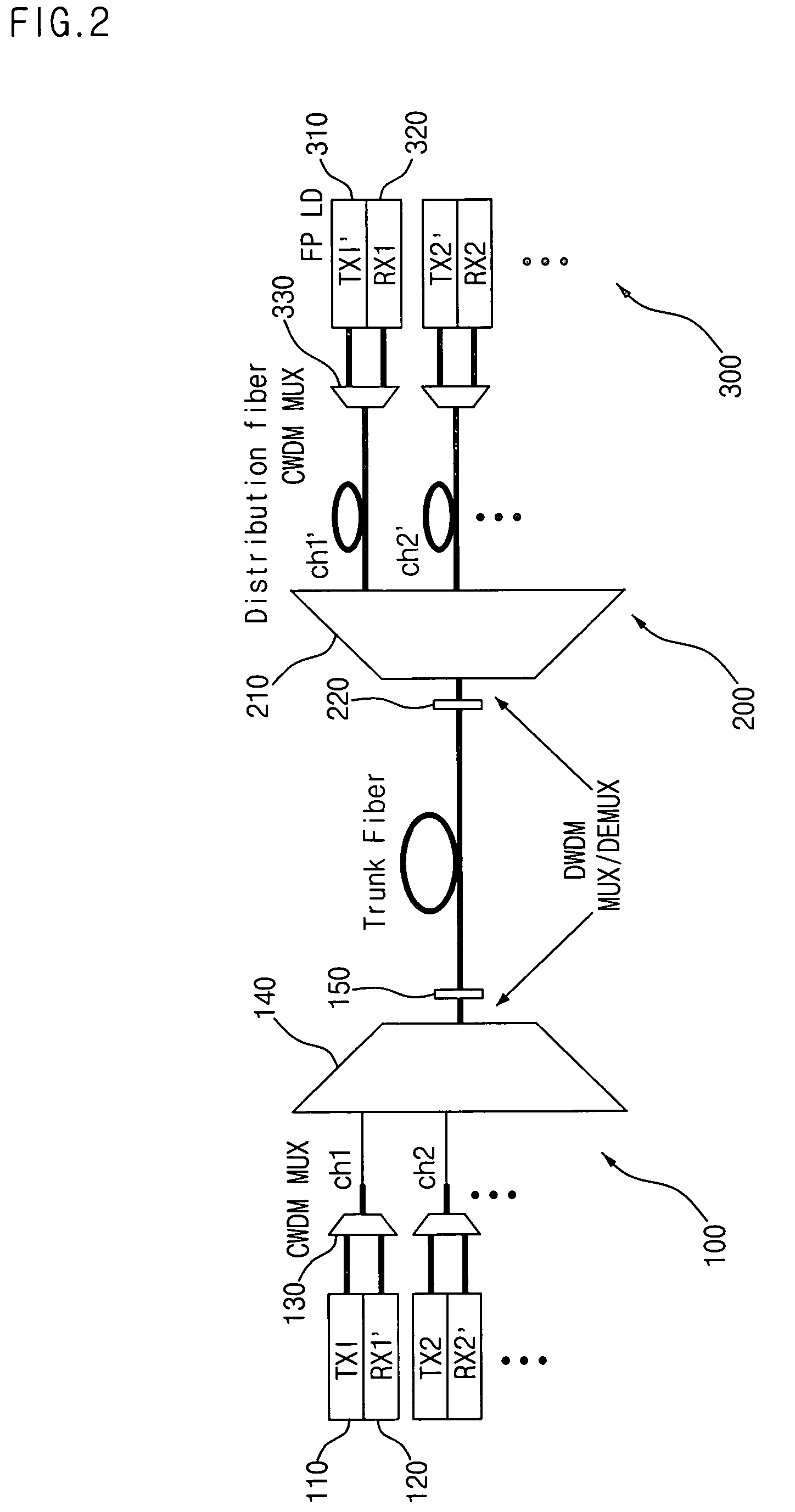
Arrangement for deploying co-existing gpon and xgpon optical communication systems
ActiveUS20140219660A1Simple componentsIncrease the split ratioMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemEngineering
A passive, coexisting 10 Gb / s passive optical network (XGPON) and Gb / s passive optical network (GPON) is created by using a pair of counter-propagating laser pump sources at a network-based optical line terminal, in combination with a feeder fiber, to create distributed Raman amplification for the upstream signals associated with both GPON and XGPON systems. A passive remote node is located at the opposite end of the feeder fiber, in the vicinity of a group of end-user locations, and includes a cyclic WDM and a pair of power splitters for the GPON and XGPON signals such that the GPON signals are thereafter directed through a first power splitter into optical network units (ONUs) specifically configured for GPON wavelengths and XGPON signals are directed through a second power splitter into ONUs configured for the XGPON wavelengths. The arrangement of the remote node allows for the reach and split ratios of the GPON and XGPON systems to be individually designed for optimum performance.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission system and transmission wavelength control method therefor
InactiveUS20050213979A1Increase costReduce settingsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission monitoringMultiplexerTransfer system
In the wavelength division multiplexing optical transmission system according to the present invention, when setting the transmission wavelengths of the wavelength-variable optical transmitter in case of addition or expansion of the optical transmitter, each transmission wavelength is set automatically so as to match with each port wavelength of the input port in the multiplexer. Therefore, the setting workload of the optical transmitter is remarkably reduced, and occurrence of incorrect setting can be avoided. Also, with a simple and low-cost structure, the cost is restrained from increasing.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for decreasing and compensating the transmission loss at a wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network and an apparatus therefor
InactiveUS7171123B2Light loss is minimizedImprove transmission qualityLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsLength waveTransmission loss
The present invention relates to a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network. In particular, it relates to a technology for minimizing the optical loss at a wavelength-division multiplexed passive optical network based on wavelength-locked light source Thereby it improves the transmission quality and increases the transmission distance.A 4-port optical path setting device of the present invention increases the amount of light injected into an optical transmitter and thereby improves the wavelength-locking characteristic of a light source. In addition, it can decrease the optical transmission loss in an optical transmission path, and by an optical amplifier being inserted therein; it can also compensate the optical loss in an optical transmission path.In the present invention, a 4-port optical path setting device having the characteristics described above and a method for fault recovery without an additional optical loss are presented.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
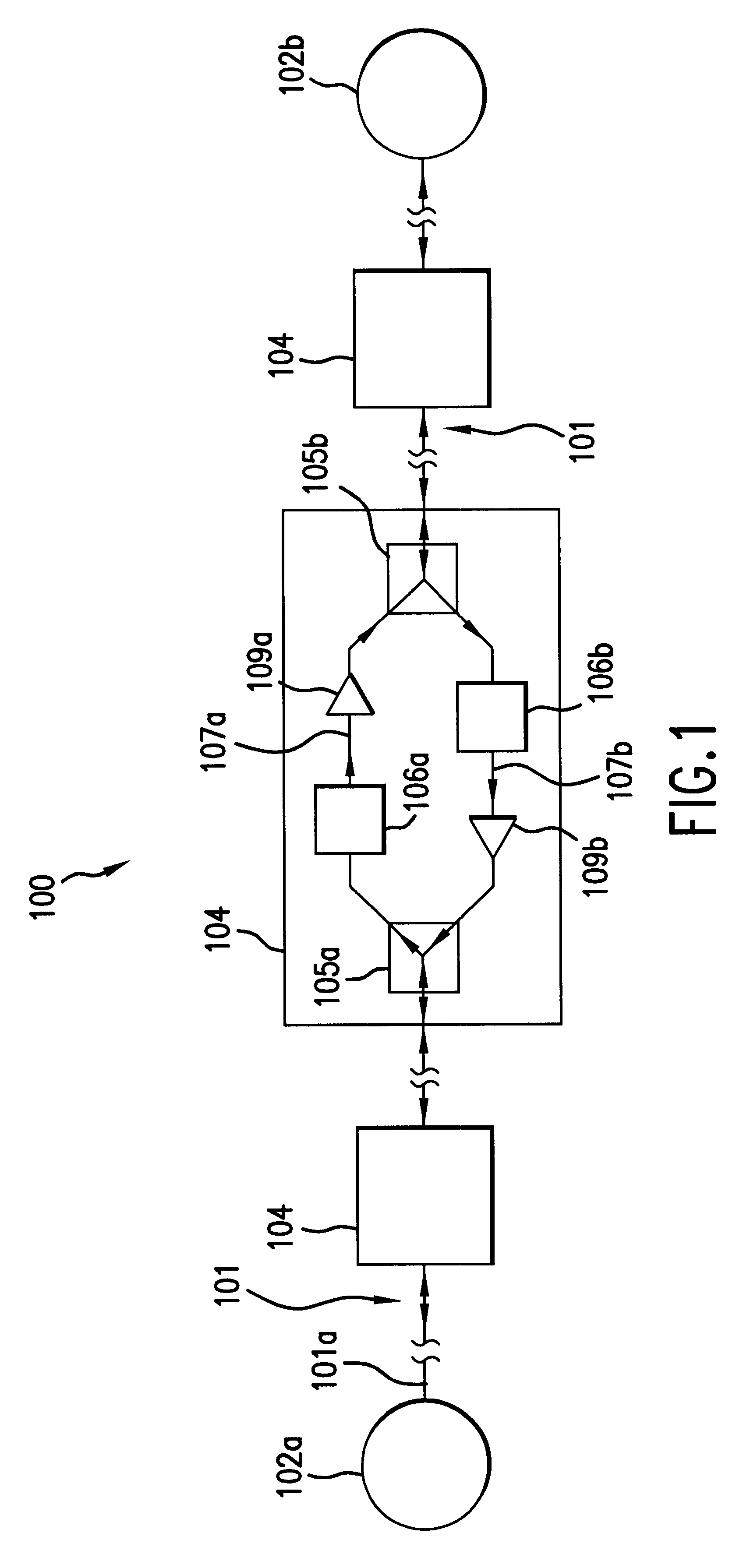
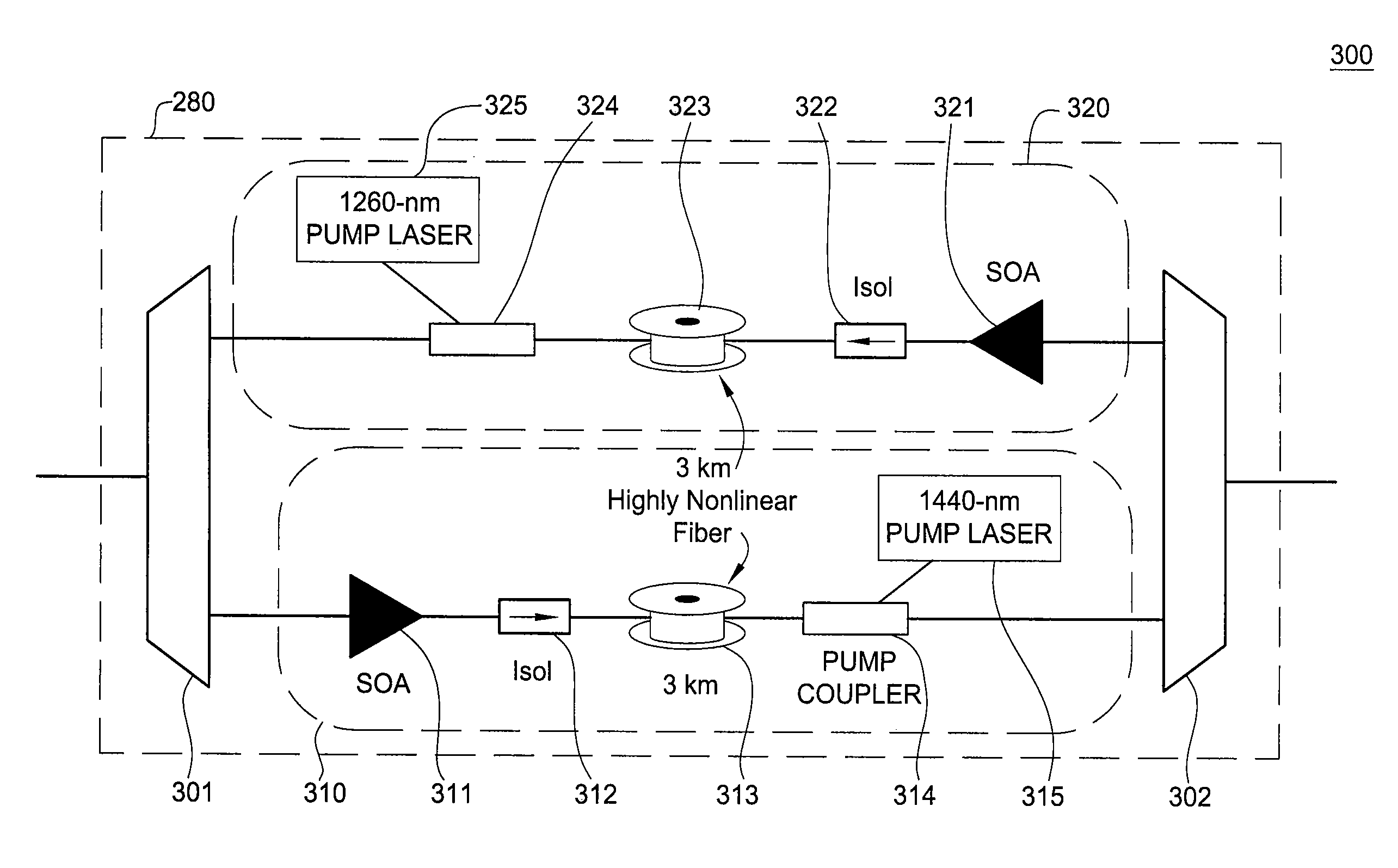
System and method for increasing capacity of undersea cables
InactiveUS6493133B1Increase capacityReducing Raman effectLaser detailsBidirectional transmissionAudio power amplifierOptical amplifier
A method of increasing usable bandwidth on a long-haul cable system having at least one optical fiber, the method comprising the steps of: (a) effecting counter-propagating first and second signals of different bands on a common long-haul optical fiber having cascaded optical amplifiers; and (b) band amplifying the first and second signals while reducing BRS in the bands.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS SUBSEA COMM LLC
Optical transceiver apparatus and wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network system
InactiveUS20120269516A1Improve signal transmission performanceImprove signal qualityWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersTransceiverLength wave
An optical transceiver apparatus includes a gain medium, a photoelectric converter, at least one AWG, and a partial reflection mirror. The at least one AWG includes two common ports and multiple branch ports. One of the two common ports functions as a signal sending port, and the other functions as a signal receiving port, where bandwidth of the signal sending port is less than that of the signal receiving port. The gain medium and the photoelectric converter are connected to one of the branch ports of the AWG. The AWG and the partial reflection mirror are configured to cooperatively perform wavelength self-injection locking on an optical signal provided by the gain medium, and output the optical signal through the signal sending port. The AWG is further configured to demultiplex an optical signal received by the signal receiving port to a branch port. A WDM-PON system is also provided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Dense wave division multiplex passive optical network system for self-implant locked Fabry-Perot laser diode
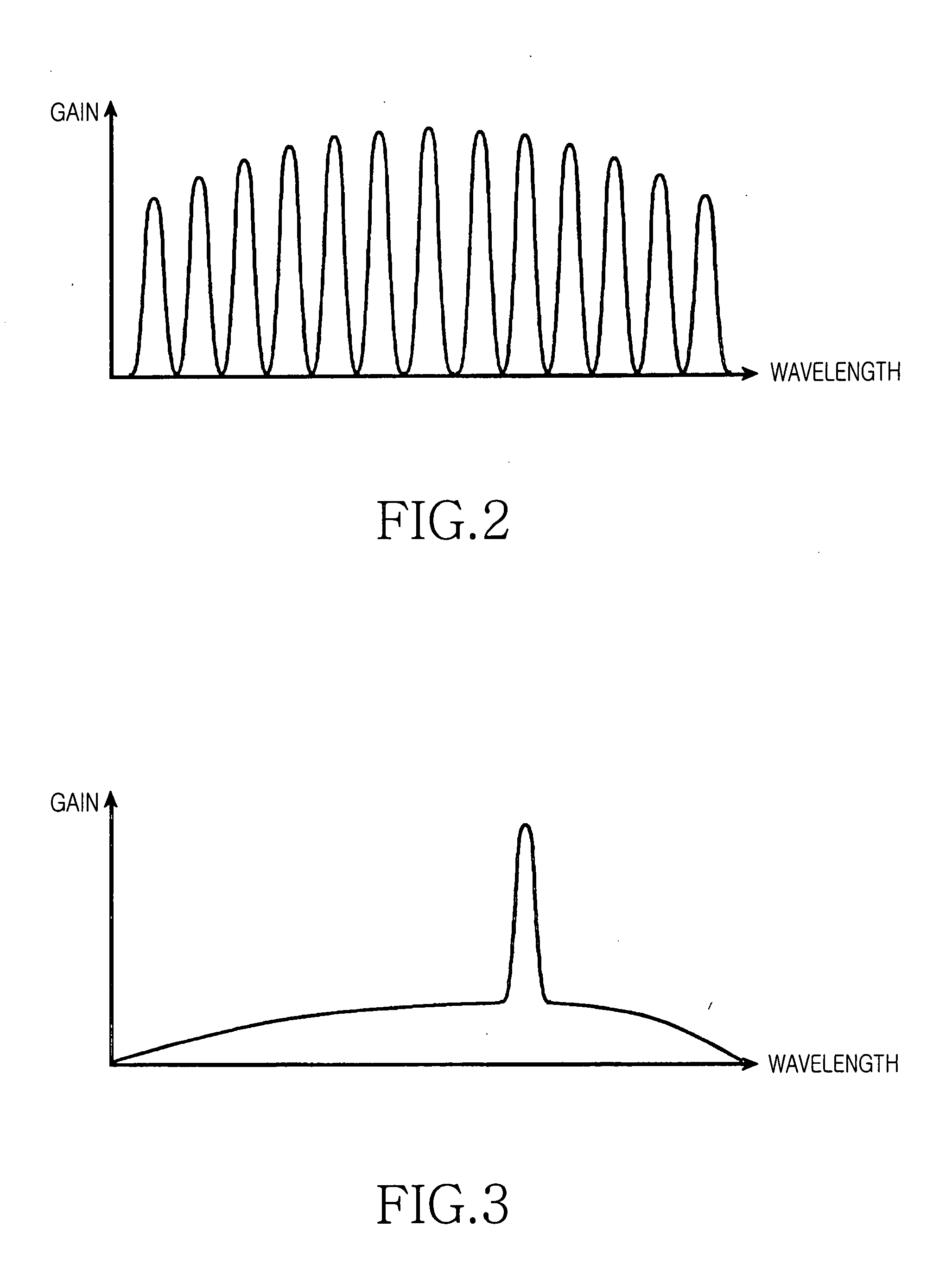
InactiveCN1497894AWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultimode transmissionInjection lockedLength wave
Disclosed is a dense wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (DWDM-PON) system utilizing self-injection locking of Fabry-Perot laser diodes, in which output optical signals of different wavelengths are partially fed back by a partial mirror, so as to injection-lock the Fabry-Perot laser diodes, respectively. In accordance with this system, inexpensive Fabry-Perot laser diodes can be used as respective light sources of a central office and optical network units (ONUs). Accordingly, it is possible to minimize the system construction costs, as compared to conventional optical networks.
Owner:崔埈国
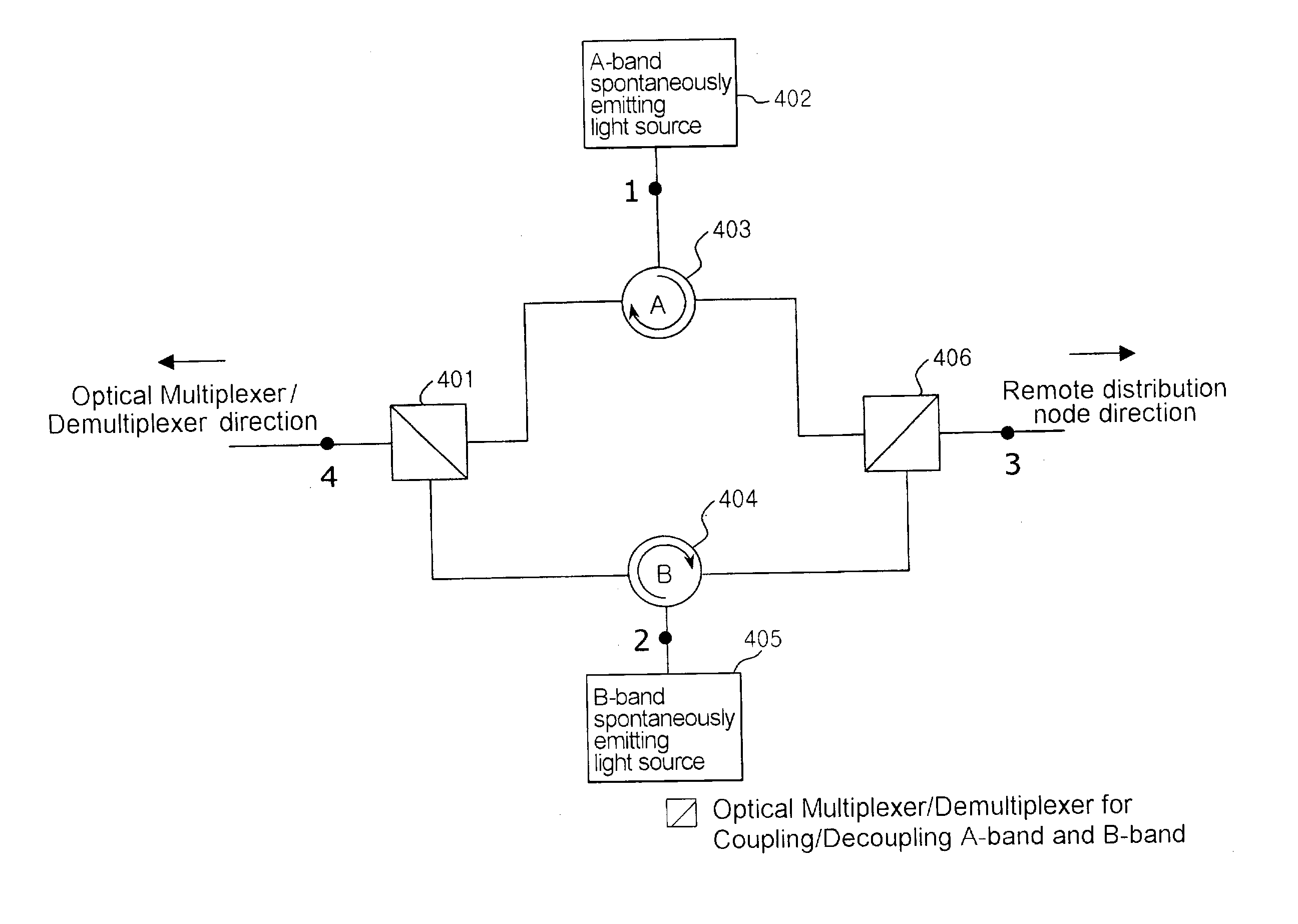
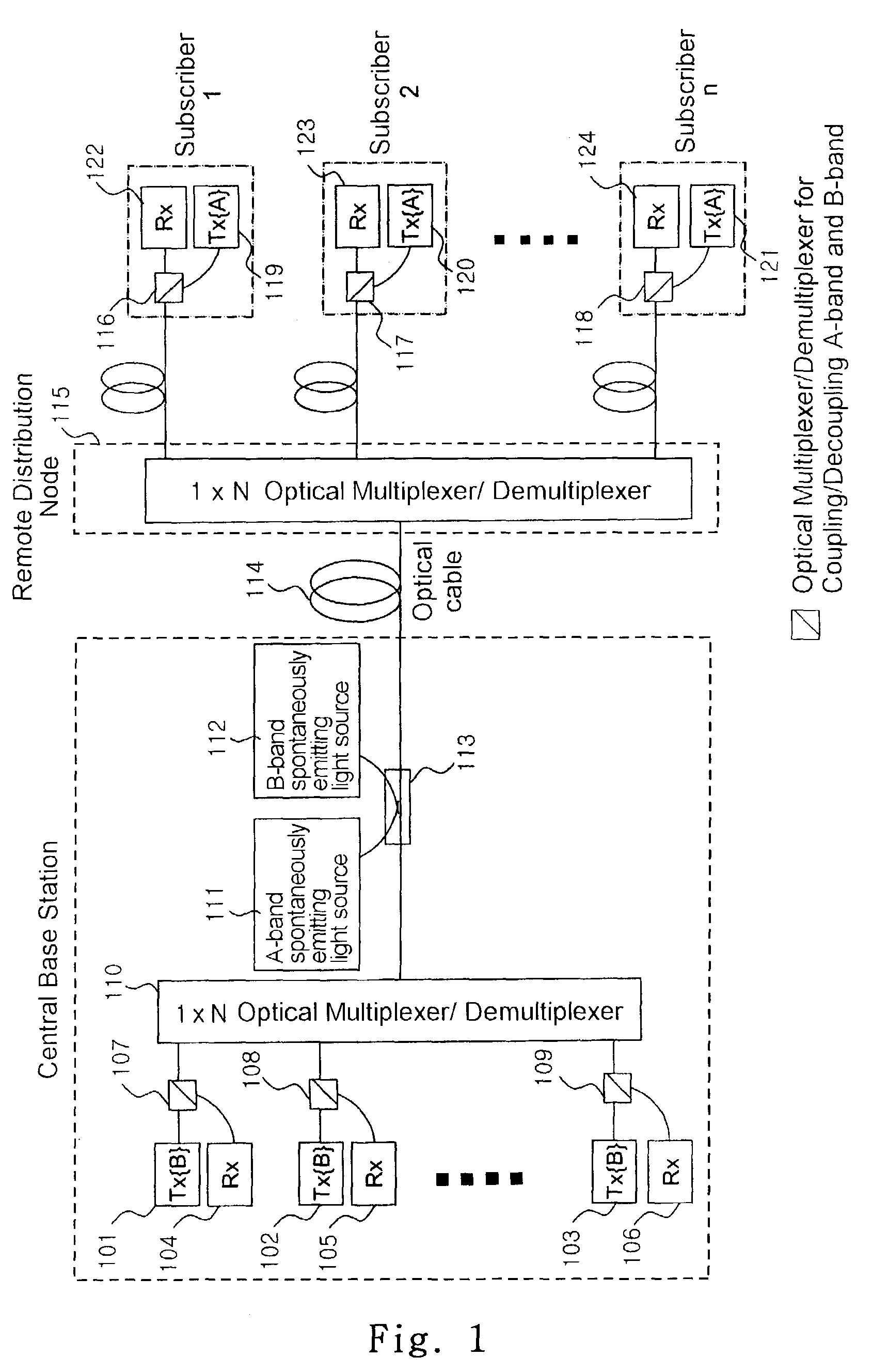
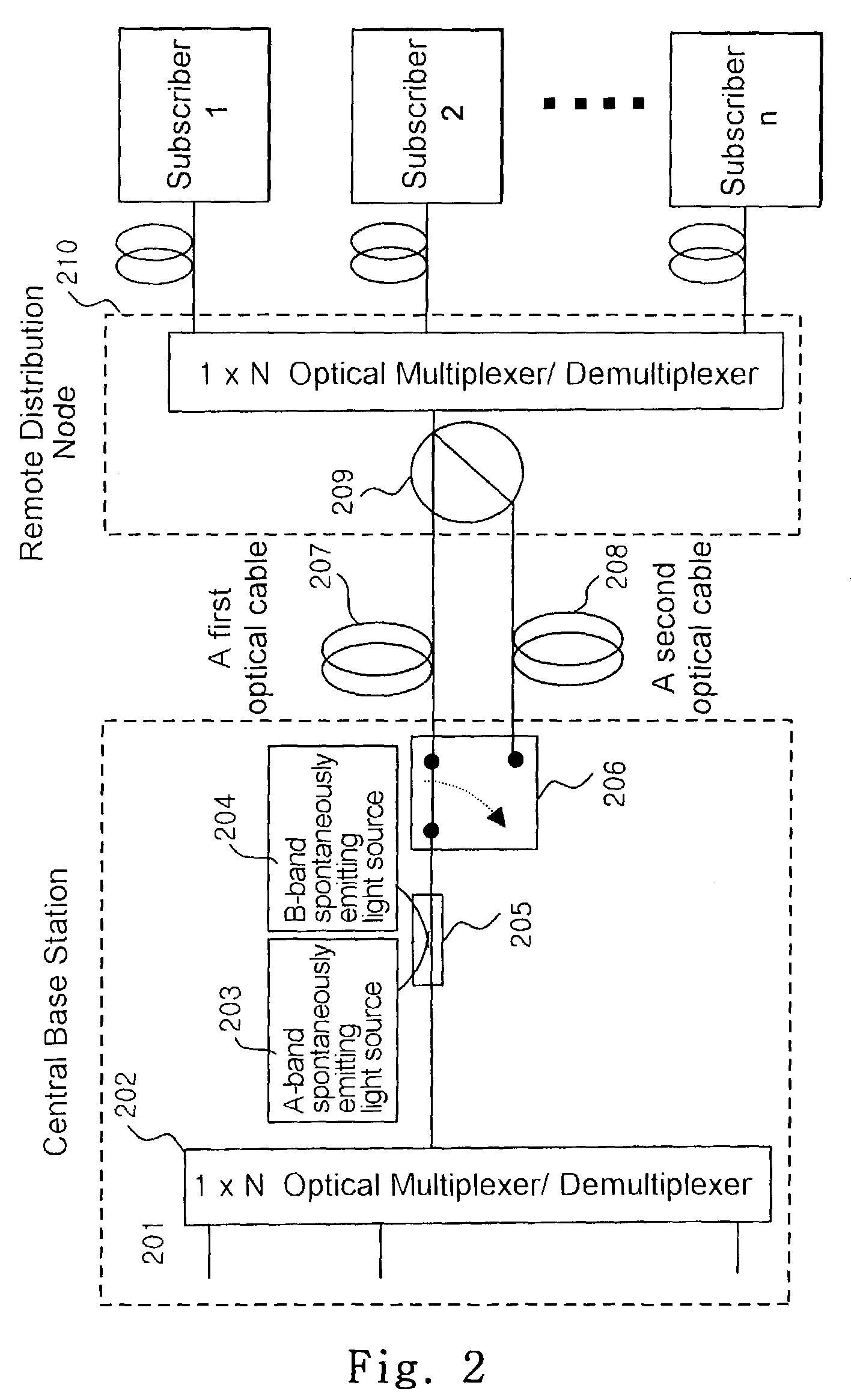
Distributed terminal optical transmission system
ActiveUS7505687B2Enhanced signalNetwork is requiredWavelength-division multiplex systemsBidirectional transmissionAudio power amplifierEngineering
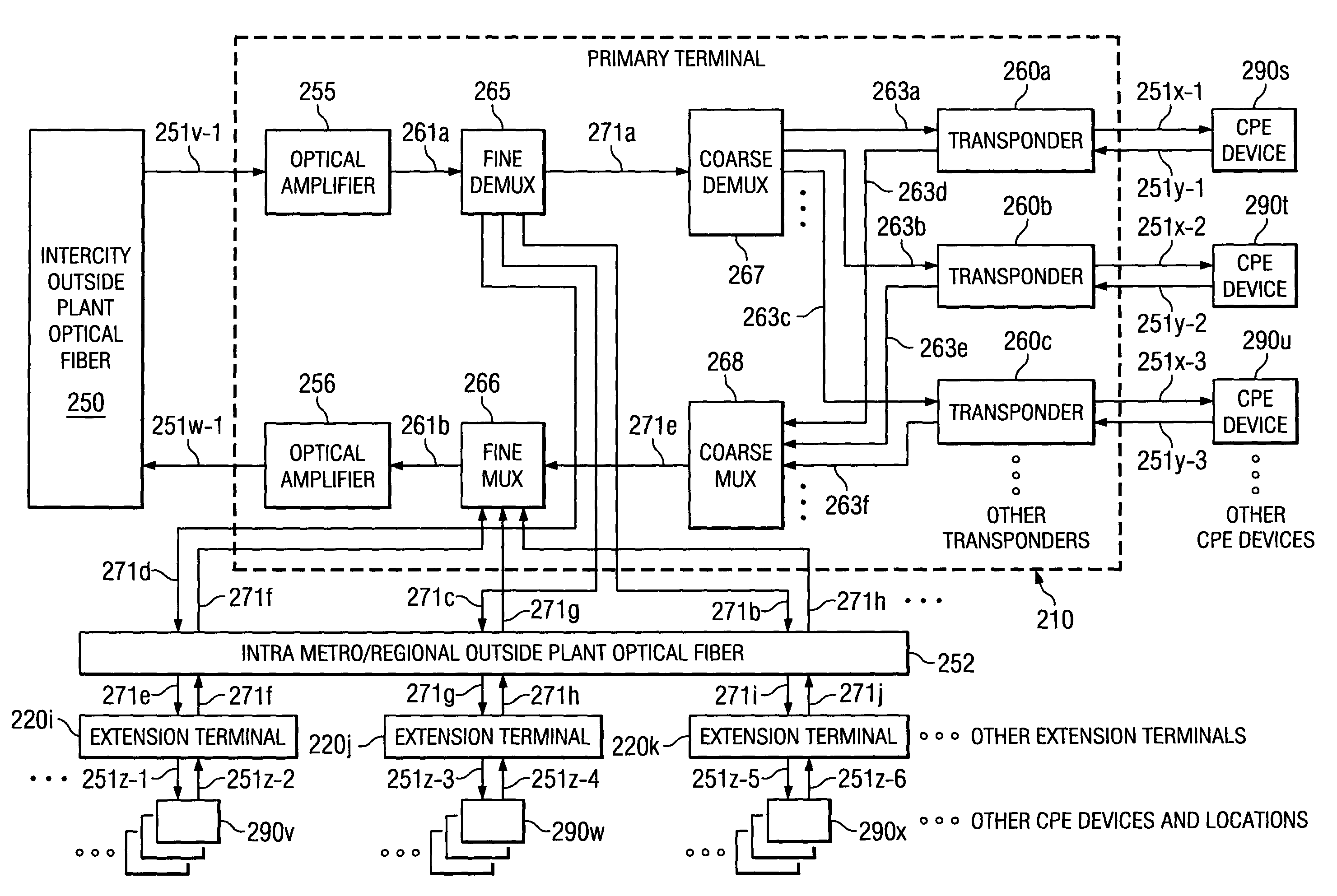
The invention facilitates optical signals generated from customer premise equipment (CPE) at the edges of the metro domain networks. The CPEs are connected to extension terminals that transform the optical signal originating at the CPE into a suitable format for long haul transmission. The optical signal then propagates to a primary terminal where the signal is multiplexed with other optical signals from other extension terminals. The multiplexed signals are then transmitted over LH or ULH network to a second primary terminal where the signal is then demultiplexed from other optical signals and transmited to the proper extension terminal. At the extension terminal, the demultiplexed optical signal is transformed from its LH format back into a format suitable for inter-connection to a CPE. Using this architecture, the signal under goes optical-to-electrical conversion only at the extension terminals or end points. These end points can be located in lessee's facility. The only equipment located in lessor's facility is the primary terminal containing line amplifiers and add / drop nodes.
Owner:PIVOTAL DECISIONS
Dense wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network system utilizing self-injection locking of Fabry-Perot laser diodes
InactiveUS7167649B2Minimizing system construction costLow costTime-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsInjection lockedLength wave
Disclosed is a dense wavelength division multiplexing-passive optical network (DWDM-PON) system utilizing self-injection locking of Fabry-Perot laser diodes, in which output optical signals of different wavelengths are partially fed back by a partial mirror, so as to injection-lock the Fabry-Perot laser diodes, respectively. In accordance with this system, inexpensive Fabry-Perot laser diodes can be used as respective light sources of a central office and optical network units (ONUs). Accordingly, it is possible to minimize the system construction costs, as compared to conventional optical networks.
Owner:CHOI JUN KOOK
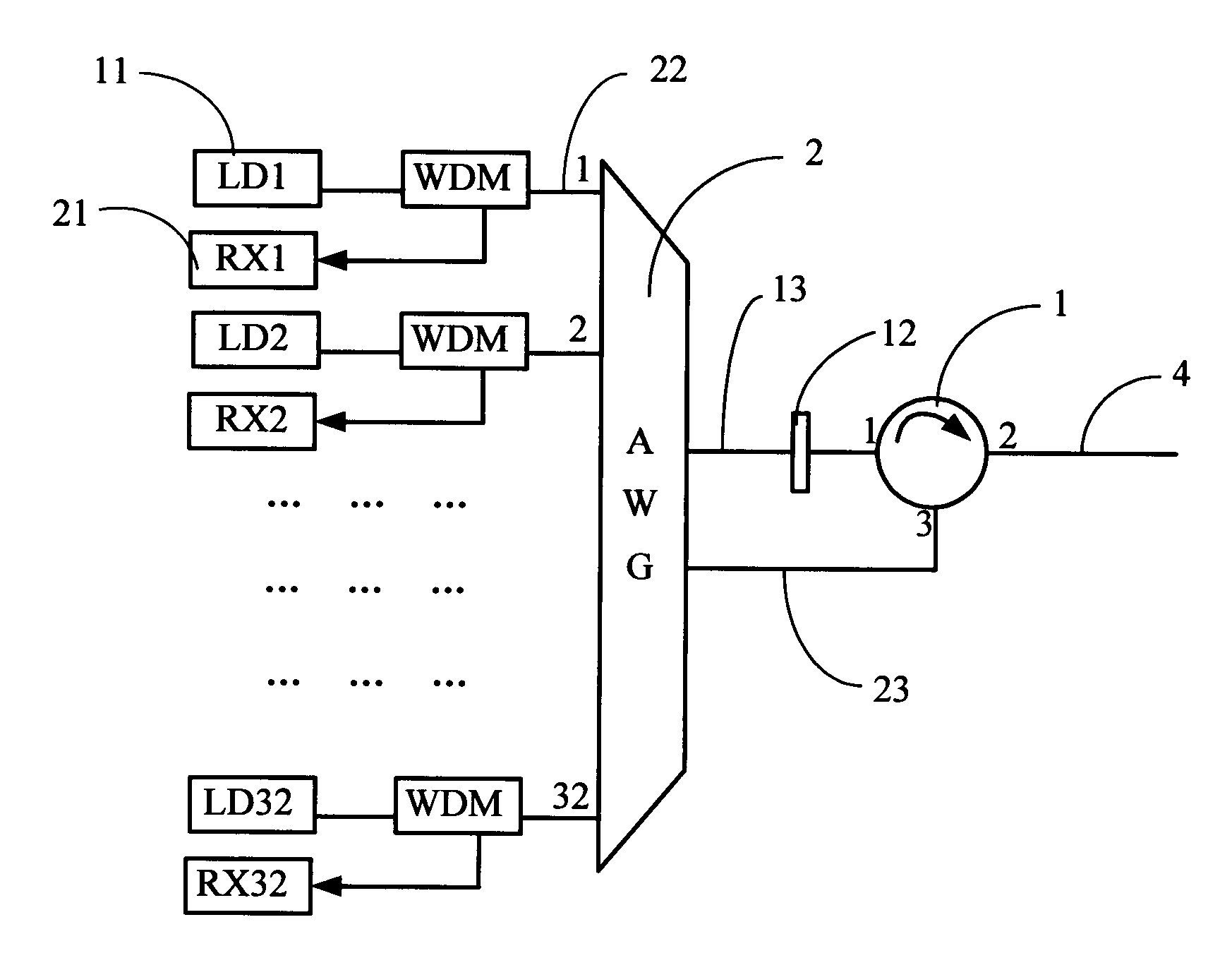
Method and apparatus for enabling multiple optical line termination devices to share a feeder fiber
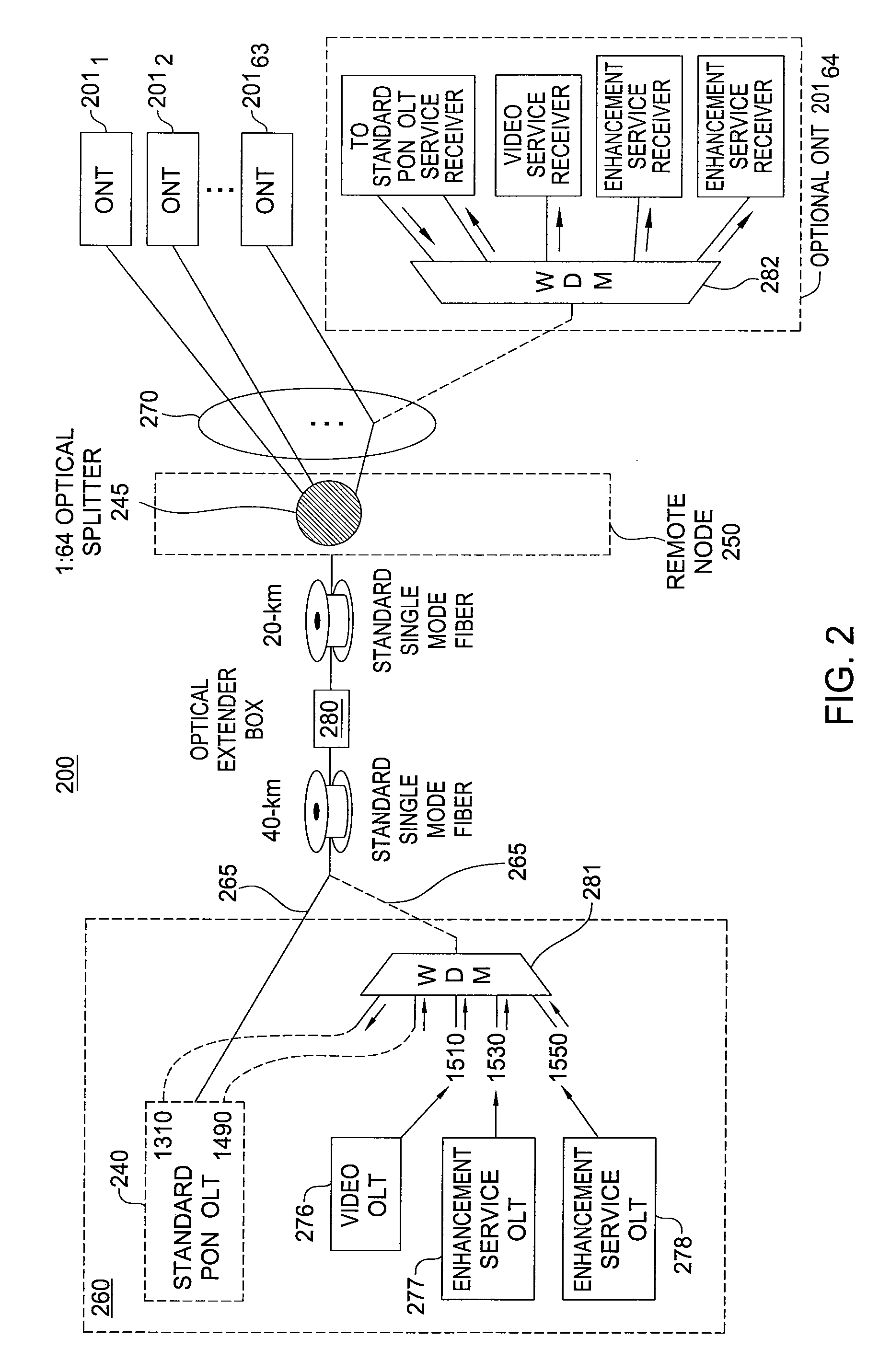
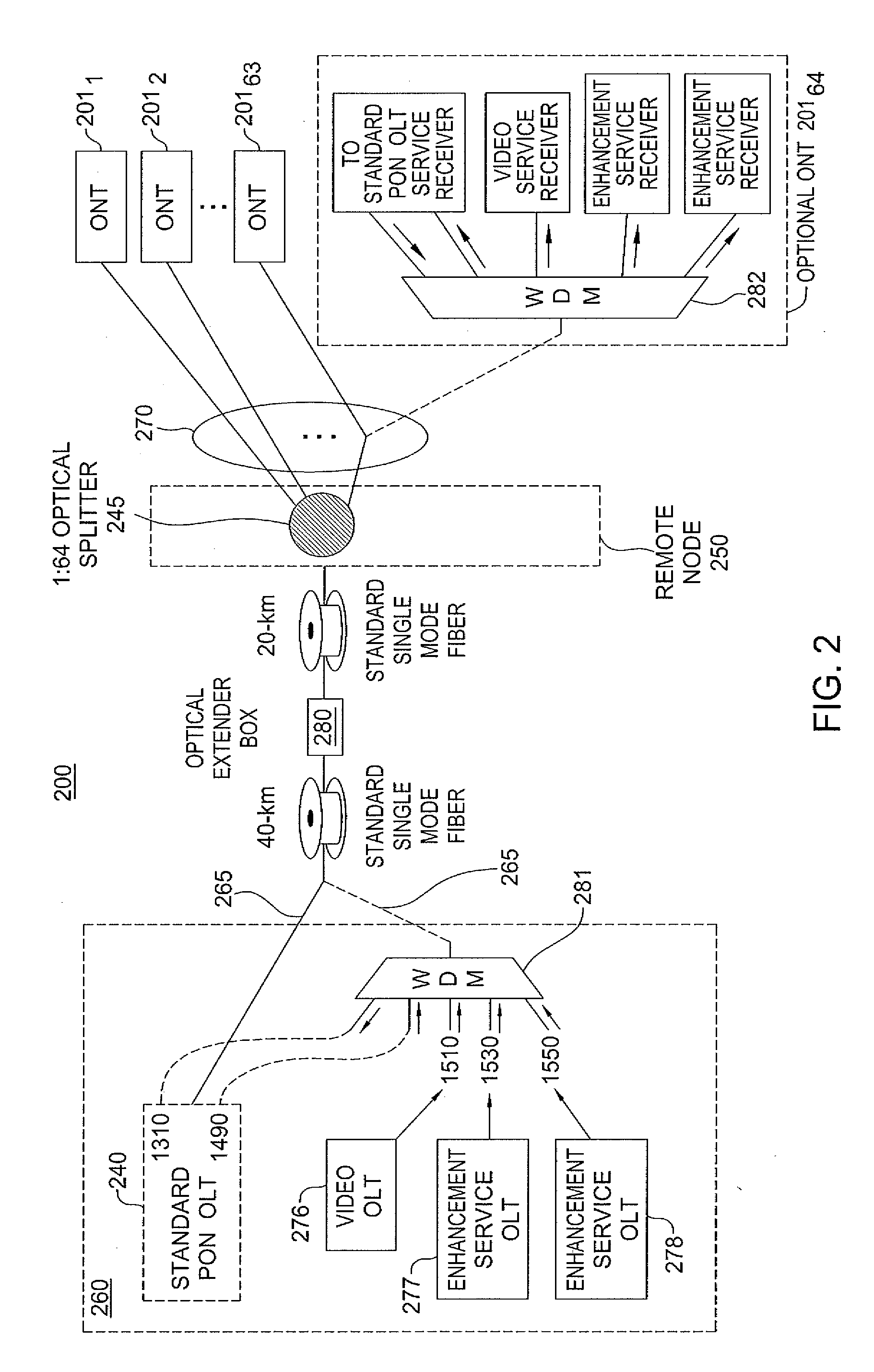
A method and apparatus for enabling multiple optical line termination (OLT) devices to share a feeder fiber are disclosed. For example, the optical network comprises a plurality of optical line termination (OLT) devices, where each OLT device having a transceiver for sending and receiving optical signals. The optical network further comprises a wave division multiplexer (WDM) combiner, coupled to the plurality of OLT devices, for combining optical signals received from the plurality of OLT devices. The optical network further comprises an optical extender box comprising at least one hybrid SOA-Raman amplifier, wherein the optical extender box is coupled to the WDM combiner via a first standard single mode fiber section. Finally, the optical network further comprises at least one optical splitter coupled to the optical extender box via a second standard single mode fiber section.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method and apparatus for enabling multiple optical line termination devices to share a feeder fiber
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Temperature controlled multi-channel transmitter optical subassembly and optical transceiver module including same
ActiveUS20140241726A1Laser optical resonator constructionWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransceiverLaser array
A temperature controlled multi-channel transmitter optical subassembly (TOSA) may be used in a multi-channel optical transceiver. The temperature controlled multi-channel TOSA generally includes an array of lasers optically coupled to an optical multiplexer, such as an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG), to combine multiple optical signals at different channel wavelengths. The lasers may be thermally tuned to the channel wavelengths by establishing a global temperature for the array of lasers and separately raising local temperatures of individual lasers in response to monitored wavelengths associated with the lasers. A temperature control device, such as a TEC cooler coupled to the laser array, may provide the global temperature and individual heaters, such as resistors adjacent respective lasers, may provide the local temperatures. The optical transceiver may be used in a wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) optical system, for example, in an optical line terminal (OLT) in a WDM passive optical network (PON).
Owner:APPLIED OPTOELECTRONICS
Optical communication devices having optical time domain reflectometers
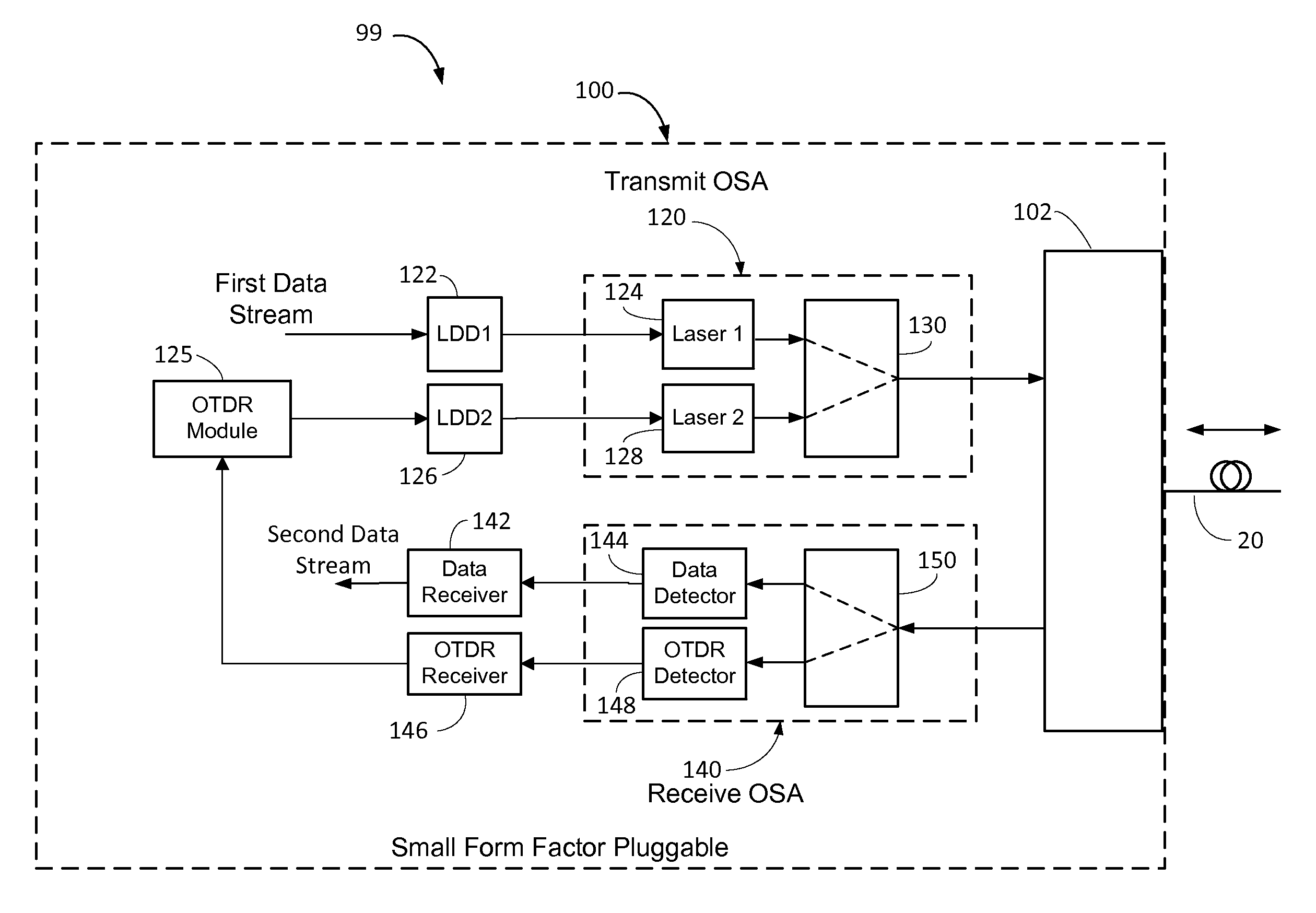
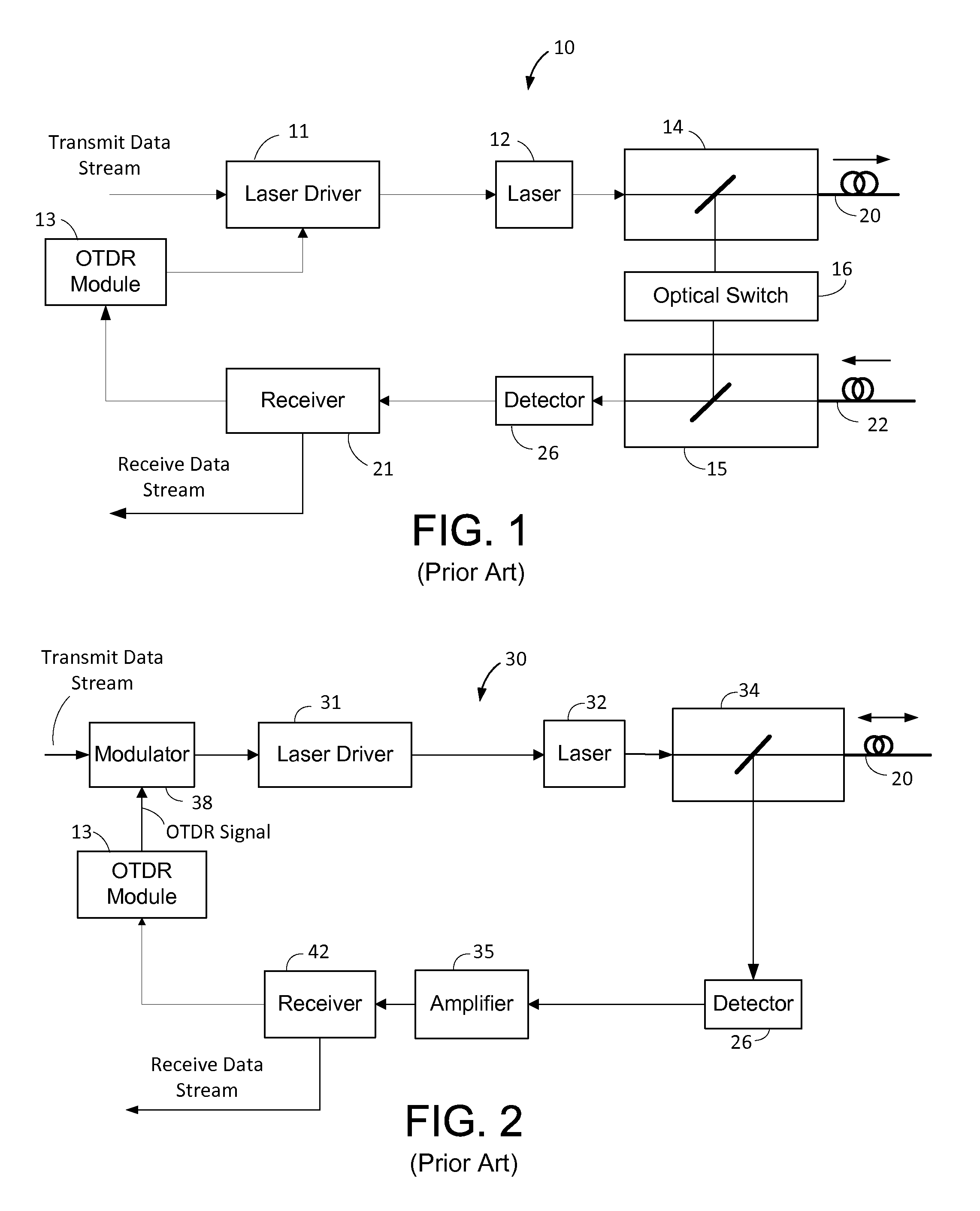
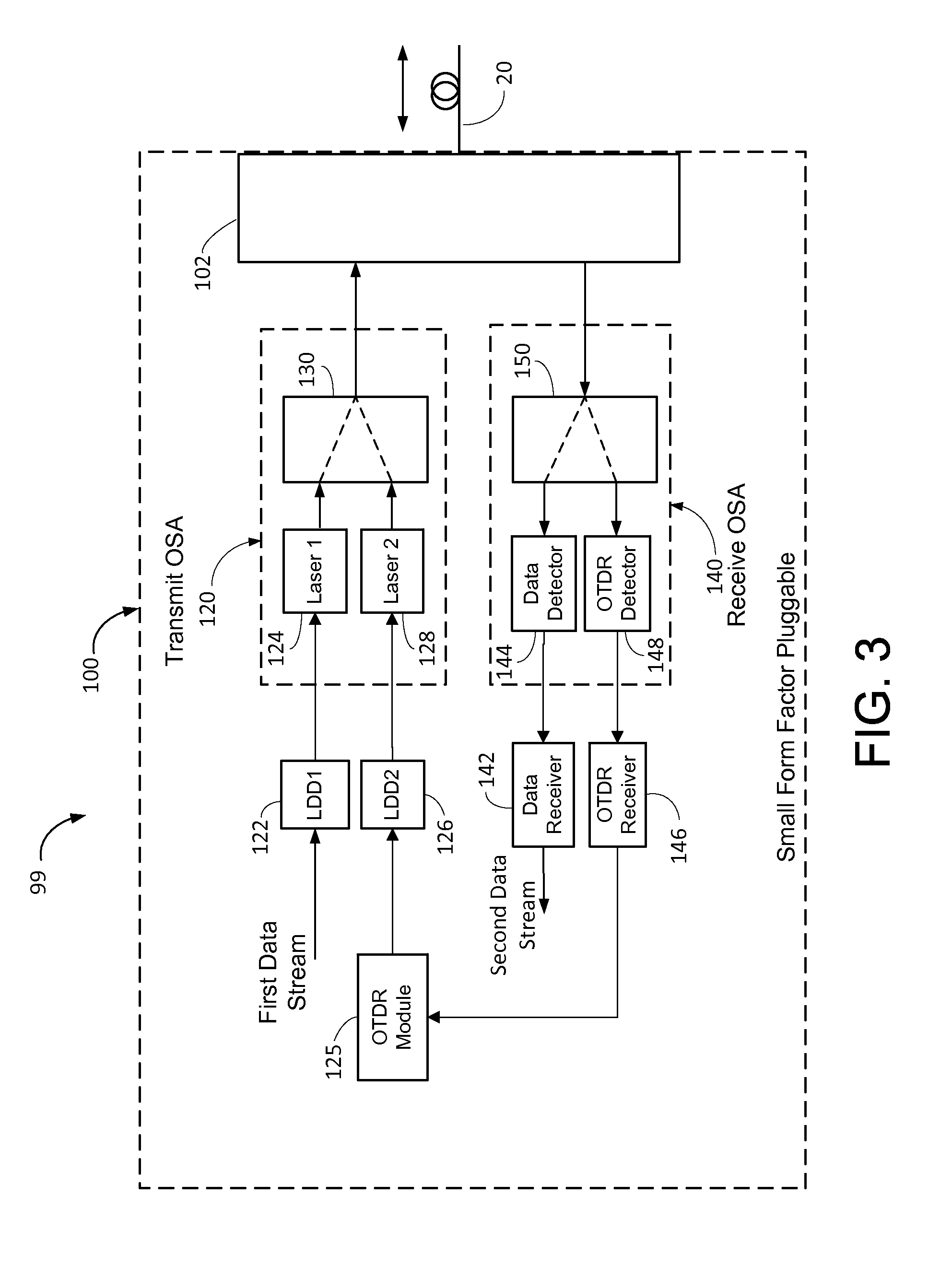
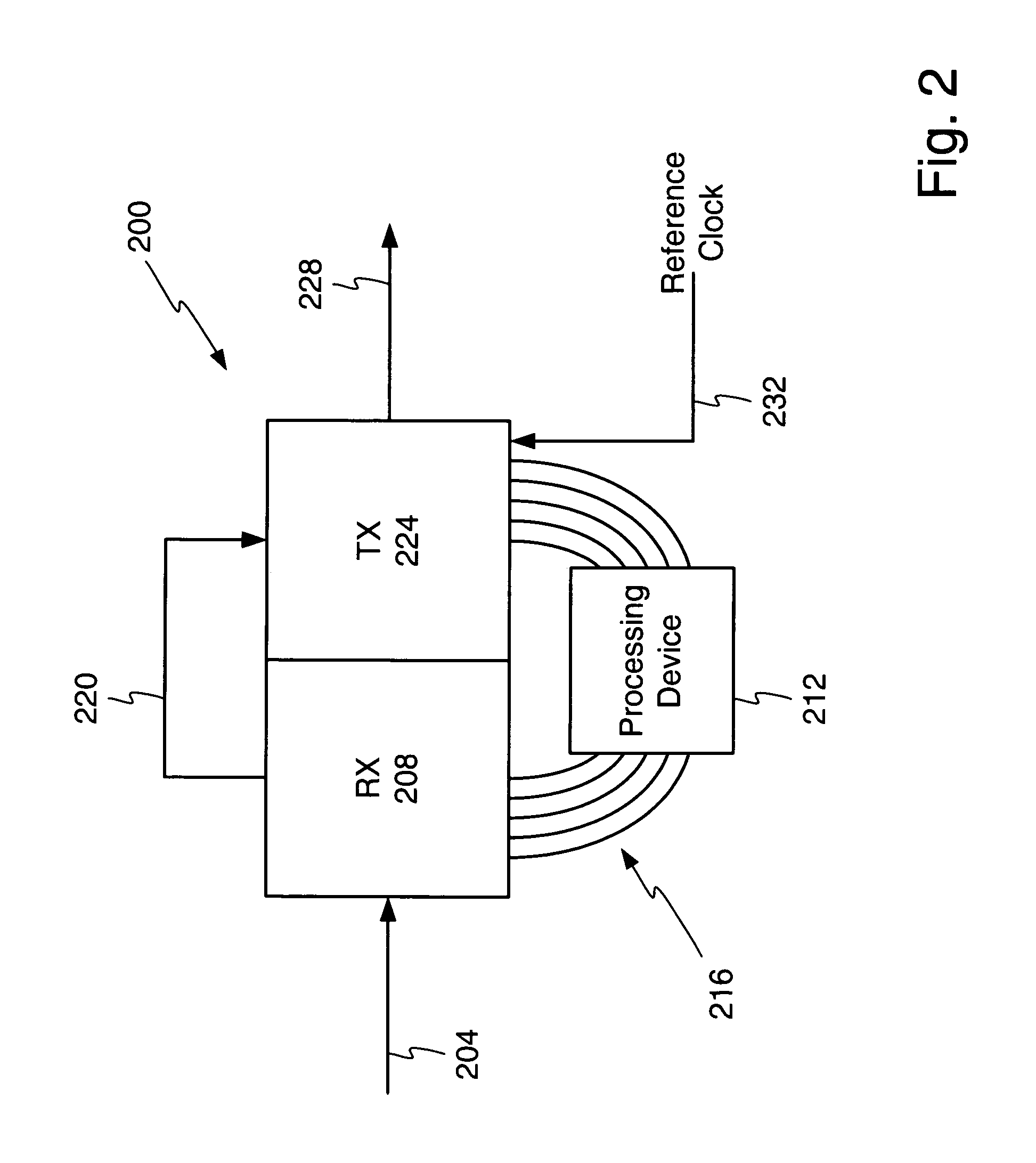
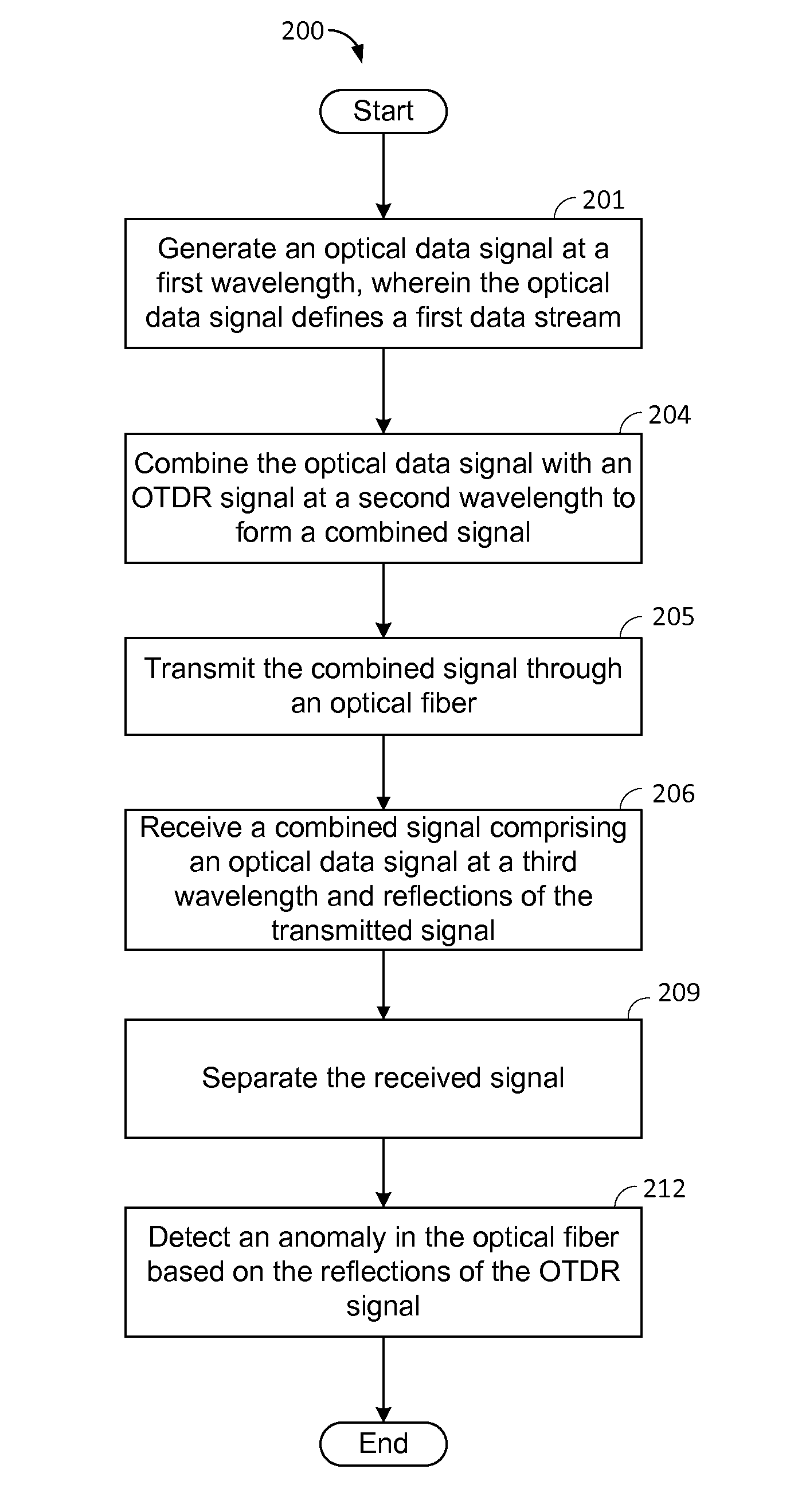
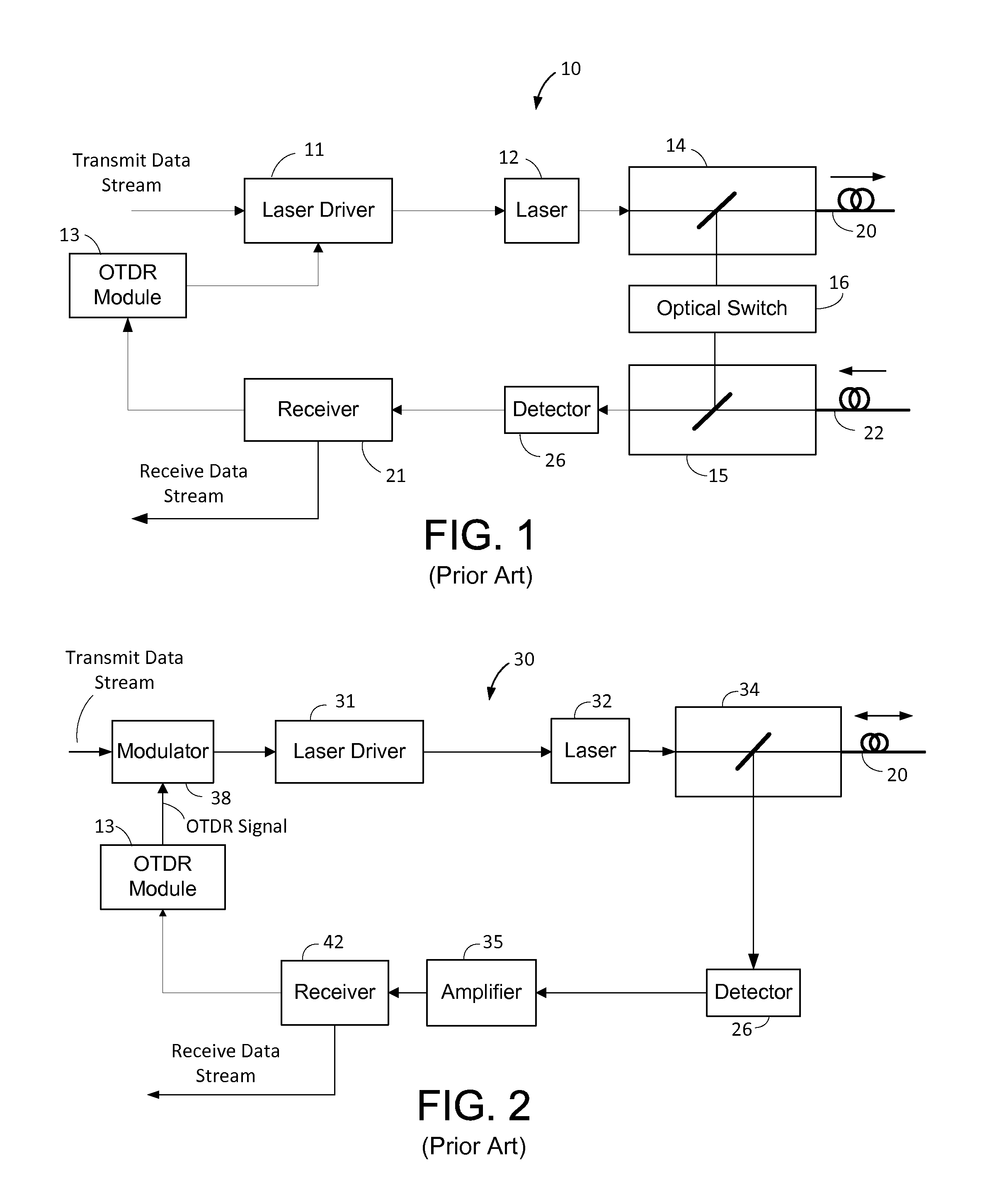
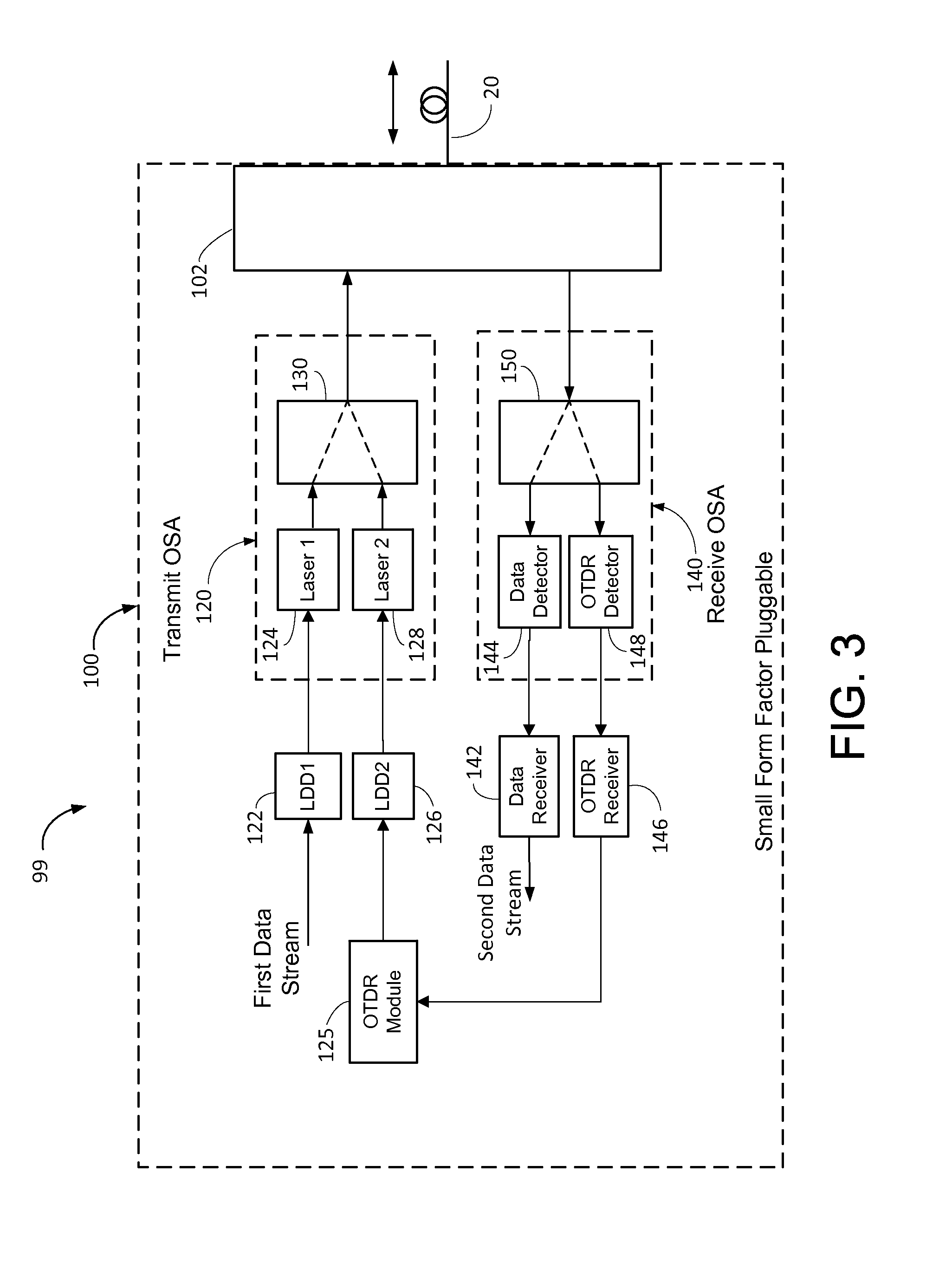
ActiveUS9143228B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringTime domainSmall form factor
A small form factor pluggable (SFP) device has an embedded optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR) for detecting anomalies along an optical fiber. The SFP device has a plurality of optical subassemblies (OSAs) that are used to transmit an optical data signal at a first wavelength, transmit an optical OTDR signal at a second wavelength, and receive an optical data signal at a third wavelength. The OTDR signal is effectively isolated from the data signals based on wavelength, and samples of returns of the OTDR signal are analyzed to detect at least one anomaly along the optical fiber.
Owner:ADTRAN
Module to module signaling
A method and apparatus configured to transmit module data between optic modules over a primary communication channel, such as an optic fiber configured to carry network data or outgoing data. A control center may send the module data, such as any type of DDMI data, over the optic fiber to control one or more aspects of the optic module system. The optic module may also be configured to send module data regarding any aspect of module status or operation, to a control center, via the optic fiber. Use of the primary communication channel, normally reserved for only network data, allow for module to module communication or module to control center communication without need of cumbersome two wire interface or supplement channels. Optic module data communication may occur concurrent with network data transmission. Optic module data back-up may occur via the optic channel to provide rapid re-load of important optic module data.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
Optical communication devices having optical time domain reflectometers
ActiveUS20130272694A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringTime domainSmall form factor
A small form factor pluggable (SFP) device has an embedded optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR) for detecting anomalies along an optical fiber. The SFP device has a plurality of optical subassemblies (OSAs) that are used to transmit an optical data signal at a first wavelength, transmit an optical OTDR signal at a second wavelength, and receive an optical data signal at a third wavelength. The OTDR signal is effectively isolated from the data signals based on wavelength, and samples of returns of the OTDR signal are analyzed to detect at least one anomaly along the optical fiber.
Owner:ADTRAN
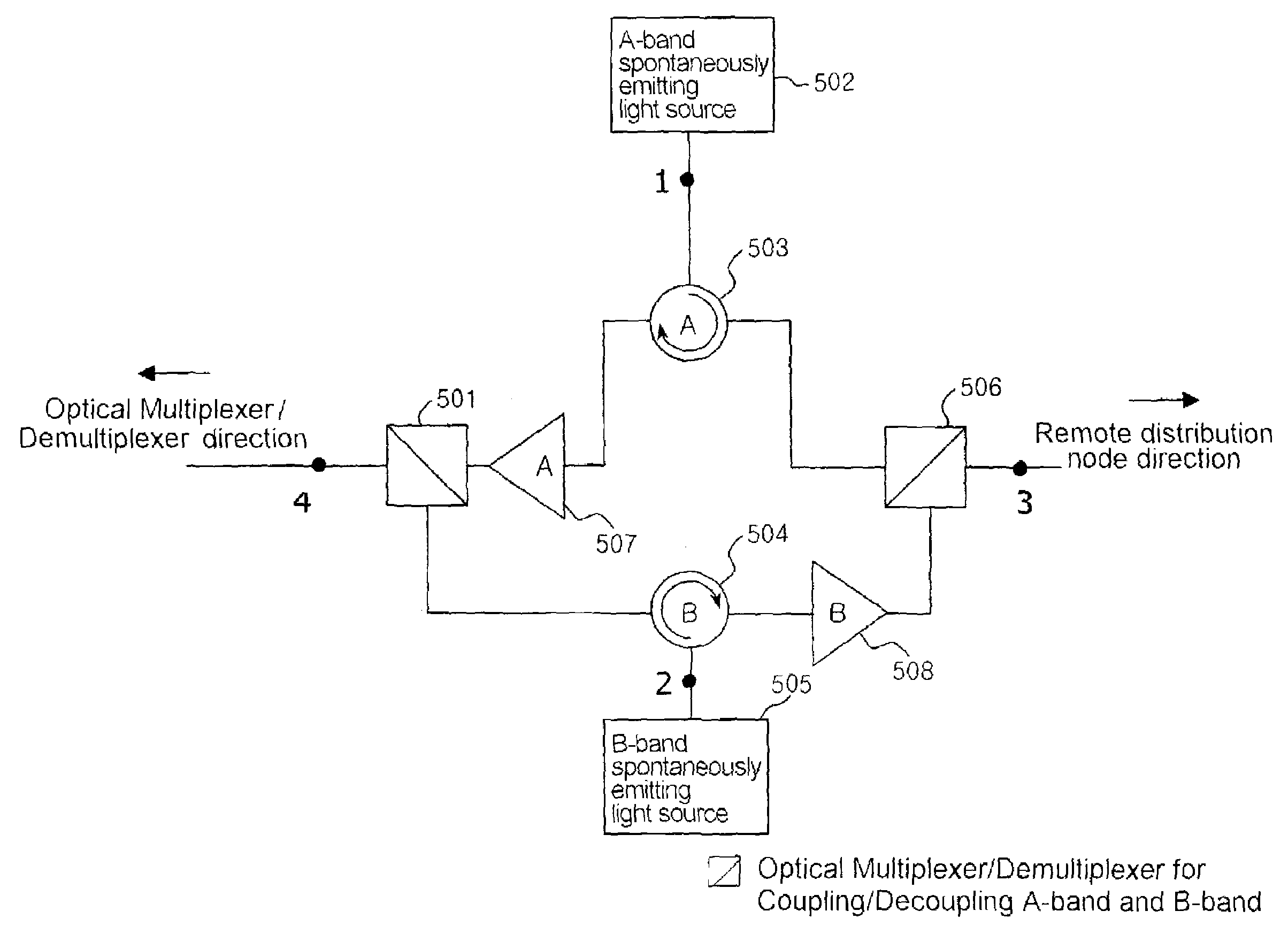
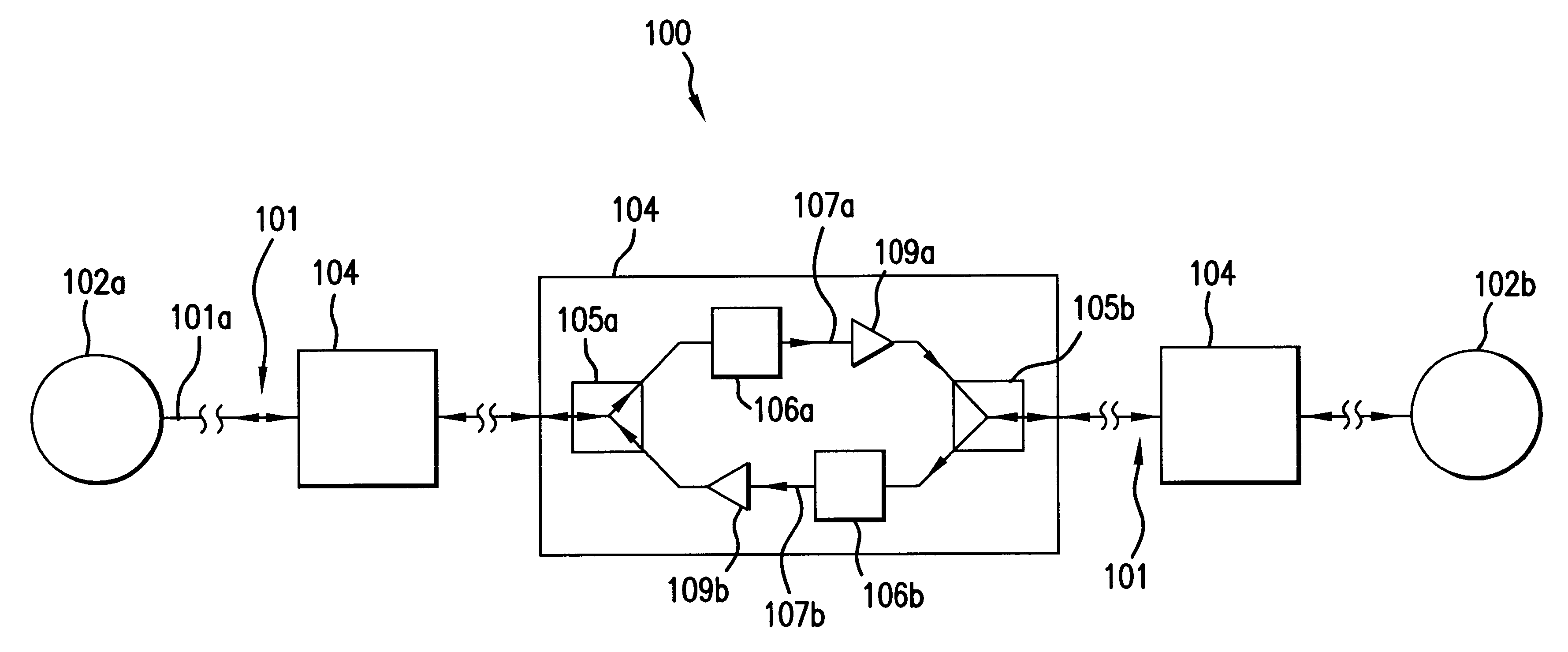
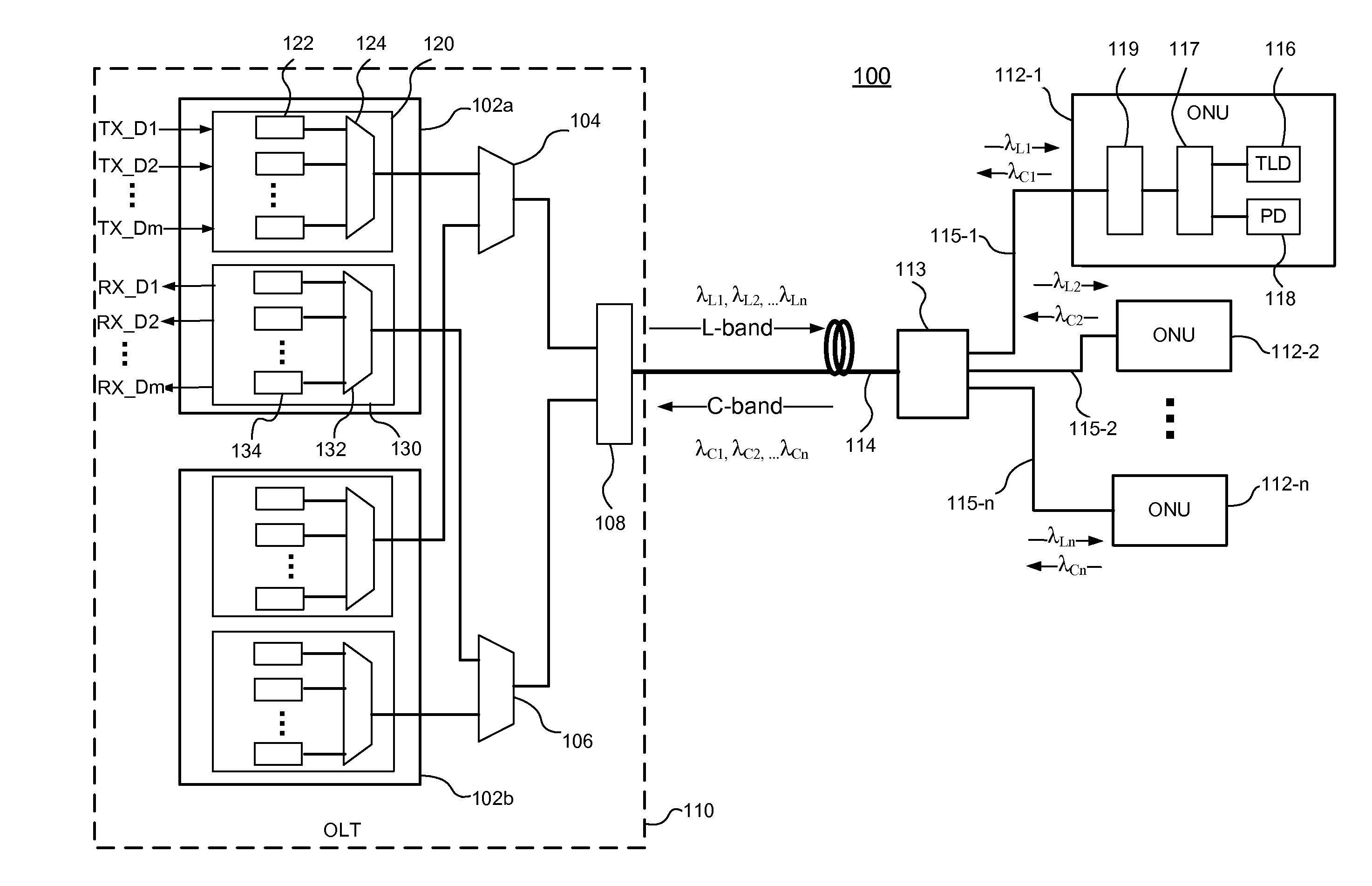
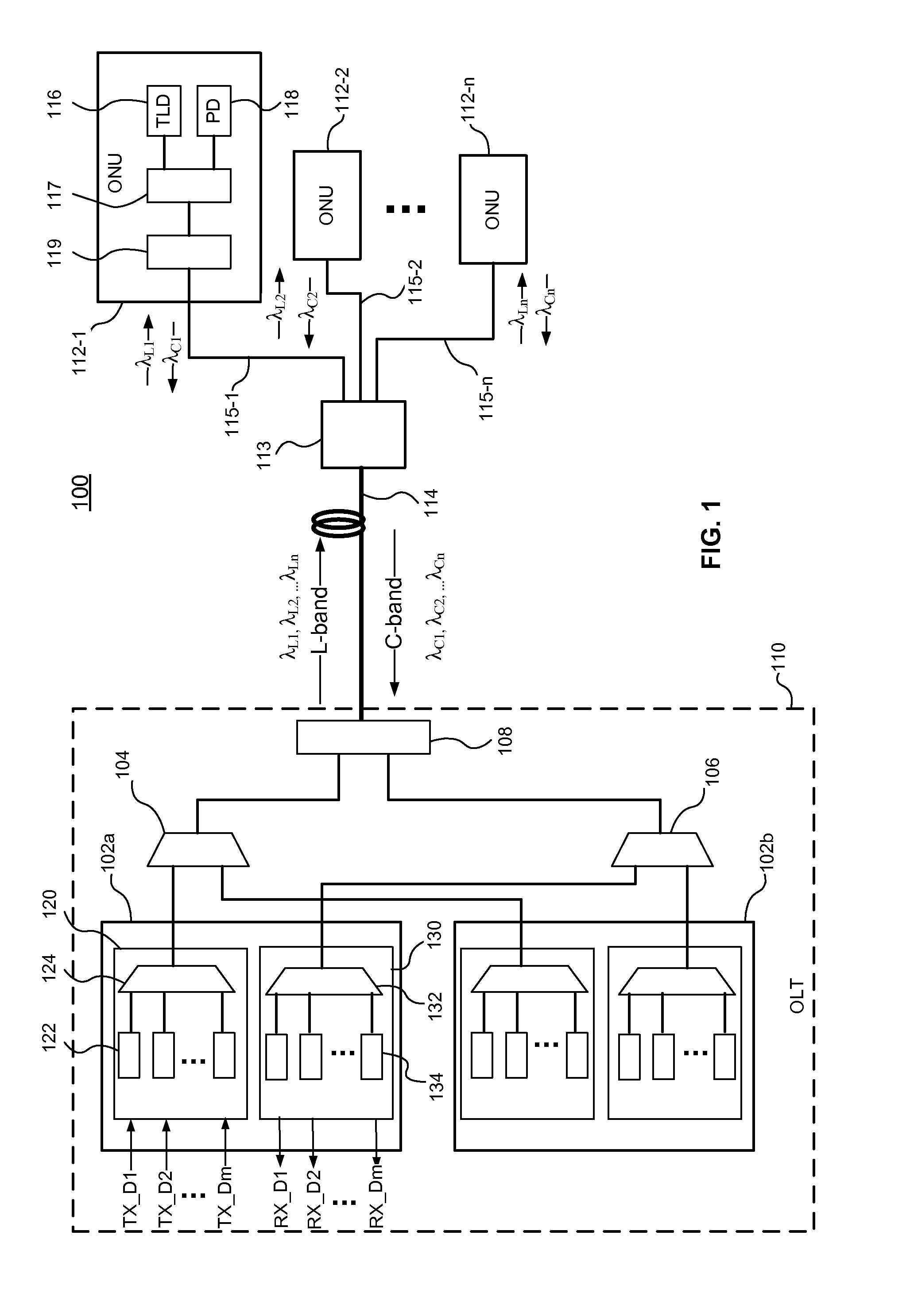
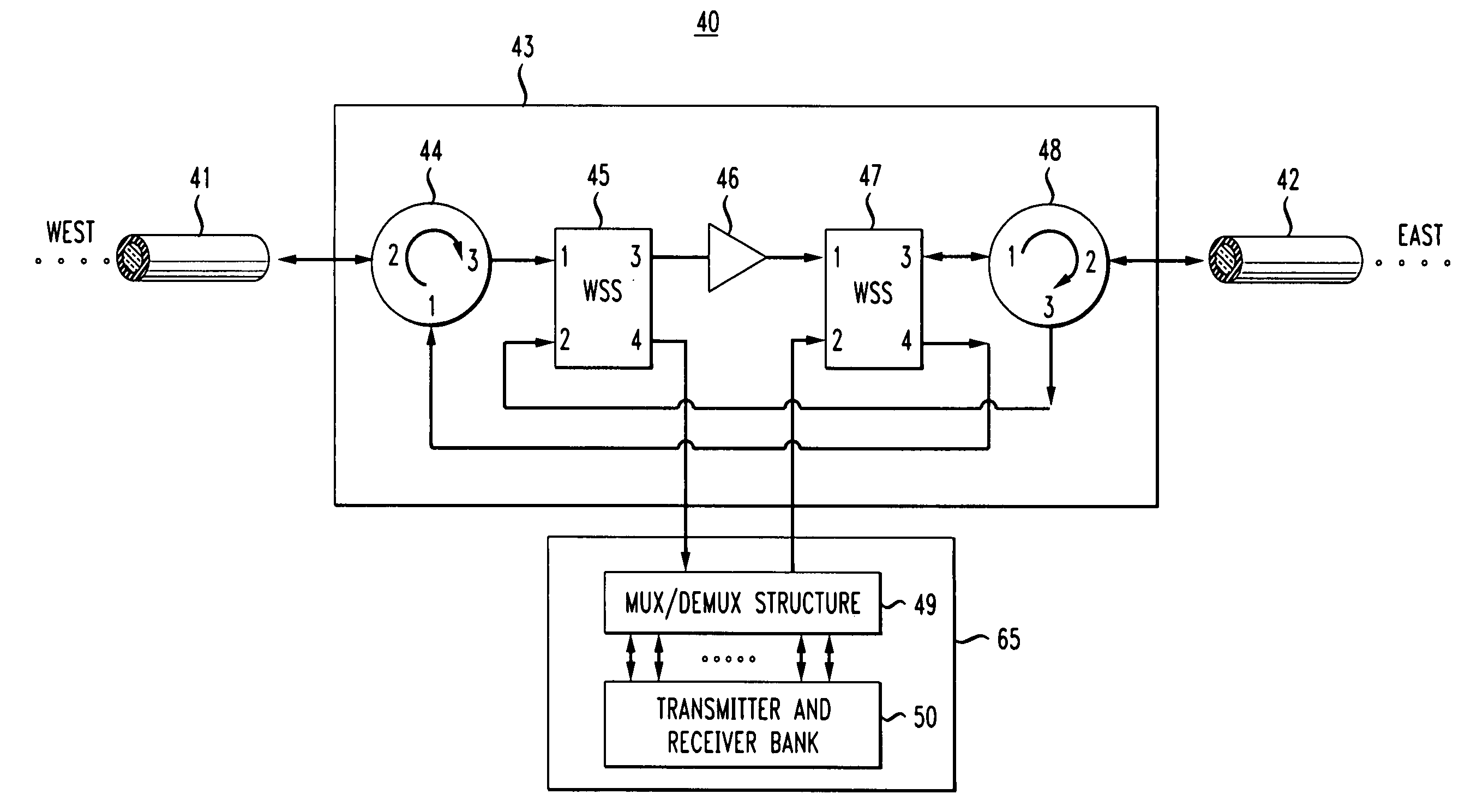
Dynamic allocation of bandwidth in a bidirectional optical transmission system
InactiveUS20070003283A1Good removal effectWavelength-division multiplex systemsBidirectional transmissionTransport systemCommunications system
A bidirectional optical communications system that is operable to dynamically allocate wavelengths for transmission in either direction in an optical fiber. The dynamic allocation is controlled by programmable optical devices. The programmable optical devices may be well known programmable devices such as wavelength selective switches and wavelength blockers or any other programmable optical device capable of dynamically allocating wavelengths between the two directions in the optical fiber. In addition, the programmable optical devices may be any combination of such wavelength selective switches, wavelength blockers or other programmable optical devices with other optical devices such as optical circulators, gain blocks, add / drop multiplexers, or fixed optical filters. Such a bidirectional optical communications system enables the dynamic allocation of bandwidth in an optical fiber without the need to replace components, such as fixed optical filters, and without disturbing communications on all the wavelengths transmitted in the optical fiber.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Methods and apparatus for generating local oscillation signals
InactiveUS6978091B1Low costPrevent theftMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTelevision systemElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Popular searches
Electromagnetic network arrangements Distortion/dispersion elimination Star-type electromagnetic networks Scattering properties measurements Photometry using electric radiation detectors Particle suspension analysis Radiation pyrometry Investigating moving fluids/granular solids Photoelectric discharge tubes Material testing goods
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com