Low-melting-point alloy casting positioning technology in turbine blade machining
A steam turbine blade, low melting point technology, applied in positioning devices, metal processing equipment, metal processing machinery parts, etc., can solve the problems of increased product materials and processing time, inability to use clamping methods, large processing deformation, etc., to achieve saving The effects of time and raw materials, good mechanical properties, and small design standard errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
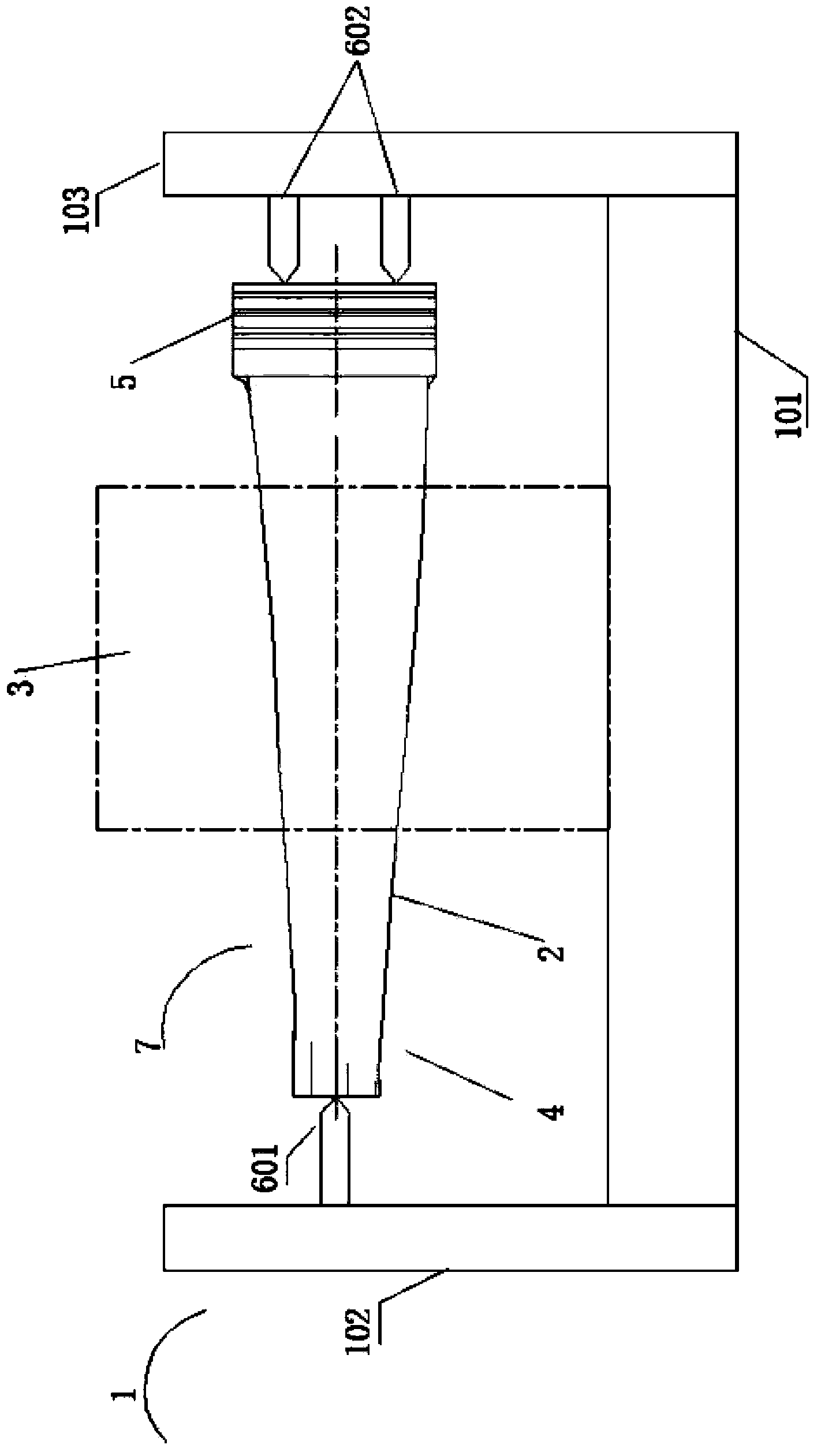
[0037] like figure 1 , is a schematic diagram of the assembly of the positioning tool, the positioning box and the blade of the present invention, the positioning tool 1 has a bottom plate 101, two vertical column plates 102 and 103, a single top 601, a double top 602, and the blade crown 4 conflicts with the single top 601 , the blade root 5 conflicts with the double apex 602. It can be seen that the center of gravity of the isosceles triangle formed by the straight line where the single apex 601 and the double apex 602 are located can basically coincide with the center of gravity of the blade 7, forming the most stable triangular positioning. The blade steam channel 2 passes through the positioning square box 3 .
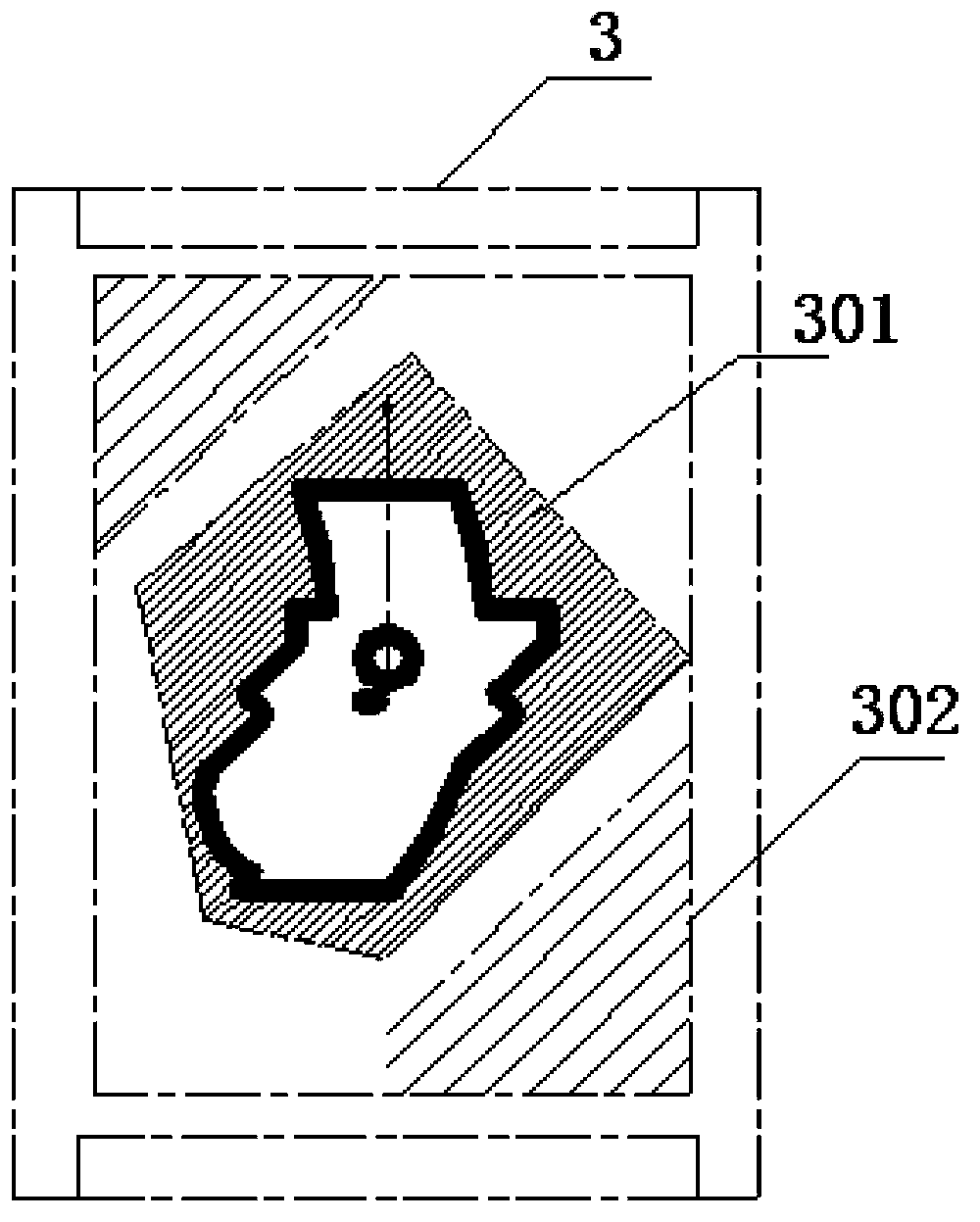
[0038] like figure 2 , is a side sectional view of the positioning square box, and the positioning square box 3 has a cavity 301 and a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com