A porous grade composite medical gel scaffold constructed by 3D printing and its preparation method
A 3D printing, porous-level technology, applied in the field of biomedical engineering materials, can solve the problems of reducing 3D printing efficiency, difficulty in sol shaping, difficulty in maintaining size, etc., to achieve good bone conduction, good biocompatibility, and good biological active effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
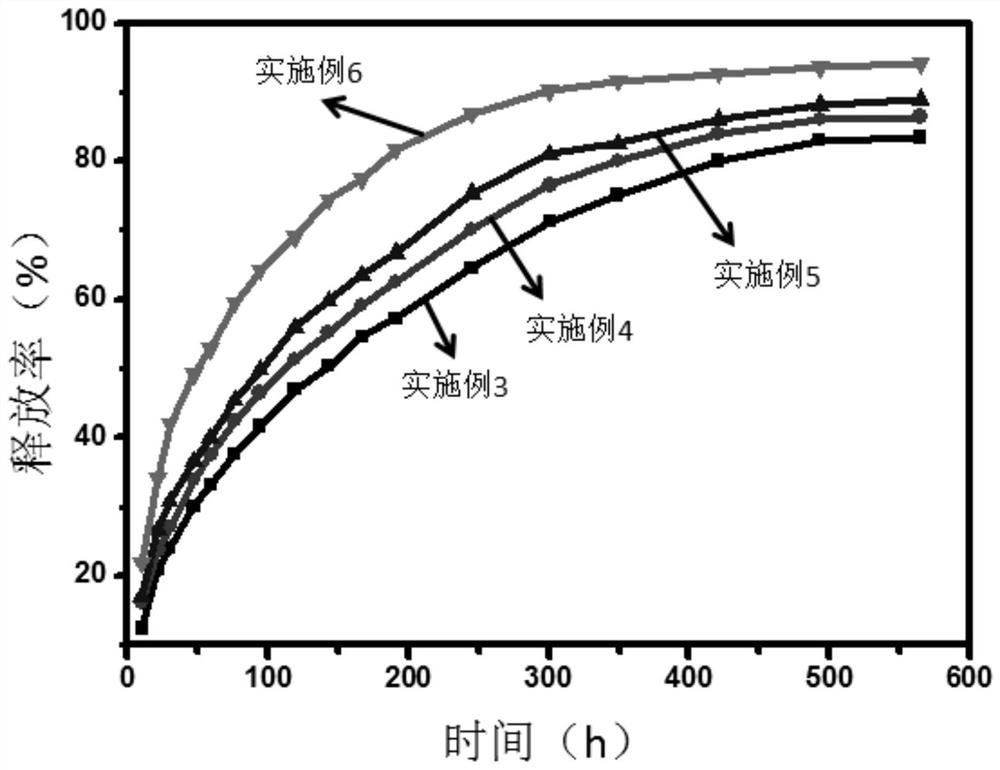
[0025] The porous-grade composite medical gel scaffold constructed by 3D printing in this embodiment is composed of the following raw materials according to the mass percentage: 7.6% of hydroxyapatite, 0.76% of mesoporous silica with a drug curcumin loading of 90%, Gluconolactone 15.3%, the balance is sodium alginate.
[0026] A method for preparing a porous-grade composite medical gel support constructed by 3D printing, comprising the following steps:
[0027] (1) Weigh 0.3g of hydroxyapatite (HAP) and add it to 30mL of deionized water, stir at room temperature for 30min to make HAP evenly dispersed, then add 3g of sodium alginate (SA) and continue stirring at room temperature for 2h to obtain a pre-crosslinking solution ;
[0028] (2) Add 0.03 g of drug-loaded mesoporous silica and 0.6 g of gluconolactone (GDL) to the pre-crosslinking solution obtained above, stir rapidly with a glass rod to obtain a slightly crosslinked hydrogel glue solution and fill it into a syringe, r...
Embodiment 2
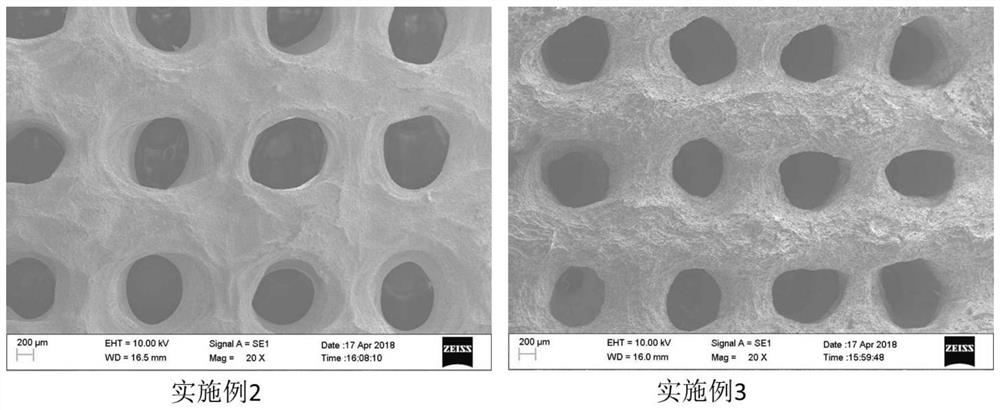
[0032] The porous-grade composite medical gel scaffold constructed by 3D printing in this embodiment is composed of the following raw materials according to the mass percentage: 19.6% of hydroxyapatite, 1.96% of mesoporous silica with a drug curcumin loading of 90%, Gluconolactone 13.1%, the balance is sodium alginate.
[0033] The preparation method of the porous grade composite medical gel support constructed by 3D printing comprises the following steps:
[0034] (1) Weigh 0.9g of hydroxyapatite (HAP) and add it to 30mL of deionized water, stir at room temperature for 30min to make HAP evenly dispersed, then add 3g of sodium alginate (SA) and continue stirring at room temperature for 2h to obtain pre-crosslinked solution;
[0035] (2) Add 0.09 g of drug-loaded mesoporous silica and 0.6 g of gluconolactone (GDL) to the pre-crosslinking solution obtained above, stir rapidly with a glass rod to obtain a slightly crosslinked hydrogel glue solution and fill it into a syringe, r...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The porous-grade composite medical gel scaffold constructed by 3D printing in this embodiment is composed of the following raw materials according to the mass percentage: 28.9% of hydroxyapatite, 1.73% of mesoporous silica with a drug curcumin loading of 90%, Gluconolactone 11.6%, the balance is sodium alginate.
[0040] The preparation method of the porous-grade composite medical gel scaffold constructed by 3D printing in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0041] (1) Weigh 1.5g of hydroxyapatite (HAP) and add it to 30mL of deionized water, stir at room temperature for 30min to disperse HAP evenly, then add 3g of sodium alginate (SA) and continue to stir at room temperature for 2h to obtain the pre-mixed joint solution;
[0042] (2) Add 0.03 g of drug-loaded mesoporous silica and 0.6 g of gluconolactone (GDL) to the pre-crosslinking solution obtained above, stir rapidly with a glass rod to obtain a slightly crosslinked hydrogel glue solution and fill it ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com