A carbonyl reductase mutant mut-accr (e144a/g152l) and its application and coding gene
A mut-accr, reductase technology, applied in oxidoreductase, application, genetic engineering, etc., can solve the problems of poor substrate tolerance and low enzyme activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] The gene sequence of AcCR was translated into its amino acid sequence by standard methods, searched in the PDB database with this sequence, and selected 4RF2, 1ZJY, 1NXQ and 1ZK3 (database The name of the protein sequence) tertiary structure as a template, homology modeling, and energy minimization, the tertiary structure model of carbonyl reductase AcCR was obtained. Further use Ramachandran Plot and Profile-3D to evaluate the structural rationality of each amino acid residue in the homology modeling results and the matching degree between the protein model and the amino acid sequence of the protein. It is determined that the model built is reasonable and can be used for subsequent experimental analysis. The tertiary structure of carbonyl reductase AcCR was docked with the coenzyme NADH, and the mutation hotspots of carbonyl reductase were predicted by HotSpot 2.0, and the 144E and 152G sites were selected as mutation sites.
Embodiment 2
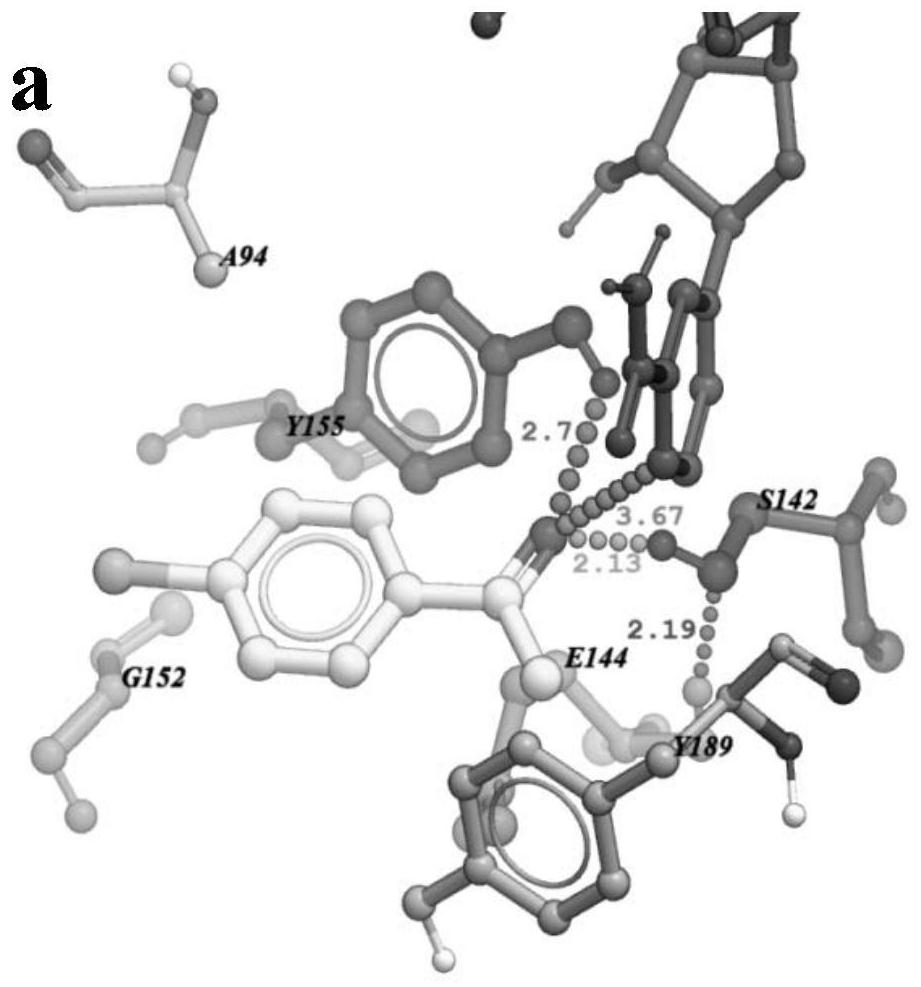
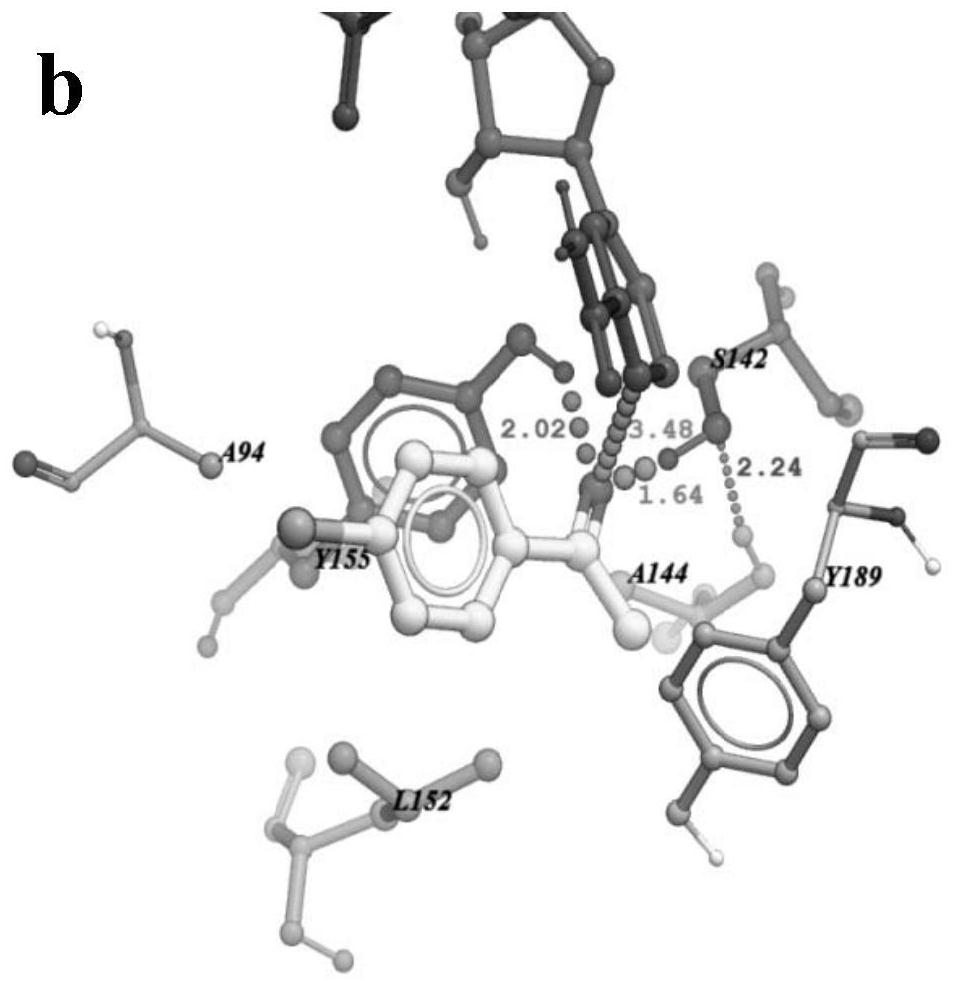
[0026] The changes between carbonyl reductase and 4'-chloroacetophenone before and after mutation were analyzed by molecular docking; carbonyl reductase AcCR, mutant mut-AcCR (E144A / G152L) were docked with 4'-chloroacetophenone, respectively, The changes in the distance and force between the enzyme active site Ser142, Tyr155 and the coenzyme NADH nicotinamide ring C4 located on the substrate 4'-acetophenone were analyzed. see results Figure 1a , Figure 1b The docking results of AcCR and mut-E144A / G152L with 4'-chloroacetophenone are shown. from Figure 1a , Figure 1b It can be seen that the distance between the catalytic site S142, Y155 and the hydrogen atom at the 4-position of the NADH nicotinamide ring and the carbonyl oxygen atom of 4’-chloroacetophenone is significantly reduced after the mutation, shortening respectively (22.4%), with (5.2%). After the mutation, the steric hindrance between the substrate and the active center of the enzyme is reduced, which is...
Embodiment 3
[0028] The plasmid pGEX-mut-E144A / G152L containing the mutant mut-AcCR (E144A / G152L) gene was obtained by amplifying the whole pGEX-acr plasmid using PrimeSTAR Max DNA Polymerase.
[0029] Primers used for site-directed mutagenesis: the mutation primer at site E144A is Primer1: 5'-ATCTGTCTTCCATTGCCGGACTGAT-3';
[0030]Primer2: 5'-ATCAGTCCGGCAATGGAAGACAGAT-3'; the mutant primer at position G152L is
[0031] Primer3: 5'-ACCCAATGTTGGCCGCCTATAAC-3';
[0032] Primer 4: 5'-GTTATAGGCGGCCAACATTGGGT-3'.
[0033] The PCR amplification system and reaction conditions used for site-directed mutagenesis are as follows:
[0034] Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification System
[0035]
[0036] PCR reaction conditions:
[0037]
[0038] After the reaction, the reaction product was treated with restriction endonuclease DpnI to act on the Gm6A^TC site to digest the template plasmid in the system. The reaction system is:
[0039]
[0040]
[0041] Place the prepared digest...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com