Sewing machine
A sewing machine and sewing needle technology, which is applied to sewing machine components, sewing machine needle holders, sewing equipment, etc., can solve the problem of determining the amount of up and down movement of difficult sewing needles.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0058] [Sewing Machine Outline]
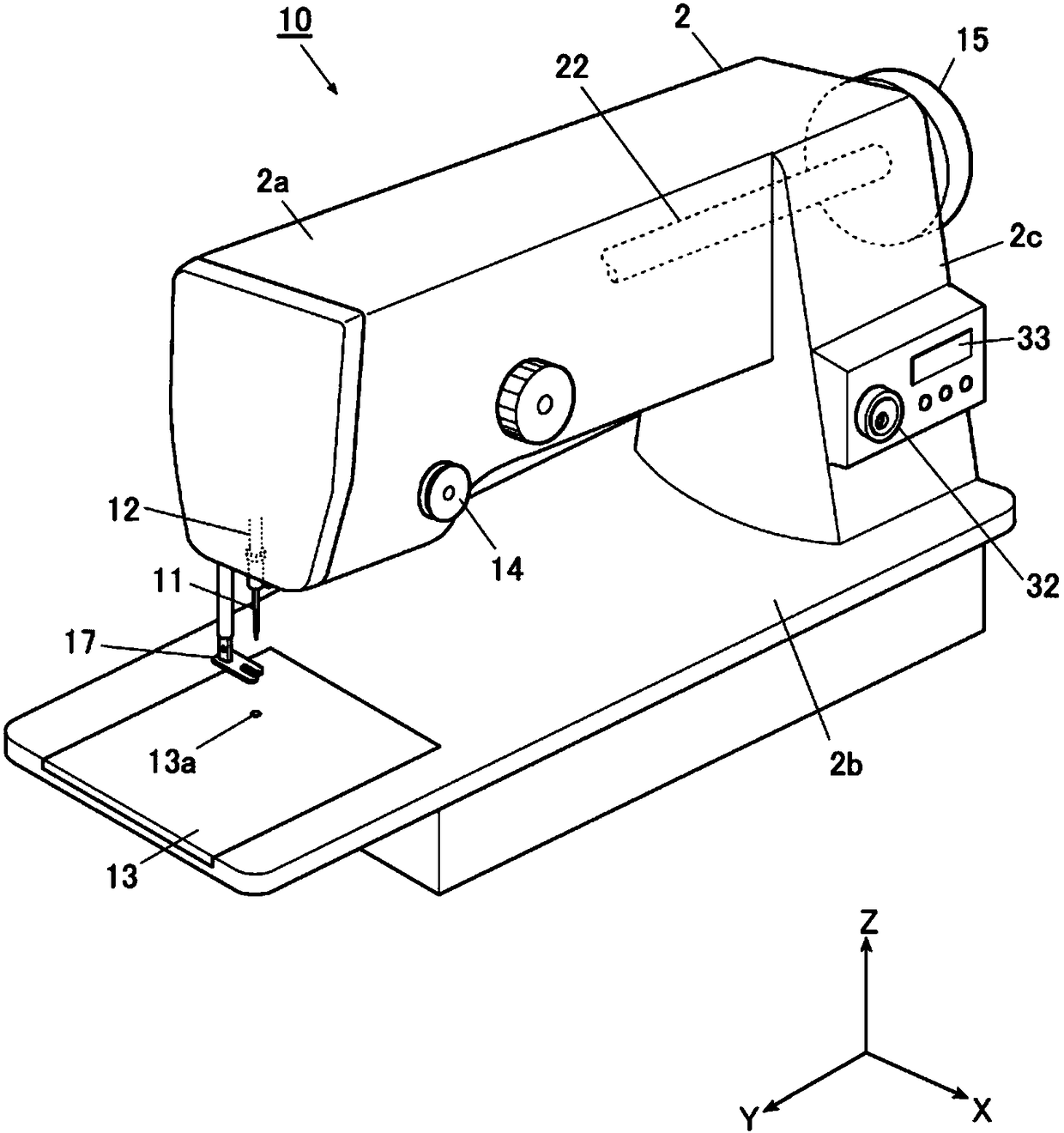
[0059] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail based on the drawings. figure 1 It is a perspective view which shows the whole structure of the sewing machine 10 which is this embodiment. In addition, in the following description, the direction horizontal and parallel to the longitudinal direction of the sewing machine arm portion 2a described later is referred to as the Y-axis direction (left-right direction), and the direction horizontal and perpendicular to the Y-axis direction is referred to as the X-axis. As for the direction (front-back direction), the vertical up-down direction is defined as the Z-axis direction (up-down direction).
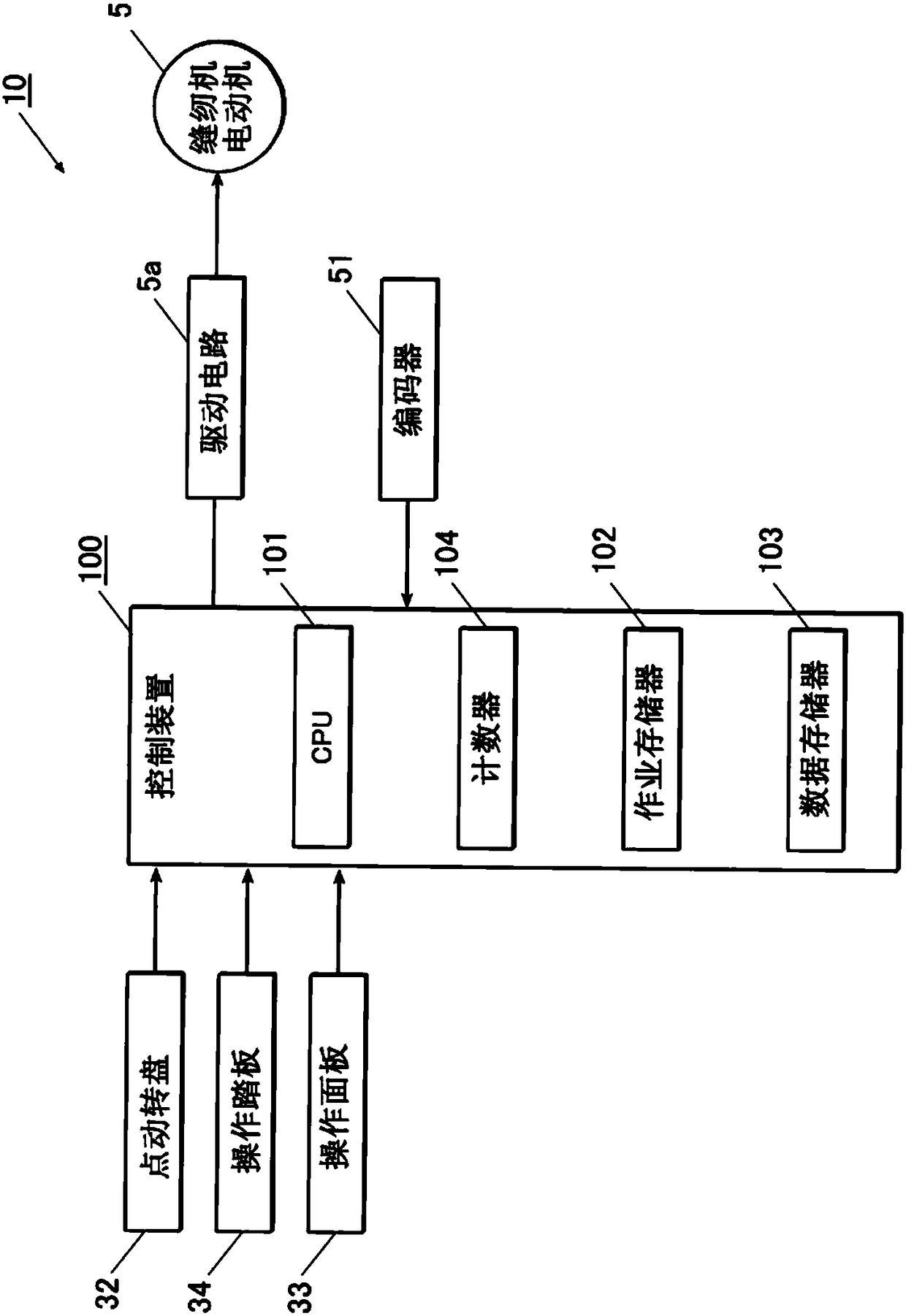
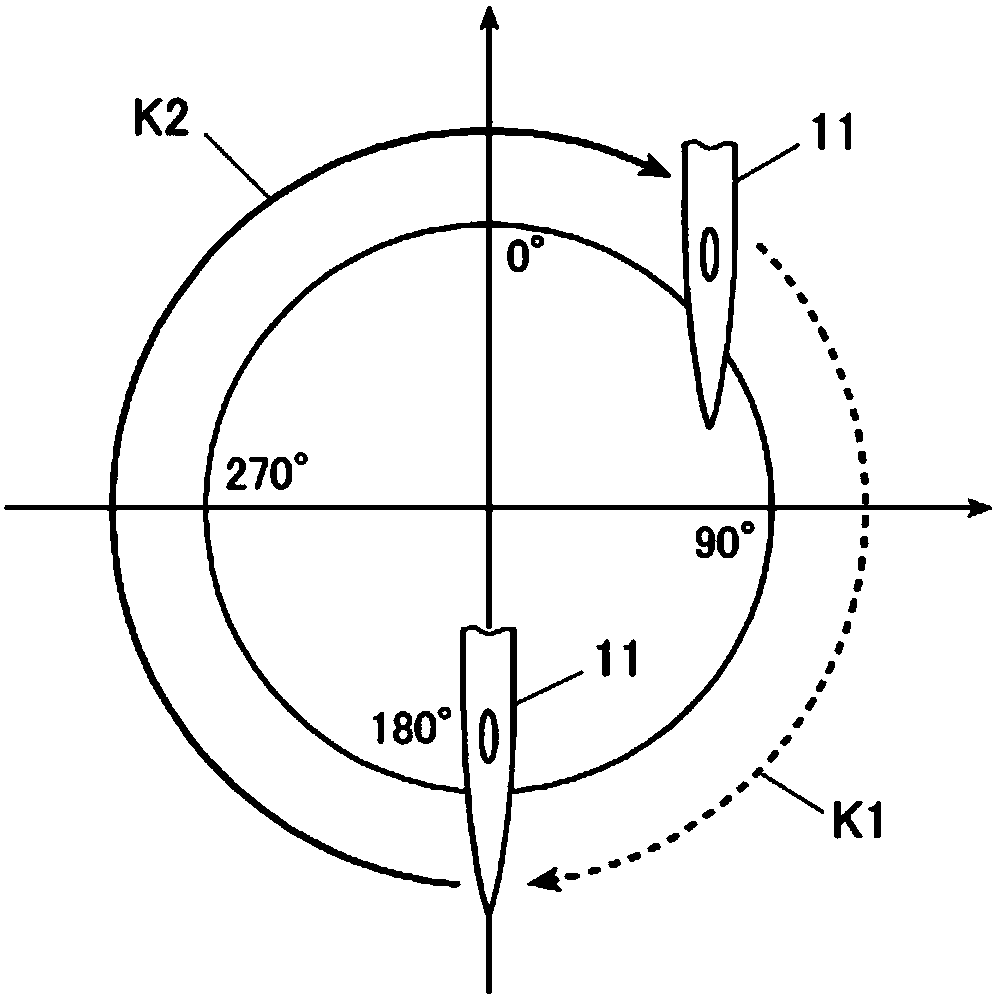
[0060] like figure 1 As shown, the sewing machine 10 is a so-called lockstitch sewing machine, which has: a sewing machine frame 2, which supports the overall structure; a sewing needle up and down movement mechanism (illustration omitted), which makes the needle bar ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com