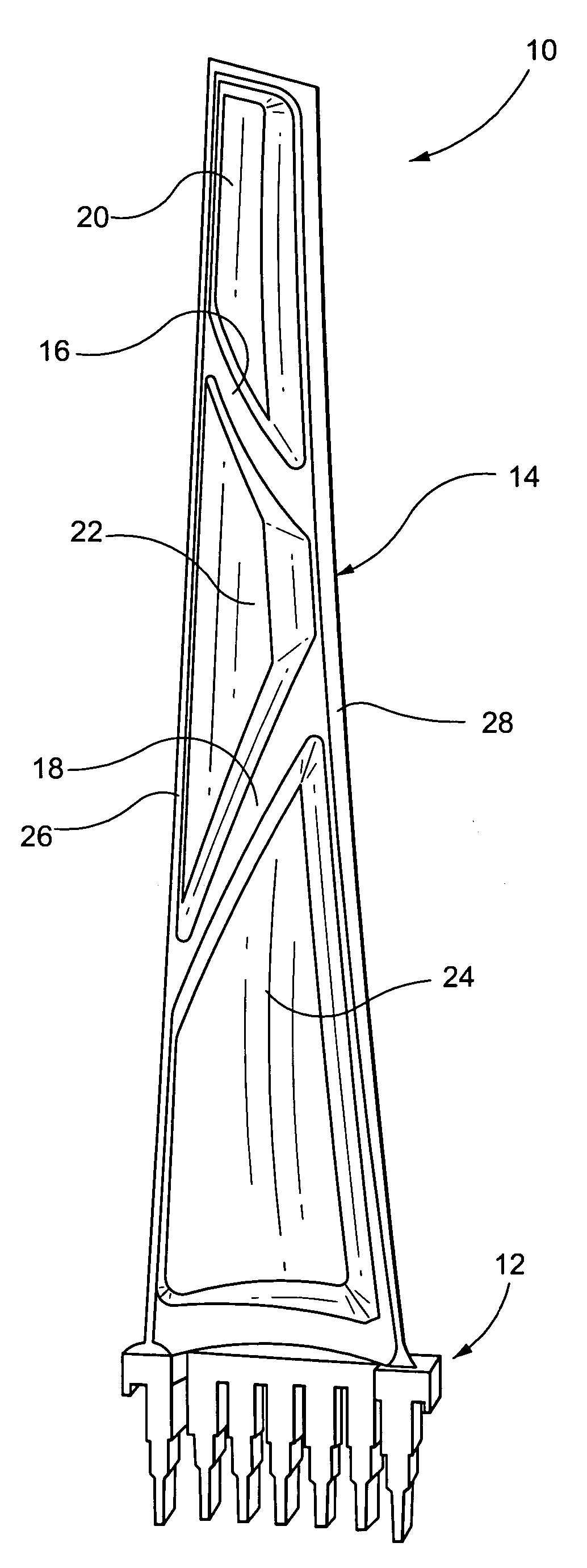
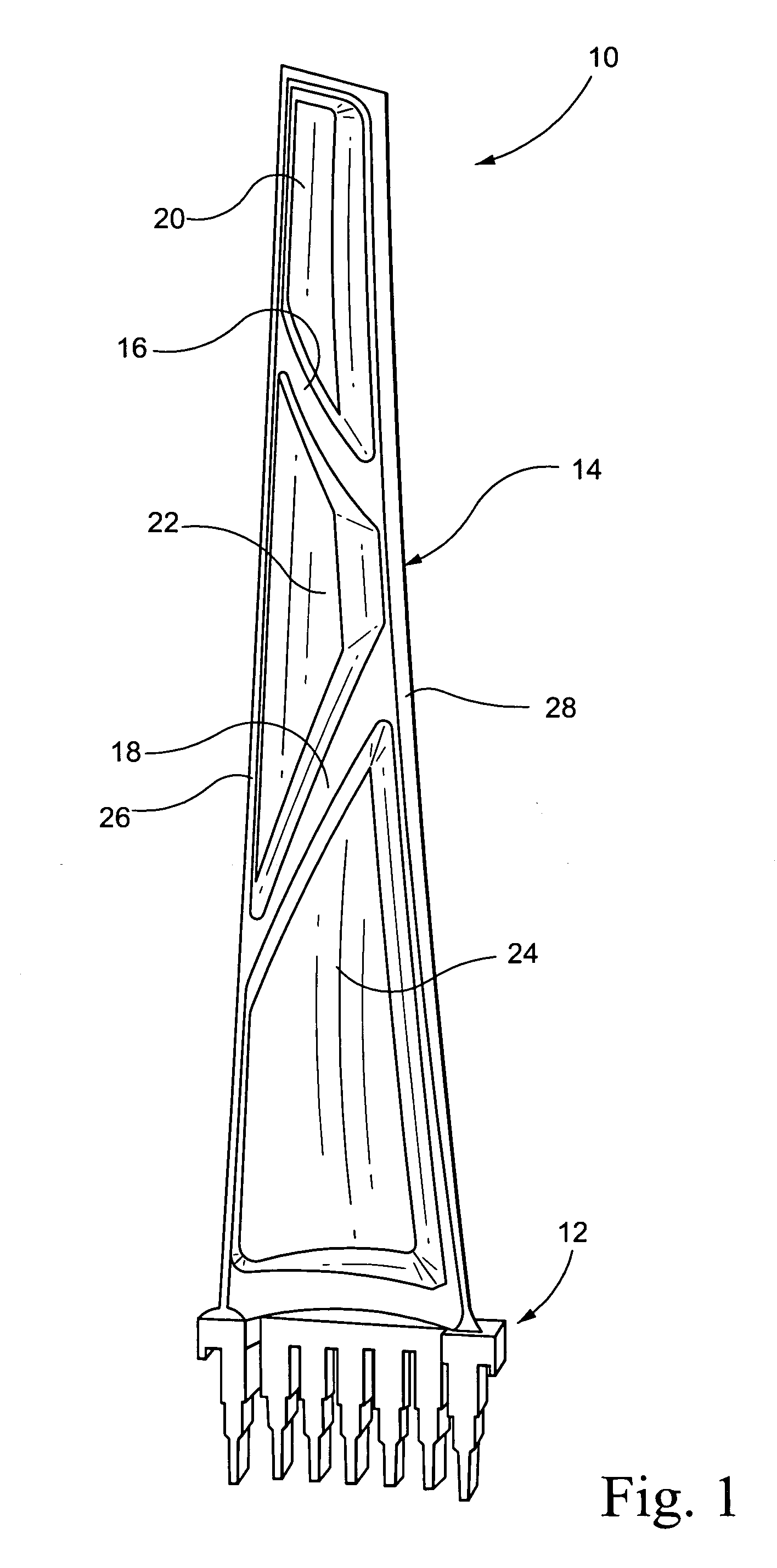
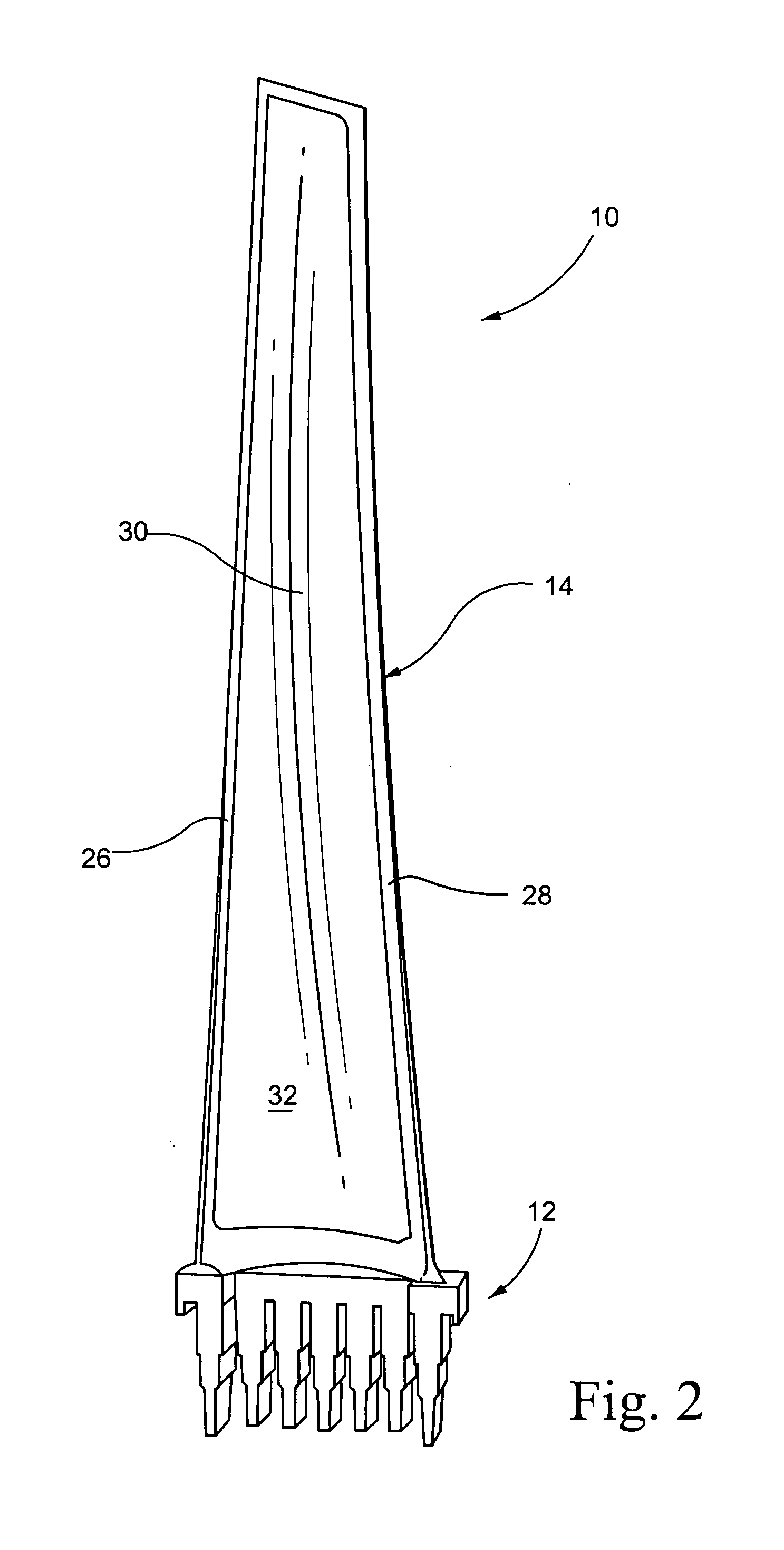
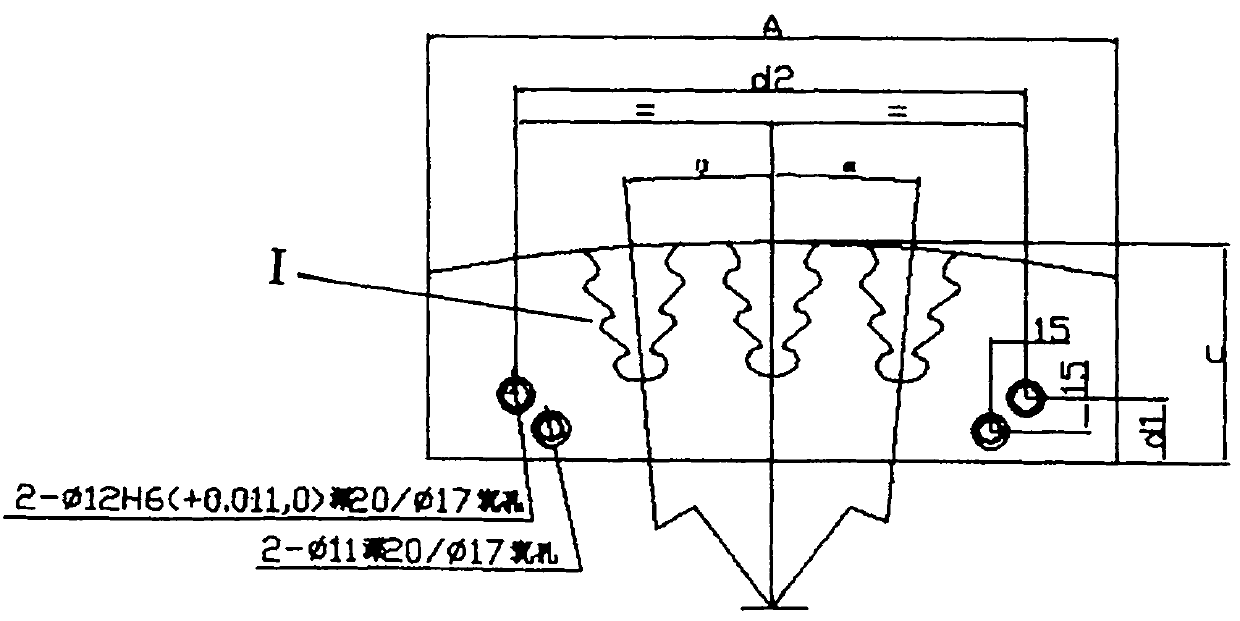
Patents
Literature
577 results about "Steam turbine blade" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
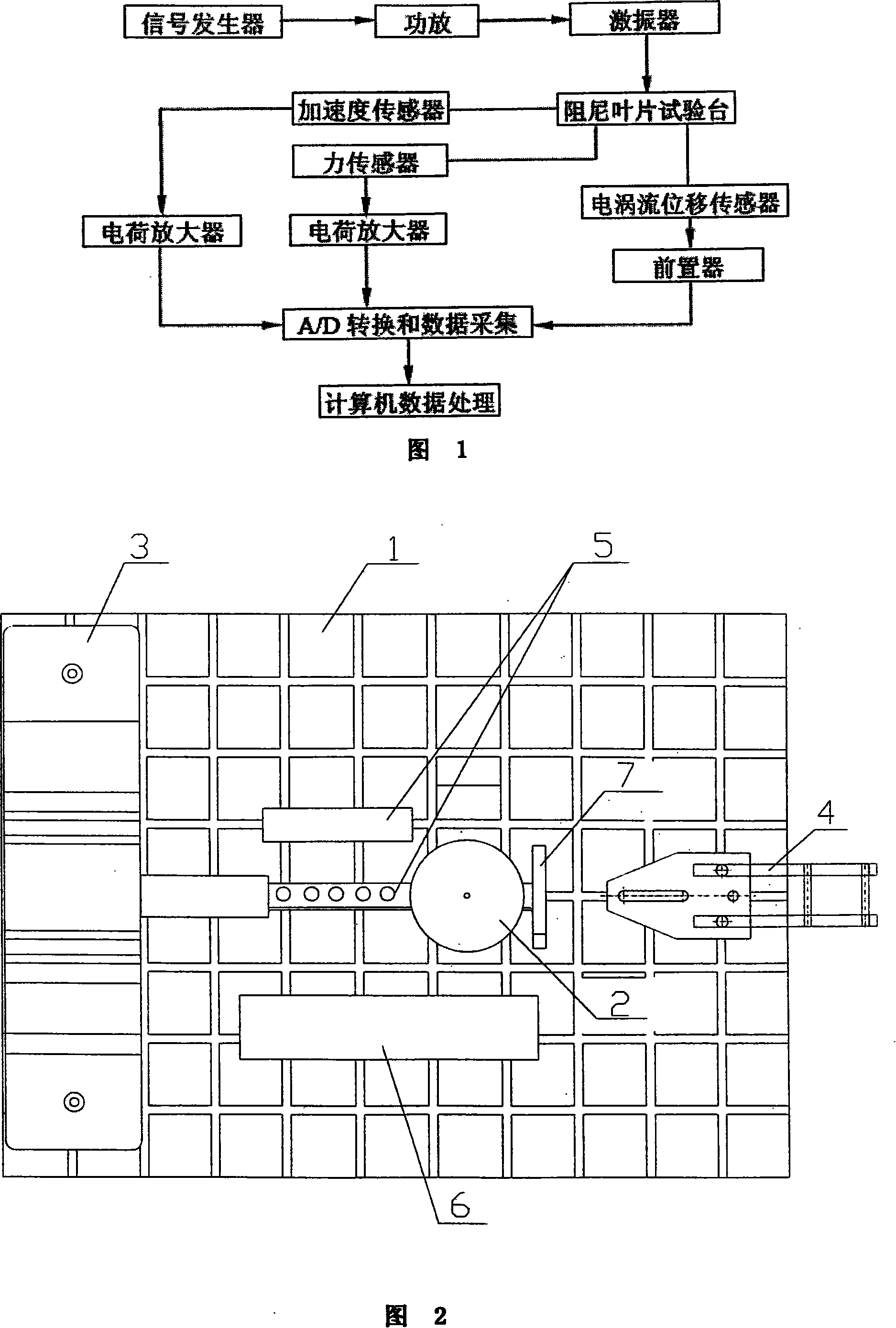
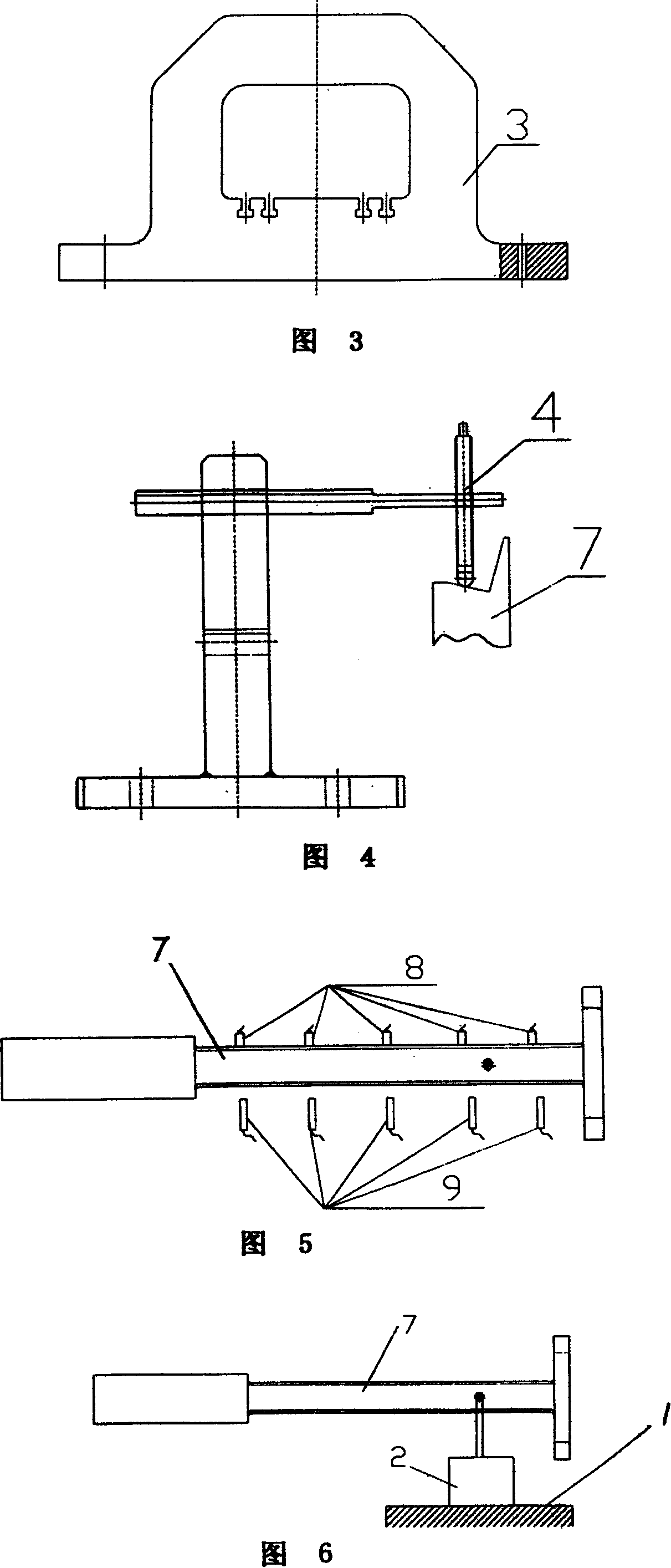
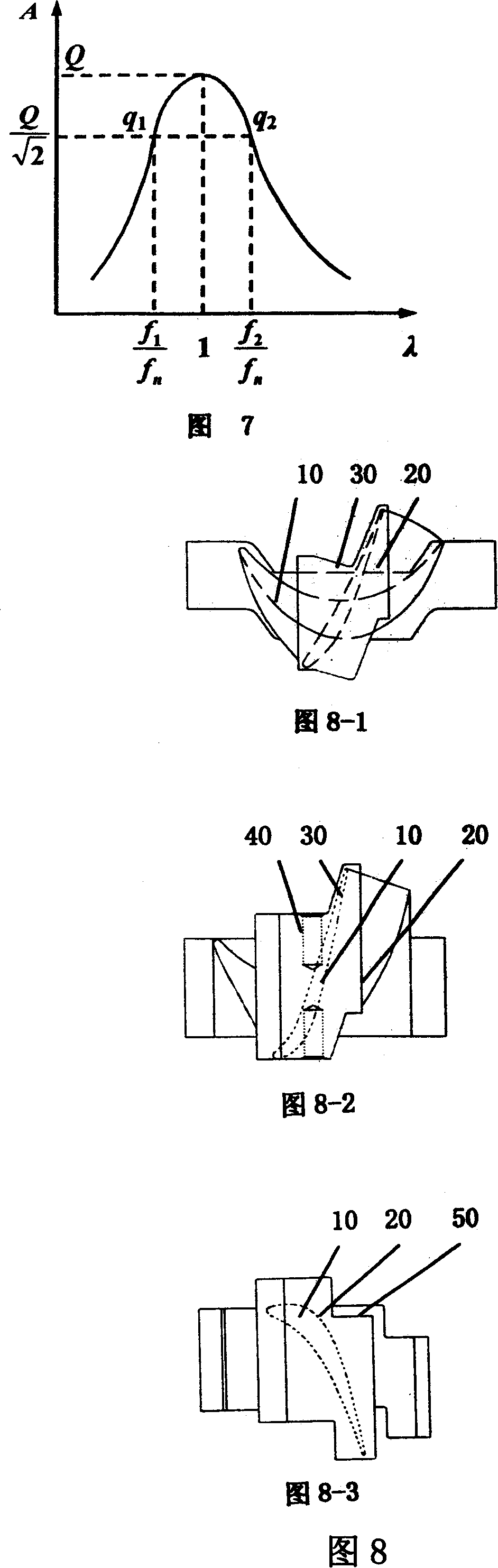
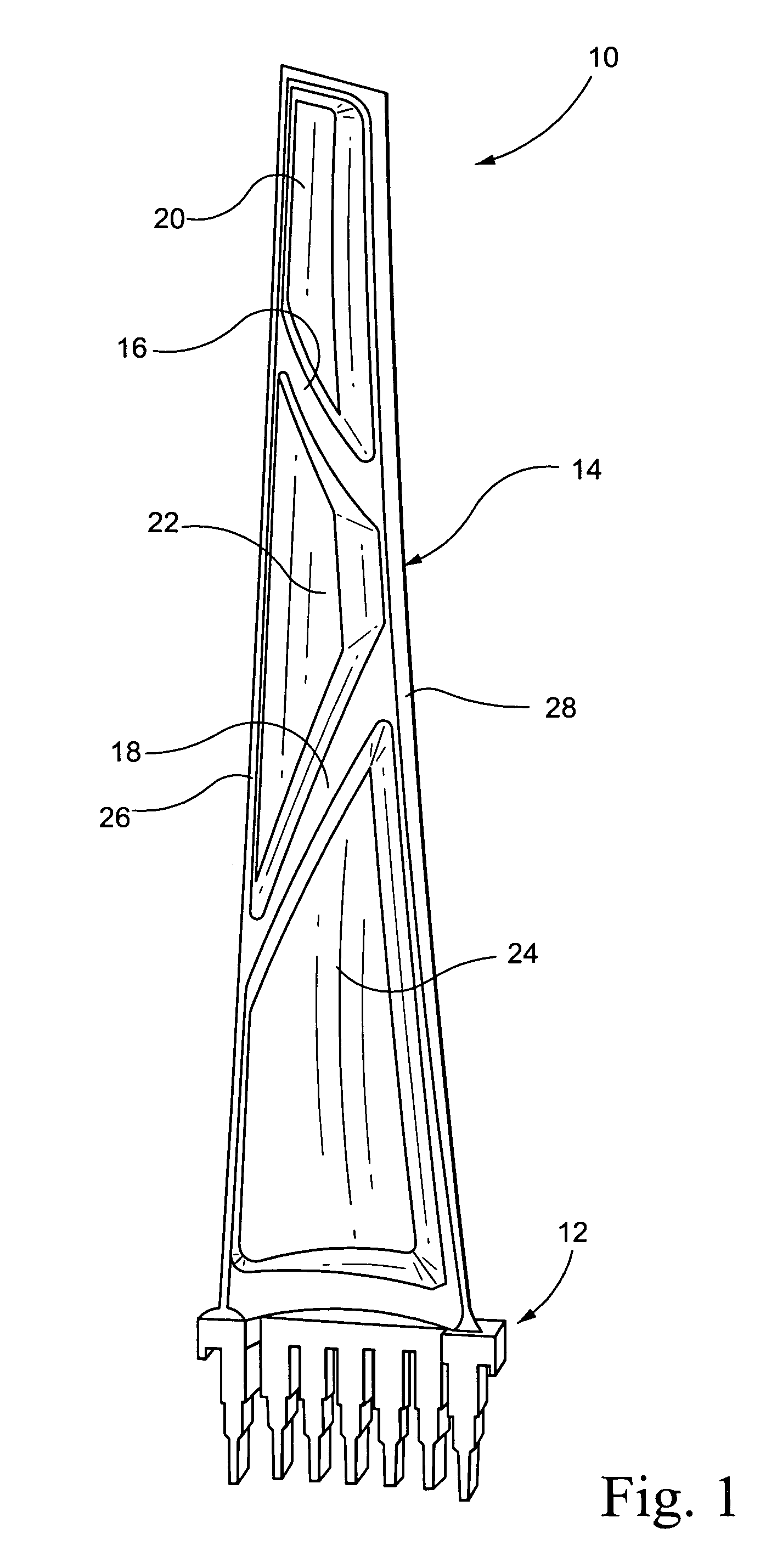
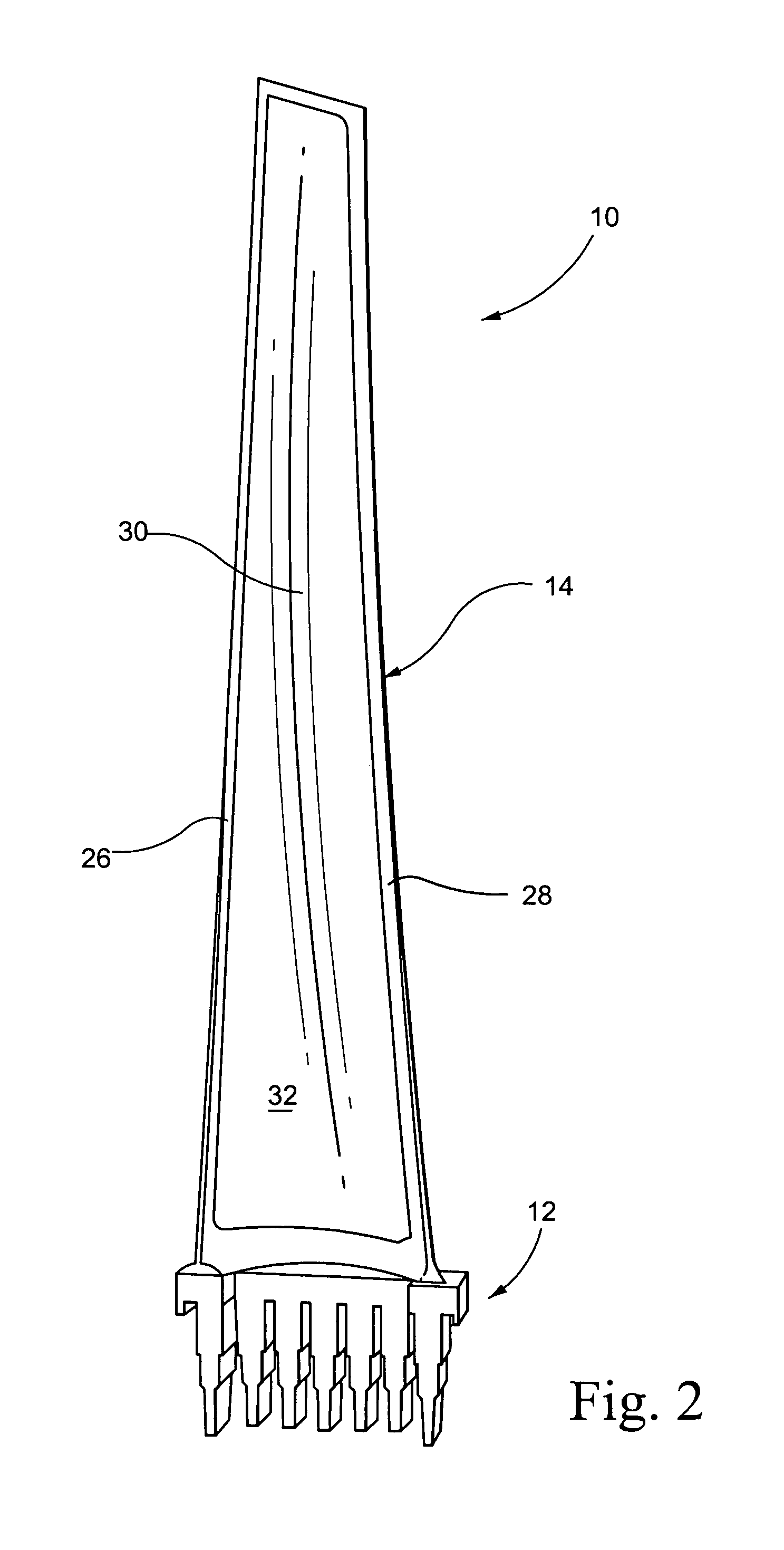
Turbine blade vibration test method and device
ActiveCN101122541AProven Vibration MechanismReasonable designVibration testingElasticity measurementMathematical modelEngineering
The invention discloses a steam turbine blade vibration test method and device. The method steps are that firstly, a blade force vibration status is analyzed and a blade excitation force mathematical model is built. Secondly, an excitation force is imposed on the blade by a vibration source. The frequency of the excitation force is regulated until resonance is generated between the blade and the vibration source. Vibration characteristics parameters values of the blade under the excitation force are measured. Thirdly, blade damping characteristics parameters, including modal damping ratio, damper contact stiffness and blade dynamic stress, are worked out according to the vibration characteristics parameters values. The device includes a test bed, a blade clamping mechanism arranged on the test bed, an excitation generator, a vibration parameter detector and a data processing system. The excitation vibration generator is fixed on the test bed. The excitation vibration head of the excitation vibration generator is fixed with the blade. Corresponding to the blade, the vibration parameter detector transforms the vibration signals of the blade into electric signals, which are input into the data processing system. The invention proves the vibration mechanism of the damping blade. A calculation model of the damping blade is constructed through the test parameters. Experience design is terminated. The blade design is standardized to step into a scientific design orbit.
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD +1
Method and apparatus for turbine blades milling with once clamping
InactiveCN1613590ASimple interfaceEasy to operateMilling equipment detailsNumerical controlSteam turbine blade
A technology for milling the blade of steam turbine by fixing it on the 5-coordinate numerally controlled machine-tool once includes such steps as improving the coarse machining module of Turbsoft program for 5-coordinate numerally controlled machine tool by adding the blade-milling module, fixing the steel blank of blade onto said machine-tool, and milling under the control of said program.
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD
Turbine blade erosion tester
ActiveCN101140210AWeather/light/corrosion resistanceUsing mechanical meansVacuum pumpingSteam turbine blade
The invention relates to a turbine blade water erosion test device which simulates the blade water erosion caused by the high-speed impact of water drip in a low-pressure cylinder of the turbine through the impact between the high-speed rotating blade and the water drip. A DC motor is used as a prime motor, and the rotary speed is improved through a gear speeder to drive a turntable provided with a test blade to rotate; a vibrator drives a nozzle connected with the water drip to produce the water drip, and the water drip axially moves to impact with a test piece; in addition, the system has also a vacuum-pumping system and a drainage system in order to ensure the normal operation of the test. The test device can study the change relations of deformation action and crack growth condition of the turbine blade materials with various factors under the high-speed impact of liquid drip, and provides the basic test data for deeply knowing the impact mechanism of high-speed liquid and solid and the water erosion protection of the turbine blade.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Mixed tuned hybrid blade related method
InactiveUS7147437B2Reducing and more effectively damping vibrationIncrease dampingPropellersRotary propellersFilling materialsSteam turbine blade
A steam turbine blade includes a shank portion and an airfoil portion. The airfoil portion is formed with at least one pocket filled with a polymer filler material chosen as a function of natural frequency impact on the turbine blade or as a function of the damping characteristics of the filler materials. A steam turbine rotor wheel includes a plurality of blades secured about a circumferential periphery of the wheel, each blade having one or more pockets in the airfoil portion, the plurality of blades divided into two groups of blades. The pockets of one group of blades are filled with one or more polymer filler materials, and the pockets of the other group of blades filled with one or more polymer filler materials, wherein the polymer filler materials in the one group of blades creates different natural frequencies or damping characteristics in the blades of the one group than the polymer filler materials in the blades of the other group. The two groups of blades are assembled on the rotor wheel in accordance with a predetermined pattern.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
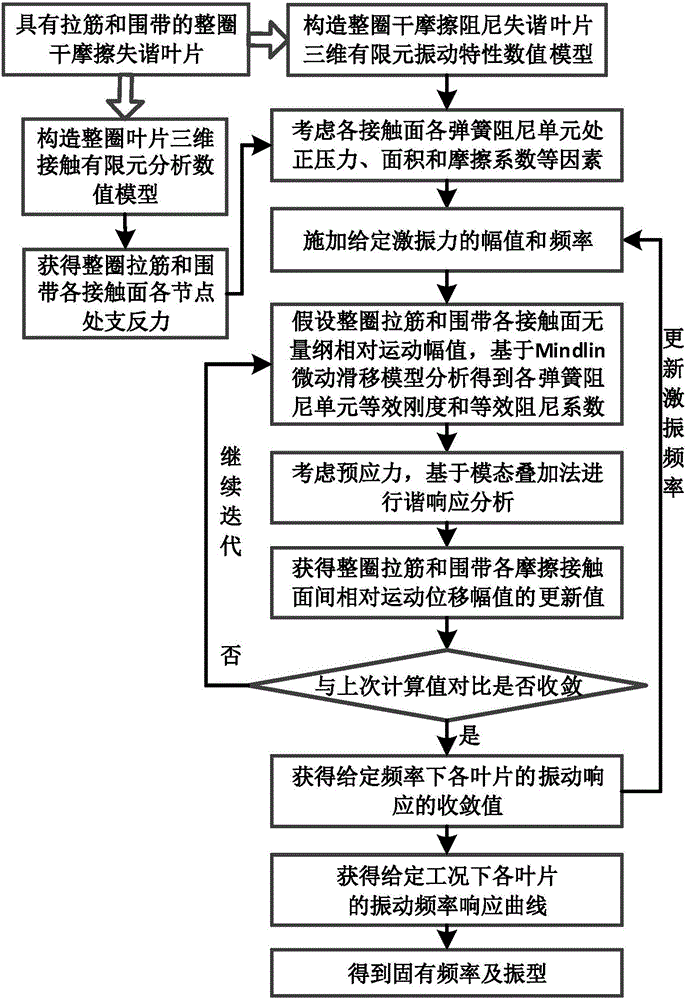
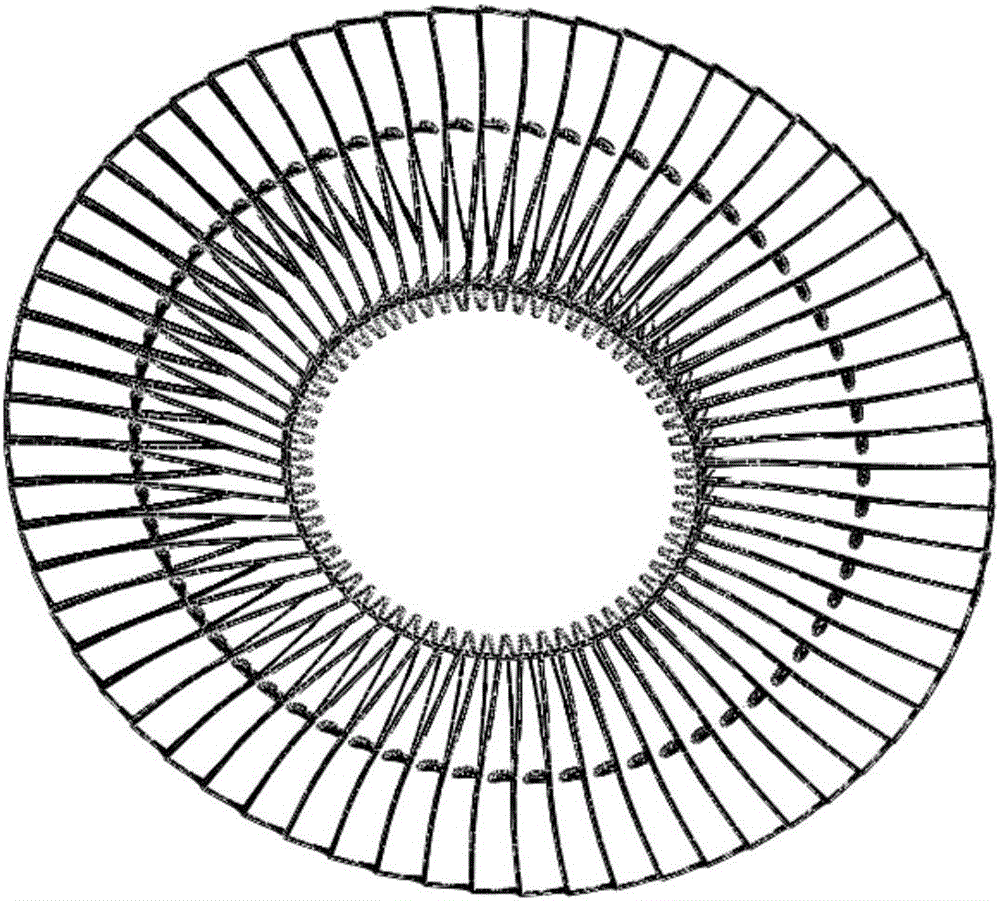
Vibration analysis method for dry frictional damping mistuned blades with tendons and shroud bands
ActiveCN106528982AHigh precisionShort analysis timeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationVibration amplitudeFrictional coefficient
The invention discloses a vibration analysis method for dry frictional damping mistuned blades with tendons and shroud bands. The method comprises the steps of for actual mistuned states of the blades of a steam turbine, performing three-dimensional contact finite element analysis firstly to obtain support reactions of nodes of contact surfaces of the tendons and the shroud bands of the entire circle of the blades; secondly establishing a contact surface relationship by adopting spring damping units, considering positive pressures, areas and frictional coefficients at the spring damping units, and building a dry frictional damping mistuned vibration analysis model based on a Mindlin micro-sliding friction model and a harmonic balance method; thirdly considering a pre-stress and adopting harmonic response analysis for obtaining convergency values of vibration responses of the blades through iterative solving; and through cyclic calculation, obtaining vibration amplitude response curves of the dry frictional mistuned blades, and performing further extraction to obtain an inherent frequency and a vibration mode. The method is of important significance for dry frictional damping mistuned analysis of the blades and improvement of mistuned bladed disk vibration.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Machining process of axial-flow type turbine blade
The invention discloses a machining process of an axial-flow type turbine blade. The machining process of the axial-flow type turbine blade comprises the following steps that two side faces are machined on a square blank stock through an end face end mill on an ordinary milling machine through two process of rough milling and finish milling, another two side faces are machined with the two machined side faces as base planes, and then the two end faces are machined through the end face end mill; a steam outlet side face is machined on one side face through two process of rough milling and finish milling, the position, close to the steam outlet side face, of the blade root end face is marked as C, a face which forms an acute angle with the steam outlet side face and is adjacent to the steam outlet side face is marked as N and is the inner radial surface, and the other three side faces are machined to be a parallelogram through rough milling and finish milling; central holes are drilled in the blade root end face and the blade crown end face; the blade type is roughly milled through the end face end mill, the blade root is roughly milled, and finally the blade crown is roughly milled; then the blade is installed on a five-axis numerical control machining center for alignment and is machined in a finish mode; a process head at the blade root end face is roughly sawn through a sawing machine; the turbine blade is detected according to the requirements of a drawing.
Owner:南京赛达科技有限公司
Manufacturing process of fir blade root type steam turbine blade
ActiveCN104028983AReduce Process RiskLow costPositioning apparatusMetal-working holdersSteam turbine bladeMachining
The invention discloses a manufacturing process of a fir blade root type steam turbine blade. The manufacturing process comprises the steps that A, a process head of a blank of the blade is machined; B, the process head is located through three center holes of the blank of the blade, the process head is clamped through a fixture during machining, rough machining and finish machining are conducted on all parts, except the blade root, of the blade, a blade crown is machined at the blade crown end during finish machining according to the process datum, and the blade crown and a blade root middle body form a large spatial locating surface; C, a fixture for blade root milling is adopted, the machined spatial locating surface is used for locating, and rough machining and finish machining are conducted on the blade root of the blade; D, a blade steam passage is polished. By the adoption of the machining method, the traditional square box pouring technique is eliminated, the machining risk is lowered, and cost is reduced. Meanwhile, a large surface is no longer machined through locating of a small surface, and the small surface is machined through locating of the large surface instead; as a result, the manufacturing accuracy of the large steam turbine blade is greatly improved, and the positional accuracy between the large surface and the small surface is ensured.
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD
Low-melting-point alloy casting positioning technology in turbine blade machining
ActiveCN103350213AGuaranteed machining accuracyShorten the timePositioning apparatusMetal-working holdersSteam turbine bladeAlloy
The invention discloses a low-melting-point alloy casting positioning technology in turbine blade machining. The low-melting-point alloy casting positioning technology is achieved through the following steps: (1) conducting rough machining on a blade; (2) matching the blade with a positioning tool, wherein the blade is transversely arranged after the rough machining on the blade is completed, a blade crown at the head of the blade is abutted against a single tip of the positioning tool, a blade root at the tail of the blade is abutted against double tips of the positioning tool, and a blade steam passage in the middle of the blade penetrates through a positioning square box; (3) casting tin-bismuth alloy molten liquid molten at a certain temperature in the positioning square box, and casting and cooling the positioning square box at the same time until tin-bismuth alloy is solidified and fixed; (4) conducting fine machining on the blade crown and the blade root; (5) melting the tin-bismuth alloy again, pouring out the tin-bismuth alloy molten liquid from the positioning square box, and removing the positioning square box; (6) conducting fine machining on the blade steam passage. The low-melting-point alloy casting positioning technology in the turbine blade machining can meet the requirements for machining blades of various shapes and sizes, the positioning effect is good, and raw materials are greatly saved.
Owner:常州市三维技术成套设备有限公司
Universal hold-down mechanism of steam turbine blade drill jig
InactiveCN101791765AReliable compressionSimple structurePositioning apparatusMetal-working holdersSteam turbine bladeEngineering
The invention relates to a universal hold-down mechanism of a steam turbine blade clamp, comprising a frame composed of an upper cover plate, a lower cover plate, a left cushion block and a right cushion block, wherein the upper cover plate and the lower cover plate are respectively provided with a corresponding slide way which is provided with a plurality of notches; a universal slide block is arranged between the upper cover plate and the lower cover plate; the upper side and the lower side of the universal slide block are respectively provided with a support shaft; the support shaft on the upper side of the universal slide block is installed in the slide way in the upper cover plate; the support shaft on the lower side of the universal slide block is installed in the slide way in the lower cover plate; the universal slide block is movably connected with a pressure lever of which the axial direction is crossed with the axial direction of the support shaft; and one end of the pressure lever is provided with a pressure head. The universal hold-down mechanism comprises the slide ways, the universal slide block, the pressure lever and the pressure head, has simple structure, strong generality, low using cost and convenient operation; a blade is pressed by the pressure head; the pressure head is connected with the universal slide block which slides in the slide ways, so that the universal hold-down mechanism is flexible to adjust and has high efficiency.
Owner:WUXI AIERFU BLADE
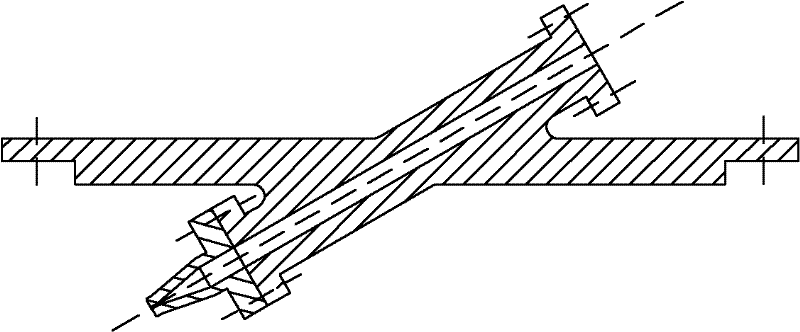
Special fixture used for processing open slot on spatial dihedral angle slope of turbine blade
ActiveCN102371491AExpand the scope of processingComply with positioning installation requirementsPositioning apparatusMetal-working holdersSurface finishBaseboard
The invention provides a special fixture used for processing an open slot on a spatial dihedral angle slope of a turbine blade, and the special fixture is characterized by comprising a slope baseboard component capable of adjusting a radial gradient, wherein a tailstock tip component and an end face positioning component are oppositely arranged at two radial ends of the slope baseboard component; a slope cushion component which is capable of adjusting an axial gradient and a height is arranged on the slope baseboard component between the tailstock tip component and the end face positioning component; a side wall positioning component is also arranged on the slope baseboard component; the side wall positioning component can axially feed a side wall positioning element which is contained in the side wall positioning component; a clamping component is also arranged on the slope baseboard component; and a pressing head capable of feeding downward is arranged at the tail end of the clamping component. The fixture provided by the invention can firmly and accurately position a device, can quickly and efficiently process the open slot meeting a design demand on a size precision and a position precision, and has ultrahigh surface glossiness.
Owner:四川省自贡市海川实业有限公司
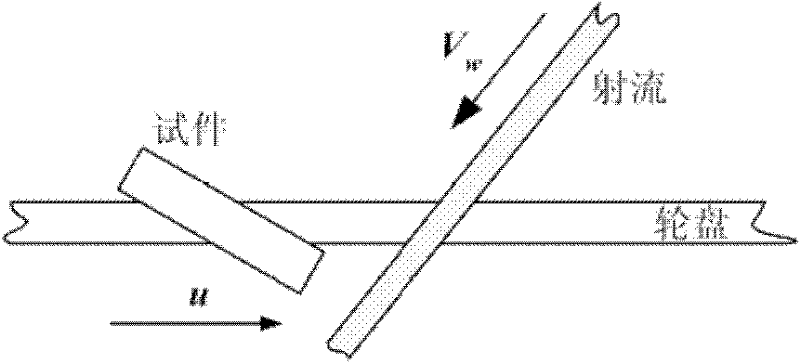
Water erosion experimental facility with/under rotary impact of high-pressure water jet
ActiveCN102252927AIncrease impact speedEasy to controlInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceElectric machineSteam turbine blade
The invention relates to a water erosion experimental facility with the rotary impact of high-pressure water jet. The facility simulates the blade erosion caused by drops in a steam turbine through the collision between high-speed jet and a rotating test piece. The facility mainly comprises a motor and a motor control cabinet, a gear case, a rotor and a test piece, a high-pressure water pump and nozzle pipelines, etc. While the rotor and the test piece rotate at a high speed, the high-pressure water supplied by the high-pressure water pump can generate high-speed jet through the nozzle. And the jet hits the test piece at a speed of the vector difference between the jet and the test piece, so that hitting speed is greatly improved. Thus, the evaluation of the water erosion resistance of the steam turbine blade material within a short period on an experiment table becomes possible.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
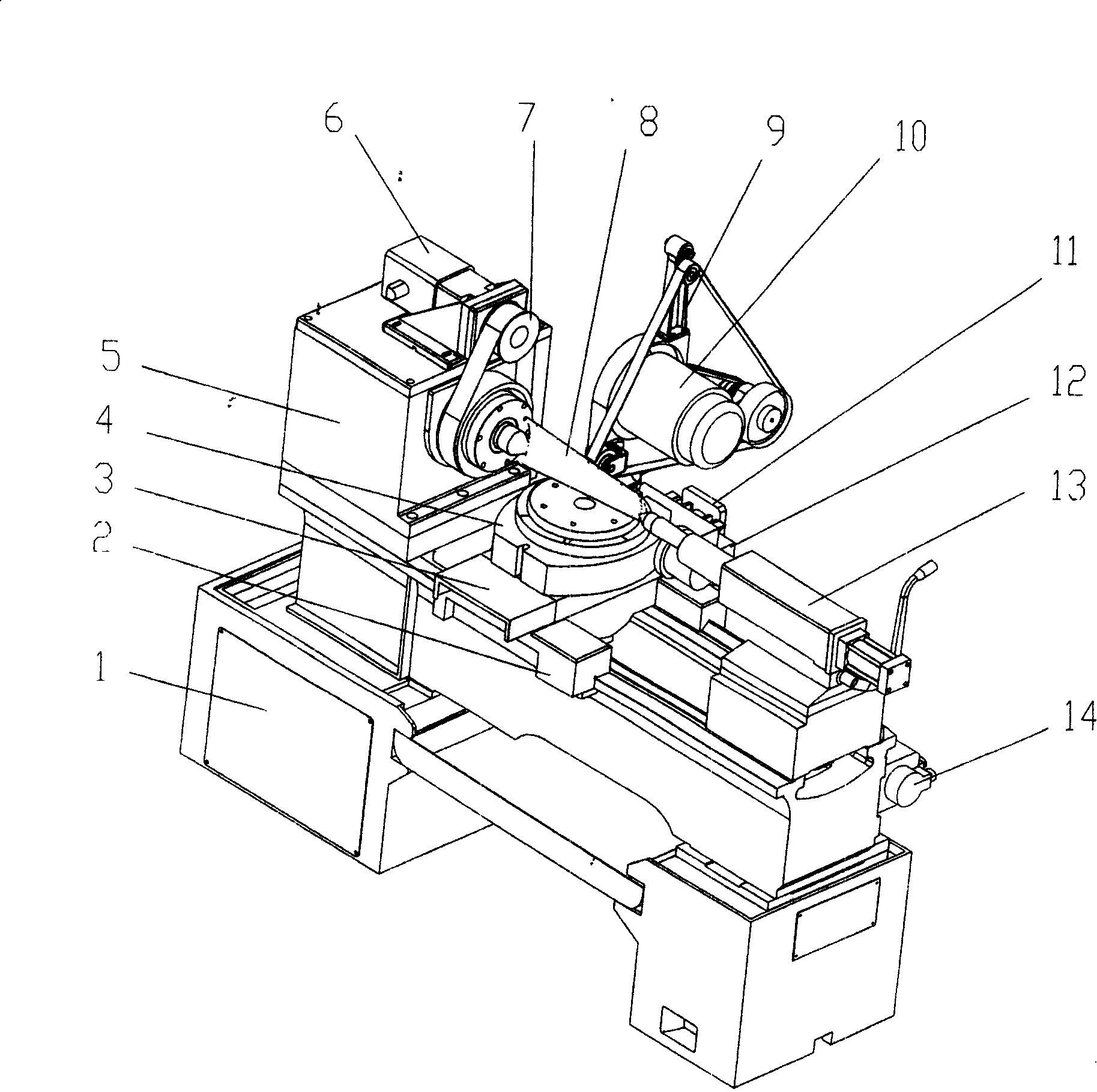
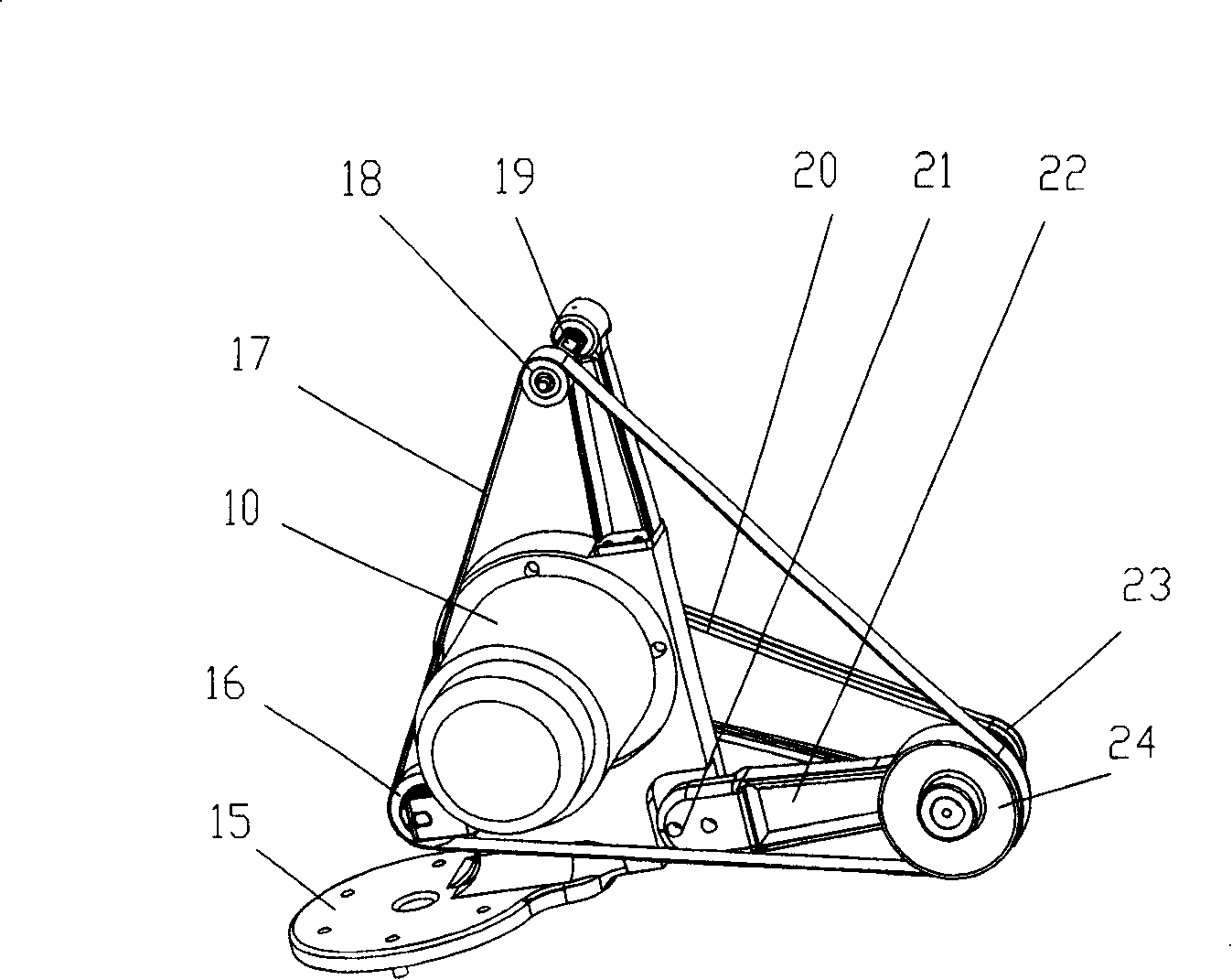
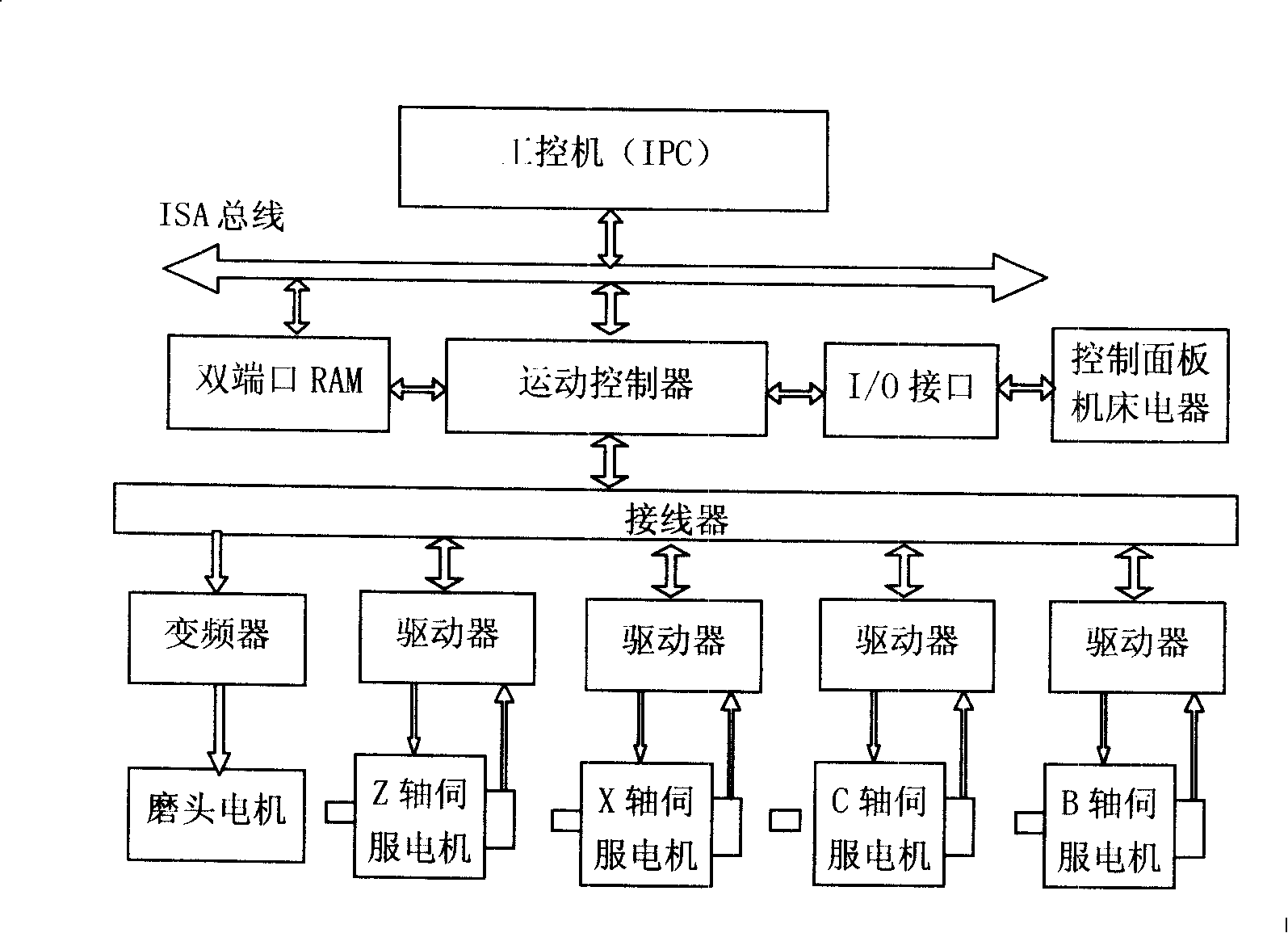
Turbine blade digital control abrasive belt grinding machine and operating method thereof
InactiveCN101234480AImprove grinding efficiencyGood grinding precisionBelt grinding machinesGrinding feed controlDigital controlSoftware modules
The invention discloses a turbine blade numerical control belt grinder and a control method thereof, which relates to a grinding and processing device of a turbine blade and the control method thereof, and is characterized in that: a belt wheelhead and an open numerical control system is provided on the basis of the basic parts of the original machine tool; the belt wheelhead is provided with a grinding belt tightening device and a transmission belt tightening device; a Z-axis serving motor drives a big carriage; an X-axis serving motor drives a small carriage; a C-axis drives a head frame; a B-axis drives a turret; a D-axis is a belt wheelhead motor; and each motor is connected with the control system; the control system is provided with a memory, a control circuit and a blade grinding and a controlling software module. During the operation, the original parameter is firstly input; then a blade grinding and controlling software module is automatically setting up by the system to generate a processing program, make error analysis and machining simulation; and finally a blade actual grinding processing is carried out. The turbine blade numerical control belt grinder is a five-axis and four-linkage numerical control belt grinder, and has the advantages of high efficiency, good accuracy, simple structure, low cost, and convenient control.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
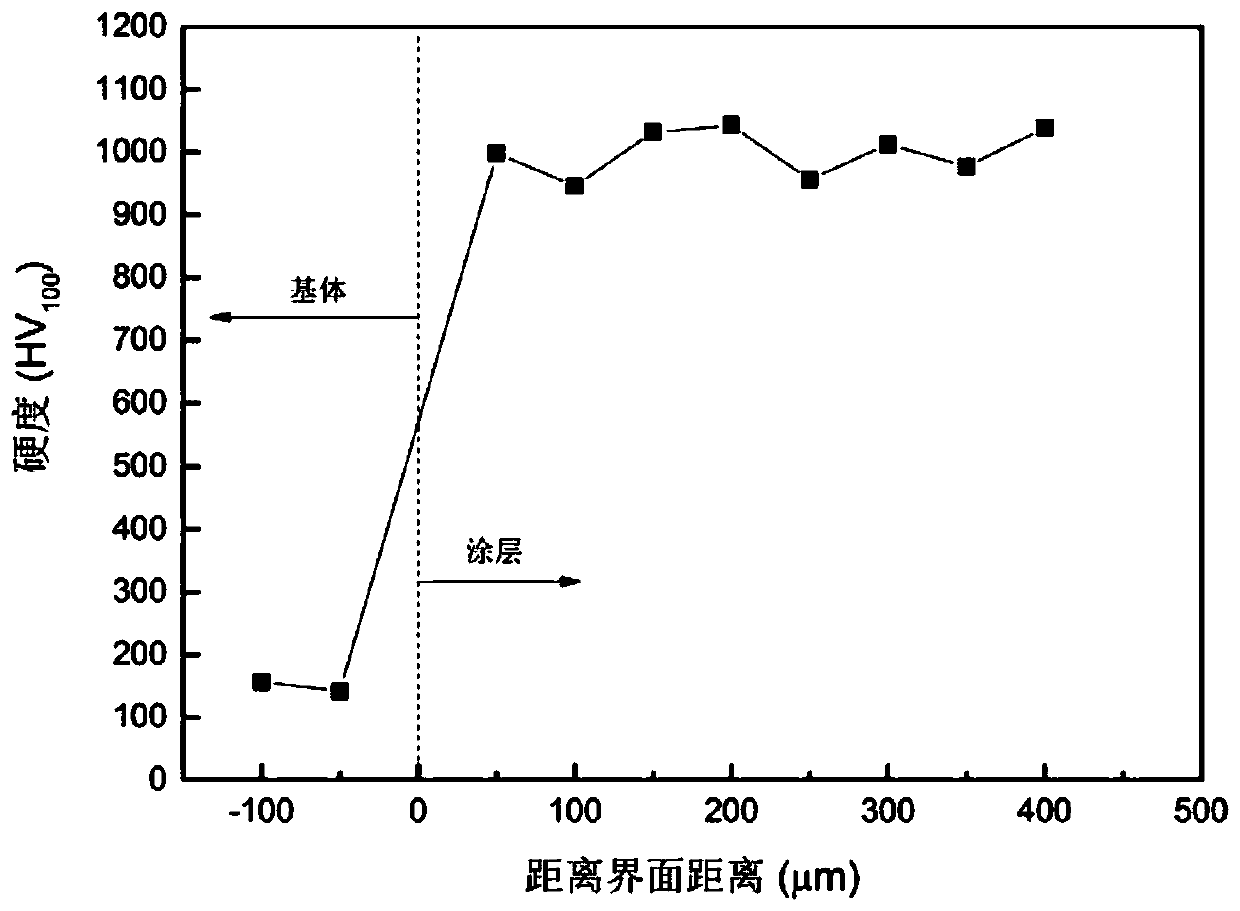
Method for preparing air inlet edge surface wear-resistant anti-corrosion alloy coating of tail stage blade of steam turbine
InactiveCN102453896AMelting fastFreeze fastMetallic material coating processesNumerical controlEdge surface
The invention relates to a method for preparing an air inlet edge surface wear-resistant anti-corrosion alloy coating of a tail stage blade of a steam turbine. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that: 1) the air inlet edge surface of the tail stage blade of the steam turbine is pre-treated; 2) alloy powder is selected, and an automatic powder conveyor is regulated; 3) light beams are regulated; 4) the wear-resistant anti-corrosion coating laser cladding is carried out, a DL-HL-T5000 type CO2 laser is adopted, a work table is a SIMENS numerical control laser processing machine, a synchronous powder conveyor is adopted for conveying the alloy powder into a laser molten pool, high-power focus laser beams and an automatic powder conveying head are fed in the specified direction of the air inlet edge surface of the blade, and uniform and compact laser cladding layers are formed on the blade surface through processing; and 5) flaw detection is carried out after the cladding. According to the method, the laser cladding is adopted for uniformly cladding the alloy powder with the wear-resistant anti-corrosion performance onto the blade of the steam turbine, the uniform and compact metallurgical combining coatings are formed, the anti-corrosion performance reaches the stainless steel level, the cladding layer and a substrate form firm metallurgical combination, and the peeling is not easy to occur.
Owner:SHENYANG DALU LASER COMPLETE EQUIP
Inspection carriage for turbine blades
ActiveUS7075296B2Avoid damageControl is neededVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingNon destructiveSteam turbine blade
An inspection carriage provides for remote inspection of the Z-shroud and snubber regions of the blades of a steam turbine, while the blades remain in the turbine. The carriage includes a non-destructive inspection probe such as a meandering wave magnetometer probe or eddy current probe mounted on a slider, so that the probe may be moved along a radial axis, skew axis, axial axis, and rotation axis. Cameras are provided on the carriage so that the probe may be remotely guided into the region to be inspected.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Mixed tuned hybrid blade related method
InactiveUS20060029501A1Reducing and more effectively damping vibrationIncrease dampingPropellersOther chemical processesImpellerFilling materials
A steam turbine blade includes a shank portion and an airfoil portion. The airfoil portion is formed with at least one pocket filled with a polymer filler material chosen as a function of natural frequency impact on the turbine blade or as a function of the damping characteristics of the filler materials. A steam turbine rotor wheel includes a plurality of blades secured about a circumferential periphery of the wheel, each blade having one or more pockets in the airfoil portion, the plurality of blades divided into two groups of blades. The pockets of one group of blades are filled with one or more polymer filler materials, and the pockets of the other group of blades filled with one or more polymer filler materials, wherein the polymer filler materials in the one group of blades creates different natural frequencies or damping characteristics in the blades of the one group than the polymer filler materials in the blades of the other group. The two groups of blades are assembled on the rotor wheel in accordance with a predetermined pattern.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Steam turbine blade fitting measuring tool and processing technology thereof
ActiveCN101947723AAvoid Batch Quality IssuesShorten the manufacturing cycleMetal working apparatusImpellerSteam turbine blade
The invention discloses a steam turbine blade fitting measuring tool and a processing technology thereof. The fitting measuring tool is a fake impeller simulating an arc of steam turbine rotor impeller, the fake impeller is provided with a plurality of blade assembling slots distributed in a radial manner, the contour line, the radial radius and the circumferential graduation of the assembling slot are all consistent with those of the assembling slot of real impeller, and the bottom of the slot is provided with a blade locking screw hole and screws. The fitting measuring tool is used for the pre-assembly of blades, in order to inspect the quality indexes of assembly in advance, avoid the quality-related problem of blades in batch, reduce maintenance rate, enable blades to meet the assembly requirement in production workshop, enhance working efficiency, shorten assembly period of unit, and lower economic losses.
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD
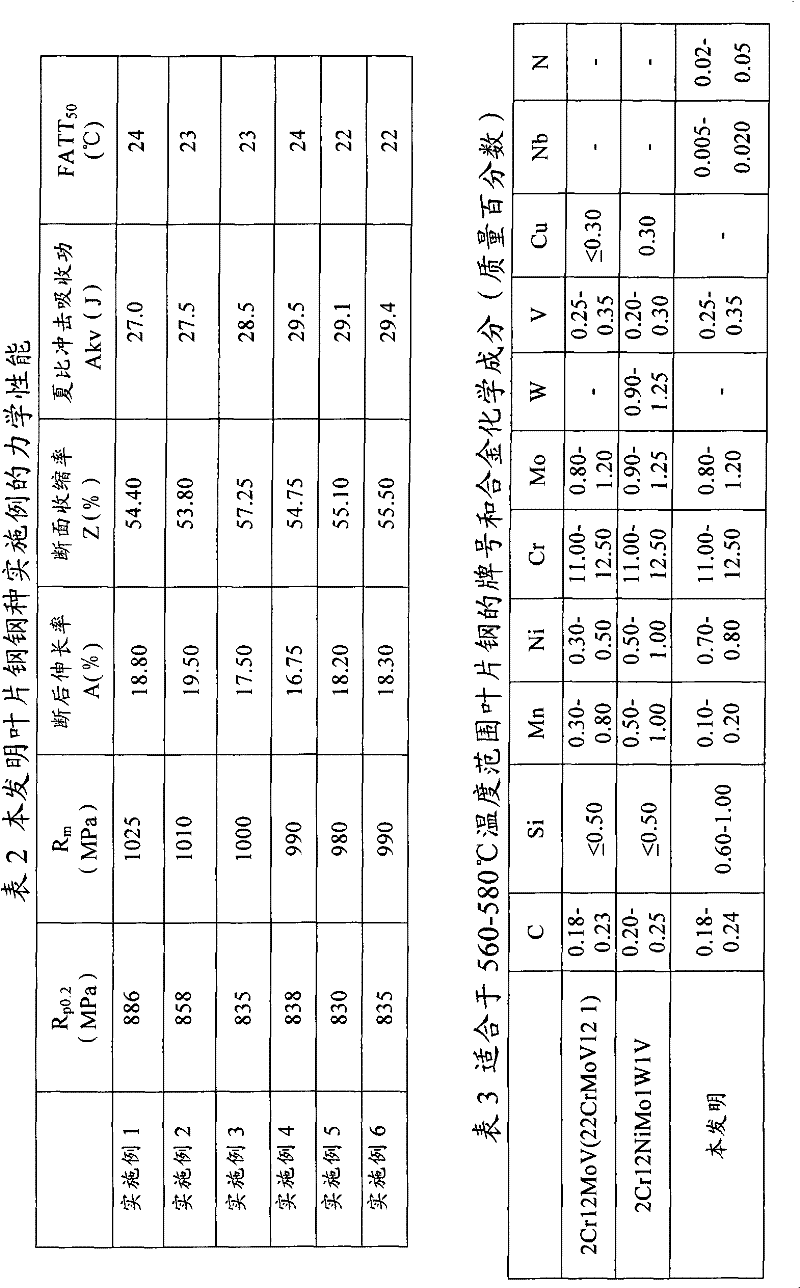
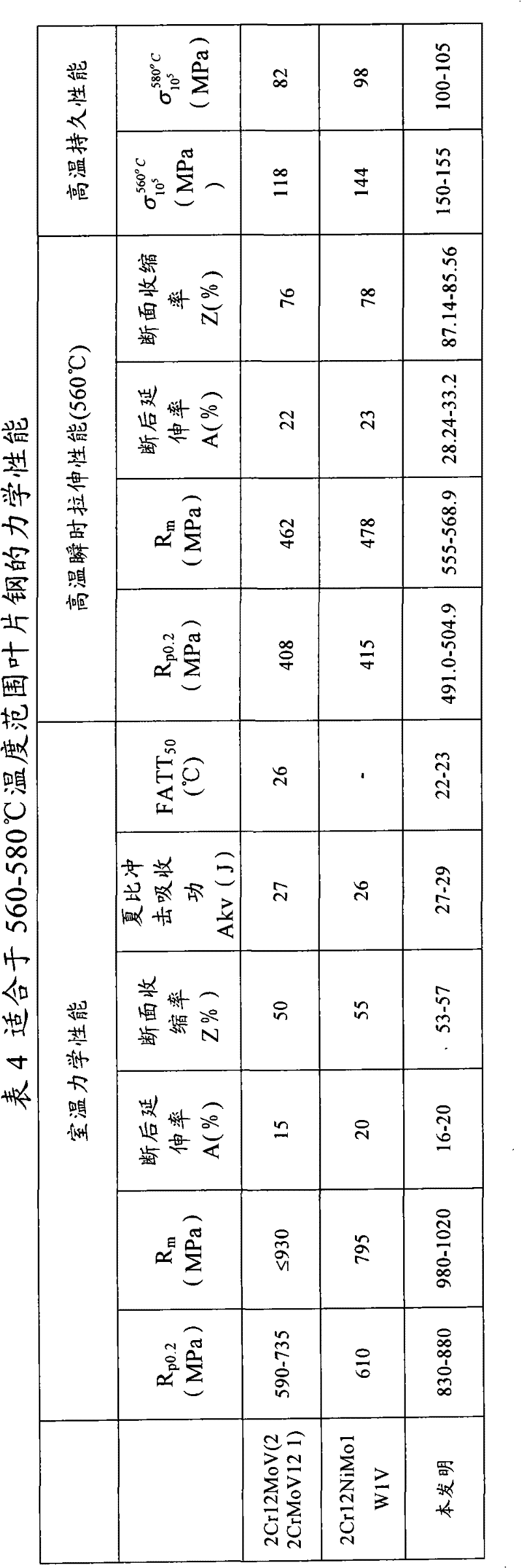
Steel used for steam turbine blades and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102477518AGood ductile-brittle transition temperature indexImprove purityMartensitic stainless steelSteam turbine blade
The invention relates to steel used for steam turbine blades, which contains the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.18% to 0.24% of C, 0.60% to 1.00% of Si, 0.10% to 0.20% of Mn, 0.80% to 1.20% of Mo, 11.00% to 12.50% of Cr, 0.70% to 0.80% of Ni, 0.25% to 0.35% of V, 0.005% to 0.020% of Nb, 0.02% to 0.05% of N, not more than 0.03% of S, not more than 0.02% of P, and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities. The manufacturing method of the steel comprises the following steps of: smelting by combination of EF, AOD and LFV; casting to form an electrode steel ingot, wherein the casting superheat degree is 40 DEG C to 70 DEG C, and the demoulding temperature of the steel ingot is controlled to be 600 DEG C to 700 DEG C; performing heat-loaded annealing on the electrode steel ingot; performing electroslag remelting on the electrode steel ingot; forging and performing heat-loaded annealing after forging; and rolling and annealing after rolling. The method produces high-performance medium-carbon martensitic stainless steel which is suitable for being applied to steam turbine blades working in a temperature range of 560 DEG C to 580 DEG C.
Owner:宝钢特钢有限公司
Inspection carriage for turbine blades
ActiveUS20060097719A1Avoid damageControl is neededVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingNon destructiveSteam turbine blade
An inspection carriage provides for remote inspection of the Z-shroud and snubber regions of the blades of a steam turbine, while the blades remain in the turbine. The carriage includes a non-destructive inspection probe such as a meandering wave magnetometer probe or eddy current probe mounted on a slider, so that the probe may be moved along a radial axis, skew axis, axial axis, and rotation axis. Cameras are provided on the carriage so that the probe may be remotely guided into the region to be inspected.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Corrosion resisting mirror plastic extrusion die steel
The invention provides a corrosion resisting mirror plastic extrusion die steel, which comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.18 to 0.26 percent of C, 0.20 to 0.40 percent of Mn, 0.80 to 1.20 percent of Si, 13.00 to 15.00 percent of Cr, 1.85 to 2.50 percent of Mo, 0.80 to 1.20 percent of Cu, 0.07 to 0.15 percent of V, less than or equal to 0.015 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.008 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.60 percent of Ni, less than or equal to 0.007 percent of N, and the balance of Fe and trace of impurities. The die steel belongs to an intermediate carbon martensitic stainless steel, residual carbides are few in an as-quenched state, so that a great deal of disperse carbides can be conveniently separated out by tempering, and the die steel has high secondary hardness and high-temperature strength; when the die steel is quenched and tempered, vanadium is separated out in a mode of M4C3 type carbide, and the stability, secondary hardness and high-temperature strength of the die steel are improved; the die steel has better antioxidation, heat resistance and mechanical processing property; in particular, the die steel has better surface polishing property and chloride ion corrosivity resistance below 500 DEG C, and long service life; therefore, the die steel can be widely used for manufacturing high-grade, precision and advanced plastic extrusion dies, tools, turbine blades, valves, shafts, fasteners and the like.
Owner:HUBEI NEW FINE METALLURGICAL TECH
Heat-resisting steel material used as vane or bolt of supercritical steam turbine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101525726AMeet the design requirementsMeet the use requirementsBlade accessoriesScrewsChemical compositionSteam turbine blade
The invention discloses a heat-resisting steel material used as a vane or a bolt of a supercritical steam turbine. The chemical composition of the material (in percentage by weight) is: 0.12 to 0.16 percent of C, 0.30 to 0.70 percent of Mn, 0.35 to 0.65 percent of Ni, 10.0 to 11.0 percent of Cr, 0.30 to 0.5 percent of Mo, 1.5 to 1.9 percent of W, 0.14 to 0.20 percent of V, 0.05 to 0.11 percent of Nb, 0.04 to 0.08 percent of N, and the balance of Fe and impurities. The chemical property of the material is that: tensile strength sigma b is more than or equal to 930MPa; yield strength sigma 0.2 is more than or equal to 765MPa; tensile stretch delta is more than or equal to 14 percent; percentage of area reduction psi is more than or equal to 32 percent; ballistic work AKv is more than or equal to 20J; and hardness HB is between 277 and 331.
Owner:SICHUAN JIANGYOU LIUHE STEAM TURBINE MATERIAL
Method for processing slots on turbine rotor for mushroom-shaped blade roots
ActiveCN101745672AImprove yieldReduced cutting edge size requirementsMilling equipment detailsNumerical controlRotational axis
The present invention relates to a method for processing slots on a turbine rotor for mushroom-shaped blade roots. Slots for blade roots are milled by a profile milling cutter on a numerical control processing center. The numerical control processing center is provided with two rectilinear motion shafts and a rotating shaft at least. The rotating shaft is a lathe rotating table. The milling cutter is arranged on the cutter head of the main shaft of the numerical control processing center, and the milling cutter is driven by the shaft to rotate. The blade is fixed on the rotating table of the numerical control processing center, the radiant line of the blade is parallel with the main shaft and penetrates through the rotating center of the table, and the slots for blade roots are orientatedto the cutter head. The milling cutter is driven by the rotating table to rotate, the blade accordingly makes circumferential motion, and interpolation compensation is made for the circumferential motion angle by the rotating table. The two rectilinear motion shafts are parallel to the central plane of the mushroom-shaped blade roots, and interpolation compensation is made for displacements of the rotating table in the direction of the rectilinear motion shafts. Thus, when the milling cutter is used for cutting any processing point on an arc curve, the cutter axial vector is always on the normal line of the processing point and points to the arc center.
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD
Refractory steel for vane of steam turbine of ultra supercritical fossil power plant and manufacturing method
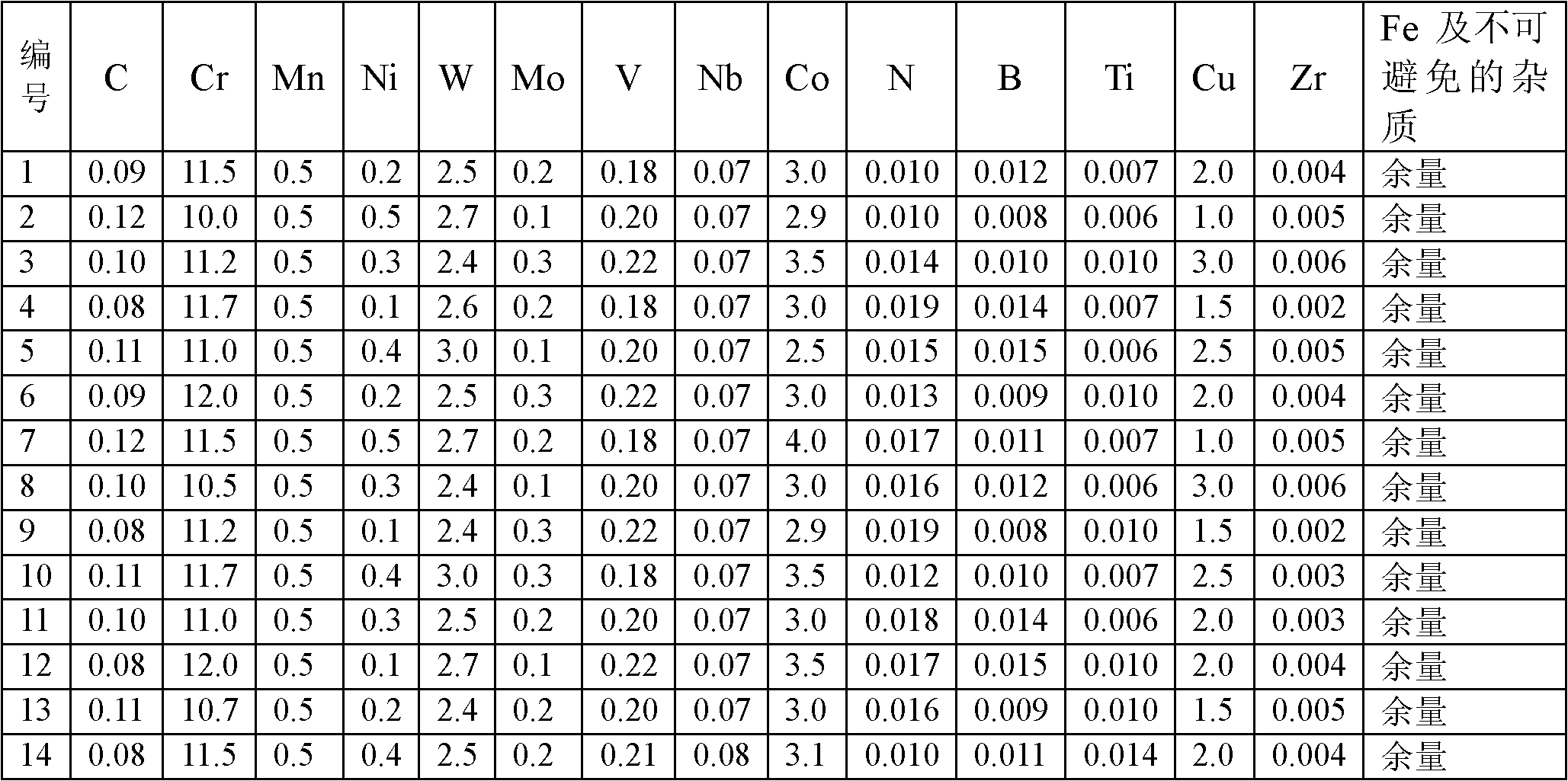
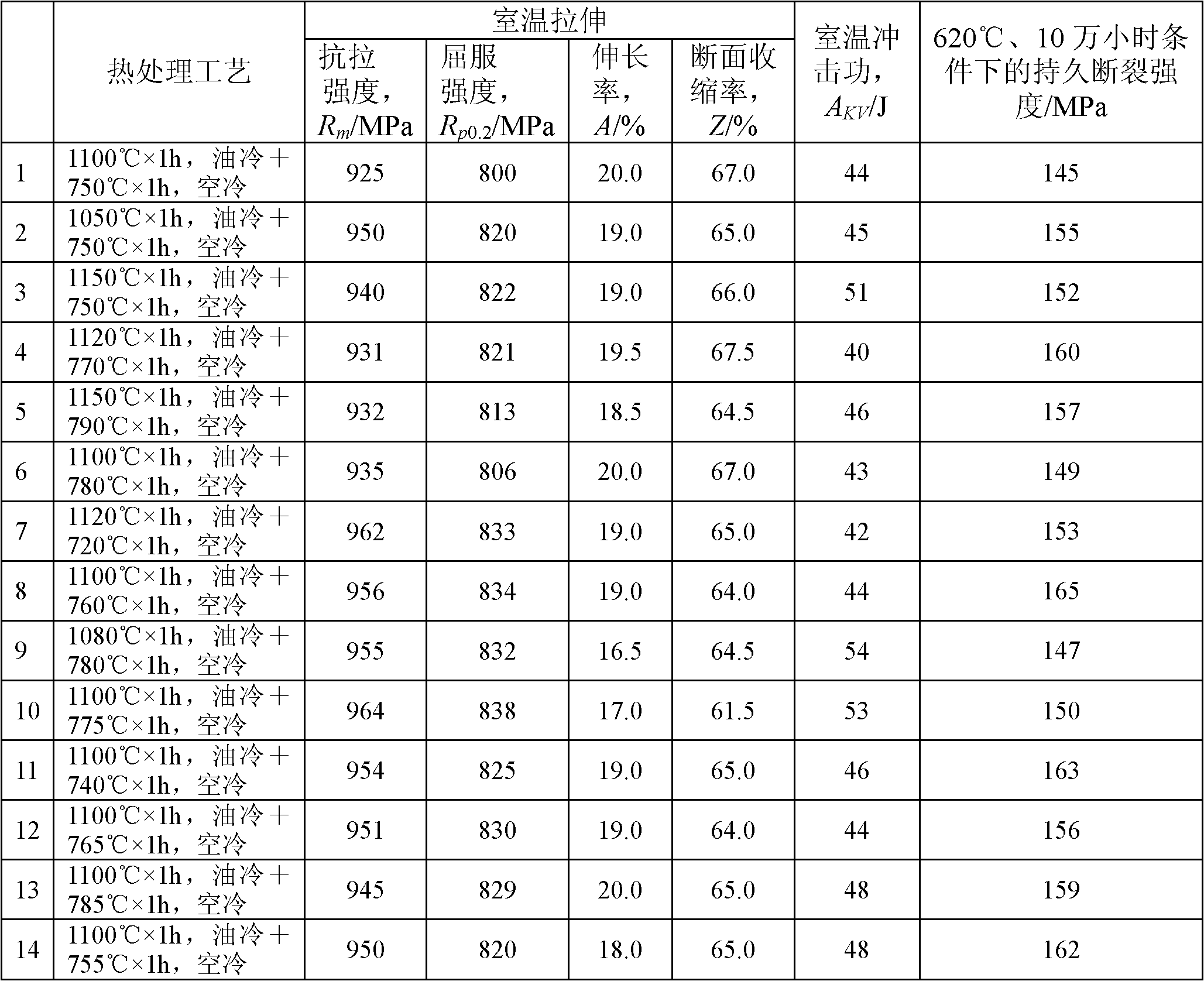
The invention provides refractory steel for a vane of a steam turbine of an ultra supercritical fossil power plant, which is characterized by comprising the following chemical components calculated according to mass percent: 10.0 to 12.0 of chromium, 0.1 to 0.6 of molybdenum, 2.4 to 3.0 of tungsten, 1.0 to 4.0 of cobalt, 0 to 0.5 of nickel, 0.2 to 1.0 of manganese, 0.010 to 0.019 of nitrogen, 0.10 to 0.30 of vanadium, 0.03 to 0.10 of niobium, 0.005 to 0.015 of titanium, 0.06 to 0.15 of carbon, 0.008 to 0.015 of boron, 1.0 to 3.0 of copper, 0.002 to 0.01 percent of zirconium and the balance asiron and unavoidable impurities; a manufacturing method of the refractory steel for the vane of the steam turbine of the ultra supercritical fossil power plant comprises the following steps: processing the compositions of the raw materials of the constituent elements sequentially by smelting and pouring so as to obtain a steel ingot of the refractory steel, then forging the steel ingot and finally, carrying out heat treatment; and the refractory steel for the vane of the steam turbine of the ultra supercritical fossil power plant and the manufacturing method are characterized in that a heat-treatment process has the steps of keeping oil cooling for 0.5 to 1h at 1050 to 1150 DEG C and keeping air cooling for 1 to 2h at 720 to 790 DEG C. The refractory steel has favorable corrosion resistance and creep resistance at high temperature, has stable tissues in the high-temperature long-time use procedure and can be used as a material of a vane for a steam turbine of an ultra supercritical fossil power plant above 620 DEG C.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
Five-axle linked tandem and parallel digital control polishing machine tool
InactiveCN1962192AAvoid health hazardsImprove work efficiencyPolishing machinesGrinding drivesSteam turbine bladeGrinding wheel
The invention relates to a five-axle couple parallel-serial digit-control furnishing machine, wherein the fixed platform (3) is above the moveable platform (4), while they are connected via four flexible connecting rods (8); the upper ends of connecting rods (8) are geared to the first servo motor (2); the abrasive wheel (5) is mounted on the movable platform (4) to gear the movable platform (4); the fixed work bench (1) is under the abrasive wheel (5); the fixed work bench (1) is mounted with digit-control rotation table driven by the second servo motor (7). The invention can realize spatial three-dimension movement and one-dimension movement. The turbine blades mounted on the digit-control rotation table can realize one-dimension rotation. Therefore, the invention can furnish complex element.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Steam turbine blade and method for manufacturing the same
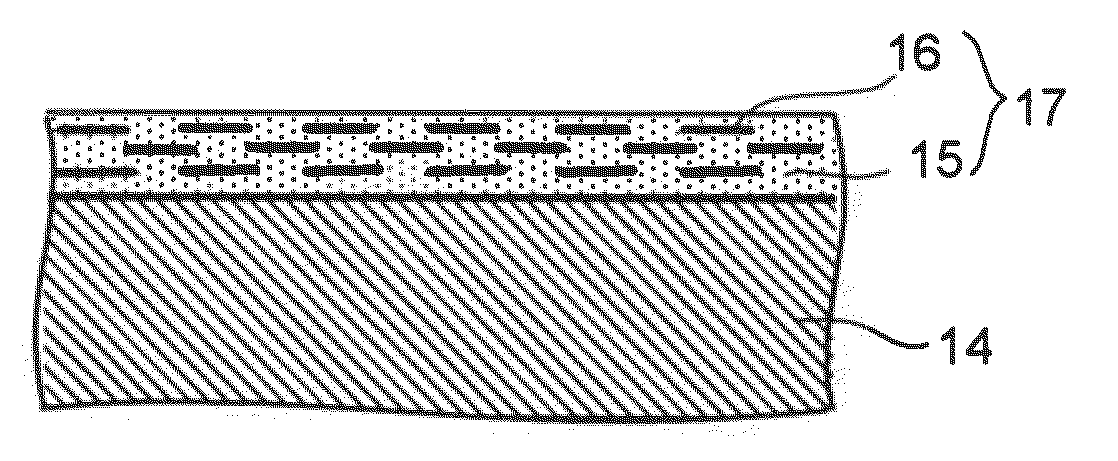
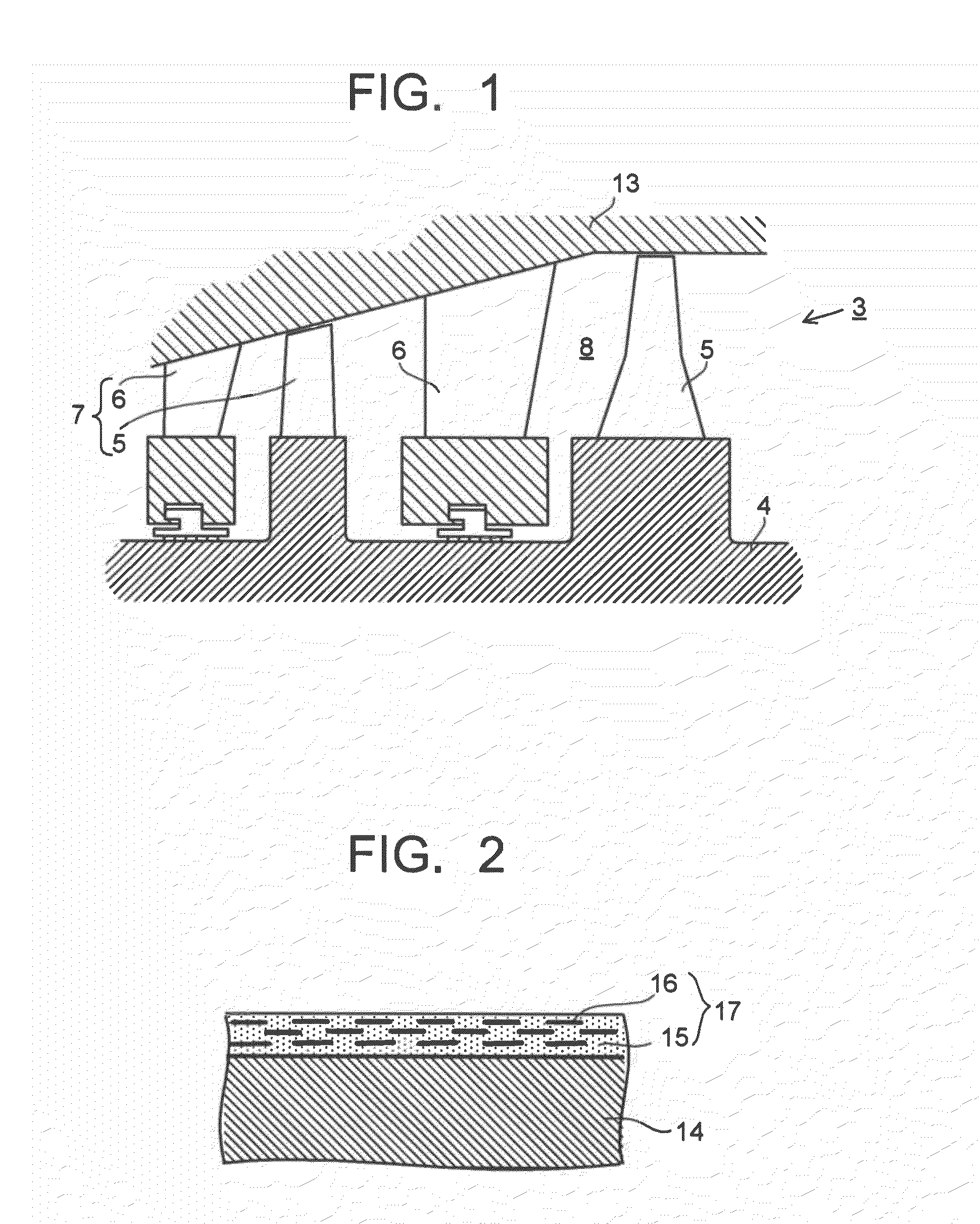
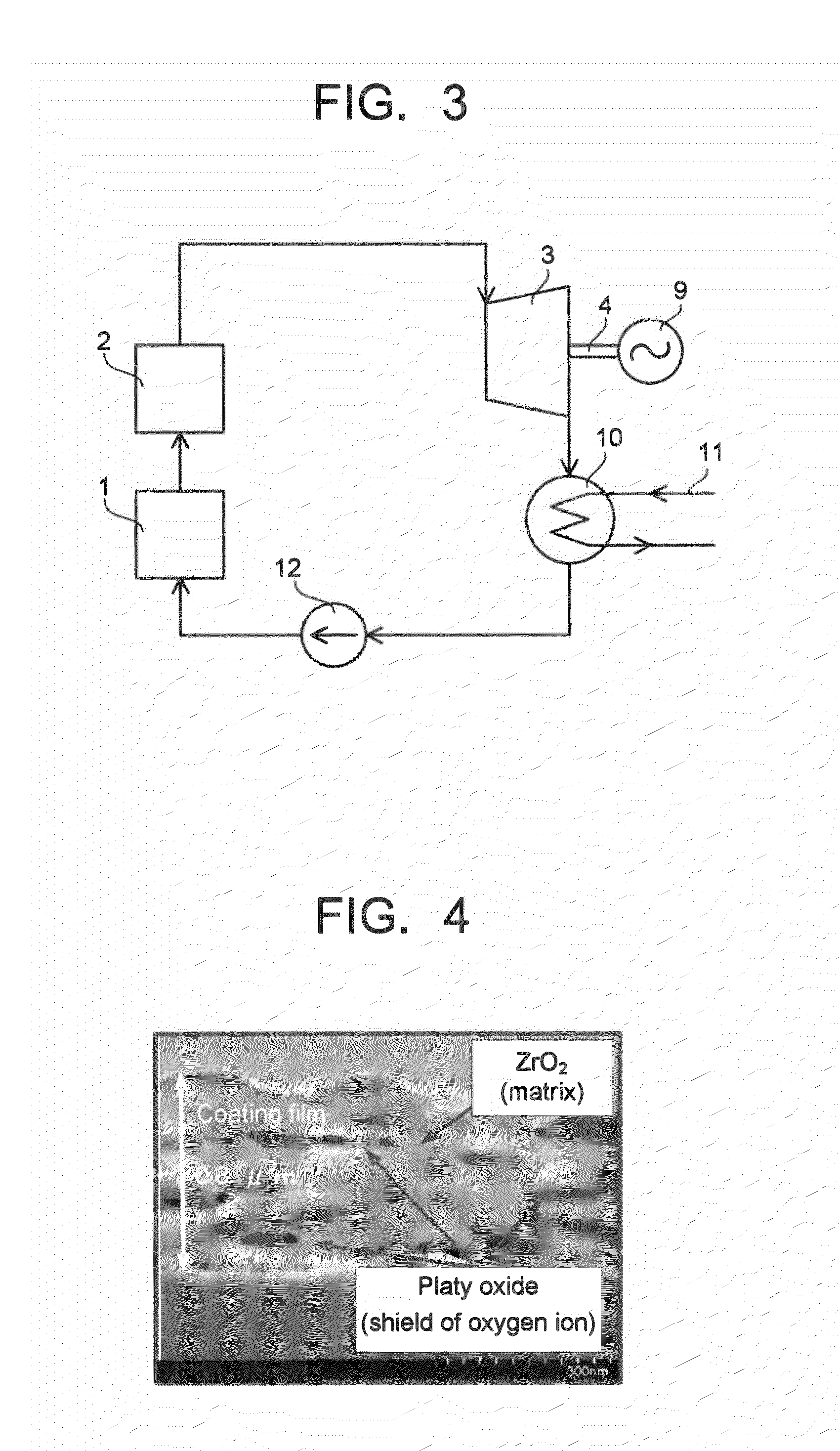
InactiveUS20100166548A1Reduce manufacturing costSimple manufacturing processPropellersPump componentsSteam turbine bladeCoating
A steam turbine blade includes a coating film formed at least a portion of a surface of the steam turbine blade, the coating film containing a ceramic matrix and nanosheet particles dispersed in the ceramic matrix. The steam turbine blade is employed as one of stator blades or one of rotor blades in a steam turbine. The steam turbine includes a turbine rotor, the rotor blades implanted in the turbine rotor, the stator blades provided in an upstream side of the corresponding rotor blades, and a turbine casing supporting the stator blades and accommodating turbine rotor, the rotor blades and the stator blades. The steam turbine is also configured such that the rotor blades are paired with the corresponding stator blades to form turbine stages arranged in an axial direction of the turbine rotor, thereby forming steam paths.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
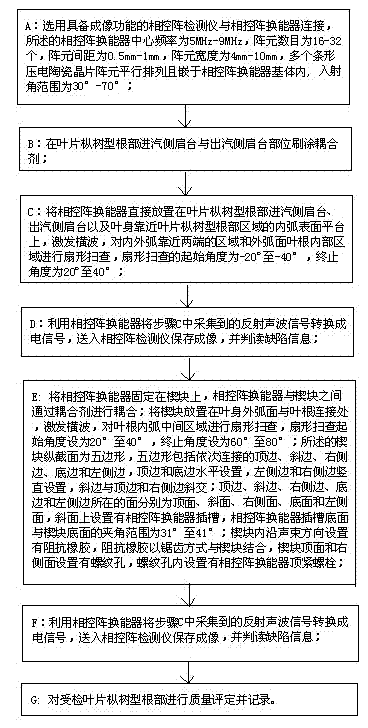
Ultrasonic imaging detecting method of mushroom type root part of blades of steam turbine and phased array energy transduction device
ActiveCN103018334AGood beam accessibilityOptimal control over focus sizeAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Image resolution
The invention discloses an ultrasonic imaging detecting method of a mushroom type root part of blades of a steam turbine and a phased array energy transduction device. According to the invention, the ultrasonic phased array detecting method and the energy transduction device which are adopted are good in acoustic beam accessibility; ultrasonic emitting acoustic beams can be changed through wedge blocks, thus the acoustic beams can enter the mushroom type root part of the blades to cover all key detecting parts so as to compressively image and inspect a component with a complex geometric shape; the focus dimension, the depth of a focusing area and the directions of the acoustic beams can be optimally controlled under the condition that a probe is not moved or is moved slightly; and the detection speed, the scope, the resolution ratio, the signal-to-noise ratio and the sensitivity can be improved; and furthermore, the imaging is clear, and the reflection echo of a defect can be quickly and accurately positioned.
Owner:STATE GRID HENAN ELECTRIC POWER ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST +2
Plasma spraying high-temperature-erosion-resistant high-entropy amorphous powder and coating thereof, coating preparation method and application
InactiveCN110699629AImprove high temperature resistanceAccelerated corrosionMolten spray coatingSteam turbine bladePetrochemical
The invention discloses plasma spraying high-temperature-erosion-resistant high-entropy amorphous powder and a coating thereof, a coating preparation method and application. The high-entropy amorphouspowder is prepared through a vacuum induction gas atomization method. The powder comprises, by atomic percent, 20% of Fe, 20% of Co, 20% of Ni, 20% of Cr, 10% -16% of B and 4% -10% of Si; the particle size of the powder obtained after screening is 300-400 meshes. The preparation method of the high-entropy amorphous coating comprises the steps that (a) a workpiece is pretreated; (B) a high-entropyamorphous powder material is prepared; and (c) the high-entropy amorphous coating is prepared through a plasma spraying technology. The amorphous content of the high-entropy amorphous coating is morethan or equal to 98%, the porosity is smaller than 1%, the bonding strength is more than 50MPa, the Vickers hardness is more than 900Hv, and the excellent high-temperature-erosion-resistant performance is achieved. The plasma spraying high-temperature-erosion-resistant high-entropy amorphous powder can be widely applied to high-temperature-erosion-resistant and corrosion-resistant protection of key components such as power plant boilers, petrochemical engineering pipelines and smoke turbine blades, and the service life of mechanical engineering equipment can be remarkably prolonged.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV +1
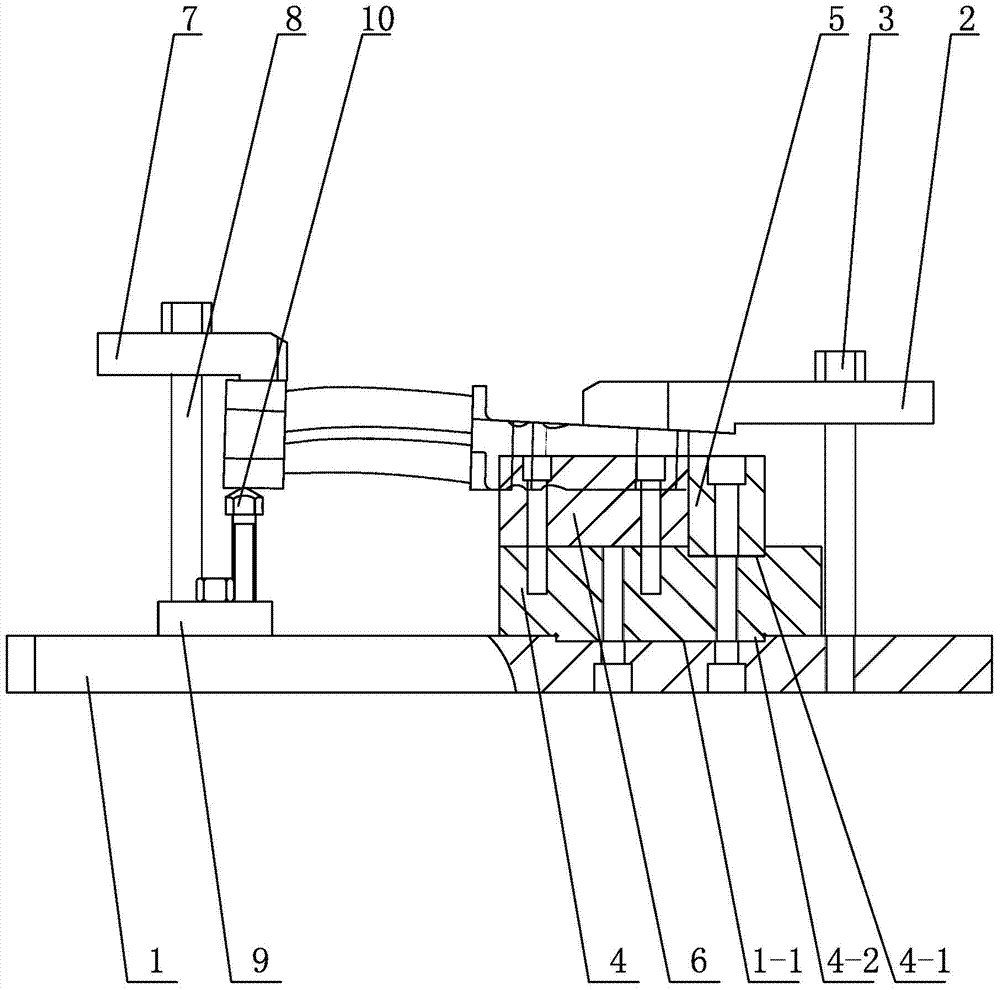
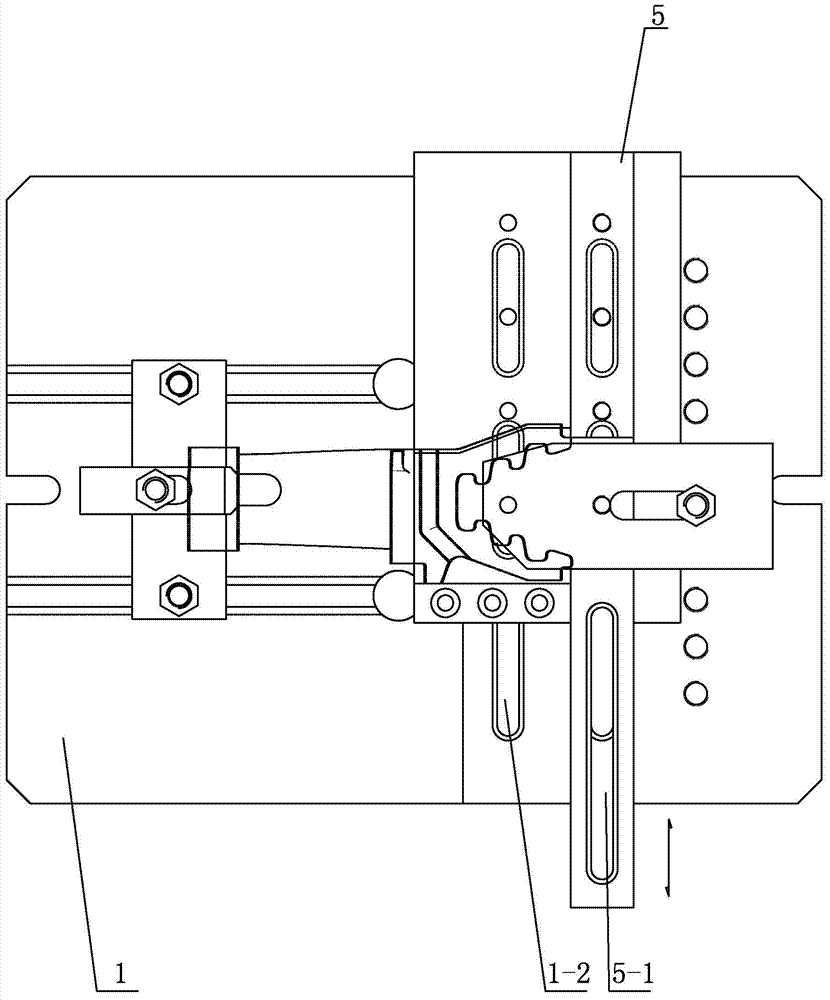
Fixture for clamping steam inlet and outlet sides of intermediates of blade roots during milling
ActiveCN103586712AReduce in quantityLow costPositioning apparatusMetal-working holdersSteam turbine bladeEngineering
The invention discloses a fixture for clamping steam inlet and outlet sides of intermediates of blade roots during milling, and relates to a fixture. The fixture comprises a bottom plate, an oblique pressure plate mechanism, a flat pressure plate, a first double-end stud, a guide slider, a positioning slider and a barrier. The bottom plate is horizontally arranged, the lower end of the first double-end stud is inserted in the upper surface of the bottom plate, the upper end of the first double-end stud is connected with the flat pressure plate, the lower surface of the flat pressure plate is parallel to the upper surface of the bottom plate, the guide slider is arranged on the upper surface of the bottom plate and is positioned below the flat pressure plate, the positioning slider and the barrier are mounted on the upper surface of the guide slider side by side via a plurality of bolts, and the oblique pressure plate mechanism is arranged on the upper surface of the bottom plate. The fixture has the advantages that problems of large quantities of fixtures, waste of labor and troublesome management and operation when intermediates of blade roots of blades of steam turbines are clamped during milling can be solved; the fixture is used for blade machining.
Owner:HARBIN TURBINE
Ultrasonic imaging detection method for blade fir-type root of turbine
ActiveCN103698399AOptimal control over focus sizeDepth is easy to controlAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasound imagingSteam turbine blade
The invention discloses an ultrasonic imaging detection method for a blade fir-type root of a turbine. The method comprises the following steps: (A) connecting a phased array detector with a phased array transducer; (B) coating the blade fir-type root with a coupling agent; (C) directly arranging the phased array transducer on a steam inlet side shoulder and a steam outlet side shoulder of the blade fir-type root and in an area, close to the blade fir-type root, of a blade body to perform sector scanning; (D) storing a formed image through the phased array detector, and interpreting defect information; (E) fixing the phased array transducer on a wedge block, and arranging the phased array transducer at a joint of the outer arc surface of the blade body and the blade root to perform sector scanning on the middle area of the inner arc of the blade root; (F) storing the formed image through the phased array detector, and interpreting the defect information; and (G) performing quality evaluation on the detected blade fir-type root, and keeping a record. According to the method, the blade fir-type root of a complicated geometrical shape can be subjected to comprehensive, accurate, quick and intuitive imaging inspection, so that the problems of small detection range and large detection failure area of an existing detection method are solved.
Owner:STATE GRID HENAN ELECTRIC POWER ELECTRIC POWER SCI RES INST +2
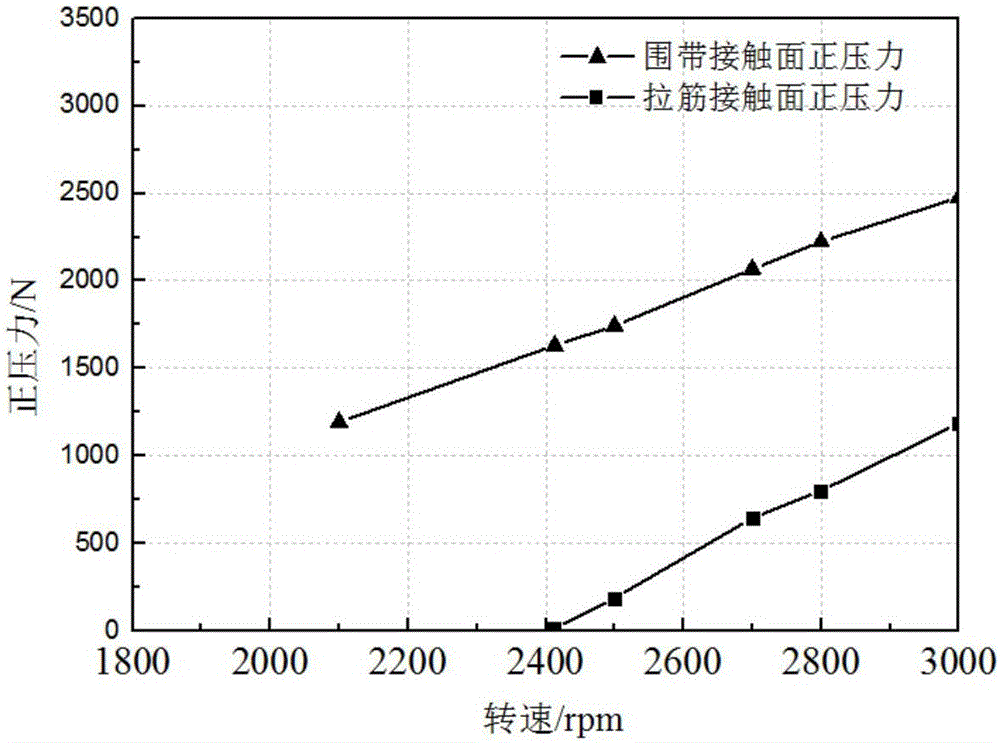
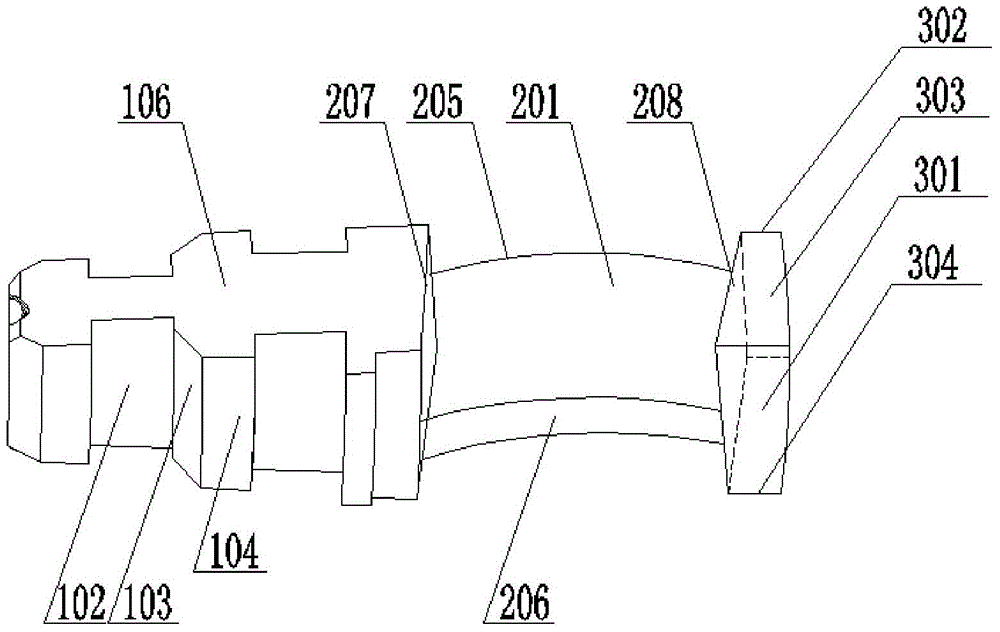
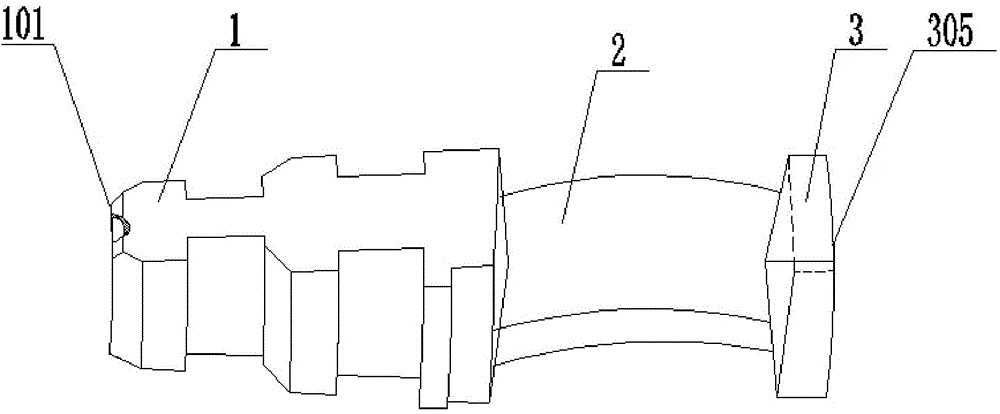
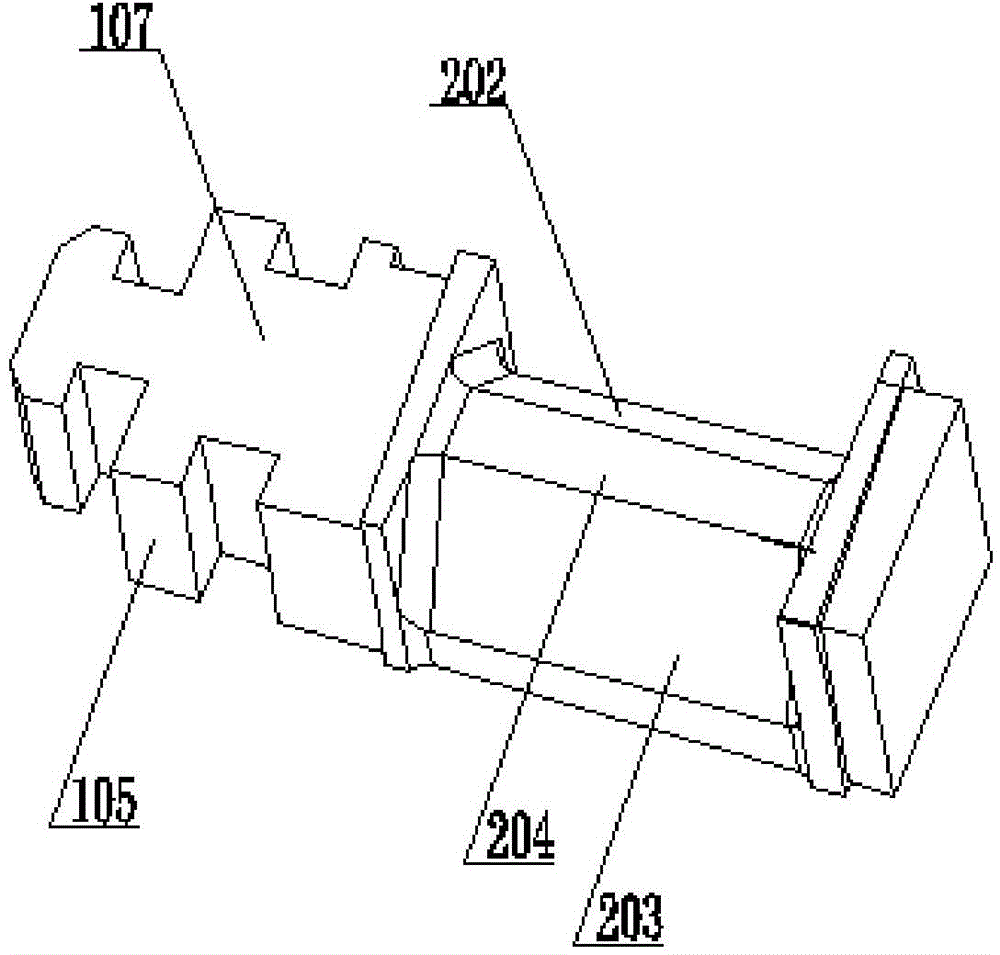
Testing apparatus for steam turbine blade with shroud ring and boss lashing wire structures
ActiveCN103743556ASolution is difficult to achieveSolve the problem of inconvenient measurementMachine part testingMeasurement deviceSteam turbine blade
Disclosed in the invention is a testing apparatus for steam turbine blade with shroud ring and boss lashing wire structures. The testing apparatus comprises a testing rack, a blade root fixing device, two sets of loading devices, a vibration excitation device, and a measurement device. The blade root fixing device is fixed at a base plate of the testing tack. The loading devices are fixed in groove holes of side plates by two loading plate support units; one set of the loading device is used for providing a circumferential torque for the shroud ring of the turbine blade; and the other set of loading device is used for providing a circumferential torque for the boss lashing wire of the turbine blade. The vibration excitation device is fixed at groove holes of the side plates by two exciter support standing plates. And the measurement device is fixed at the testing rack. According to the invention, the testing apparatus can be used for simulating measurement of steam turbine blades that have different lengths and have the shroud ring and boss lashing wire structures on the actual operation condition, thereby laying the foundation of further development of the steam turbine blade with the shroud ring and boss lashing wire structures.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Shot blasting check method for surface defects of blades
ActiveCN101520404AImprove fatigue resistanceUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisSteam turbine bladeLiquation
The invention relates to a shot blasting check method for surface defects of blades. Turbine blades processed by the method can clearly show various surface defects easily generated in materials during processes, and specifically the method can check that the defects are the liquation of the materials, various processing burns, hardening and the like in the processes. The method is characterized in that the method for surface shot blasting achieves the show of the surface defects of the blades.
Owner:WUXI TURBINE BLADE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com