Piezoelectric motor with variable speed and torque and using method thereof
A piezoelectric motor and torque technology, which is applied to piezoelectric effect/electrostrictive or magnetostrictive motors, generators/motors, electrical components, etc. Can not increase and other problems, to achieve the effect of high torque to weight ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
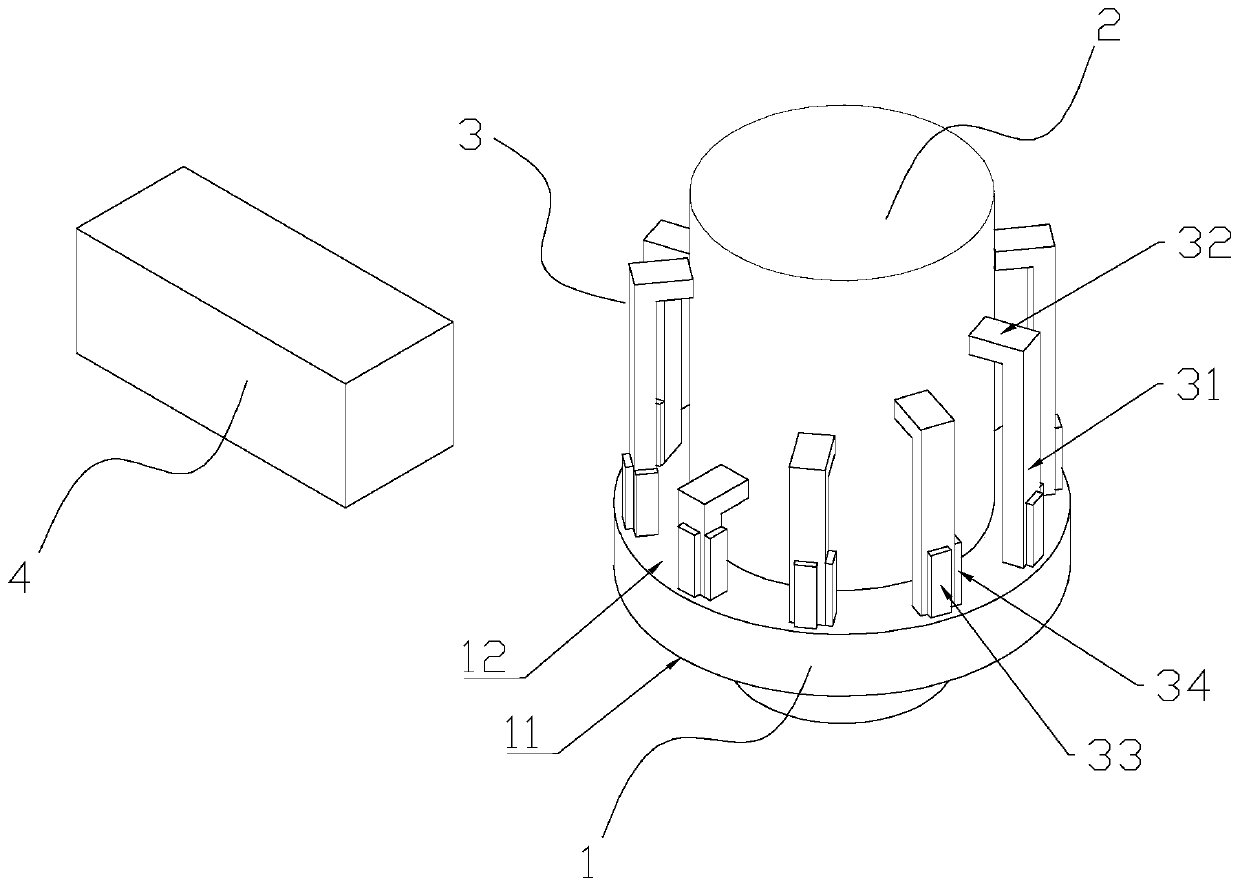
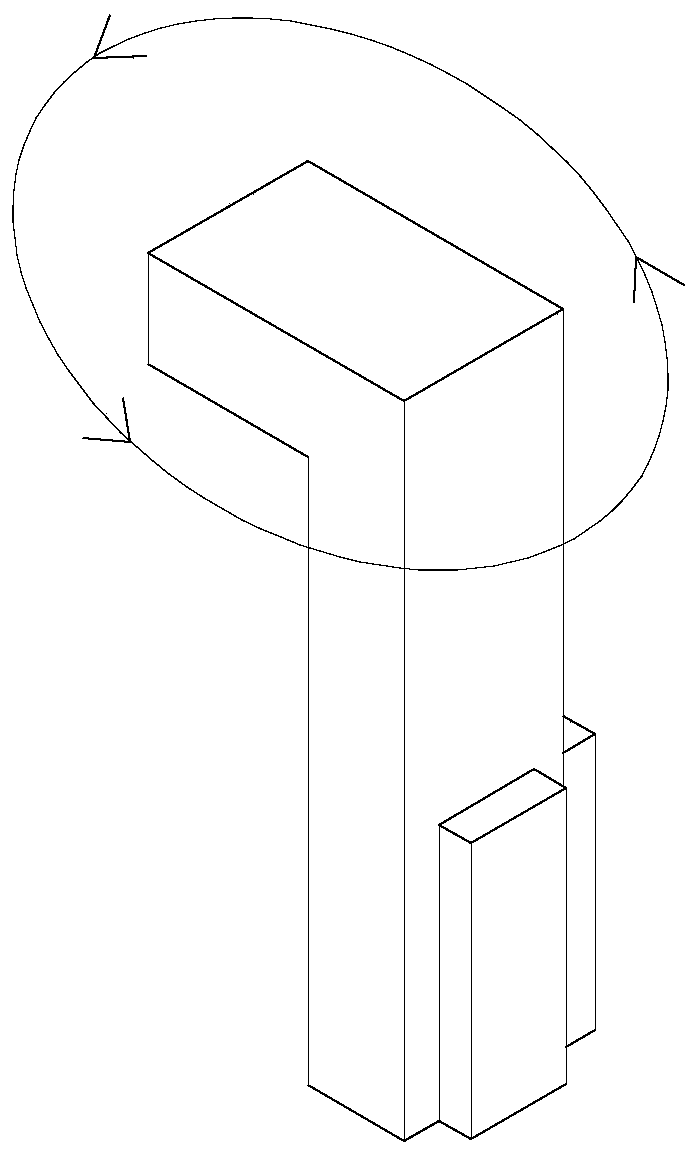
[0024] like figure 1 As shown, a piezoelectric motor with variable torque and rotating speed includes an annular stator base 1, the stator base 1 includes a first end face 11 and a second end face 12, and a rotatable rotor 2 is provided in the middle of the stator base 1, The second end surface 11 of the stator seat 1 is provided with a driving part 3, and the driving part 3 is driven by the driver 4. The driving part 3 includes multiple groups of driving legs with different lengths. The number of driving legs in this embodiment is preferably five groups. The number of driving feet in the group is not less than two and the lengths are equal. The driving feet of the same group are evenly arranged along the circumference of the second end face 12. The number of driving feet in this embodiment is preferably two; because the length of the driving feet is different, the resonant frequency Also different, the driving frequency of the driver 4 driving different groups of driving feet...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A method for using a piezoelectric motor with variable torque and rotational speed, the method comprising:
[0029] 1) Select the driver that matches the rotor speed
[0030] Introduce the calculation formula of the rotor speed v
[0031] v=f*X qn *60 / 2*3*π*r
[0032] Among them, f is the driving frequency of the driver; X qn is the swing amplitude of each driving foot in the direction perpendicular to the rotor radius, q is the number of groups, n is the number of driving feet of any driving group; rotor radius r;
[0033] According to the above measured parameters and the required rotor speed, the drive frequency f required for the output speed is calculated. Since the frequencies of driving different groups of drive legs are different, the drive legs that meet the drive frequency f can be determined;
[0034] 2) Select the number of driving feet that output the rotor torque
[0035] Introduce the calculation formula of rotor torque
[0036] M=(λ q1 +λ q2 +......
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com