Evaluation method of material remaining life based on image analysis of surface microtopography features
An image analysis and topographic feature technology, applied in the direction of analyzing materials, conducting material analysis by optical means, and testing the strength of materials by applying repetitive force/pulsation force, etc. Metal fatigue mechanism is complex and other problems, to achieve the effect of simple relationship, easy engineering application and promotion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] An example of the method for evaluating the remaining life of materials based on image analysis of surface micro-topography features according to the present invention includes the following steps:
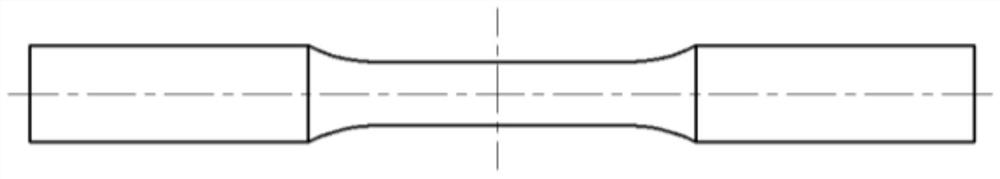
[0029] (1) Fatigue tests with controlled strain amplitudes of 0.003, 0.004, 0.005, 0.008 and 0.01 were carried out with rough ground samples until failure, and the average total fatigue life N was determined f , in order to reduce the influence of random errors, the fatigue life of multiple smooth specimens under different strain amplitudes was tested, and the average value was taken as the material life N under different strain amplitudes f , see Table 1, and the dimensions of the metal smooth round bar specimens are shown in figure 1 .
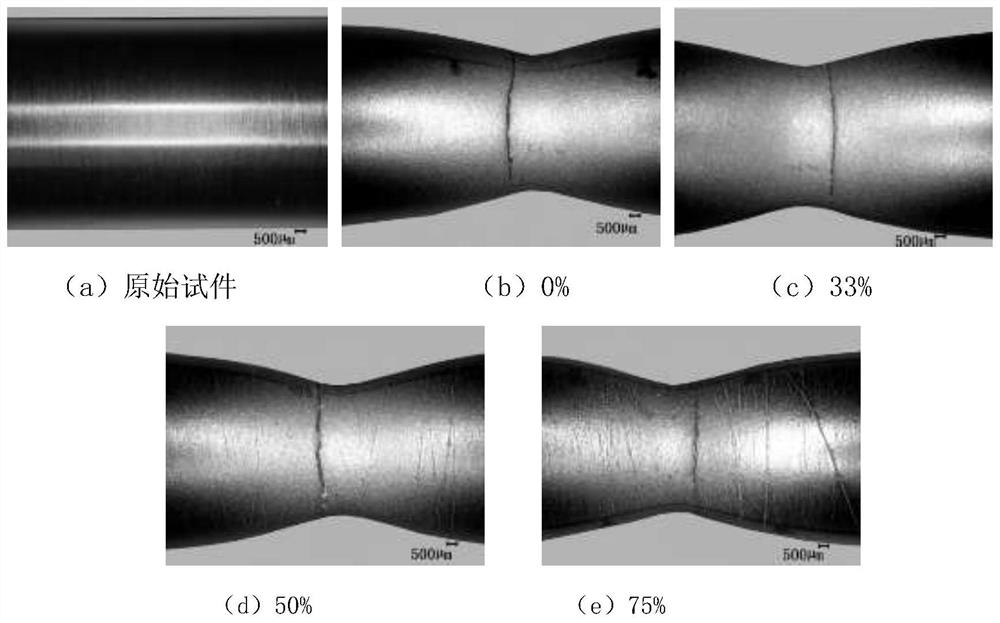
[0030] (2) Carry out N / N f (N / N f = number of pre-fatigue cycles / average total fatigue life) of pre-fatigue tests with 33.3%, 50% and 75% respectively, N / N f The relative life of the representative sample experienced N cycles of consu...
Embodiment 2
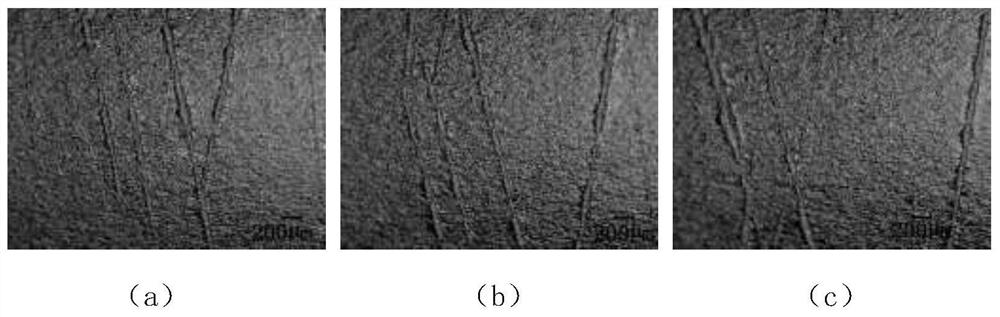
[0039] This embodiment is a test example of the method for evaluating the remaining life of a material based on the image analysis of the surface micro-topography feature of the present invention on specimens with different surface smoothness. In order to further explore the applicability and rationality of this method for evaluating the remaining life of materials for different surface finishes, two kinds of specimens with different surface finishes were tested, such as Figure 7 shown. The difference between the two types of rough grinding and fine grinding is that the surface finish of the test piece is different due to the different types of sandpaper used when the grinder is used for polishing. Figure 8 It is the surface morphology of the rough and fine ground specimens under the 500-fold optical microscope lens. By comparing the pictures, it can be seen that the initial cracks on the surface of the rough ground specimens are wider than that of the fine ground specimens....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com