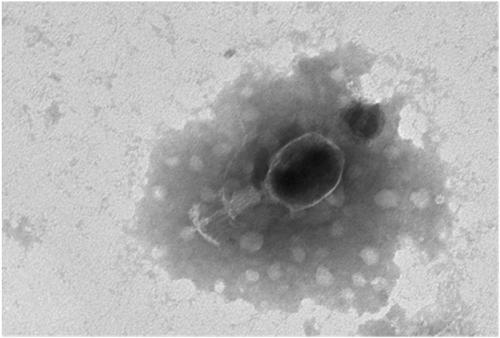
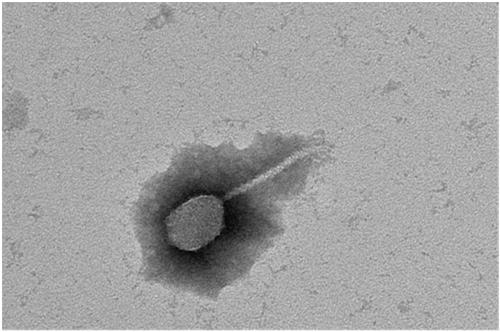
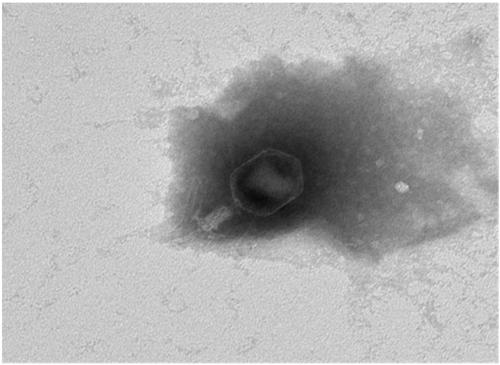
Bacteriophage composition and application in inactivating antibiotic-resistant pathogenic bacteria
A technology of antibiotic resistance and phage, applied in the direction of phage, virus/phage, chemicals for biological control, etc., which can solve the ecological risk assessment related to the functional stability and diversity of microbial communities has not been paid attention to, resistance caused The remediation technology of compound pollution of pathogenic bacteria is rare, and has never involved the problem of pathogenic bacteria with antibiotic resistance genes. It achieves the effects of low cost preparation, diversity and stability of soil microbial ecological functions, and easy promotion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The soil samples for the test were collected from the polluted soil around the excrement accumulation pool of the Hengliang Dairy Farm in Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province. Basic physical and chemical properties of soil: 23.8% sand, 45.4% soil, 31.8% clay, pH 7.7, total nitrogen 1.7 g·kg -1 , water-soluble nitrogen 1.7 g·kg -1 , total phosphorus 1.3 g·kg -1 , total potassium 17.5 g·kg -1 , CEC 19.4 cmol kg -1 .
[0028] Take 5 g of fresh soil samples, add 50 mL of sterile water, culture at 28 °C, 150 rpm for 5 h, centrifuge at 10 000 rpm for 5 min, filter the supernatant through a 0.22 μm membrane, take 9 mL of the filtrate and 1 mL of the growth medium The Klebsiella pneumoniae suspension in the logarithmic phase was added to 40 mL LB liquid medium, and calcium chloride solid was added to make the final concentration of the solution 1 mmol L -1 , 30°C, 150rpm shaker culture for 12 hours, the obtained culture solution was centrifuged at 10 000 rpm for 5 minutes, and t...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The potting soil for the test was collected from the polluted soil around the manure accumulation pool of the Hengliang Dairy Farm in Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province. Growing Vegetables for Italian Year-Round Bolting Resistant Lettuce ( Lactuca sativa L ), Hebei Jinfa Seed Industry Co., Ltd. Basic physical and chemical properties of soil: 23.8% sand, 45.4% soil, 31.8% clay, pH 7.7, total nitrogen 1.7 g·kg -1 , water-soluble nitrogen 1.7 g·kg -1 , total phosphorus 1.3 g·kg -1 , total potassium 17.5 g·kg -1 , CEC 19.4 cmol kg -1 .
[0033] Four groups of treatments were set up in the experiment: ① control group (CK): 3 lettuces were planted in each pot (covering soil 0.5-1 cm above the seeds, room temperature 18±2°C); ② bacteriophage φYSZKA treatment (P1): on the basis of the control group Inoculate 100mL with a concentration of 10 6 pfu mL -1 The specific phage φYSZKA; ③ Phage φYSZPA treatment (P2): on the basis of the control group, inoculate 100mL with a conce...
Embodiment 3
[0036] The potting soil for the test was collected from the polluted soil around the manure accumulation pool of the Hengliang Dairy Farm in Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province. Growing Vegetables for Carrots Seoul Six Inches ( Daucus L .), Beijing Zhongnong Tianteng Vegetable Seed Company. Basic physical and chemical properties of soil: 23.8% sand, 45.4% soil, 31.8% clay, pH 7.7, total nitrogen 1.7 g·kg -1 , water-soluble nitrogen 1.7 g·kg -1 , total phosphorus 1.3 g·kg -1 , total potassium 17.5 g·kg -1 , CEC 19.4 cmol kg -1 .
[0037] Four groups of treatments were set up in the experiment: ① Control group (CK): 3 carrots were planted in each pot (covering soil 0.5-1cm above the seeds, room temperature 20±2°C); ② Phage φYSZKA treatment (P1): Inoculation on the basis of the control group 100mL concentration is 10 6 pfu mL -1 The specific phage φYSZKA; ③ Phage φYSZPA treatment (P2): on the basis of the control group, inoculate 100mL with a concentration of 10 6 pfu mL -...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com