Multifunctional experimental device for Lenz's law
An experimental device, the technology of Lenz's law, applied in the field of physical science experimental devices, can solve the problems such as the inability to intuitively demonstrate the opposite magnetic field of the solenoid, the single form of the demonstration device, unfavorable learning and understanding of Lenz's law, etc., so as to deepen the understanding. and understanding, the experimental results are intuitive, and the use of flexible effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
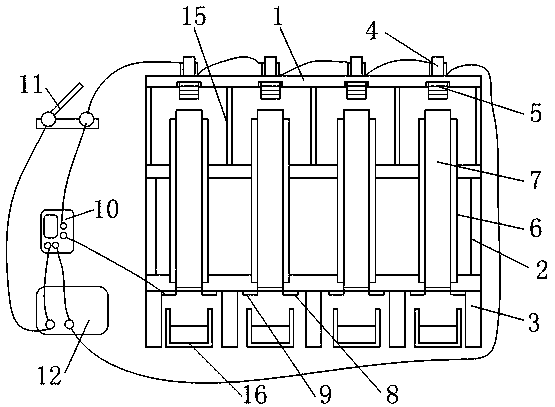
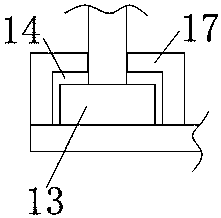
[0032] In order to solve the technical problem of the single form of Lenz's law demonstration device in the prior art, this embodiment provides a multifunctional Lenz's law experimental device, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes the first bracket 1, the second bracket 2 and the third bracket 3 stacked in sequence from top to bottom, the first bracket 1 and the second bracket 2 are detachably connected, the second bracket 2 and the third bracket 3 The first support 1, the second support 2, and the third support 3 are all made of non-magnetic, non-conductive, high-transparency plexiglass material, and the top surface of the top wall of the first support 1 is provided with four copper Coil 4, the bottom surface of the top wall of the first support 1 is provided with four grooves for placing the magnet 5, the top wall of the second support 2 is provided with four round holes for the solenoid to pass through, and the top wall of the third support 3 The wall is provided with fou...
Embodiment 2
[0042] The difference from the above-mentioned embodiment is that this embodiment uses an enameled wire with a diameter of 1.5 mm to uniformly wind 300, 900, 1500, and 2100 turns of the solenoid on the plexiglass tube, and selects 4 groups with the same thickness and diameter. The cylindrical magnet 5 is made to be adsorbed in the grooves on the lower side of 4 groups of copper coils 4, the constant current source 12 switch is turned off, and the speed at which the magnet 5 falls is observed, and the time taken by the 4 groups of magnets 5 to fall can be checked by the timer 10. The influence of the number of turns of the solenoid on the hindering effect of the magnet 5 is compared under the same wire diameter.
Embodiment 3
[0044] The difference from the above-mentioned embodiment is that this embodiment adopts two solenoids, which are respectively 2.0 mm in diameter enameled wire and 1500 turns uniformly wound on the plexiglass tube, and a width of 2.0 mm and a thickness of A second-generation high-temperature superconducting tape with a diameter of 0.1 mm is evenly wound on a solenoid with 1500 turns on a polytetrafluoroethylene tube. The high-temperature superconducting tape outside the polytetrafluoroethylene tube needs to be packaged in a low-temperature container; two groups are selected Cylindrical magnets 5 with the same thickness and diameter are adsorbed in the grooves on the lower side of the two sets of copper coils 4, the constant current source 12 switch is turned off, and the falling speed of the magnets 5 is observed, and the two sets of magnets 5 are checked by the timer 10. The falling time can be used to compare the influence of the solenoid and the polytetrafluoroethylene tube ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com