Method for detecting the number of fallen particles during working process of valve
A working process, particle counter technology, applied in measurement devices, mechanical valve testing, individual particle analysis, etc., can solve problems such as the quality of semiconductor or photovoltaic modules, and achieve the effect of easy operation and simple detection principle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
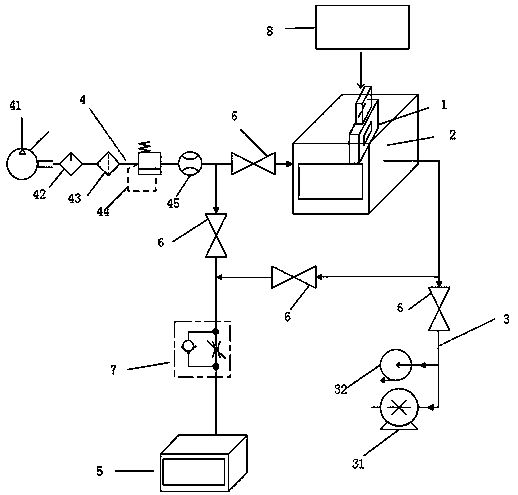
[0058] The method for detecting the number of particles falling off during the working process of the valve provided in this embodiment is specifically (for the convenience of illustration, combined with figure 1 Be explained):
[0059] Step 1: Connect the gas inlet device 4, the vacuum device 3 and the particle counter 5 on the cavity 2, insert the valve 1 to be tested into the cavity 2, connect the valve 1 to be tested to the valve driving device 8 to be tested, and the valve to be tested The driving device 8 drives the valve 1 to be tested to open and close; the valve I6 is installed on the connecting pipeline between the gas inlet device 4 and the cavity, and the valve II61 is installed on the pipeline connecting the gas inlet device 4 and the particle counter 5. 5. Install valve Ⅲ62 on the pipeline connected to cavity 2, and install valve Ⅳ63 on the pipeline connected to vacuum device 3 and the cavity; first close valve Ⅰ6, valve Ⅱ61, valve Ⅲ62, open valve Ⅳ63, and contro...
Embodiment 2
[0064] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, except that the gas is introduced into the cavity through the gas inlet device first, and then the gas enters the cavity and then enters the particle counter 5 for counting, records the number a1 displayed by the particle counter, and then After clearing the particle counter 5, pass the gas of the same flow rate into the particle counter 5 that has been reset to count through the gas inlet device, record the number b1 displayed by the particle counter, and calculate the number of particles falling off c1=a1-b1 .
Embodiment 3
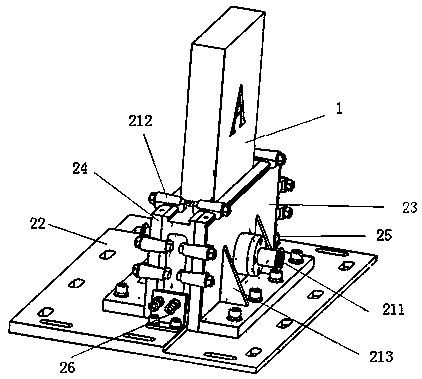
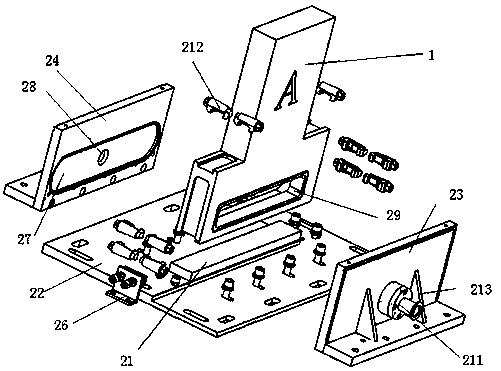
[0066] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, except that the structure of the cavity is further limited in this embodiment, and the specific structure of the cavity 2 is as follows: the cavity 2 includes a bottom plate 22, a fixing splint flange 23, Movable splint flange 24, positioning block 25 and movable clamping device 26, fixed splint flange 23, movable splint flange 24, positioning block 25 and movable clamping device 26 are fixed on the base plate 22, fixed splint flange 23 and movable clamping device The splint flange 24 is close to the valve to be tested 1 ( figure 2 The housing of the valve to be tested is illustrated in the figure, and the internal structure diagram is not drawn for simplicity) The positive and negative sides (sides A and B in the figure) realize the fixing of the positive and negative sides of the valve to be tested 1, the positioning block 25 and the movable clamp The tightening device 26 is close to the both sides of the valve 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com