A sample preparation method for graphite optical microstructure characterization
A technology for optical microscopy and sample preparation, which is applied in the preparation, sampling, and scientific instruments of samples for testing. It can solve the problems of poor sample grinding and polishing effects, improve the surface quality of samples, compact texture, and improve surface smoothness. degree of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
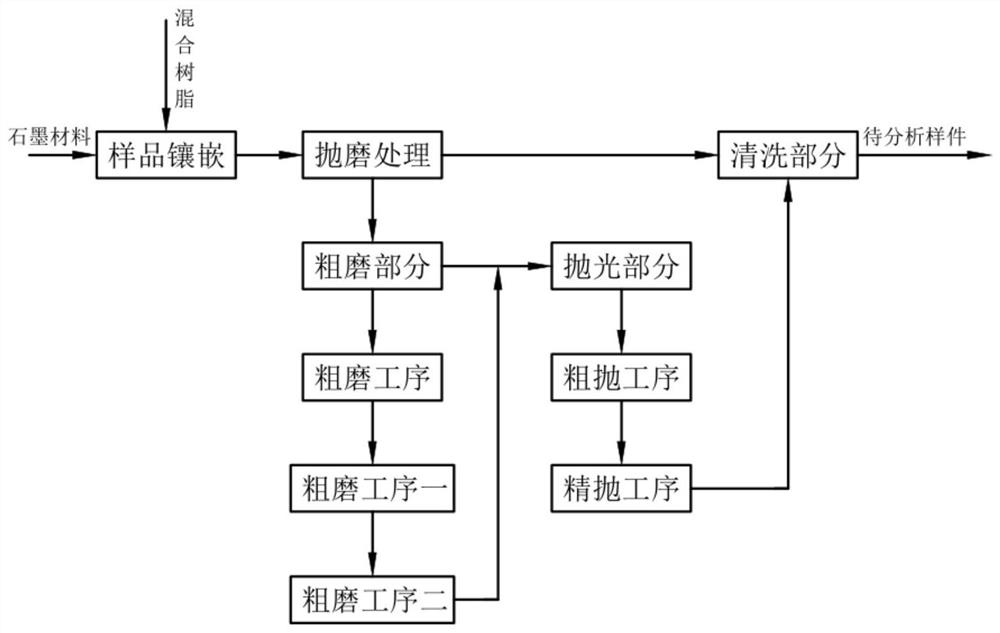
[0045] According to the drawings in the manual figure 1 A sample preparation method for optical microstructure characterization of graphite in this example is described.
[0046] A sample preparation method for graphite optical microstructure characterization, comprising the following steps:
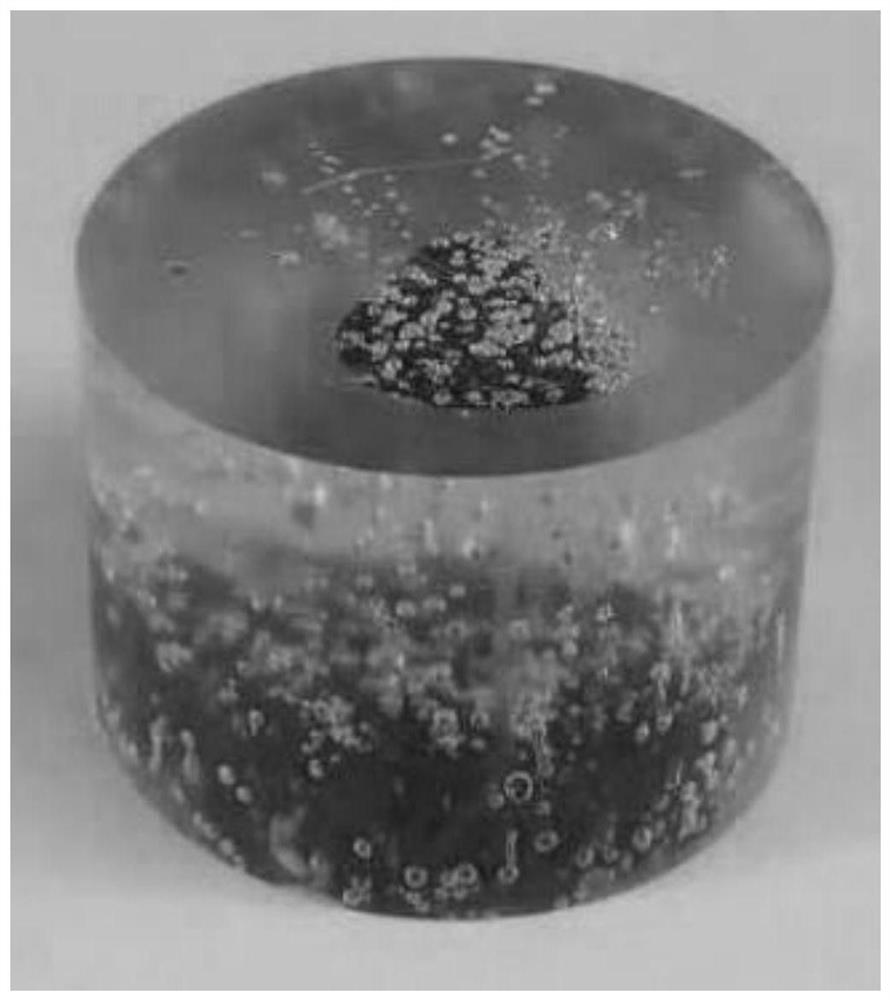
[0047] (a) Sample inlay, after the graphite material and the mixed resin are exhausted by vacuuming through the inlay equipment, the graphite material and the mixed resin are mixed by pouring to form a compact and solid sample to be ground;
[0048] (b) Grinding and polishing treatment, the plurality of samples to be ground formed by the step (a) are clamped on the sample holder on the grinding and polishing equipment in a horizontal positioning manner, and the samples are respectively pressed in an elastic pressurized manner through the loading plate. While the sample on the fixture is being pressurized, the sample is subjected to multi-stage grinding and polishing treatment through th...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Wherein, the same or corresponding parts as those in the first embodiment adopt the reference numerals corresponding to the first embodiment. For the sake of simplicity, only the differences from the first embodiment are described below; the difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that : The step (b) also includes a coarse grinding part, applying a ballast elastic force of 10-20N to the sample to be ground by the loading disc in a downward pressure mode, and adopting a SiC sandpaper grinding disc with a mesh number of 300-2500 to cooperate with the sample fixture Grinding the surface of the sample to be polished in a rotational friction manner with a differential speed of 100-200 rpm to form a sample to be thrown with a surface finish Ra: 5-40 μm.
[0058] Specifically, the rough grinding part includes:
[0059] In the coarse grinding process, a ballast elastic force of 10-20N is applied to the sample to be ground by the loading disc in a do...
Embodiment 3
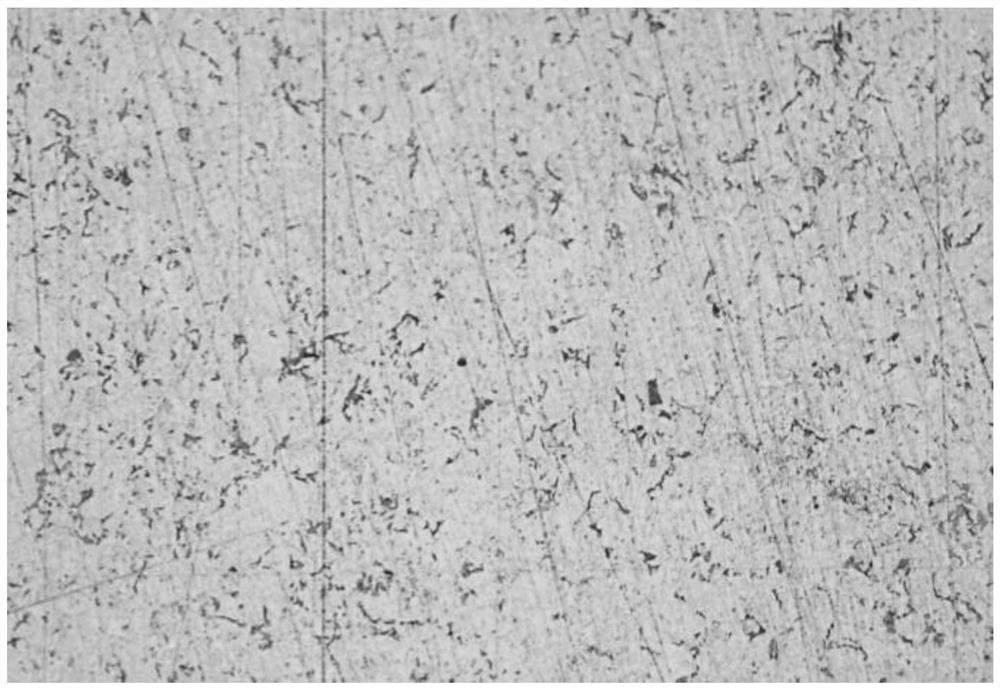
[0063] Wherein, the same or corresponding parts as those in Embodiment 2 adopt the reference numerals corresponding to Embodiment 1. For the sake of simplicity, only the differences from Embodiment 2 are described below; the difference between Embodiment 3 and Embodiment 2 is that : The step (b) also includes a polishing part. After the rough grinding process two, apply a ballast elastic force of 10-18N to the sample to be ground by the loading disc in a downward pressure mode, and use a polishing cloth grinding disc and the sample to be polished to The rotating friction method with a differential speed of 100-400 rpm is combined with a polishing solution of 0.05-6 μm to polish the sample to be polished; to form a sample to be analyzed with a surface finish Ra: 0.02-0.04 μm, flat and clear texture.
[0064] Specifically, the polishing part includes:
[0065] In the rough polishing process, a ballast elastic force of 10-18N is applied to the sample to be thrown by the loading p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface smoothness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com