Regulatory gene of rice dwarf brittle mutant dbc1 and its application
A technology for regulating genes and mutants, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the difficult problems of straw treatment, etc., and achieve the effect of regulating rice cell division and promoting breeding research
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
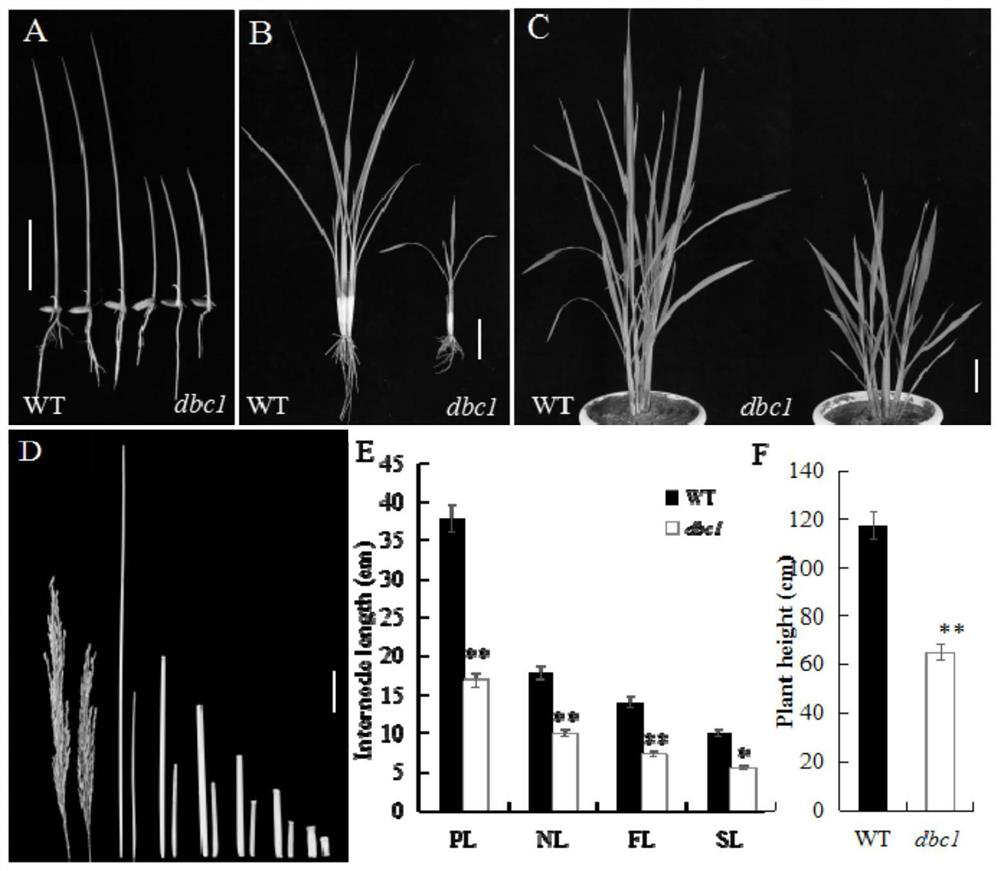
[0060] Implementation 1: Cloning, sequencing and functional verification of rice dwarf brittle mutant gene DBC1
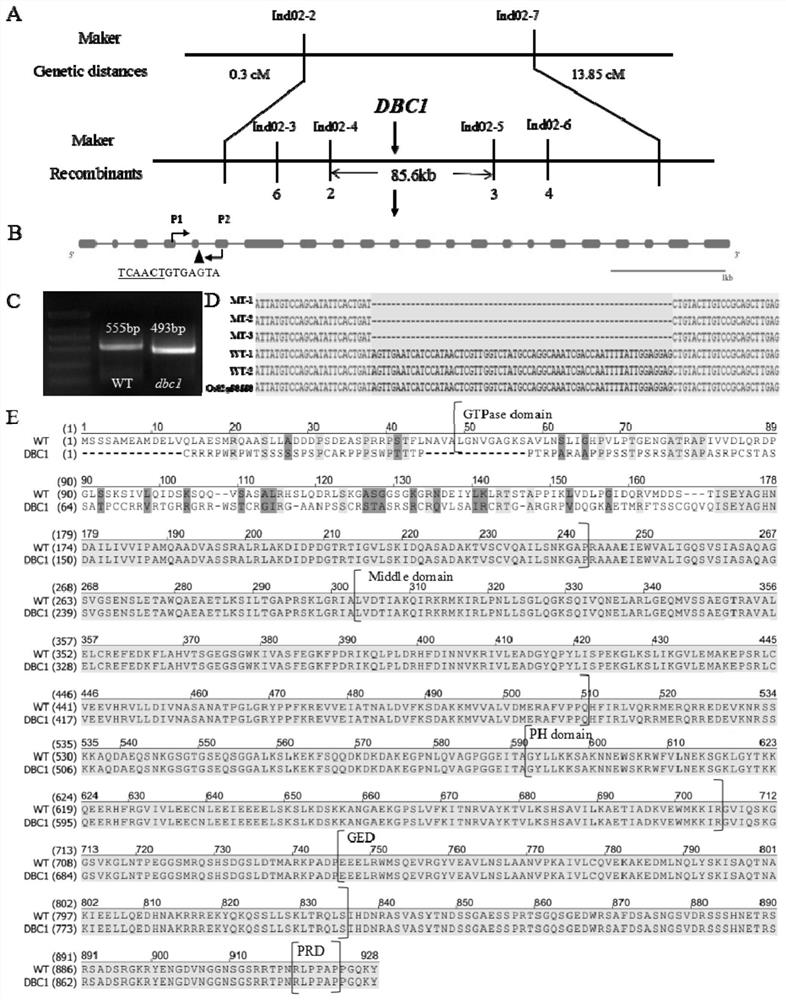
[0061] 1. Cloning and sequencing of rice dwarf brittle gene DBC1
[0062] On the basis of fine mapping of the mutant gene DBC1 in the previous stage, the present invention uses online gene prediction (http: / / mendel.cs.rhul.ac.uk), BLAST online comparison (http: / / blast.ncbi.nlm.nih .gov / ) and functional analysis of gene overexpression. Through map-based cloning and sequence comparison, it was found that the gene was due to the mutation of the 5th base of the 5th intron of the gene LOC_Os02g50550 from the normal C to T. Since genes need to be modified, spliced and spliced after transcription, that is, intron mutations may affect the splicing and editing of precursor messenger RNA. Therefore, design a pair of primers P1 and P2 with a distance of about 550bp on the cDNA, including the mutation site, see image 3 B, where the gray box represents the exon, the bla...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Example 2: Experimental analysis of the hormone response of the rice dwarf brittle mutant gene DBC1
[0066] 1) Germinate the mutant and wild-type seeds, and select the seeds with the same dew and whiteness to sow in the seedlings containing 0 and 10 -10 、10 -8 、10 -6 and 10 -4 μM gibberellin (GA) nutrient solution, placed in a constant temperature incubator for cultivation. Add equal amount of nutrient solution and nutrient solution containing gibberellin in corresponding concentration every day. The length change of the second leaf sheath was measured and counted every 24 hours until the stage of two leaves and one heart. And at the one-leaf-one-heart stage (about the 7th day), the leaves under each treatment were taken, RNA was extracted, reverse-transcribed into cDNA, and stored for future use. It was found that when the gibberellin concentration was lower than 10 -8 At μM, the growth of the second leaf sheath of the wild type and the mutant was almost indisti...
Embodiment 3
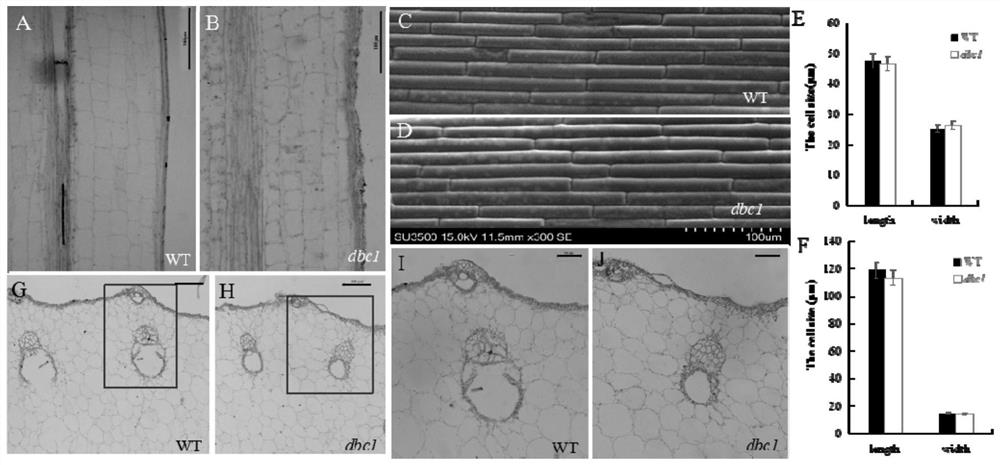
[0071] Example 3: Cell division speed experiment of mutant DBC1
[0072] Paraffin sections were used to analyze the cells at the growth point of the root tip. Under the same cell number, the average number of binucleated monocytic cells in DBC1 was 7.4, and it was 4.1 in the wild type, showing a significant level. See Figure 7 A-E. This implies that the mutant cells divide at a slower rate. RT-PCR analysis of the expression changes of cyclin-related genes in wild type, mutants and overexpression lines OE-1, RT-PCR quantitative primer sequences are shown in Table 3, the results show that the expression of cyclin-related genes in mutants Compared with the wild type, the expression of CycB, CycD, CycP and CycT was restored in the transgenic lines, see Figure 7 F. This further explains the slowed cell division in the mutant DBC1. That is, mutations in this gene cause the rate at which cells divide to slow down.
[0073] Table 3 cyclin RT-PCR quantitative primer sequence
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com