Method for verifying time domain fine structure novel code of artificial cochlea tone language
A cochlear implant and fine structure technology, applied in artificial respiration, electrotherapy, therapy, etc., can solve problems such as lack of evaluation value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
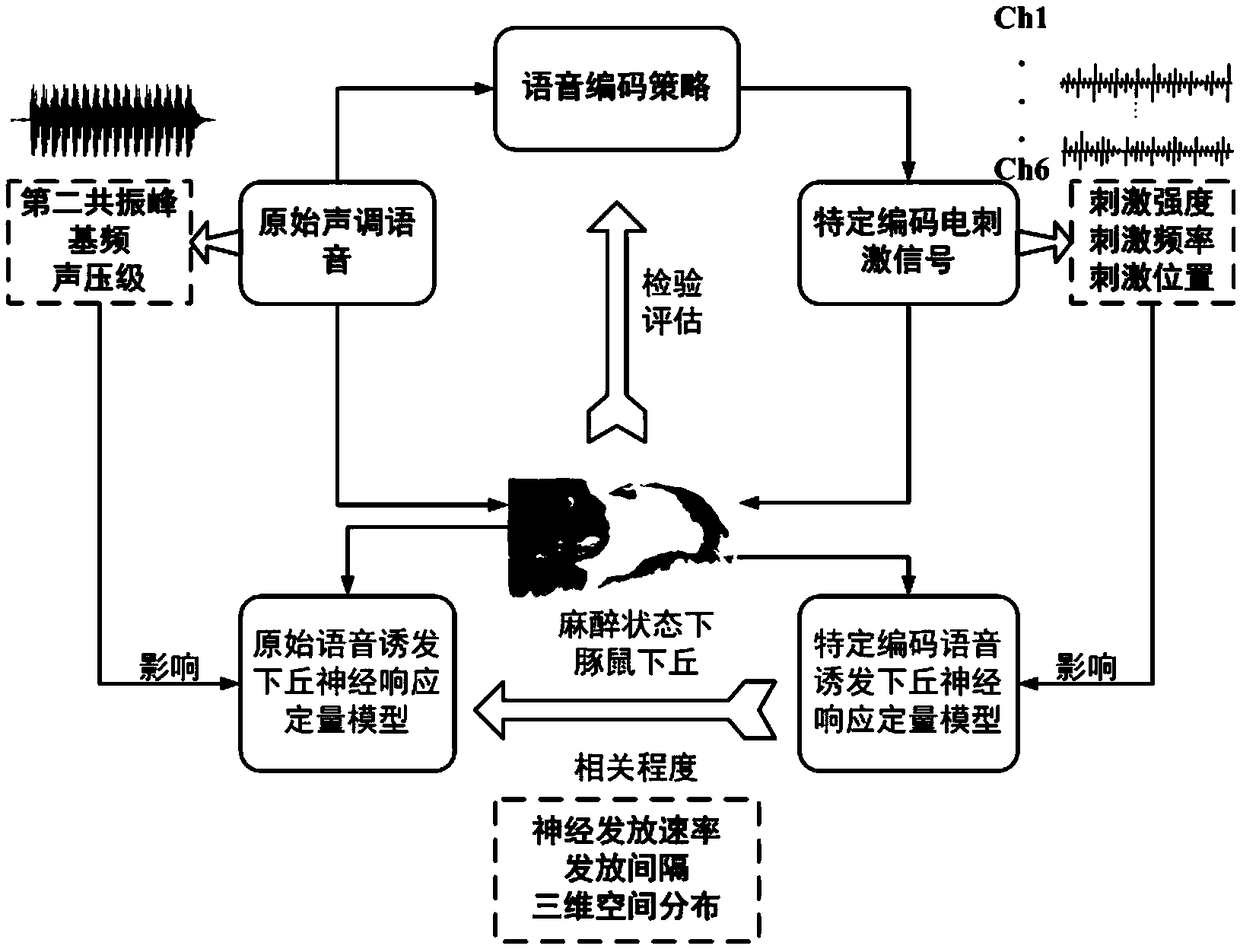
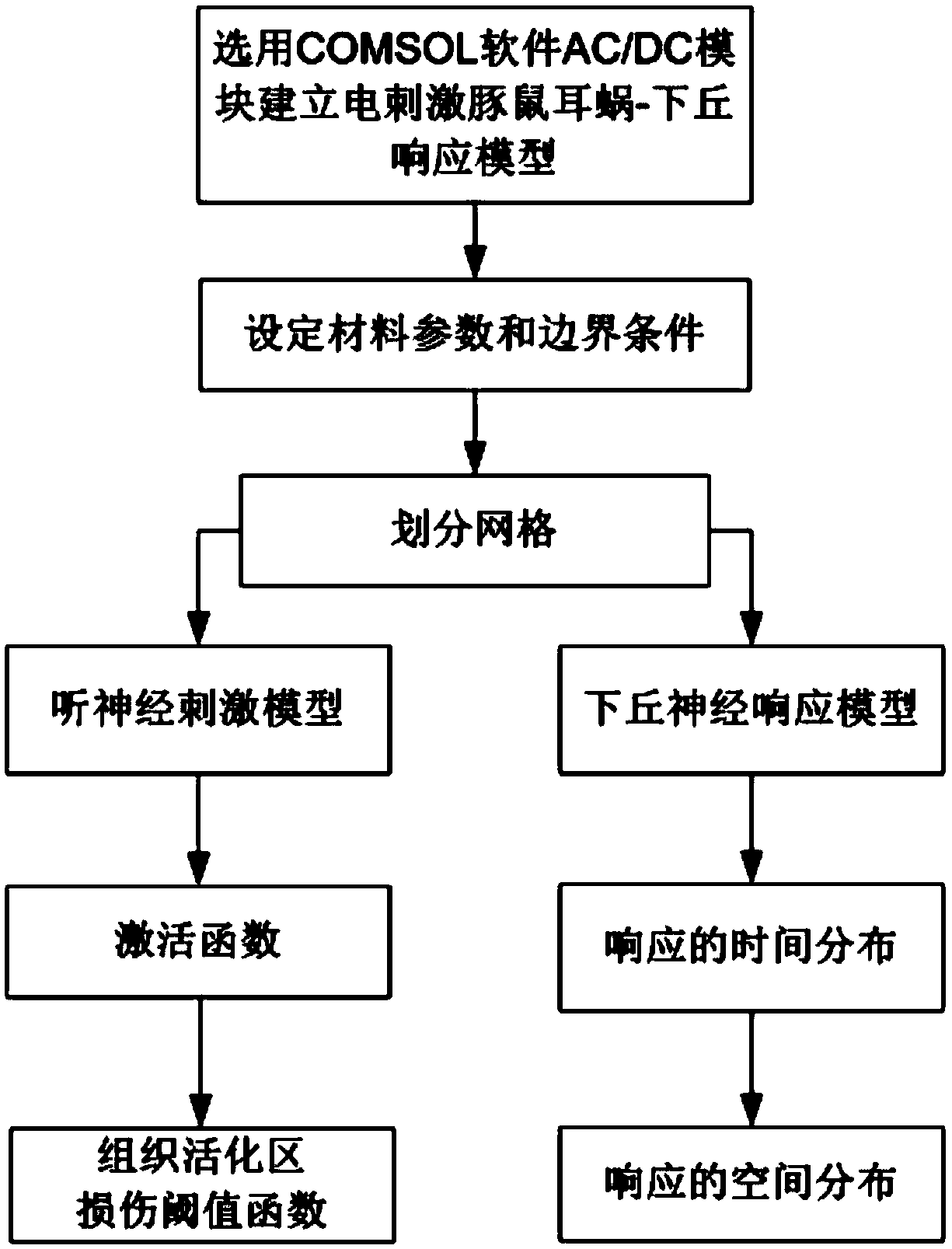
[0079] see Figure 1 to Figure 5 , a method for verifying the novel encoding of time domain fine structure of cochlear implant tone language, which mainly includes the following steps:
[0080] 1) Establish spatio-temporal quantitative model I of the original speech-induced inferior colliculus neural response. The main steps are as follows:
[0081] 1.1) Select an experimental organism model suitable for the study of auditory neural pathways.
[0082] Preferably, in this embodiment, guinea pigs are selected as the experimental organisms, and the natural auditory neural pathways of the guinea pigs are fully utilized to verify and evaluate the new time domain fine structure coding of the cochlear implant tone language.
[0083] Further, rats, Mongolian gerbils, etc. can also be selected as experimental organisms.
[0084] 1.2) Perform an audiometry curve test on the single ear of the experimental organism using the CLICK sound signal. The tests mainly include hearing thresho...
Embodiment 2
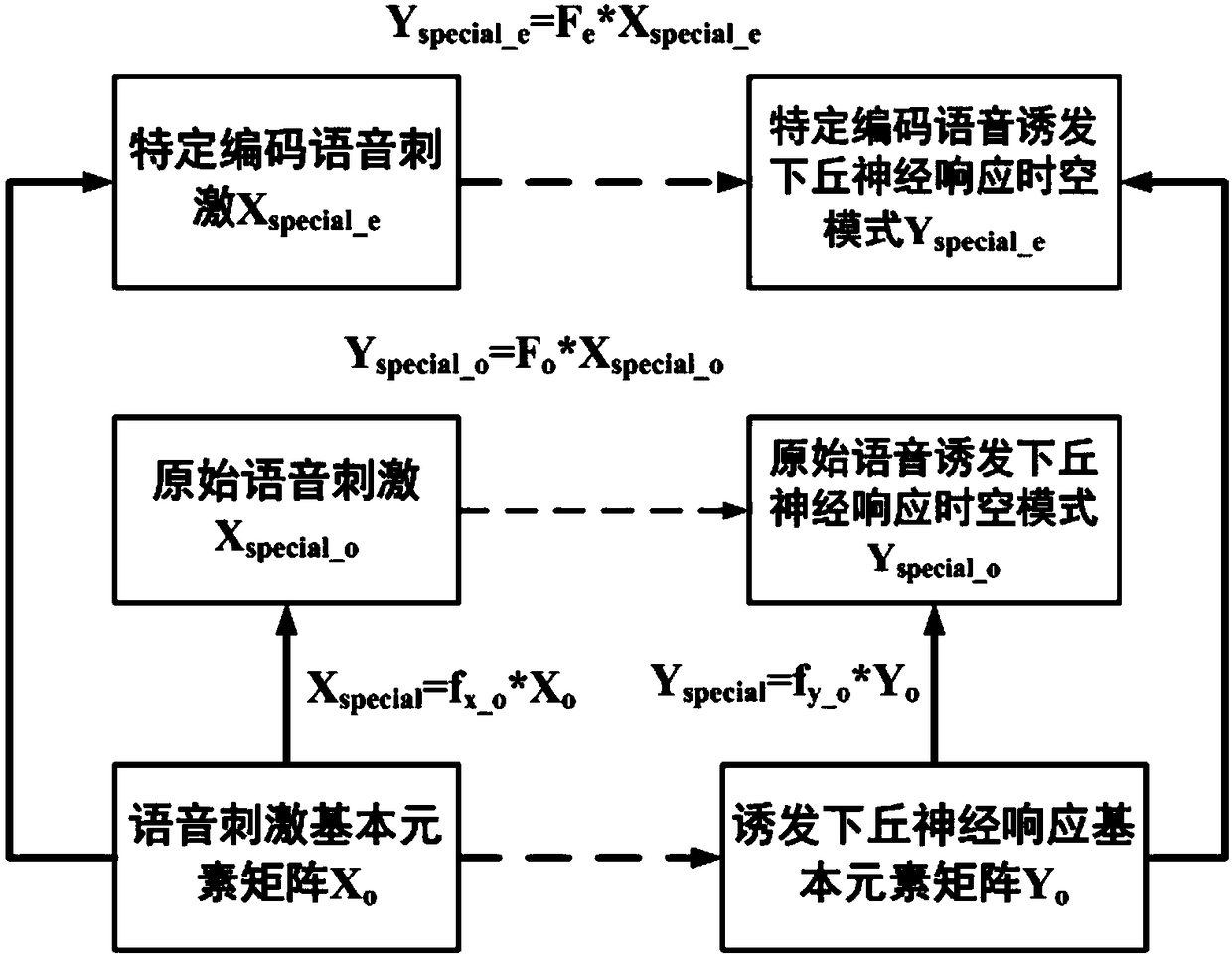
[0145] In this embodiment, the verification method of the novel encoding of the time-domain fine structure of the cochlear implant tone language is compared with the mathematical simulation method of the auditory neural network. The mathematical simulation method of the auditory neural network can be found in figure 2 . The comparison steps are as follows:
[0146] 1) Using the verification method of the novel encoding of the time-domain fine structure of the cochlear implant tone language to verify the new encoding of the time-domain fine structure of the cochlear implant tone language to be verified. The main steps are as follows:
[0147] 1.1) Select the experimental organism. In this embodiment, guinea pigs are selected as the experimental organisms.
[0148] 1.2) Establish the original speech stimulus-induced inferior colliculus nerve response mode I(Y special_o )
[0149] 1.3) Establishment of a new coded speech electrical stimulation-induced inferior colliculus n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com