Conductive ink, electronic label, its preparation method and radio frequency identification system
A conductive ink and electronic label technology, applied in the field of radio frequency identification, can solve the problem that rock corrosion cannot be monitored
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
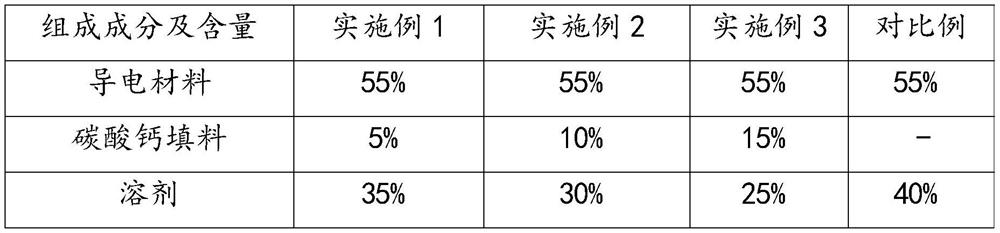
[0052] Conductive ink comprises conductive material, solvent, calcium carbonate filler and additive, and the content of each component of conductive ink is as table 1:
[0053] The content of each component of the conductive ink of table 1 (here all are mass percentages)
[0054]
[0055]
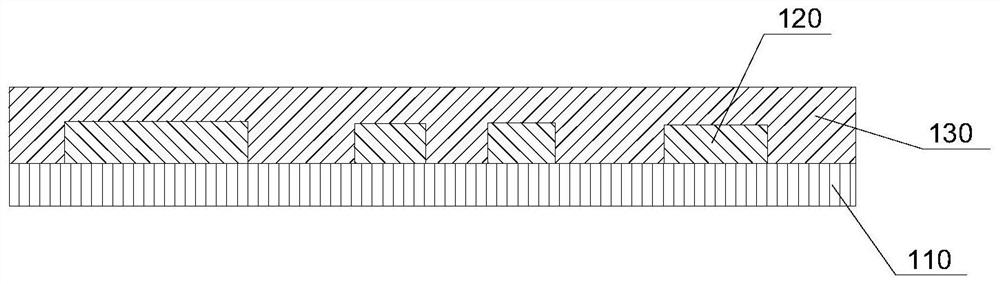
[0056] After the above-mentioned components are mixed according to the above-mentioned ratio, the conductive ink is uniformly dispersed to form a conductive ink, which is evenly coated on the top of the PET substrate by 100T screen printing method, and heated and cured at 120°C to obtain a conductive pattern with a thickness of 20 μm 120. Cover the surface of the conductive pattern 120 with a PE protective film 130, and heat emboss for 10s at a temperature of 45°C and a pressure of 0.5MPa to obtain figure 1 RFID tags shown.
[0057] The obtained RFID tags were subjected to environmental acidification and weathering simulation tests. The specific method was: the RFID tags prepared in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com