A parallel task energy-saving scheduling method based on linear programming
A scheduling method and linear programming technology, applied in energy-saving computing, climate sustainability, program startup/switching, etc., can solve problems such as easy to fall into local optimum, without considering the impact of the overall scheduling of a single task, and expand the solution space Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
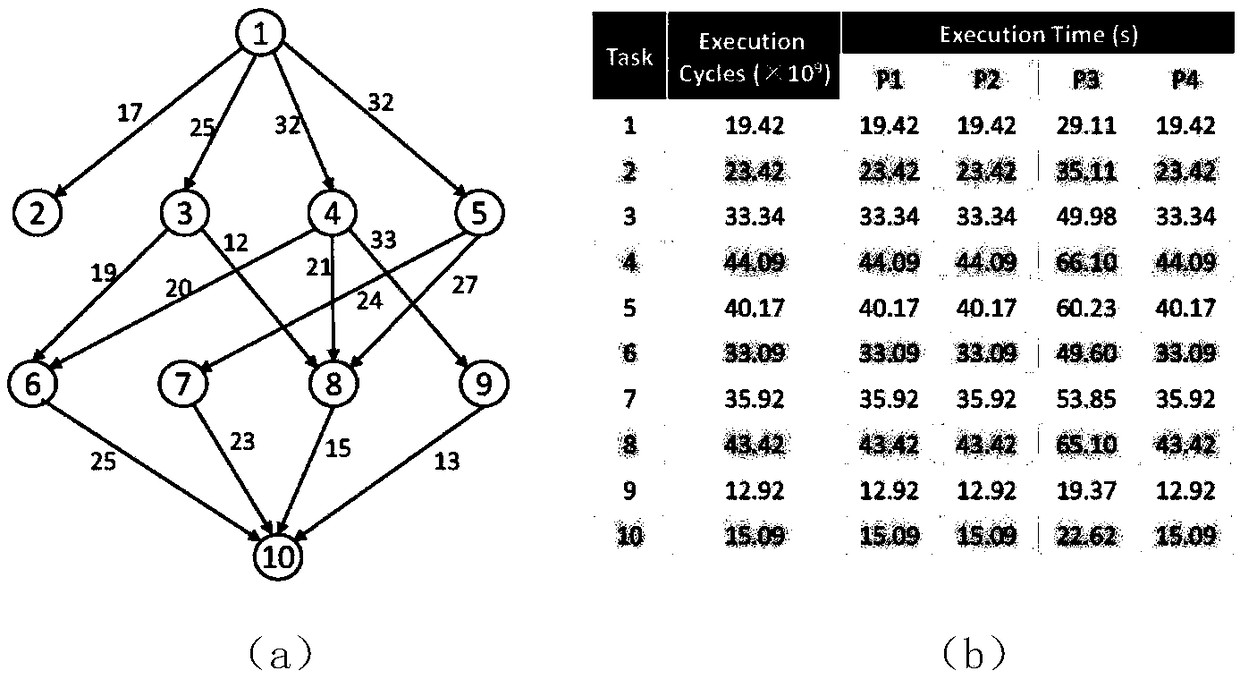
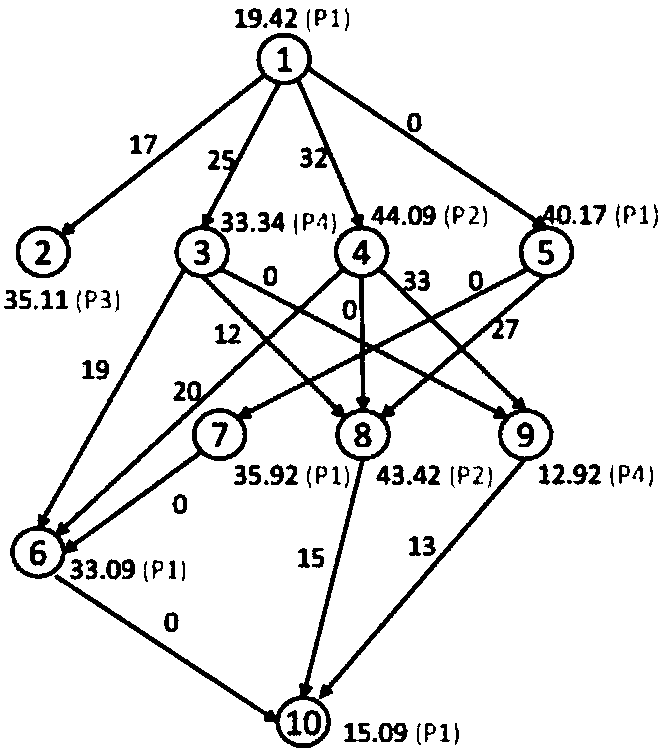
[0045] The technical solutions provided by the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments. It should be understood that the following specific embodiments are only used to illustrate the present invention and not to limit the scope of the present invention.
[0046] The energy-saving scheduling method for parallel tasks (LP-DVFS) based on linear programming of the present invention does not make any assumptions about the initial scheduling sequence, and can be used as an energy-saving re-optimization process of the existing performance-priority scheduling method. The following are the basic symbols used in the LP-DVFS method:
[0047] p: the number of processor nodes;
[0048] n: the number of tasks;
[0049] p i : The i-th processor node;
[0050] n k : The kth task;
[0051] n entry : Entry task, there is no parent node task in the DAG graph;
[0052] n exit : Export tasks, tasks with no child nodes in the DAG graph;
[0053] F i : Pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com