Tooling and method for scanning blade root defects of steam turbine
A steam turbine blade and defect technology, which is used in measuring devices, material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves, and instruments, etc., can solve problems such as fatigue cracks, complex structure of large-scale steam turbine blades, and inability to perform manual scanning.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
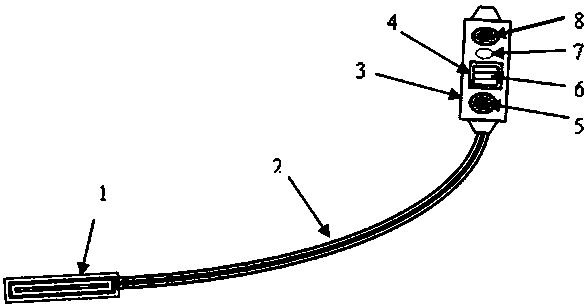
[0016] Example figure 1 As shown, the present invention is used for scanning tooling of steam turbine blade root defect and comprises handle 1, flexible operating rod 2, probe holder 3, protective cover 4, ultrasonic probe 6, couplant outlet 7 and two permanent magnets 5,8, so Both ends of the flexible operating rod 2 are respectively connected to the handle 1 and the probe holder 3, the protective cover 4 is arranged in the probe holder 3, the ultrasonic probe 6 is arranged in the protective cover 4, and the coupling agent The outlet 7 is arranged on the wall of the probe frame 3 and connected to the couplant hose, and the two permanent magnets 5 and 8 are arranged on the wall of the probe frame 3 at intervals.
[0017] Preferably, the curvature of the flexible operating rod 2 matches the curvature of the steam turbine blade. With the same curvature, the probe frame carrying the ultrasonic probe can be extended into the inner side of the blade root through the handle and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com