A kind of construction method of azoospermia mouse model
A construction method and mouse model technology, which is applied in the field of construction of azoospermia mouse models, can solve the problems of poor stability, low modeling rate, and stability of modeling rate restricting the research progress of non-obstructive azoospermia , to achieve the effect of good stability and high molding rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A kind of embodiment of the construction method of azoospermia mouse model of the present invention, comprises the steps:
[0035] (1) C57BL / 6 male mice, which are sexually mature at 8-12 weeks, are used as model animals, with a body weight of 25-30g and no more than 35g; the modeling dose (busulfan) is 40mg / kg, and the cycle is 36 days;
[0036] (2) Taking a mouse with a body weight of 25g as an example, 1mg of busulfan is needed, dissolved in 0.05ml DMSO, prepared for immediate use, diluted to 2ml with normal saline (the ratio of DMSO to the total liquid volume is 2.5%), and transported on ice to animal center;
[0037] (3) After the mice enter the animal center after routine disinfection, shake the diluent well, draw 0.5ml diluent with an insulin needle (refer to Table 1 for details), disinfect the lower abdomen with alcohol, insert the needle after it is slightly dry, and draw back to confirm that it is correct. Complete a single intraperitoneal injection;
[0038...
Embodiment 2
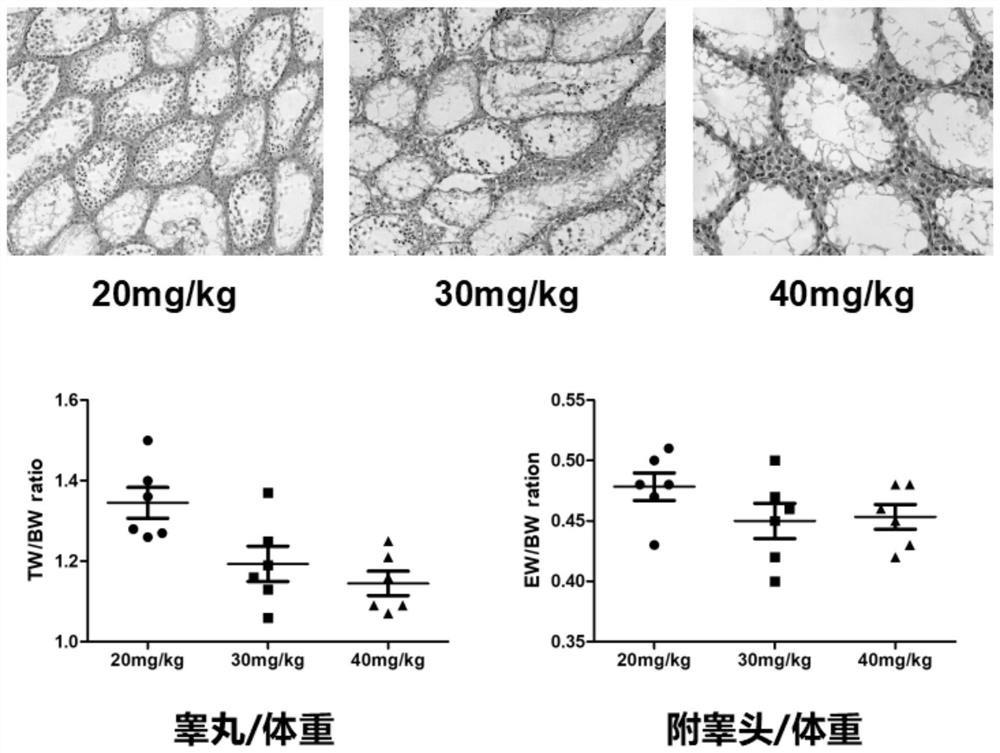
[0042] The modeling effect comparison of the busulfan of embodiment 2 different doses
[0043]Model mice were prepared using the modeling method of Example 1, the difference being the dose of busulfan, and the modeling effects of three different doses of 20 mg / kg, 30 mg / kg, and 40 mg / kg were compared. The result is as figure 1 shown by figure 1 It can be seen that, on the 36th day, in the seminiferous tubules of the mouse testis treated by two doses of 20mg / kg and 30mg / kg, spermatogenic cells were still visible, while in the seminiferous tubules of the mouse testis treated by the dose of 40mg / kg, only the same There were no spermatogenic cells in the basal part of the Sertoli cells, therefore, 40mg / kg dose of busulfan is suitable as a modeling dose.
Embodiment 3
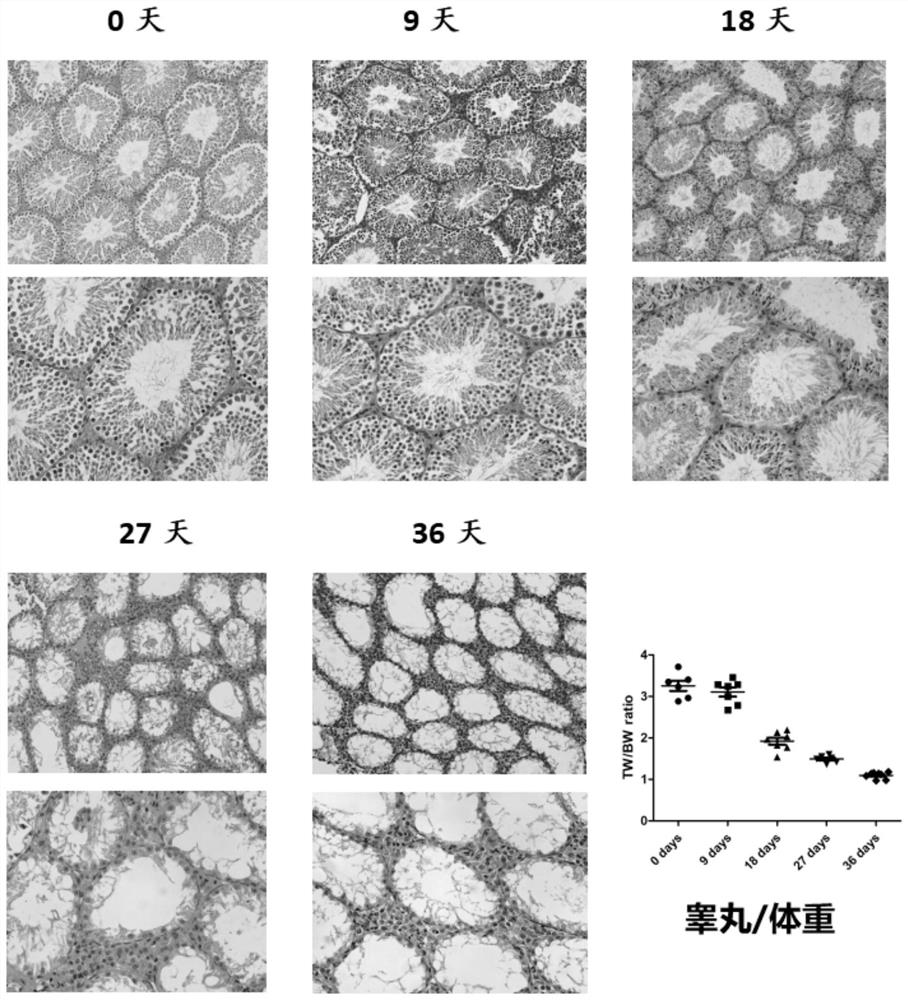
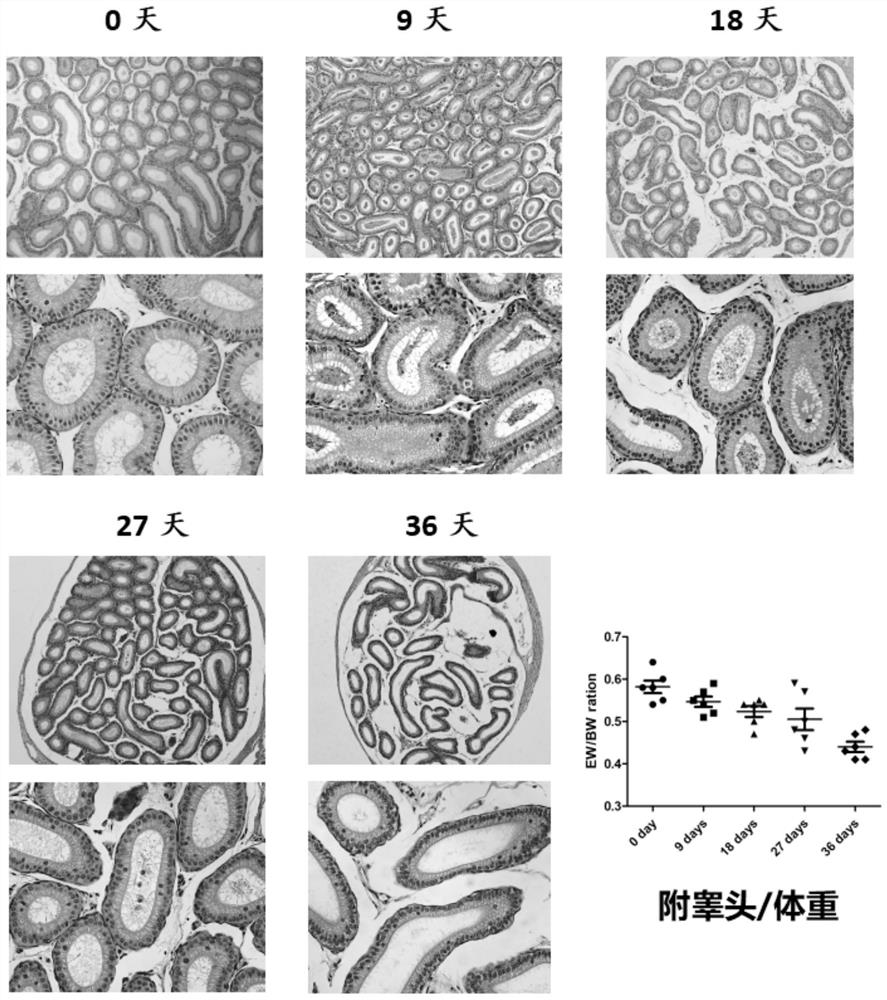
[0044] Example 3 Effects of time on the seminiferous tubules and testis of model mice
[0045] Model mice were prepared using the modeling method in Example 1, the difference being that the time after busulfan injection was different, and the changes in the testes of the mice were compared after 0 day, 9 days, 18 days, 27 days, and 36 days. The result is as figure 2 shown by figure 2 It can be seen that from the 9th day to the 18th day, the seminiferous tubules and the testis / body weight coefficient changed drastically, suggesting that the model may be in a reversible stage before the 18th day, and gradually turn into an irreversible state after the 18th day.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com