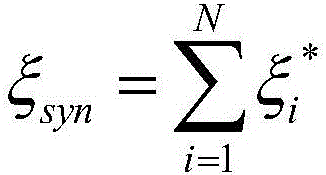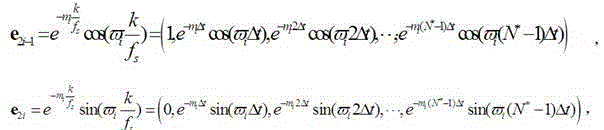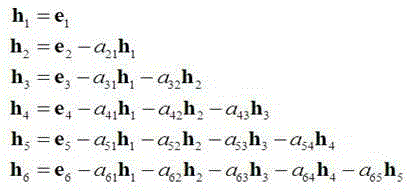Patents
Literature
58 results about "Modal damping ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
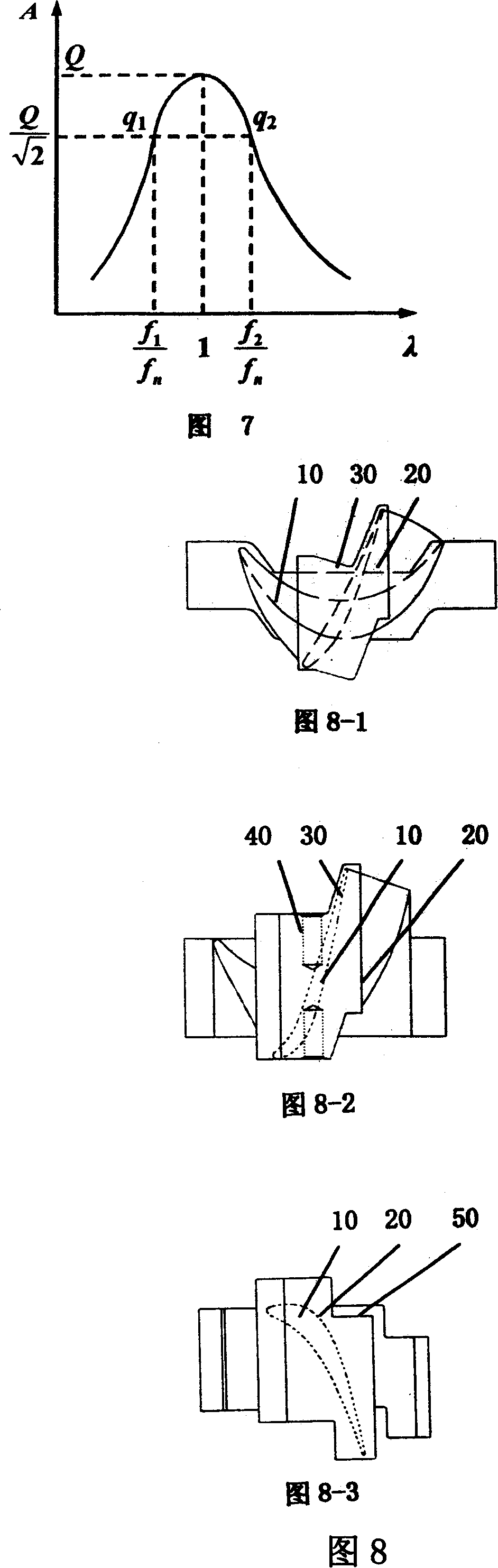
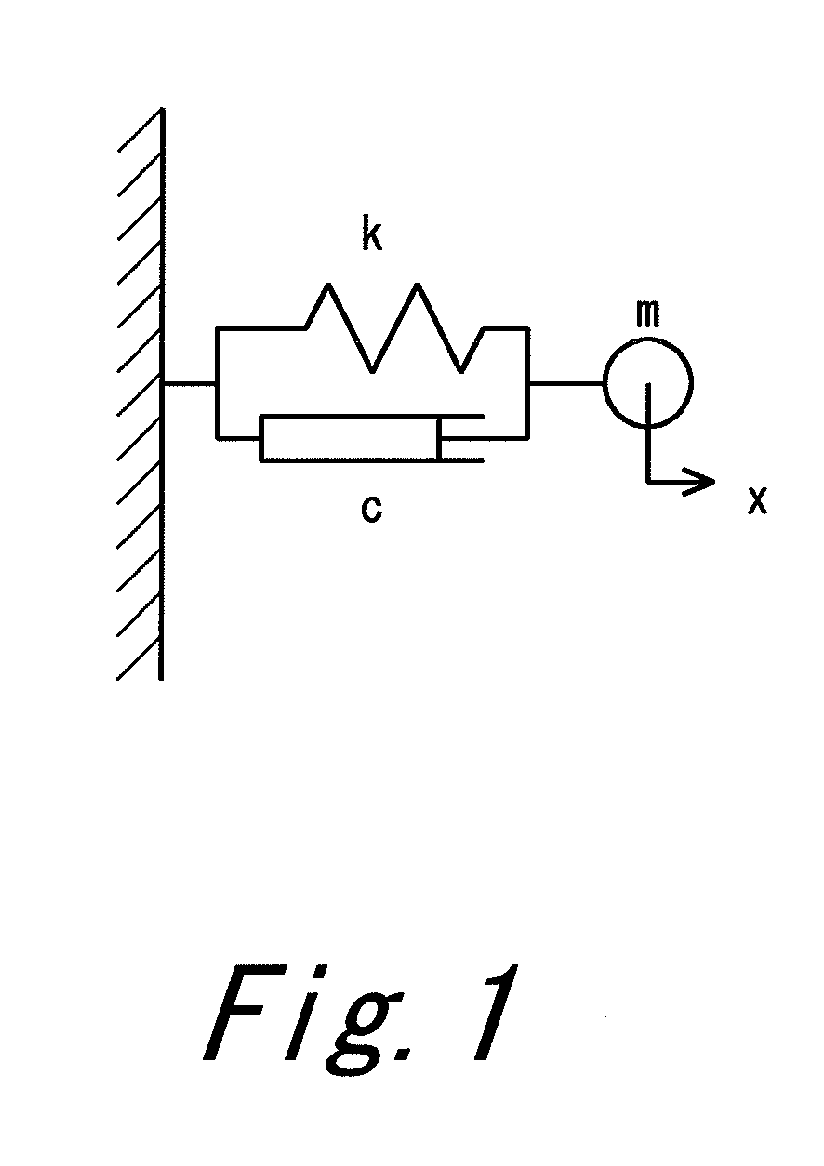
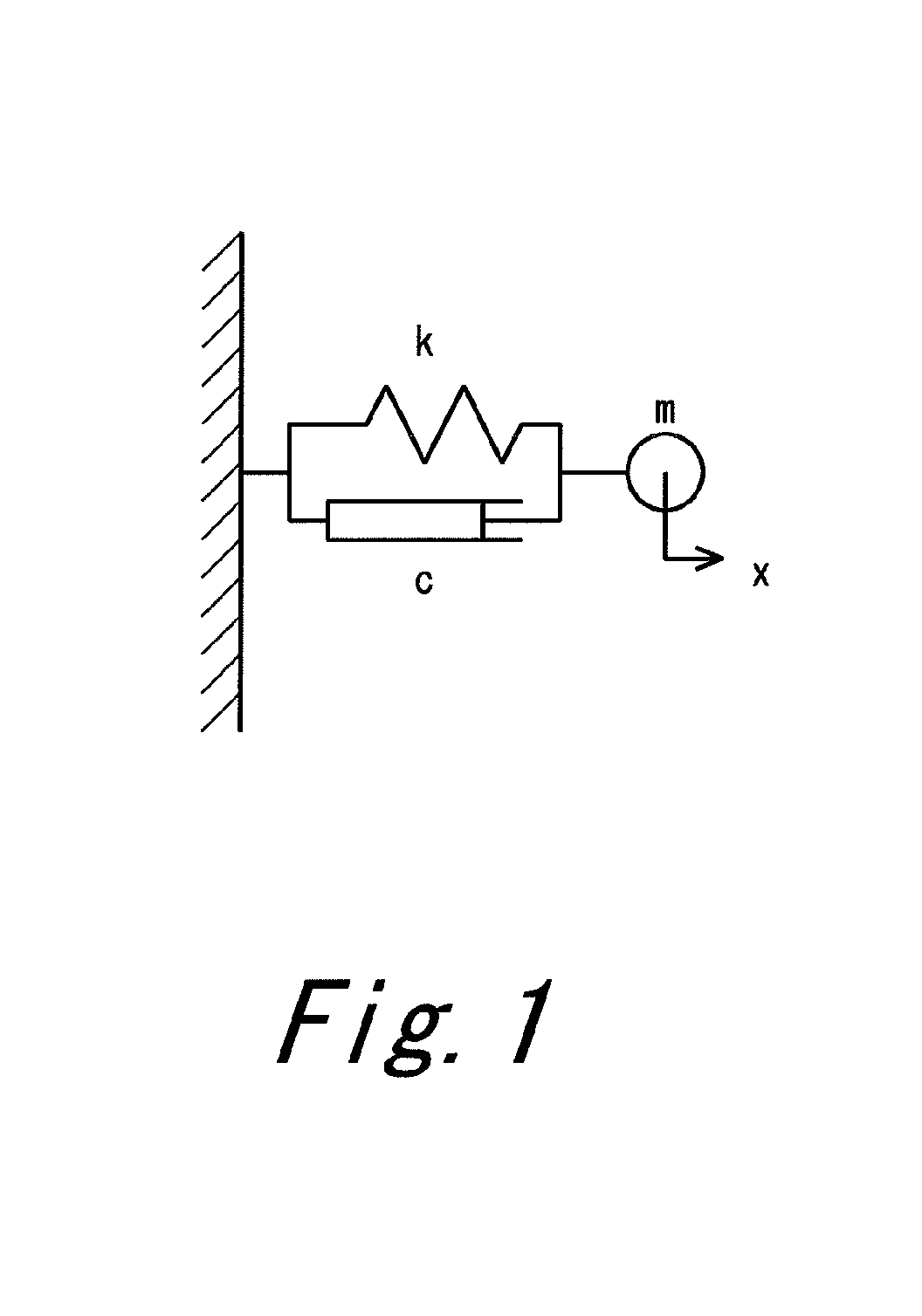
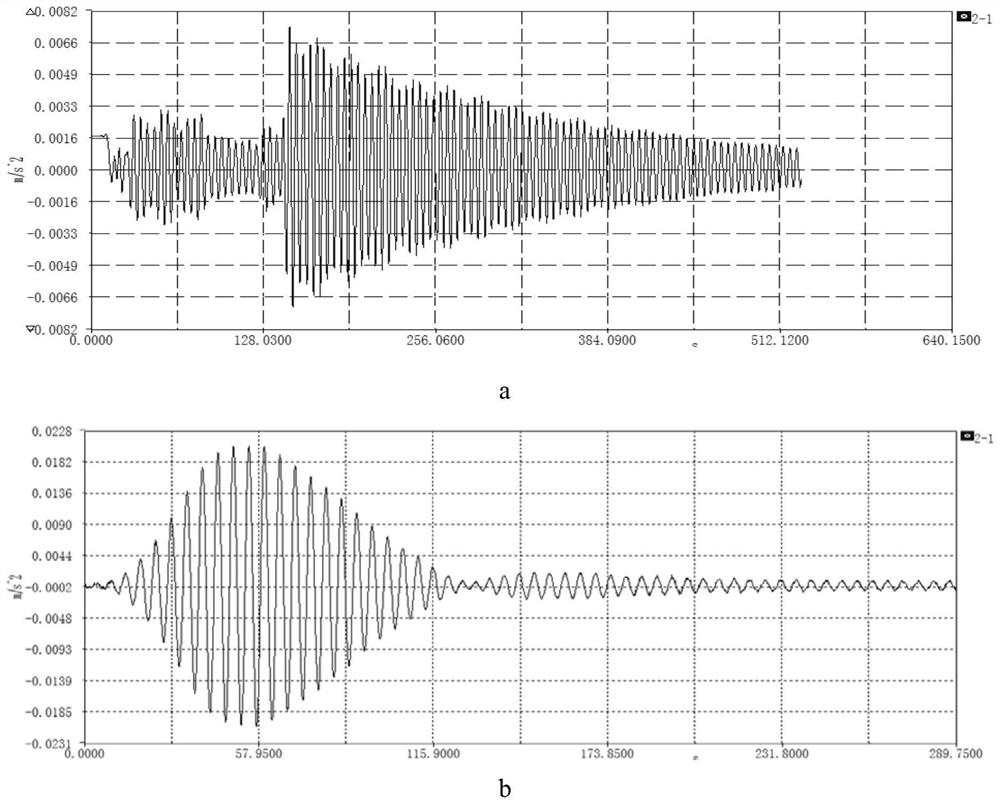
The modal damping ratio can be determined accurately with proper field tests. The ratio varies from 0.01 for lightly damped systems to 0.15 or more for highly damped systems. When experimental data is not available, use data from a similar class of systems to determine the damping properties.
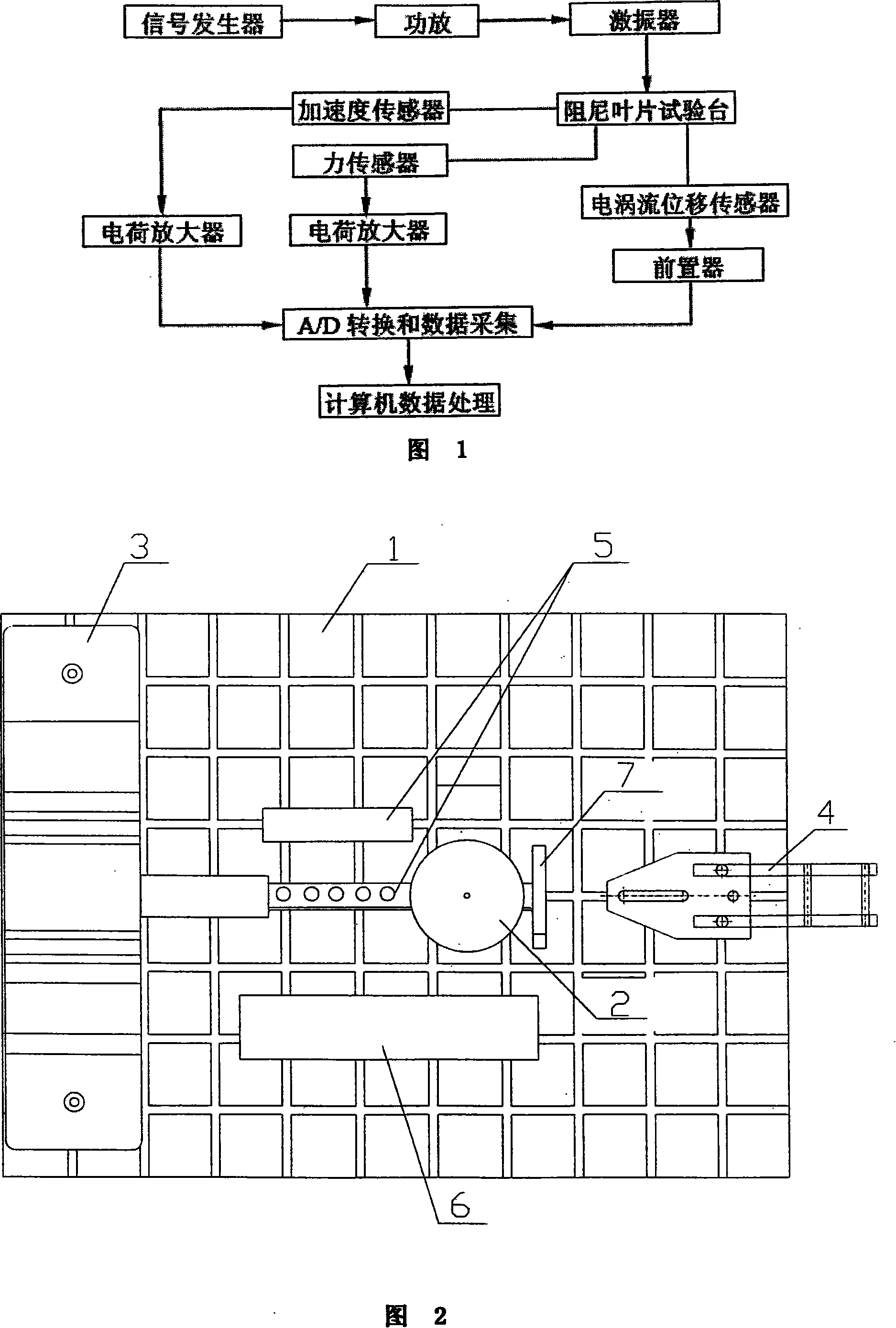
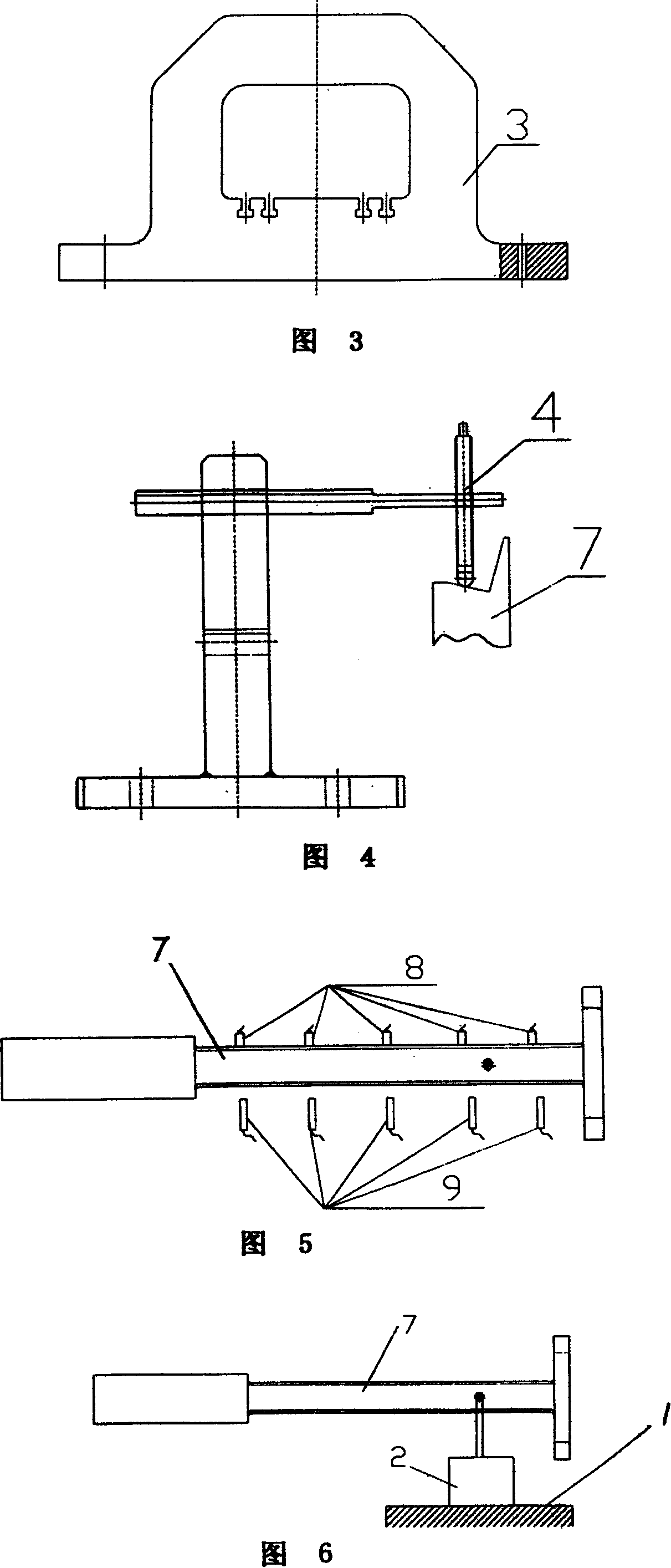
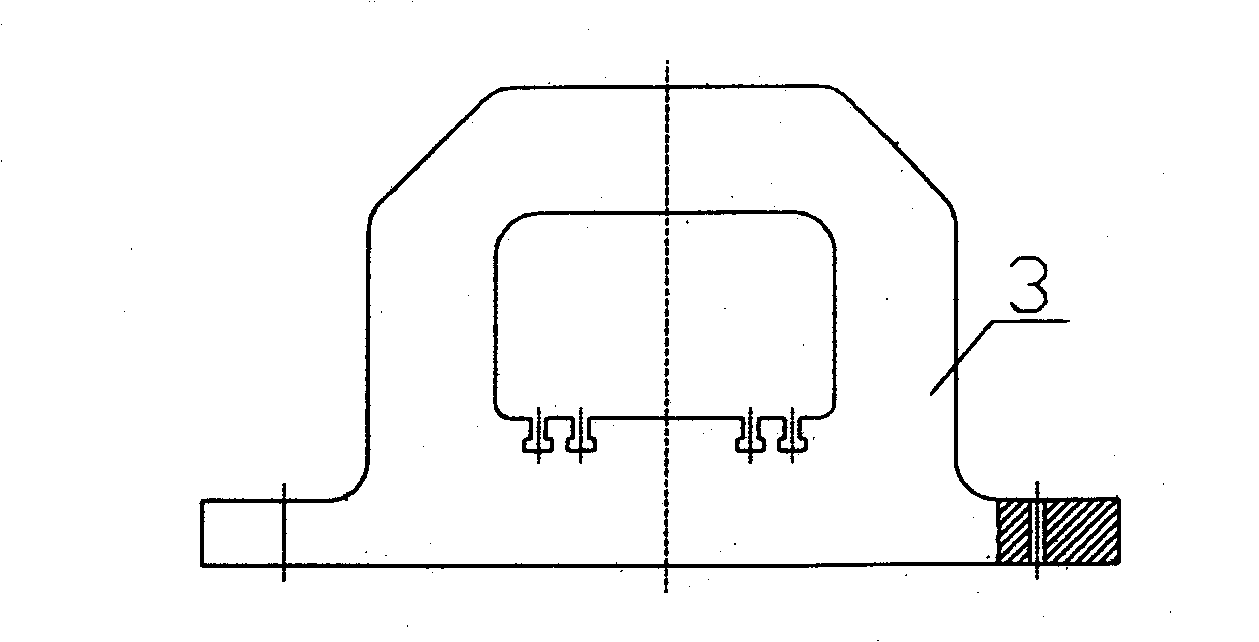
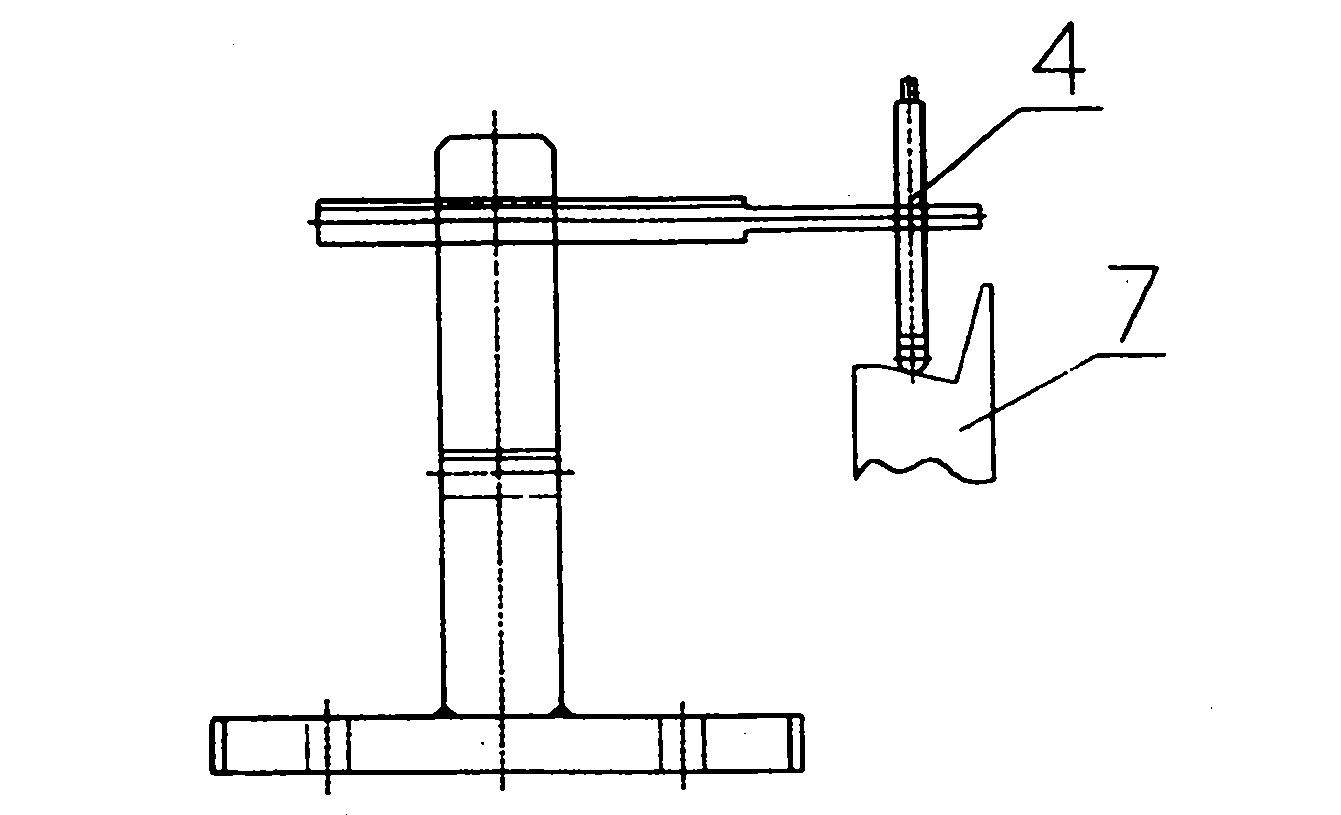
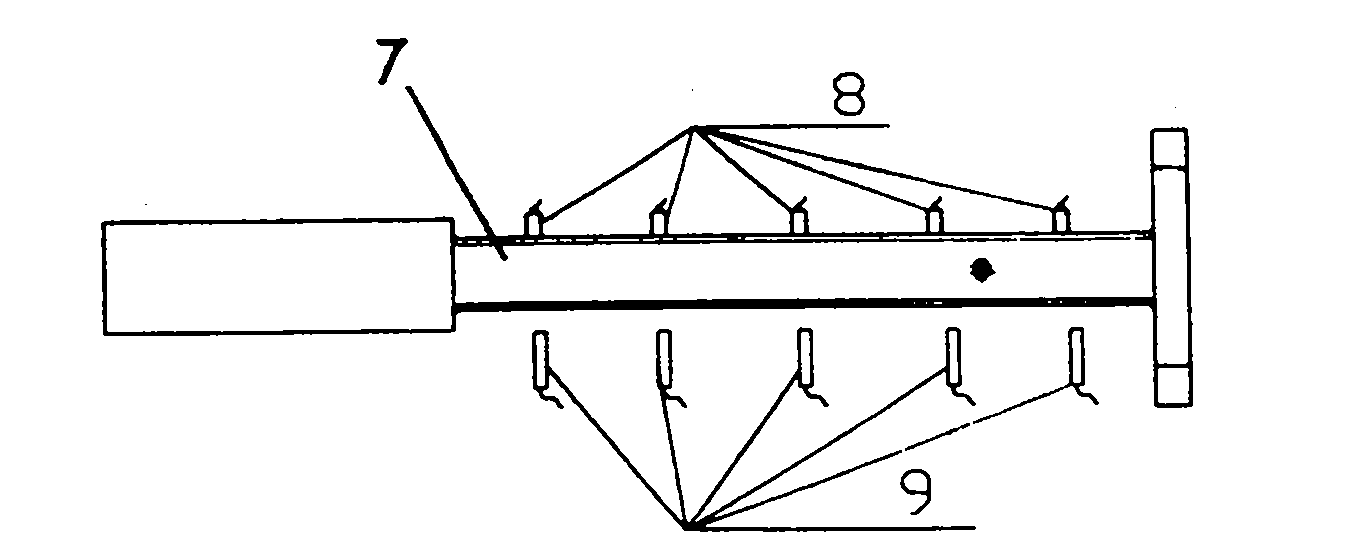
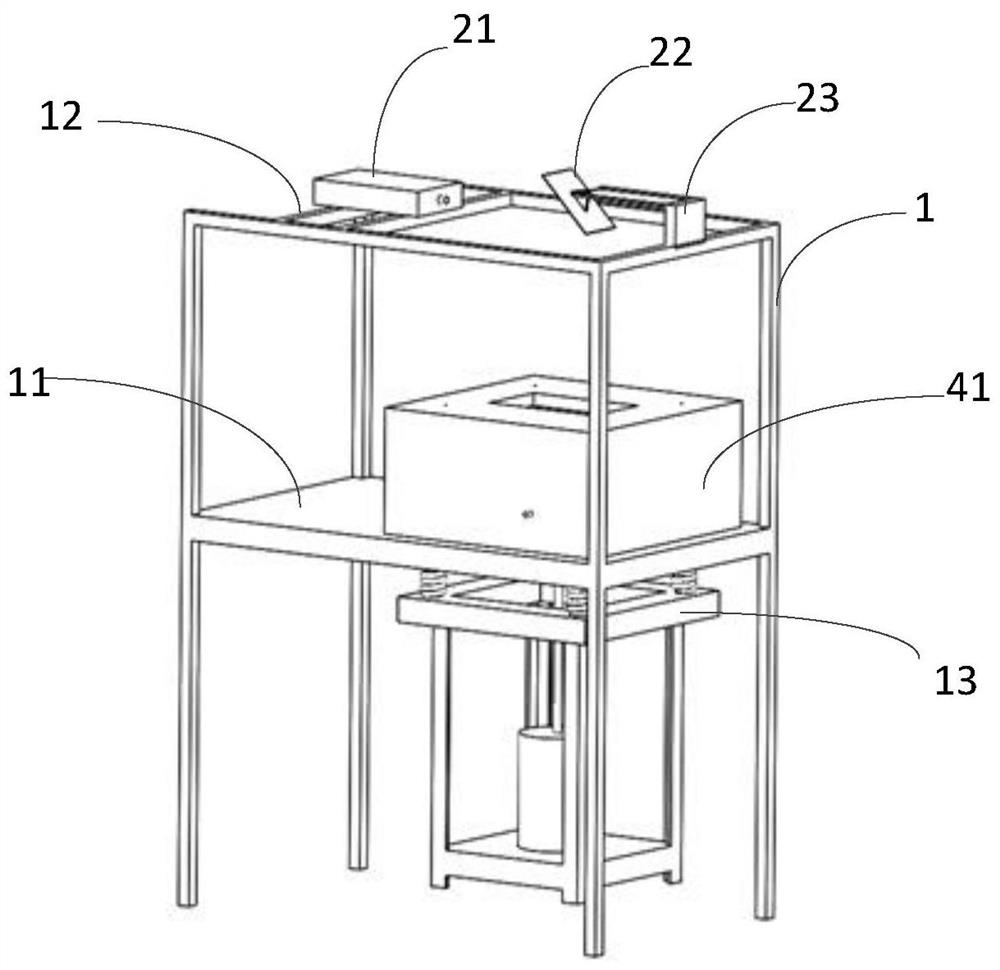
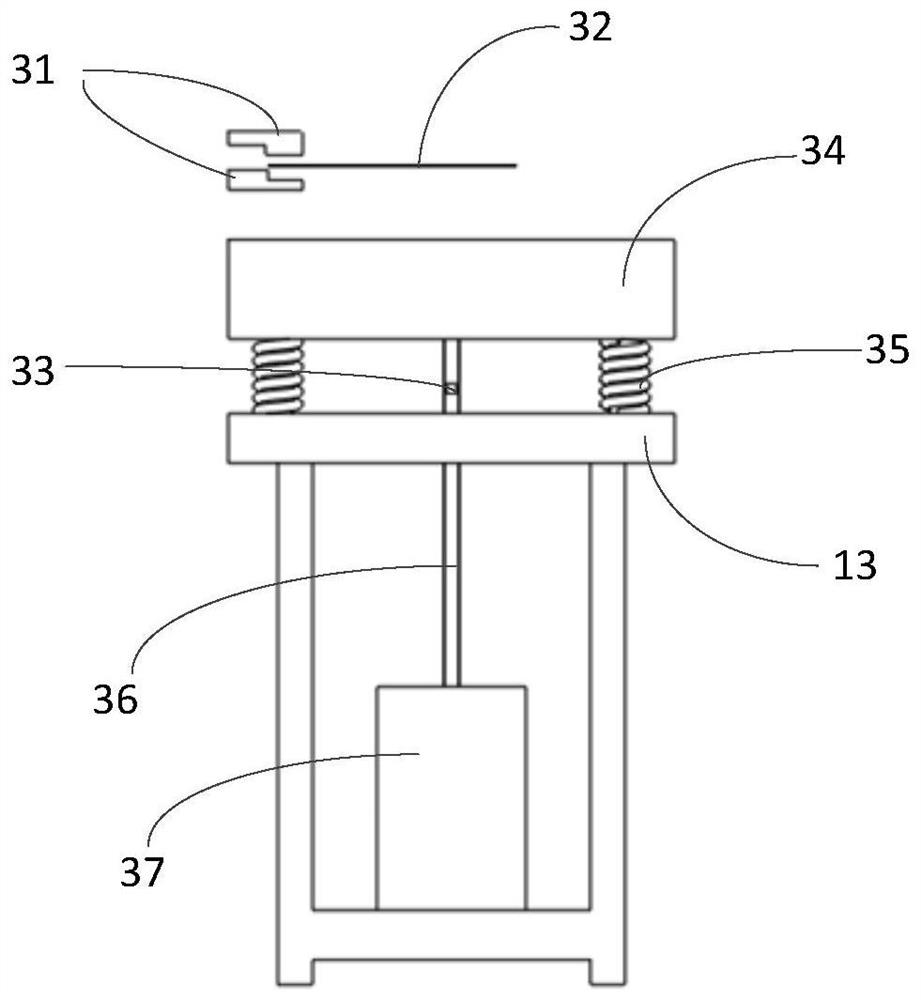
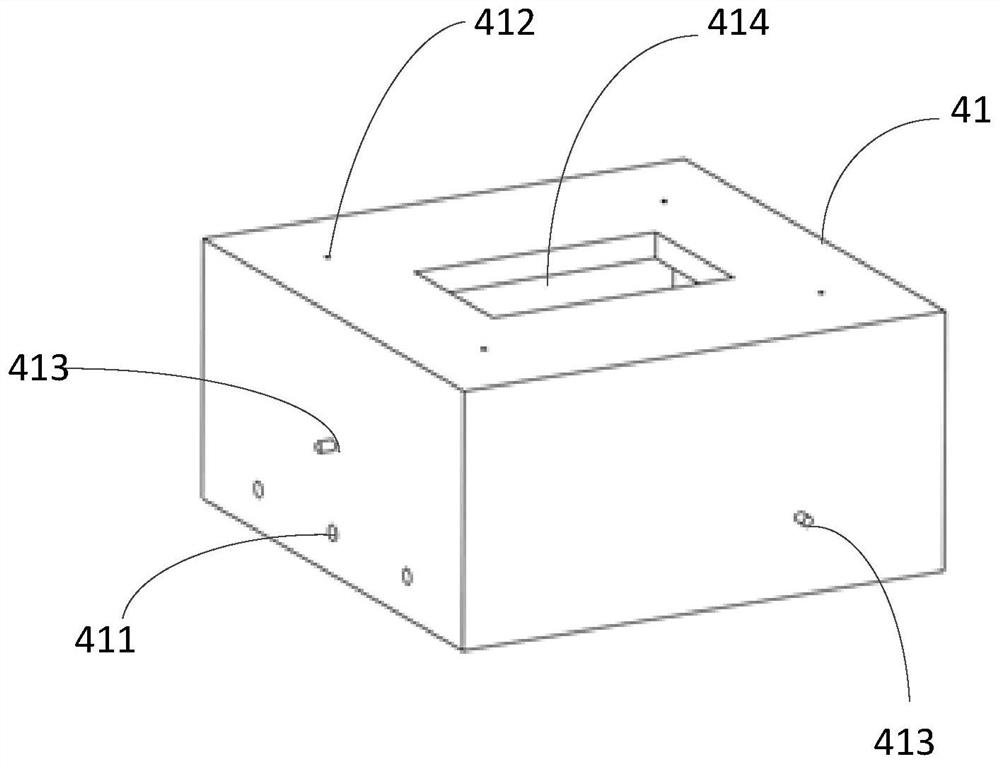
Turbine blade vibration test method and device
ActiveCN101122541AProven Vibration MechanismReasonable designVibration testingElasticity measurementMathematical modelEngineering
The invention discloses a steam turbine blade vibration test method and device. The method steps are that firstly, a blade force vibration status is analyzed and a blade excitation force mathematical model is built. Secondly, an excitation force is imposed on the blade by a vibration source. The frequency of the excitation force is regulated until resonance is generated between the blade and the vibration source. Vibration characteristics parameters values of the blade under the excitation force are measured. Thirdly, blade damping characteristics parameters, including modal damping ratio, damper contact stiffness and blade dynamic stress, are worked out according to the vibration characteristics parameters values. The device includes a test bed, a blade clamping mechanism arranged on the test bed, an excitation generator, a vibration parameter detector and a data processing system. The excitation vibration generator is fixed on the test bed. The excitation vibration head of the excitation vibration generator is fixed with the blade. Corresponding to the blade, the vibration parameter detector transforms the vibration signals of the blade into electric signals, which are input into the data processing system. The invention proves the vibration mechanism of the damping blade. A calculation model of the damping blade is constructed through the test parameters. Experience design is terminated. The blade design is standardized to step into a scientific design orbit.
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD +1
Modal damping ratio rapid calculation method based on pulse excitation response spectrum
InactiveCN106960068AAvoid damageHigh speedDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency spectrumFrequency ratio
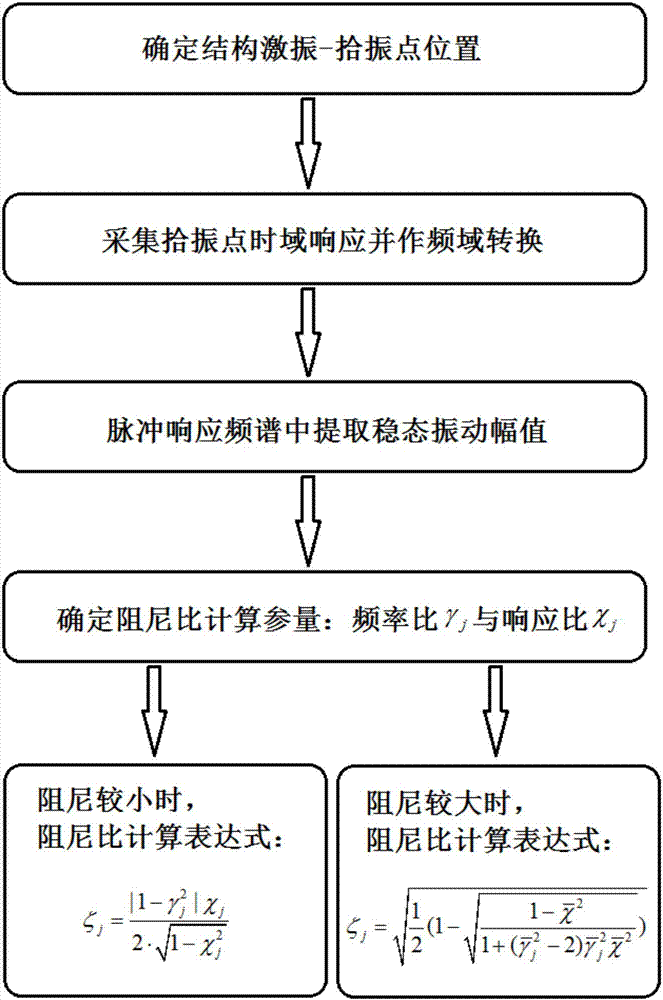
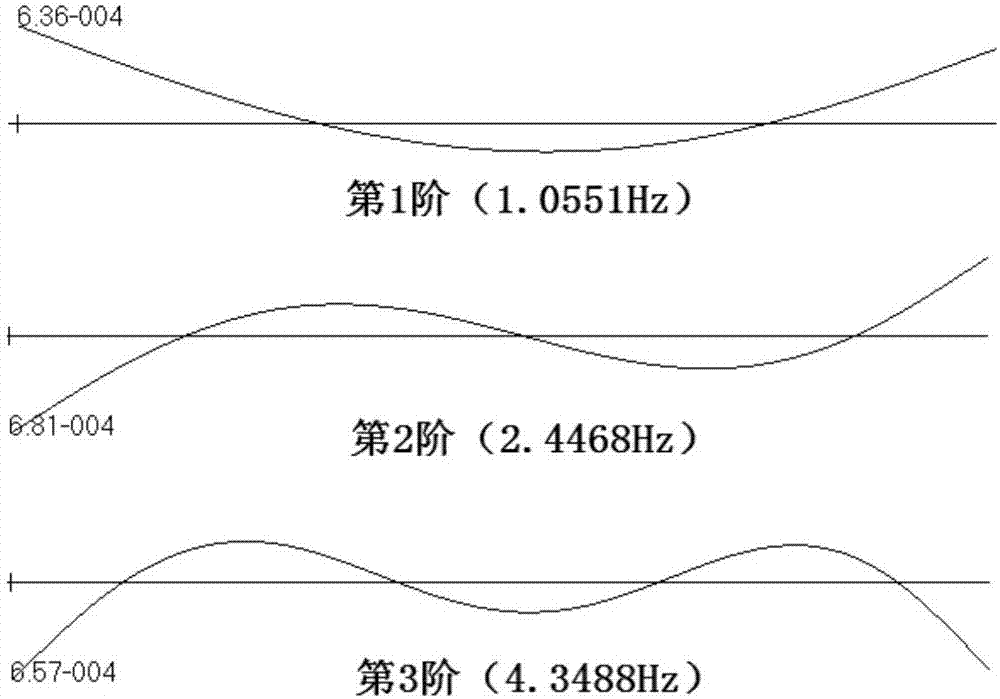
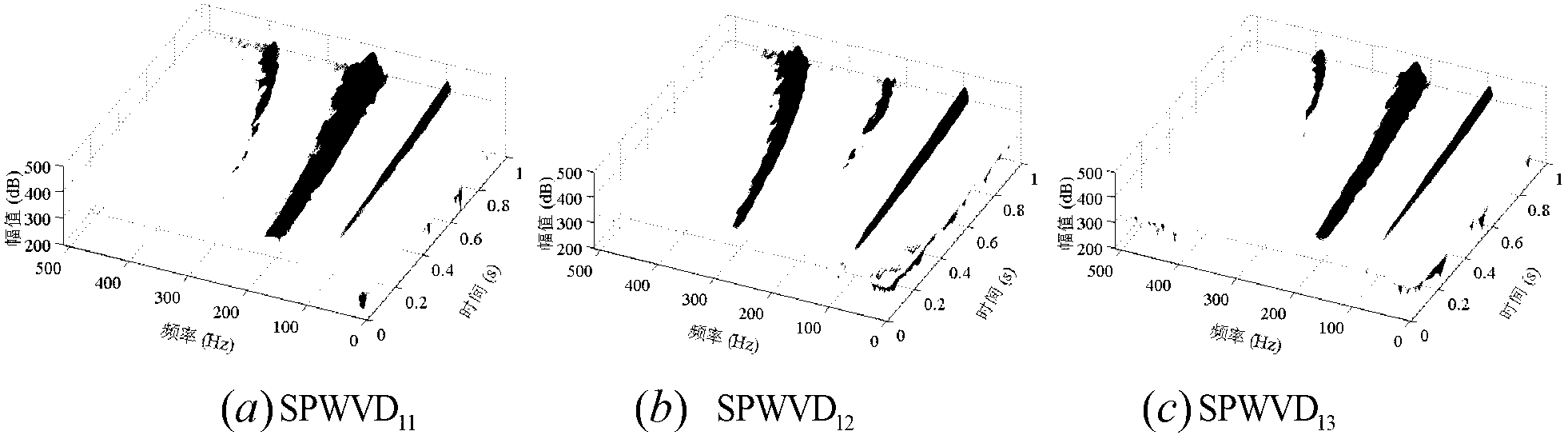
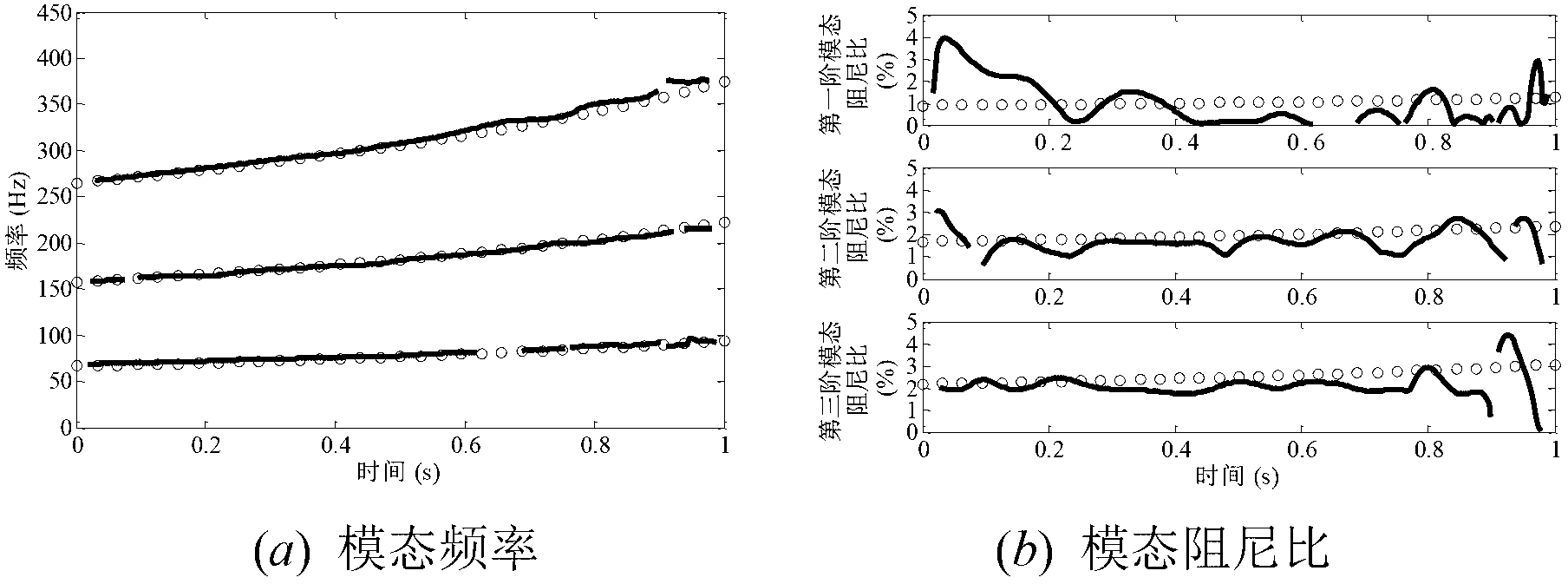
The invention discloses a modal damping ratio rapid calculation method based on a pulse excitation response spectrum. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, determining excitation and vibration pick-up positions of a structure, wherein the excitation and vibration pick-up positions are on a node and a nodal line adjacent to a modal shape, and have remarkable responses under various test modal shapes; recording a vibration pick-up point response signal by a signal acquisition device, and performing discrete Fourier transform to obtain a response spectrum; extracting corresponding responses under a resonance (or peak) frequency an adjacent frequency thereof on the basis to obtain a stable response amplitude; and lastly, calculating relevant parameters such as a frequency ratio and a response ratio in order to realize identification of a modal damping ratio of the structure. Through adoption of the method, the technical problems that semi-power points are difficult to find accurately in a conventional semi-power method, a frequency response function needed for calculating the modal damping ratio cannot be acquired sometimes in a frequency domain method since certain excitation time domain signals are difficult to measure directly, and transient components are attenuated incompletely, operations are complicated and the like in response under contact type excitation in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
Time frequency domain time varying structure modal parameter identification method based on time varying common demominator model
ActiveCN102982196AReduce engagementEasy to useSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainStructural dynamics
The invention relates to a time frequency domain time varying structure modal parameter identification method based on a time varying common demominator model and belongs to the technical field of structural dynamics. Firstly, structural dynamics response signals measured and obtained by aircraft or spacecraft structures with the time varying characteristics under the work situations are analyzed in a time frequency mode to obtain a time relative power spectral function of non-parametric evaluation corresponding to time varying structures. Then, the time varying common demominator model is used as a parametric model of the time varying structural dynamics to evaluate to-be-evaluated parameters of the time varying common demominator model through a least squares methods of the time domain. Finally, the evaluated to-be-evaluated parameters of the time varying common demominator model is utilized to calculate the model frequency and the model damping ratio corresponding to the time varying common demominator model. The time frequency domain time varying structure modal parameter identification method based on the time varying common demominator model is suitable for model parameters recognition of time varying structure in the field of aircraft and spacecraft engineering application and has the advantages of being simple and convenient to use. Furthermore, users are low in participation degree.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method, device, and system for modal damping identification
ActiveCN105426644AImprove recognition accuracyGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsDamping ratioModal damping ratio
The invention discloses a method, a device, and a system for modal damping identification. The method for modal damping identification comprises steps: obtaining amplitude-frequency data of a rotor, and phase-frequency data; according to the obtained amplitude-frequency data, drawing an amplitude-frequency curve, determining a critical rotation speed point; according to the obtained phase-frequency data, drawing and fitting a phase-frequency curve, to obtain a fitted phase-frequency curve equation; according to the fitted phase-frequency curve equation, calculating the slope of the tangent line of the critical rotation speed point in the phase-frequency curve; and according to the calculated slope, obtaining a modal damping ratio. The method for modal damping identification conveniently and accurately determines critical rotation speed from the amplitude-frequency curve. By using the slope of the tangent line of the critical rotation speed point in the phase-frequency curve and the damping ratio are in a reciprocal relationship, the modal damping ratio is identified, so as to conveniently, rapidly, and accurately obtain the modal damping ratio.
Owner:CHINA AVIATION POWER MACHINE INST
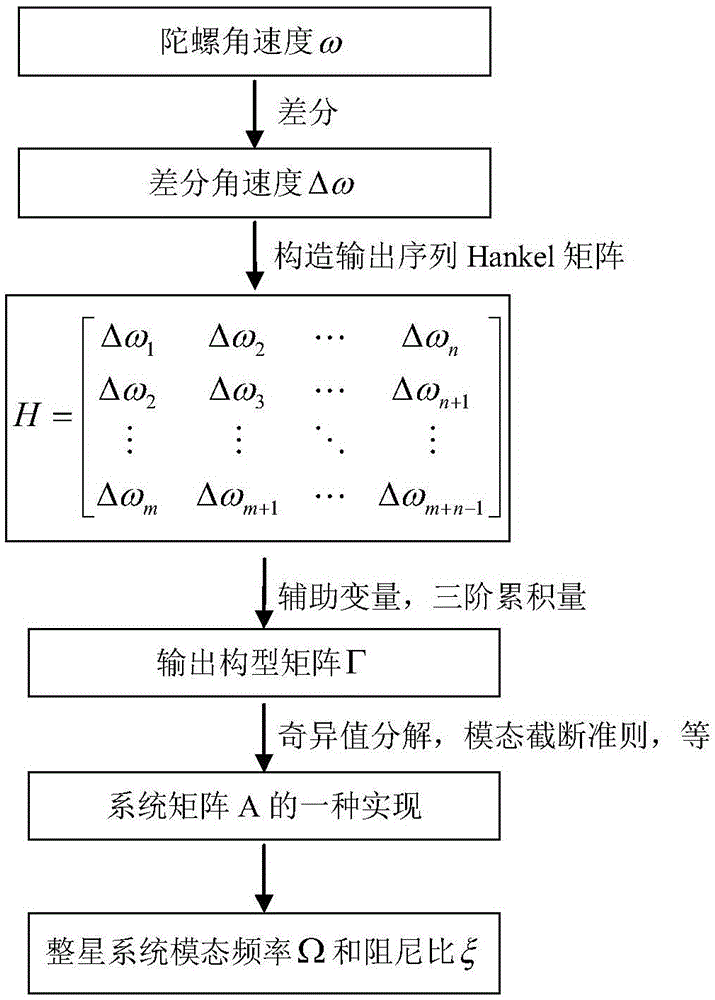
Identifying method for modal parameter of flexible satellite capable of restraining gyro noise influence
ActiveCN105157728ALow costReduce design difficultyMeasurement devicesAngular velocityModal damping ratio
The invention provides an identifying method for a modal parameter of a flexible satellite capable of restraining gyro noise influence. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing measuring data of a satellite body angular velocity while the satellite flies in an orbit to identify a modal frequency and a modal damping ratio parameter of the whole satellite; approximately regarding the measuring noise of the gyro in a short-term period as two parts, namely, constant drifting and random drifting; and performing differential treatment on the gyro data and utilizing the property of Gaussian noise three-order accumulated quantity constantly being zero to restrain the influences of the two parts of noises on an identifying result. Compared with the prior art, the identifying method for the modal parameter of the flexible satellite capable of restraining gyro noise influence can utilize the measuring data of the gyro on the satellite to perform modal parameter identification and restrain the measuring noise, so that the identification precision of the algorithm is increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINYUE METER FACTORY
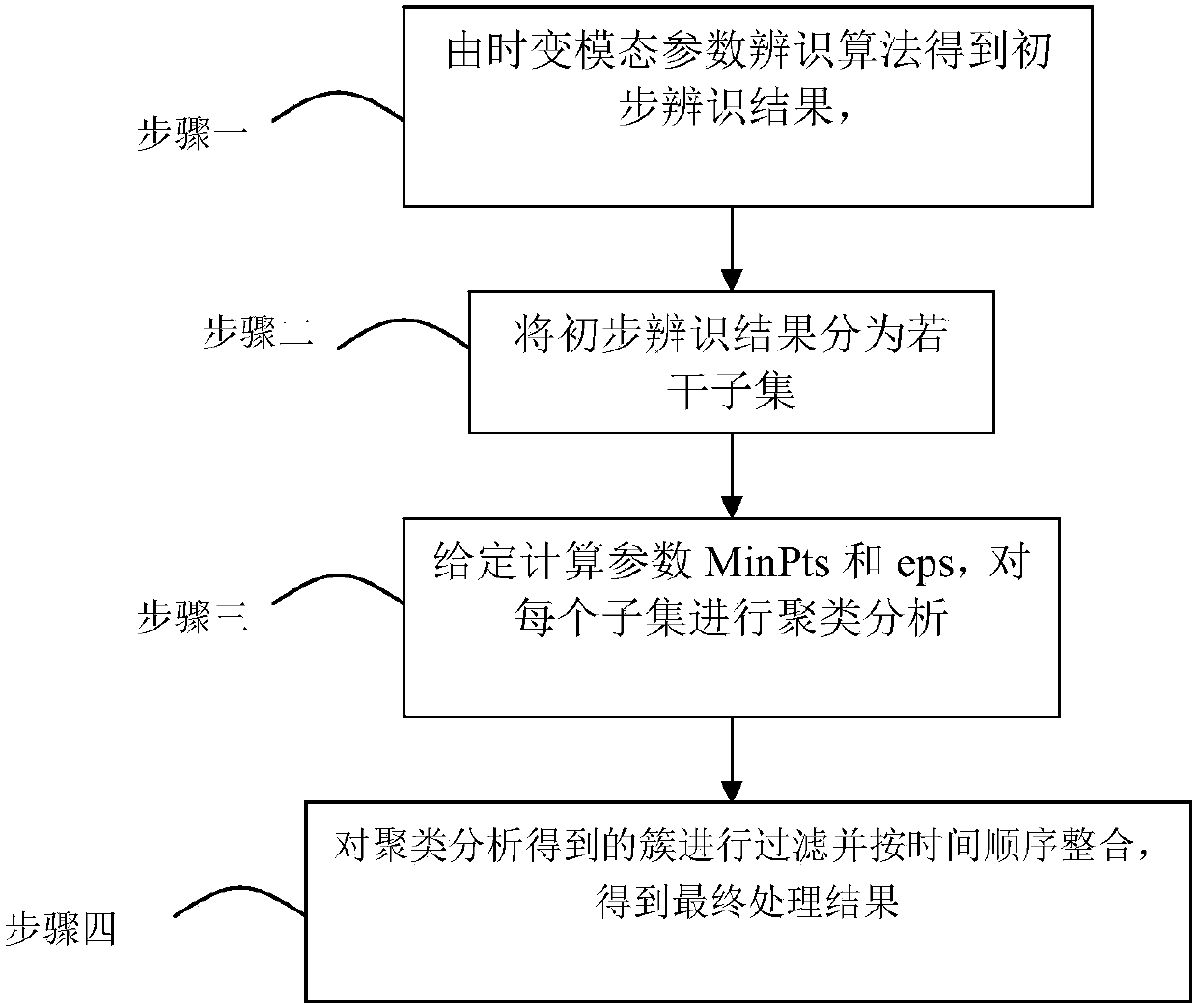
False mode removing method based on density clustering
InactiveCN107609291AImprove recognition accuracySimple calculationSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainStructural dynamics
The invention provides a false mode removing method based on density clustering and relates to a false mode parameter removing method. The problems are solved that order determination of a time domainmethod model is not easy and a false mode exists in an existing time varying mode parameter identification method and noise interference exists in a time-frequency domain method so that the false mode can be mingled in an indemnification result. The method comprises the steps that 1, the time varying mode parameter identification method is adopted for identifying an engineering structure, and a primary identification result is obtained and comprises mode frequency, mode damping ratio and corresponding time vectors; 2, a matrix is averagely divided into N subsets according to data length; 3, adensity clustering algorithm is adopted for conducting clustering analysis on each subset Di to obtain M clusters; 4, the obtained M clusters are filtered, and the identification result of which thefalse mode is removed is obtained. The false mode removing method based on density clustering is applied to the technical field of structural dynamics.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Dihedral angel optimization method capable of improving wing layout aircraft transverse course flight quality
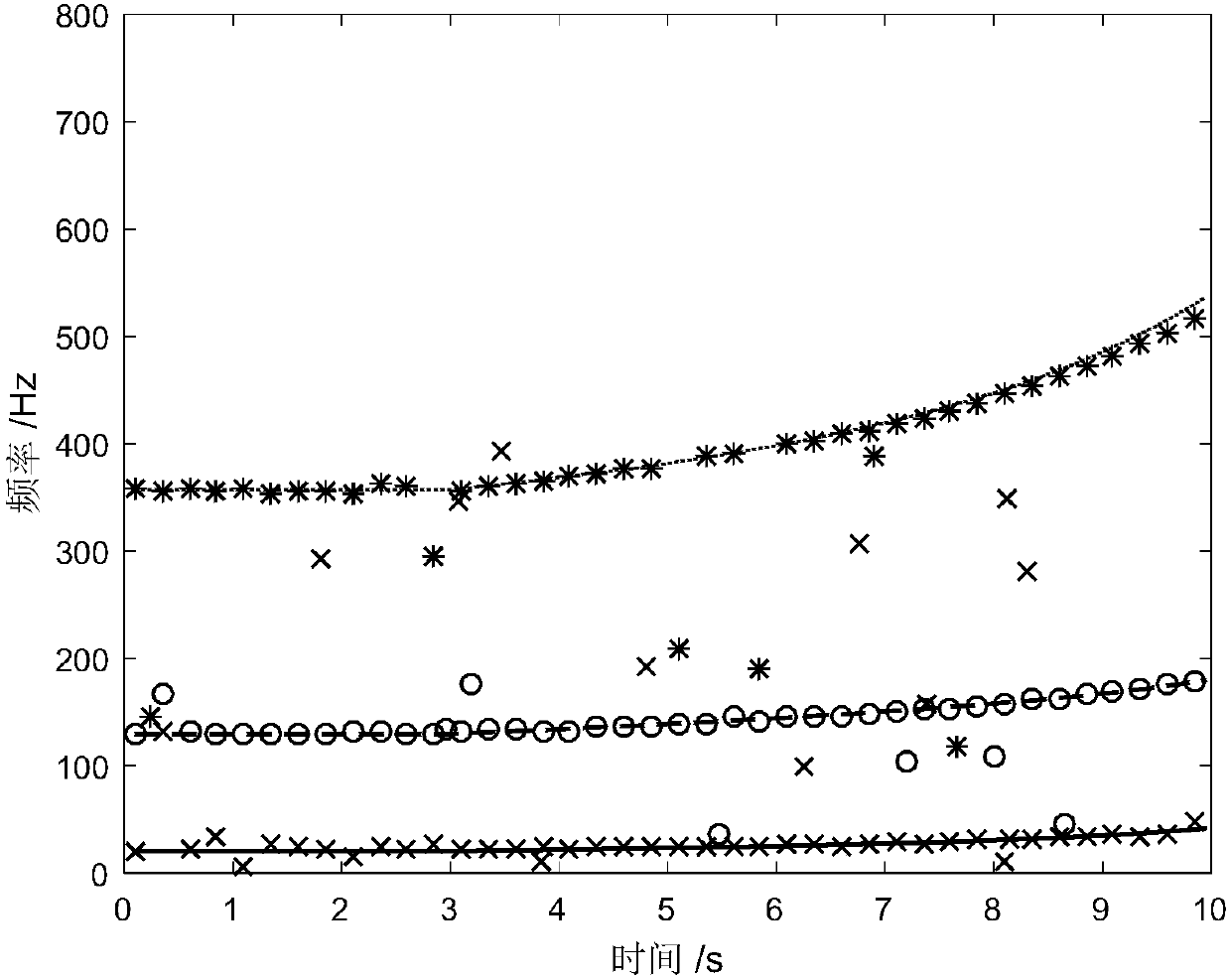
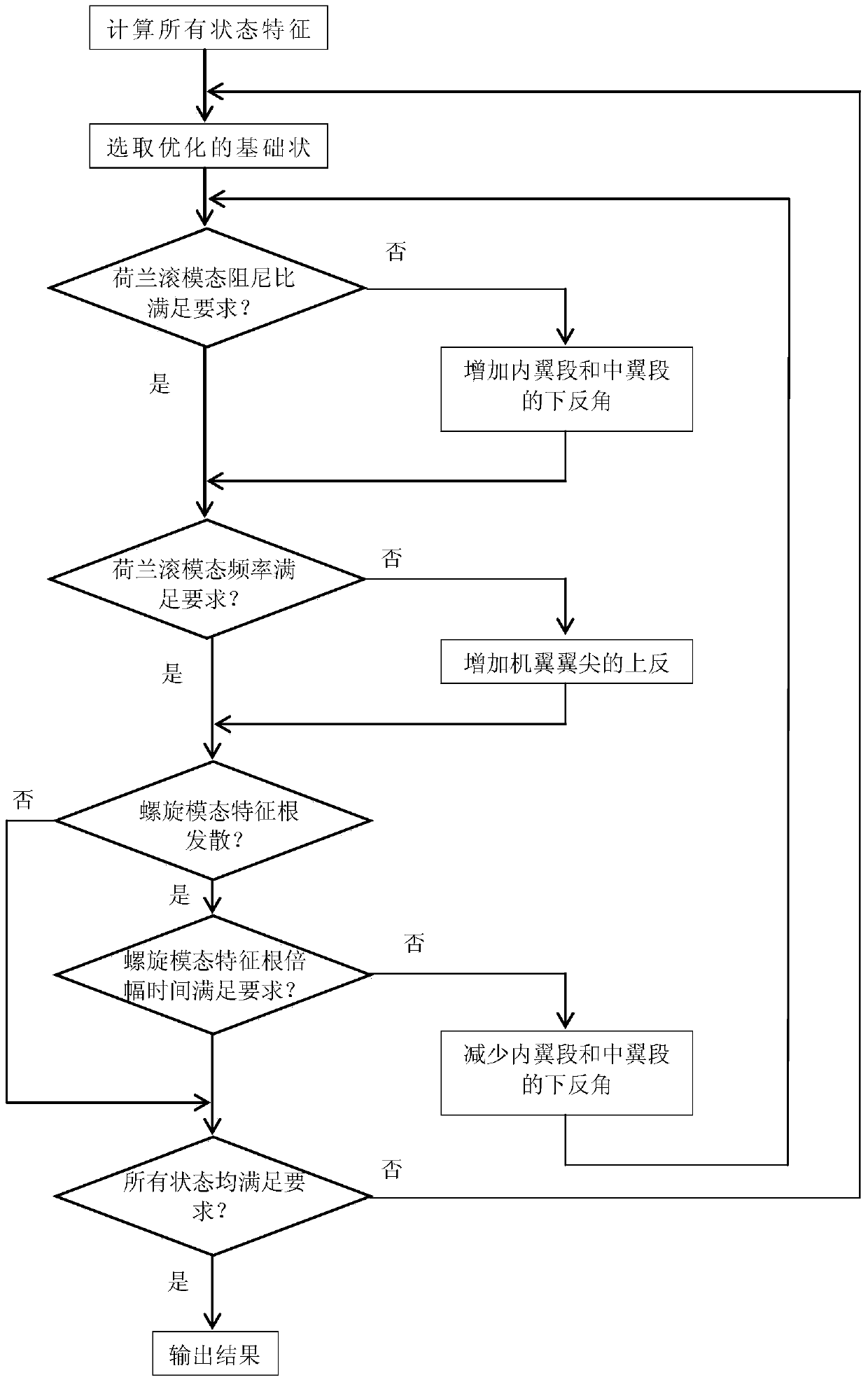
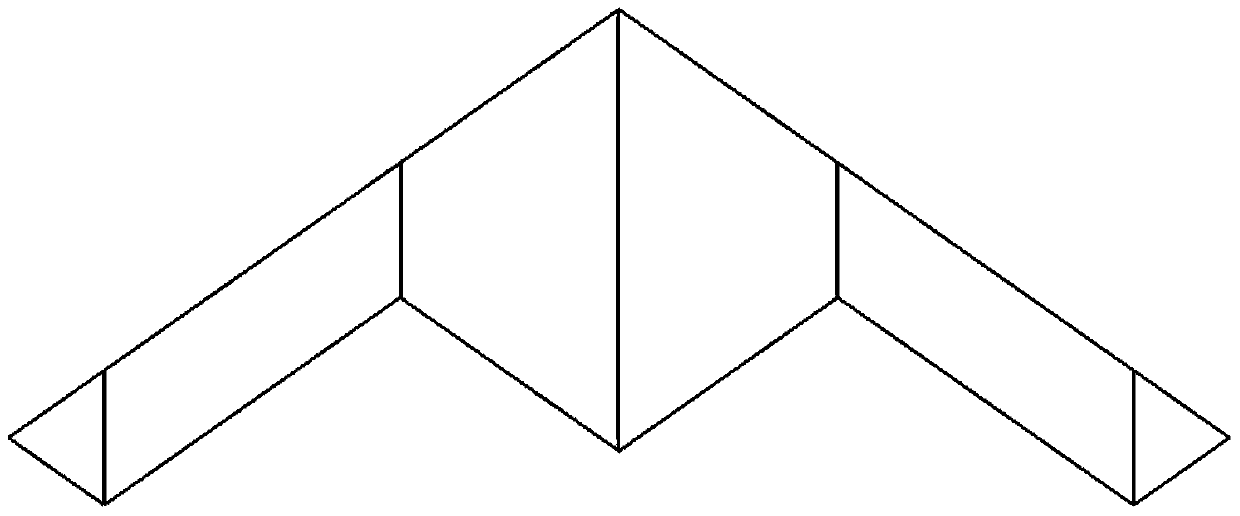
The invention discloses a dihedral angel optimization method capable of improving the wing layout aircraft transverse course flight quality. The method comprises the following steps that step 1, the worst state is obtained; step 2, the modal damping rate of a Dutch roll is adjusted; step 3, the modal frequency of the Dutch roll is adjusted; step 4, whether the spiral characteristic root of the aircraft is diffused or not is judged; step 5, through the four steps, the structure of each wing is changed and according to the new structure of each wing, the step 1 is repeated and the worst state of each wing is obtained again. The modal frequency and the modal damping rate of the Dutch roll of the wing layout aircraft are obviously improved, so that the transverse course flight quality of the aircraft is improved. The requirements for a flight control system of the wing layout aircraft are reduced and the safety of the aircraft is improved; according to the aircraft with the requirement for invisibility, serious influence on the RCS of the aircraft is not caused and the invisibility performance of the aircraft is guaranteed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
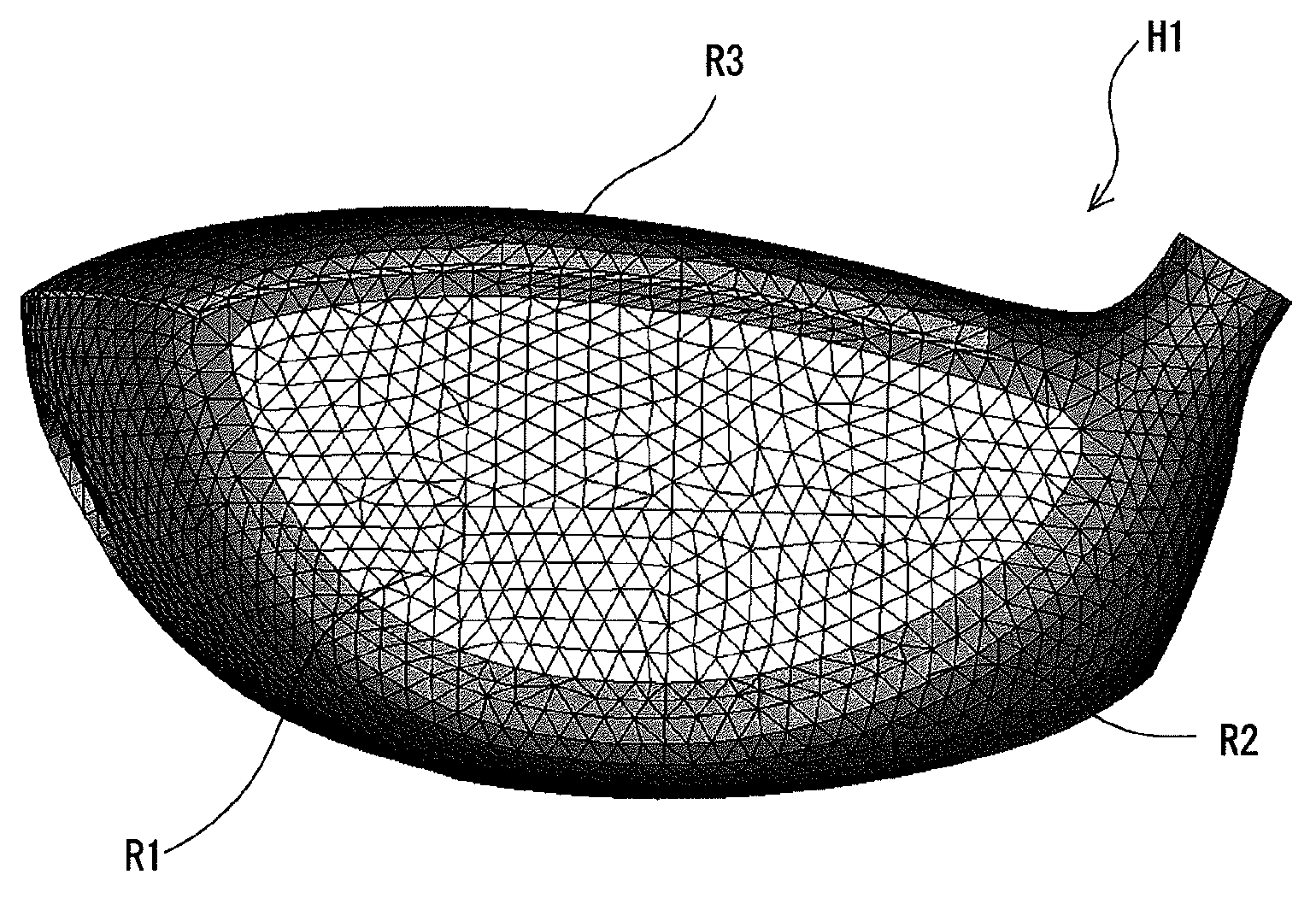
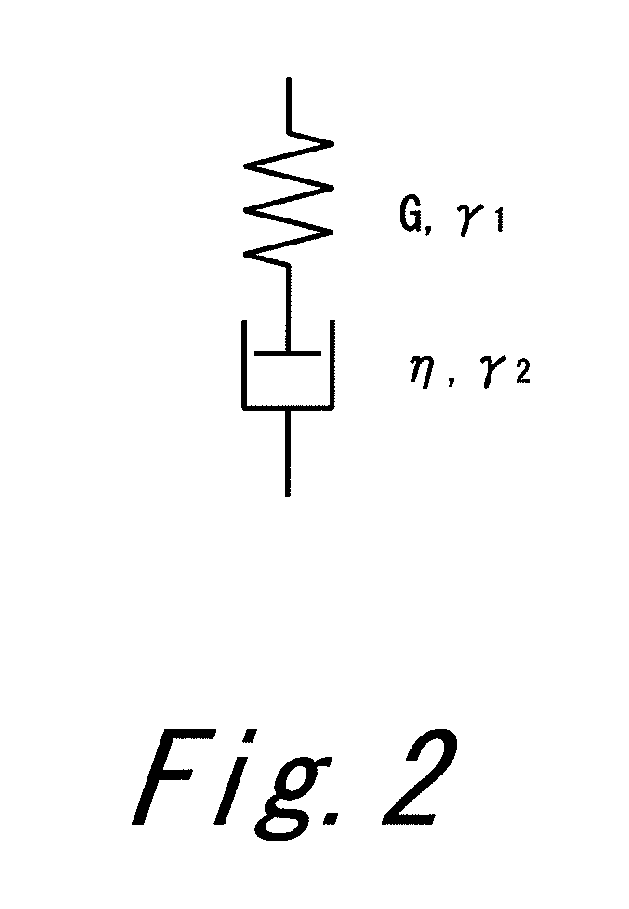
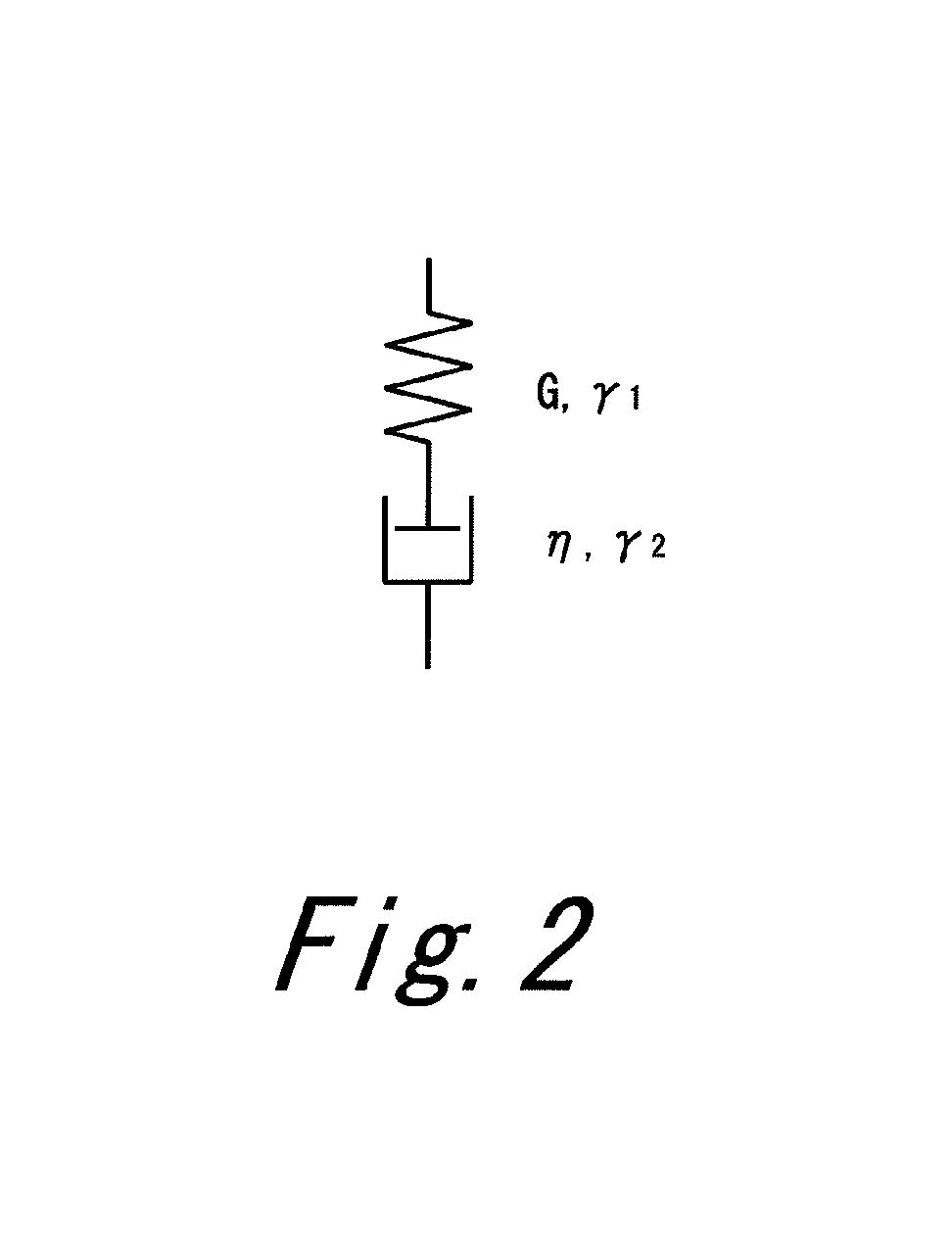
Method for predicting modal damping ratio of composite head
ActiveUS20120278048A1Precise ratioComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationMulti materialDamping ratio
A prediction method according to the present invention is a method for predicting a modal damping ratio of a composite head including two or more kinds of materials including a first material and a second material. The method includes the steps of: presuming at least a coefficient Px of a generalized Maxwell model M1 in the first material using a known material damping ratio ζ1; obtaining a calculation model of the head using the generalized Maxwell model M1; and calculating the modal damping ratio of the head based on analysis of the head using the calculation model. Preferably, the Maxwell model is further used also for the second material. Preferably, the method further includes the step of presuming a coefficient Py of a generalized Maxwell model M2 in the second material using a known material damping ratio ζ2.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
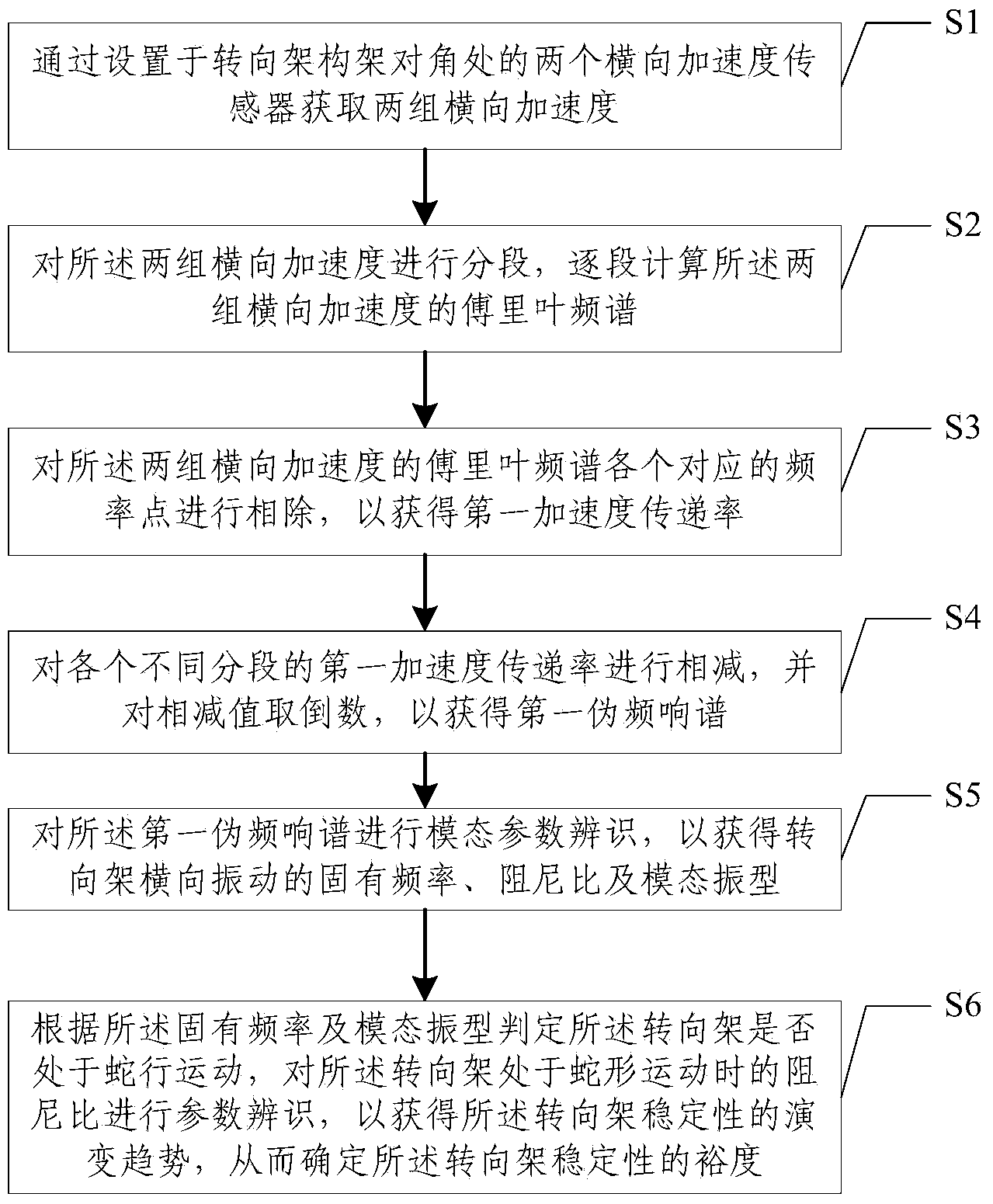
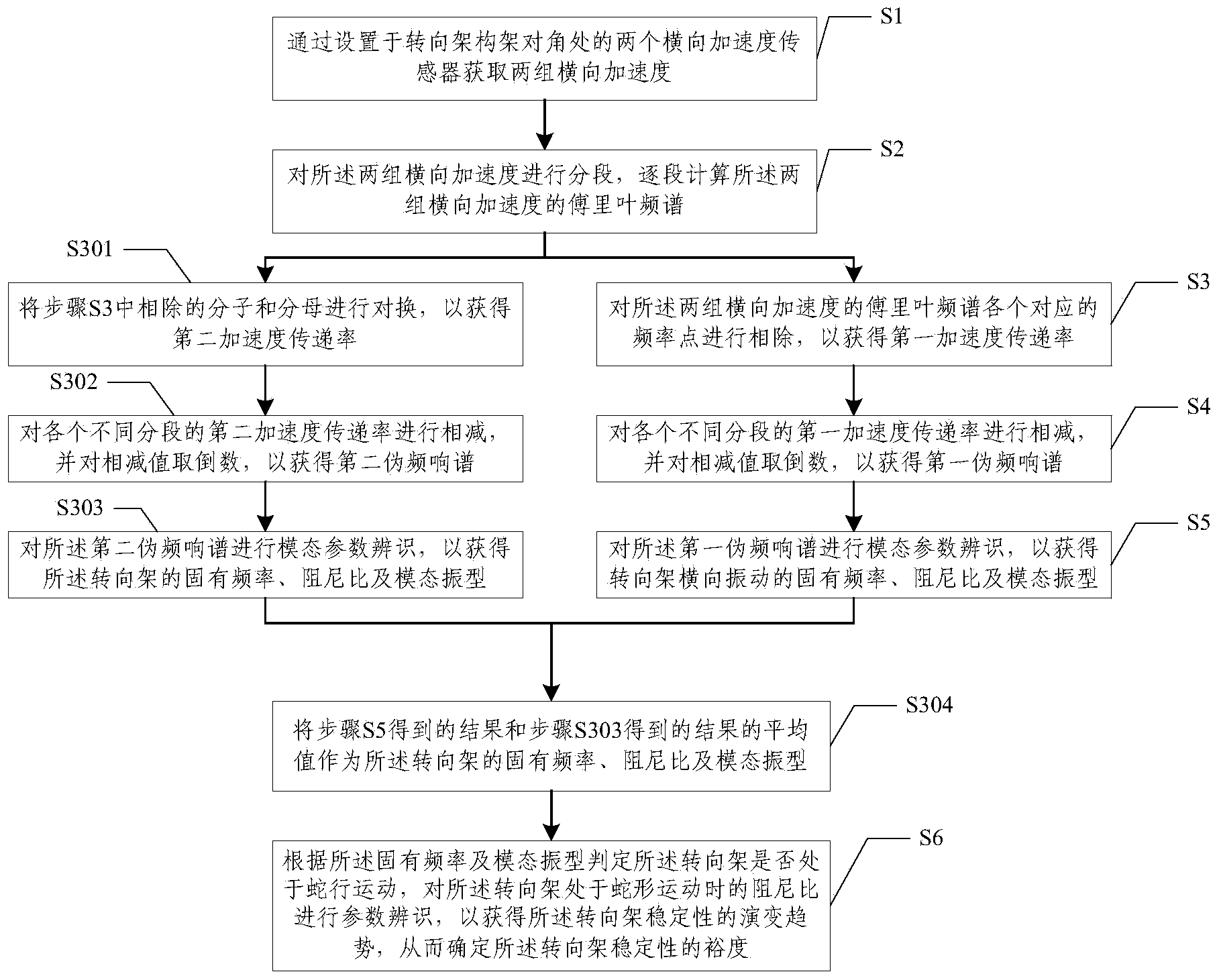
Method and device for judging movement stability of railway vehicle bogie
ActiveCN103674582AAvoid difficultiesDetermine the marginRailway vehicle testingBogieElastic vibration
The invention discloses a method and a device for judging movement stability of a railway vehicle bogie, and relates to the technical field of railway vehicles. Through cooperation of steps, in a line operation state, difficulty in recognizing snake movement vibration modal of the railway vehicle bogie is overcome, and long-term evolution trend of a railway vehicle can be acquired to determine allowance of movement stability of the railway vehicle. By the method and the device, interference, of line excitation factors like line irregularity, on recognition of snake movement modal damping ratio of the bogie can be effectively excluded, and interference, of influencing factors like elastic vibration of mounting parts and rotation excitation of rotating parts like a motor and a wheel pair on the bogie, on recognition of the snake movement modal damping ratio of the bogie can be effectively excluded.
Owner:CRRC QINGDAO SIFANG CO LTD
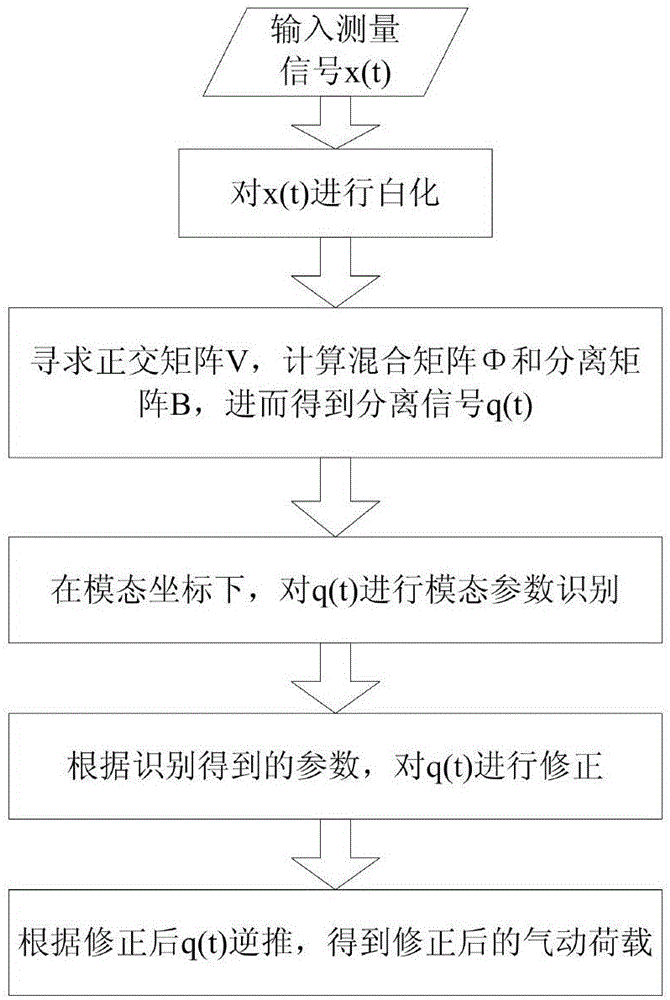
Dynamic calibration method for high-frequency force balance
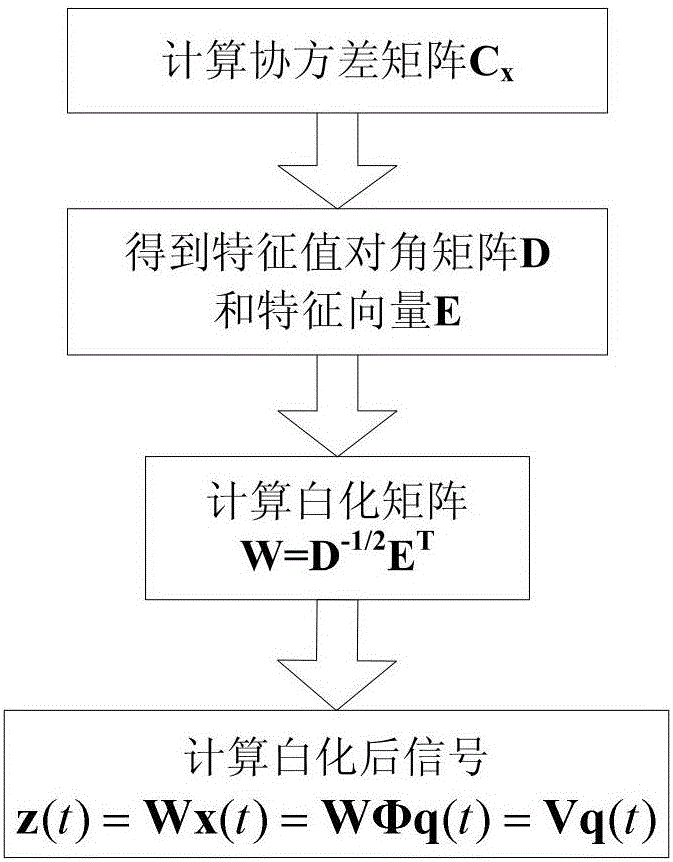
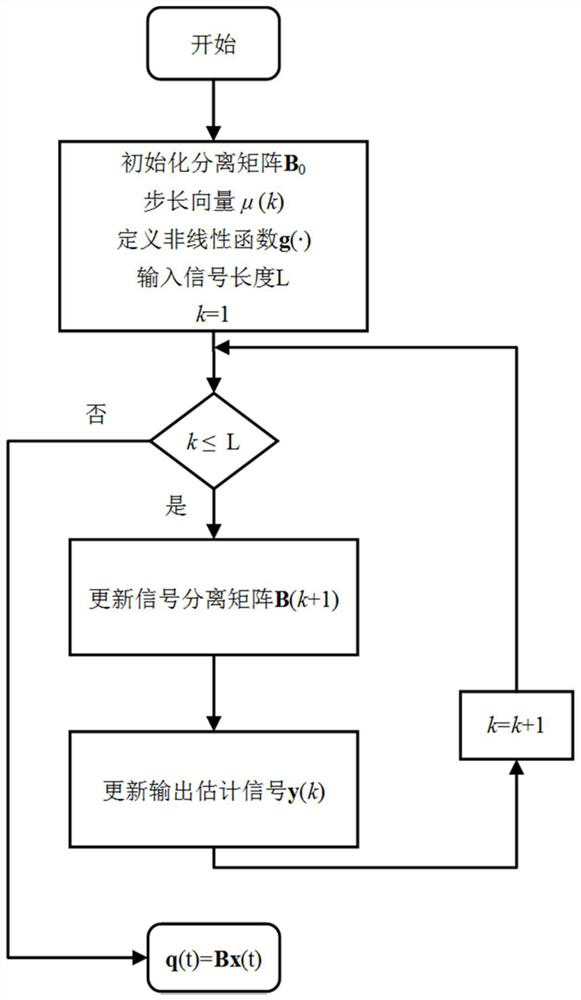
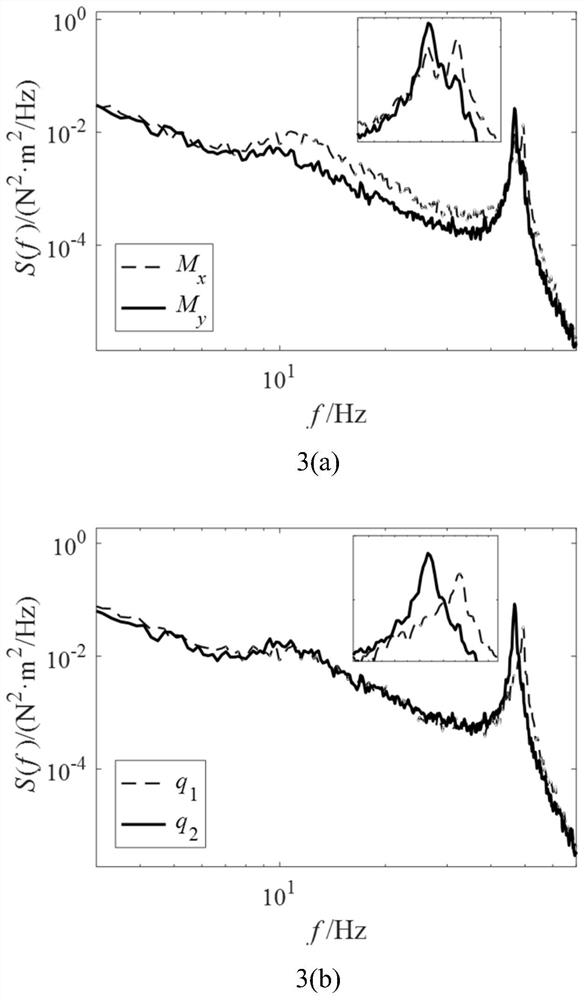
ActiveCN106709460ASimple test stepsEfficient separationAerodynamic testingCharacter and pattern recognitionCurve fittingParametric identification
The invention discloses a dynamic calibration method for a high-frequency force balance, which comprises the steps of performing whitening on a measurement signal x(t) to acquire a whitened signal z(t); seeking an orthogonal matrix V, enabling the whitened signal z(t) to equal to Vq(t), and thus acquiring a separated signal q(t); performing natural frequency and modal damping ratio recognition on the separated signal in modal coordinates; correcting the separated signal according to recognized parameters; and inversely deducing according to the separated signal to acquire a corrected pneumatic load. According to the invention, separation is performed on a coupling signal, and for independent components acquired by separation, natural frequency and modal damping ratio recognition is performed on the separated signals one by one by adopting a curve fitting method through combining aerodynamic characteristics, so that a dynamic amplification effect of a modal coupling system is corrected and eliminated, a real aerodynamic load spectrum density matrix is acquired finally, the reliability of parameter recognition and corresponding HFFB (High-Frequency Force Balance) dynamic signal calibration can be improved to the maximum extent, and an important basis is laid for subsequent accurate estimation for high-rise building prototype wind-induced responses.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Passive damping device for solar panel
ActiveCN104139873APlay a role in dampingSimple working principleCosmonautic power supply systemsModal damping ratioFlange
The invention discloses a passive damping device for a solar panel. The passive damping device is arranged between a solar panel driving mechanism and a panel support. The passive damping device comprises a middle column, an upper flange, a lower flange and a damper. The upper flange and the lower flange are connected with the top end and the bottom end of the middle column. The upper flange is connected with the solar panel driving mechanism. The lower flange is connected with the panel support. The damper is arranged on the outer side of the middle column and is connected with the upper flange and the lower flange. High-damping-characteristic viscous-elastic materials are arranged between an inner shearing piece and an outer shearing piece. The passive damping device is high in reliability, long in service life and easy to mount, the passive damping device can be directly connected between the solar panel driving mechanism and the panel support, a panel structure does not need to be changed in a large-scale mode, the extra modal damping ratio is provided for each stage of vibration mode of a solar panel system, flexibility vibration of the solar panel can decline quickly, and the purpose that satellite platform control accuracy is improved is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
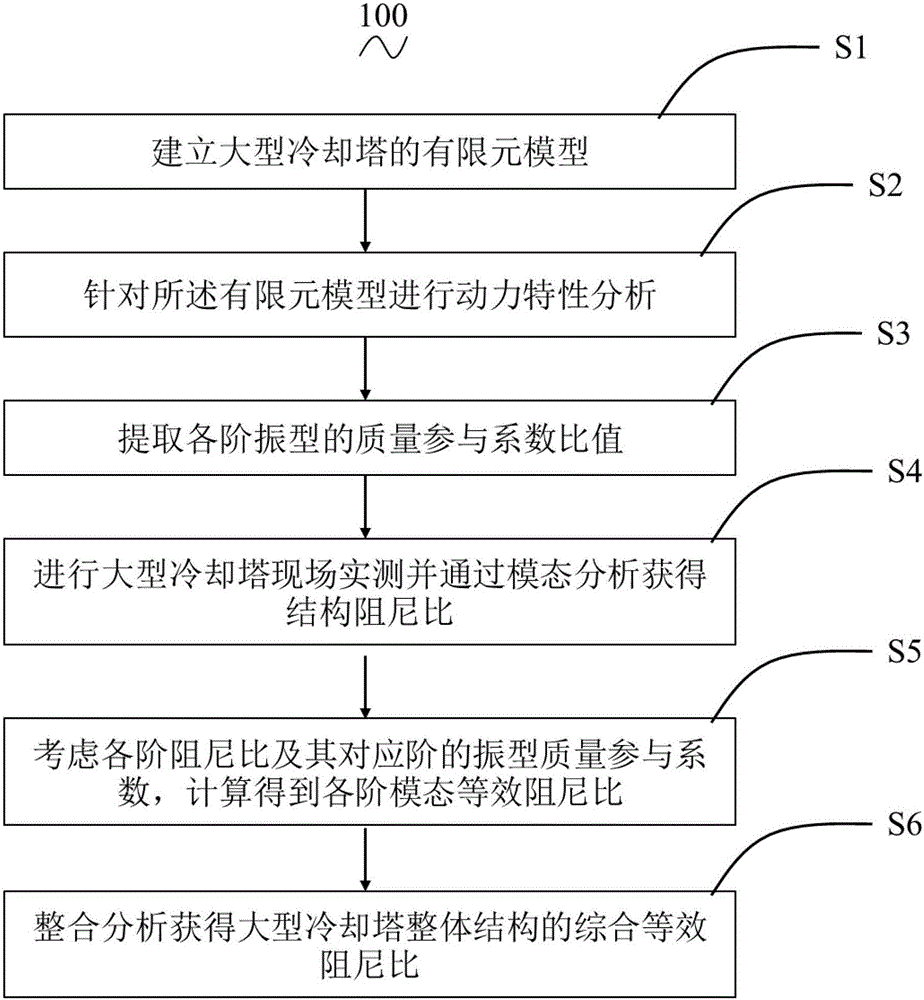
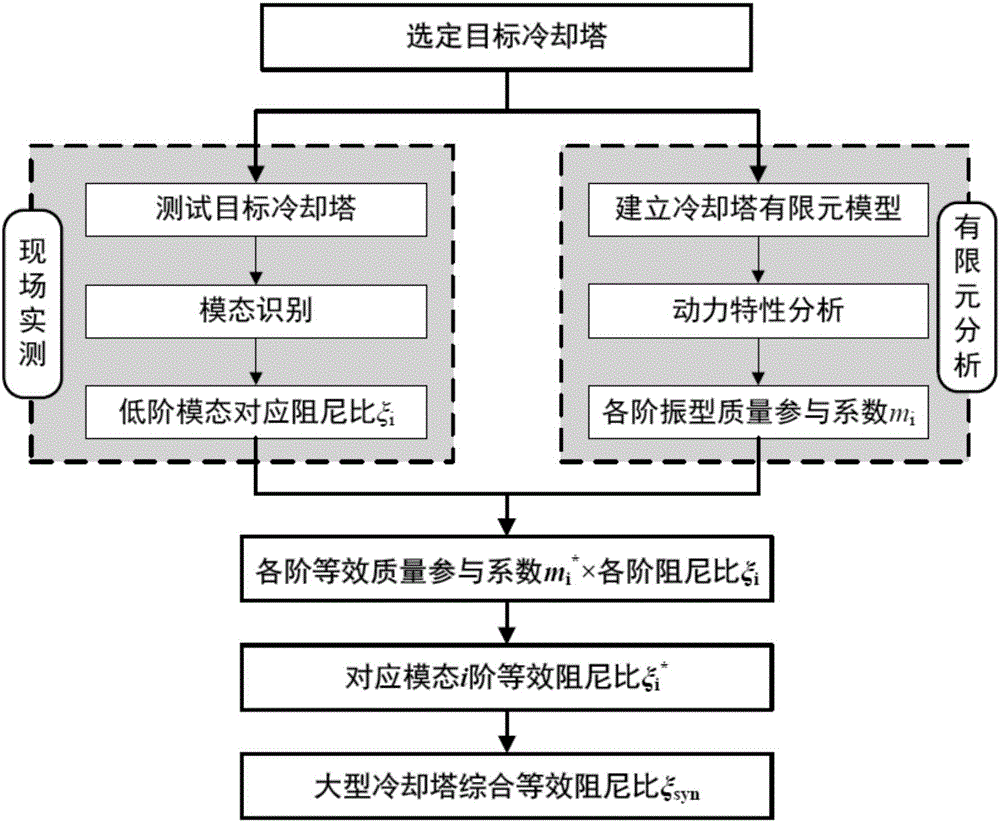
Valuation method for general equivalent damping ratio of large-scale cooling tower based on field measurement
InactiveCN106202817AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelCooling tower
The invention provides a valuation method for a general equivalent damping ratio of a large-scale cooling tower based on field measurement. The valuation method for the general equivalent damping ratio of the large-scale cooling tower based on the field measurement comprises the following steps: a, building a finite element model of the large-scale cooling tower; b, performing dynamic characteristic analysis on the finite element model; c, extracting mass participating coefficient ratios of vibration modes of all orders; d, performing the field measurement on the large-scale cooling tower to obtain a structural damping ratio by modal analysis; e, by considering all order damping ratios and vibration mode mass participating coefficients of corresponding orders, calculating to obtain equivalent modal damping ratios of all the orders; f, performing integration analysis to obtain the general equivalent damping ratio of an integral structure of the large-scale cooling tower. By using the valuation method for the general equivalent damping ratio of the large-scale cooling tower based on the field measurement, the limitation that a value range or a mean value of a damping ratio is only given out in dynamic analysis of a traditional cooling tower structure is overcome, and the accuracy and the reliability of wind resistance and earthquake proof analysis of the large-scale cooling tower are effectively improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for predicting modal damping ratio of composite head
ActiveUS8849635B2Precise ratioDesign optimisation/simulationGolf clubsMulti materialComputational model
A prediction method according to the present invention is a method for predicting a modal damping ratio of a composite head including two or more kinds of materials including a first material and a second material. The method includes the steps of: presuming at least a coefficient Px of a generalized Maxwell model M1 in the first material using a known material damping ratio ζ1; obtaining a calculation model of the head using the generalized Maxwell model M1; and calculating the modal damping ratio of the head based on analysis of the head using the calculation model. Preferably, the Maxwell model is further used also for the second material. Preferably, the method further includes the step of presuming a coefficient Py of a generalized Maxwell model M2 in the second material using a known material damping ratio ζ2.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
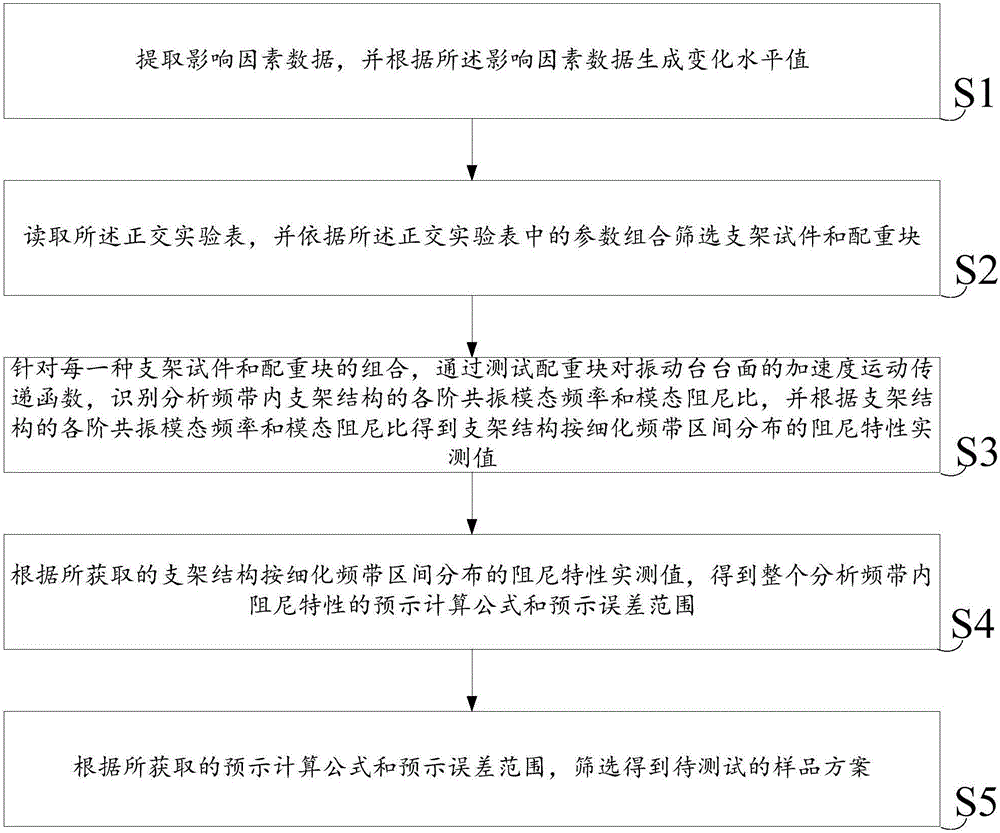
Analytical method for structural damping characteristics of spacecraft support
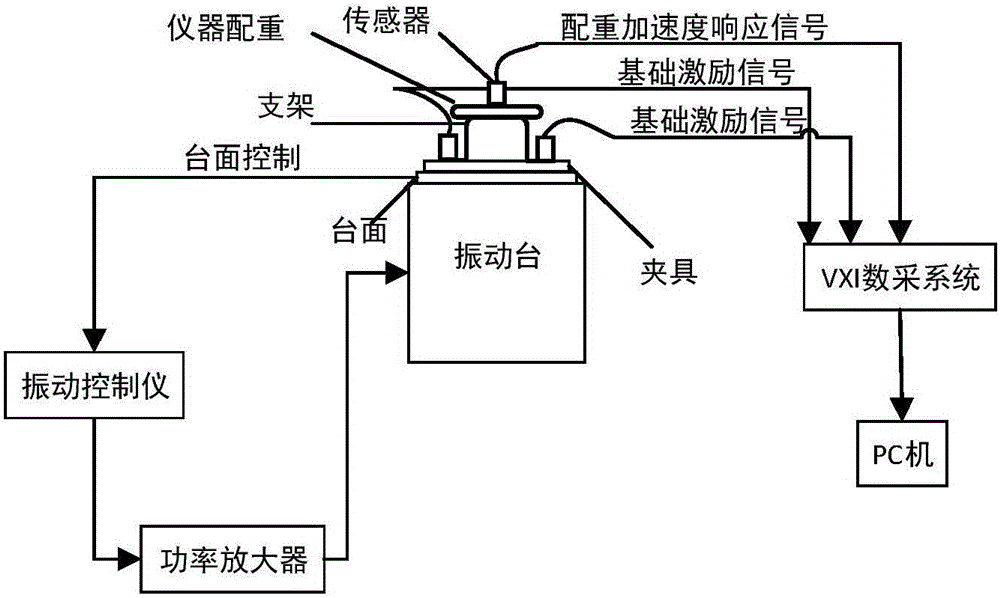
According to one embodiment of the invention, an analytical method for structural damping characteristics of spacecraft support is disclosed, which relates to the technical field of spacecraft and can greatly reduce the material cost and the production cost for measuring experiments. The method comprises the following steps: extracting influence factor data and generating a change level value according to the influence factor data; for each combination of support test pieces and counterweight blocks, analyzing for obtaining all-order resonance mode frequencies and modal damping ratios of support structures in frequency bands through a counterweight block-vibration table board acceleration movement transfer function, and obtaining the damping characteristic actual values of the support structures distributed according to refined frequency band sections; obtaining an overall prediction computational formula and a prediction error range according to the obtained damping characteristic actual values of the support structures distributed according to refined frequency band sections; and according to the obtained prediction formula and prediction error range, screening and obtaining to-be-tested sample schemes. The invention is suitable for damping tests on supports.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Three-dimensional acousto-elastic analysis method of ship for arbitrary damping processing of structure
ActiveCN108846192AEnables direct vibration and noise analysisSimple methodSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityElement model
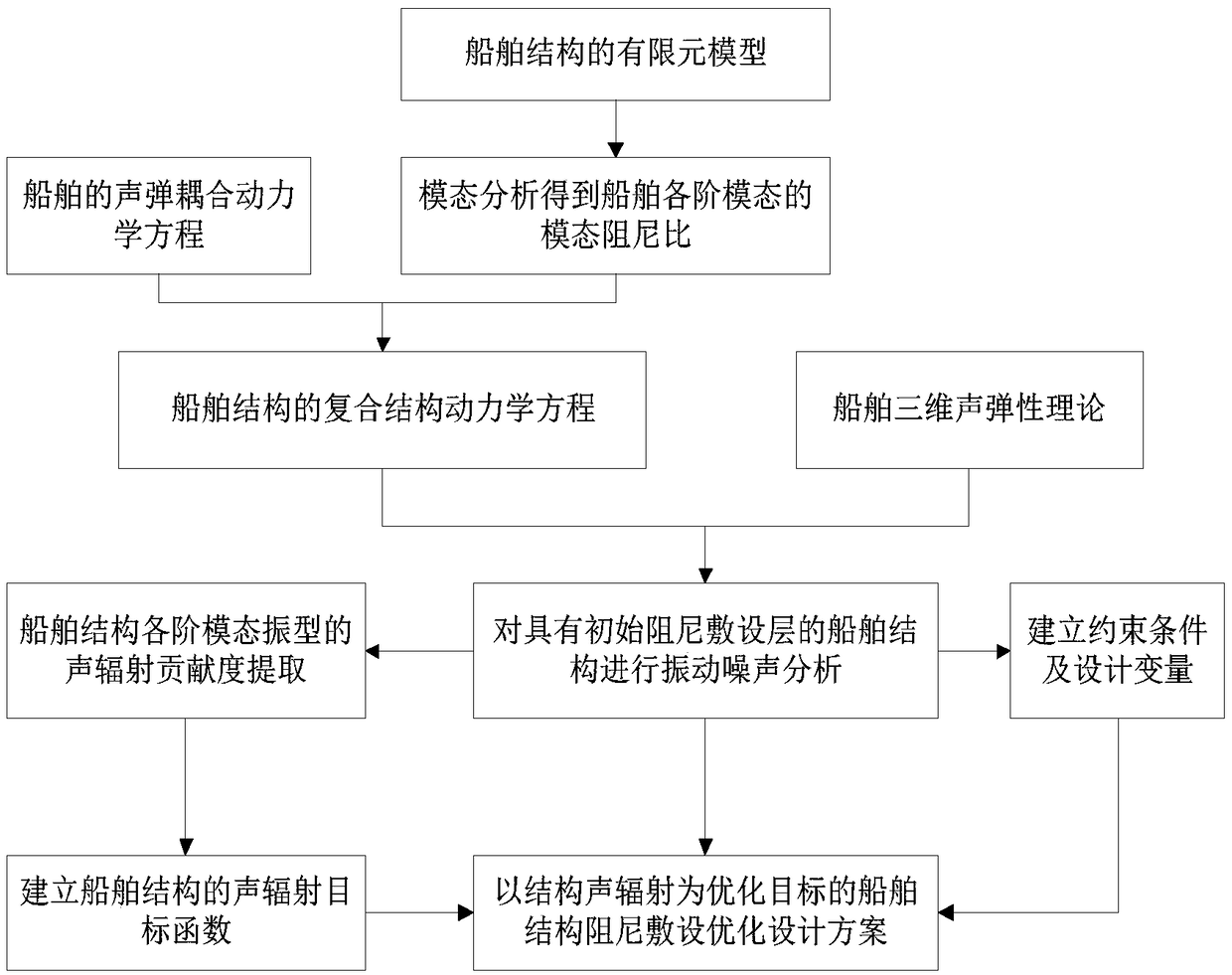
The invention discloses a three-dimensional acousto-elastic analysis method of a ship for arbitrary damping processing of a structure and relates to the technical field of acoustics. The method comprises the steps of performing modal analysis on a finite element model of a ship structure with an initial damping laying layer to obtain a modal damping ratio of modalities at various orders of the ship structure; substituting the modal damping ratio of the modalities at various orders of the ship structure into an acousto-elastic coupling dynamic equation of the ship structure to obtain a composite structure dynamic equation of the ship structure; and performing vibration noise analysis on the coupling dynamic equations by use of a three-dimensional acousto-elastic theory of the ship. A damping laying optimization design scheme for the ship structure with structural acoustic radiation as an optimization objective is provided. According to the three-dimensional acousto-elastic analysis method of the ship for arbitrary damping processing of the structure, the direct vibration noise analysis for the laying-damped ship structure is implemented, and the method can be widely used for processing of the damping structure when the vibration noise of the ship is calculated and can provide a technical support for the damping laying design of the ship.
Owner:CHINA SHIP SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH CENTER (THE 702 INSTITUTE OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDUSTRY CORPORATION)
Closely spaced mode damping ratio precisely-diagnosing method
InactiveCN103605880AAccurate diagnosisStrong engineering practicabilitySpecial data processing applicationsAttenuation coefficientGenetic algorithm
The invention discloses a closely spaced mode damping ratio precisely-diagnosing method. The method comprises constructing a standard orthogonal system through a Schmidt orthogonalization calculation method according to the number of orders of closely spaced modes and then performing inner product operation on closely spaced mode signals and the standard orthogonal system; obtaining the attenuation coefficient and the inherent frequency of every order of the closely spaced mode signals according to the Bessel inequation theorem when the closely spaced mode signals have the maximum projection in the standard orthogonal system, namely, when inner product modular square sum is maximized, wherein the maximum value of the inner product modular square sum is obtained through optimizing search of the genetic algorithm and the Newton method; obtain the damping ratio of every order of the mode through the relation of the attenuation coefficient, the inherent frequency and the damping ratio. According to the closely spaced mode damping ratio precisely-diagnosing method, the diagnosing process only requires a limited section of signals, identification is performed by performing the inner product operation on the closely spaced mode signals and the constructed standard orthogonal system, accordingly the limit of the number of orders of the modes and the size of the damping value can be avoided, and the diagnosing results are accurate; besides, the closely spaced mode damping ratio precisely-diagnosing method is also applicable to the damping identification of non-closely spaced mode signals.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
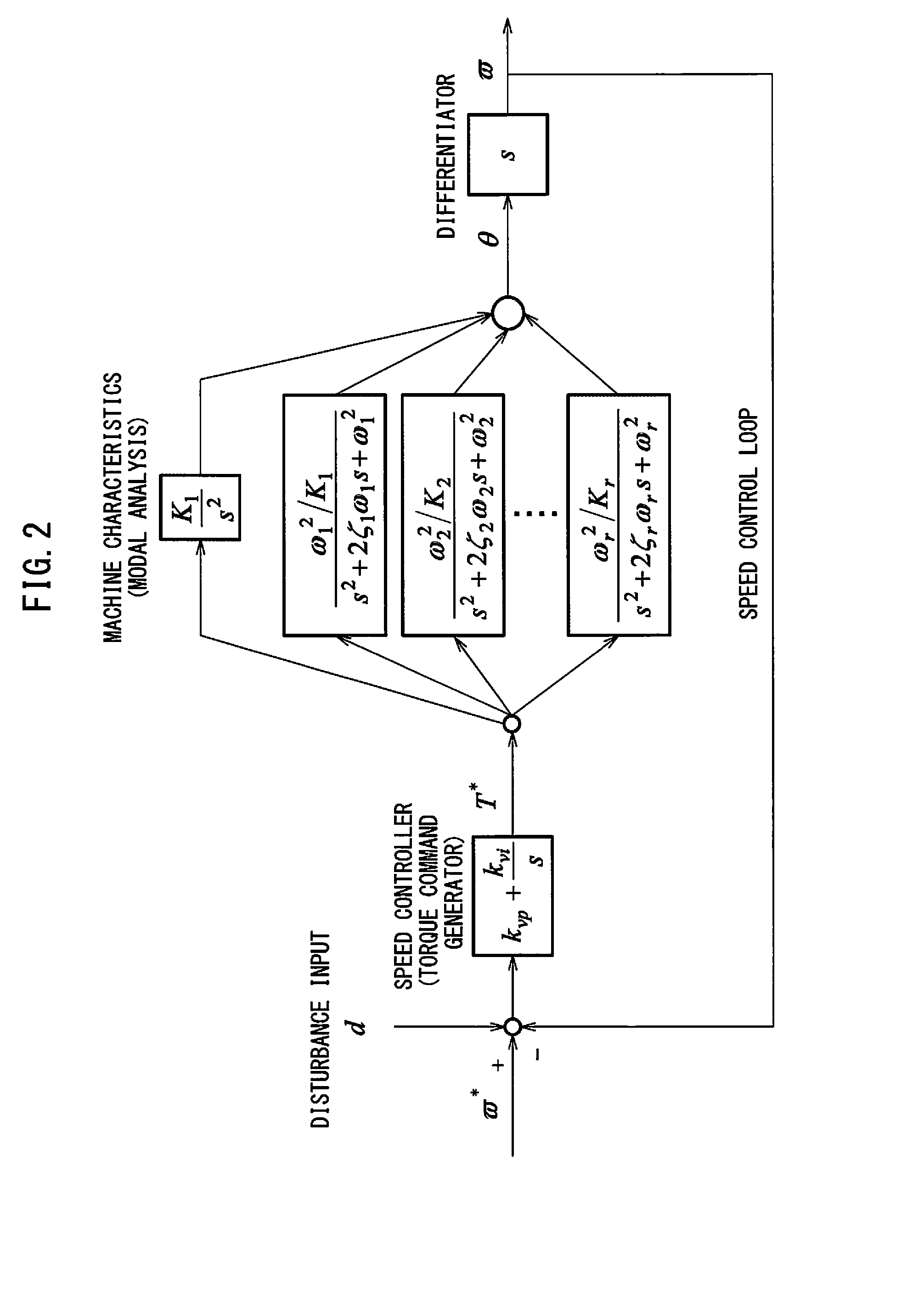
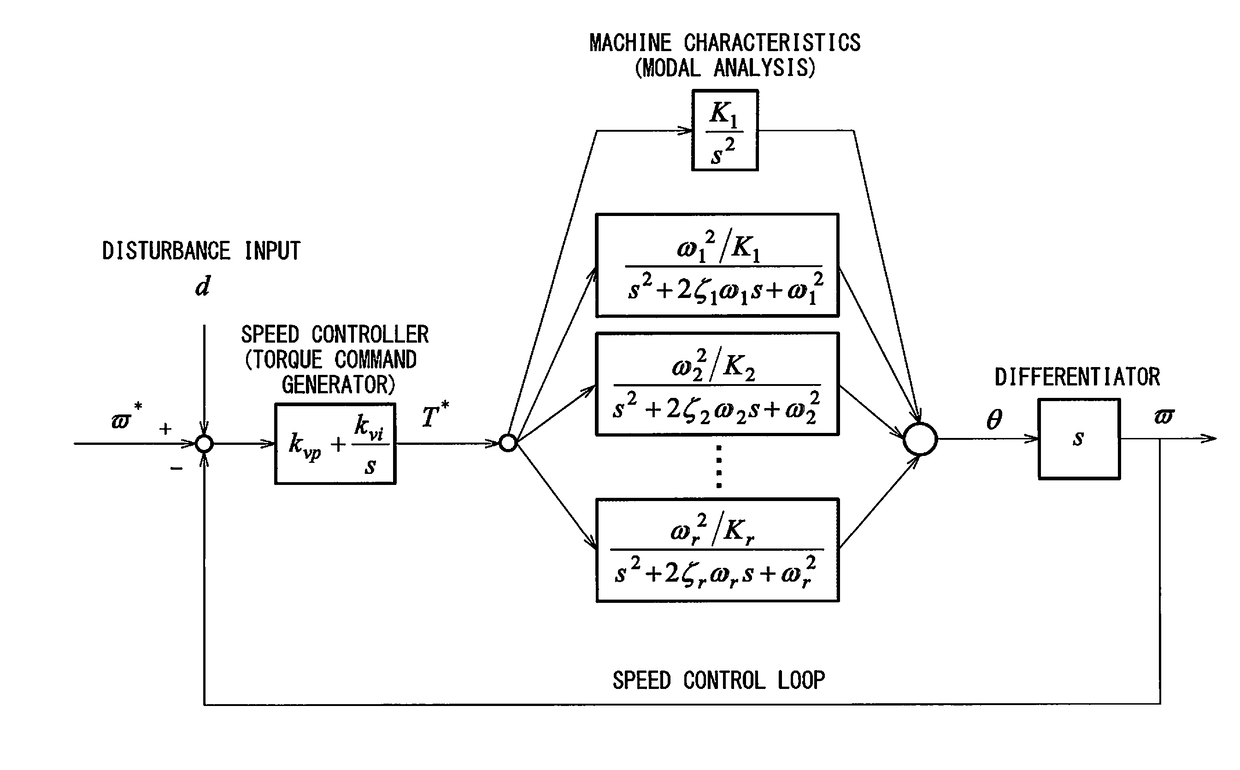
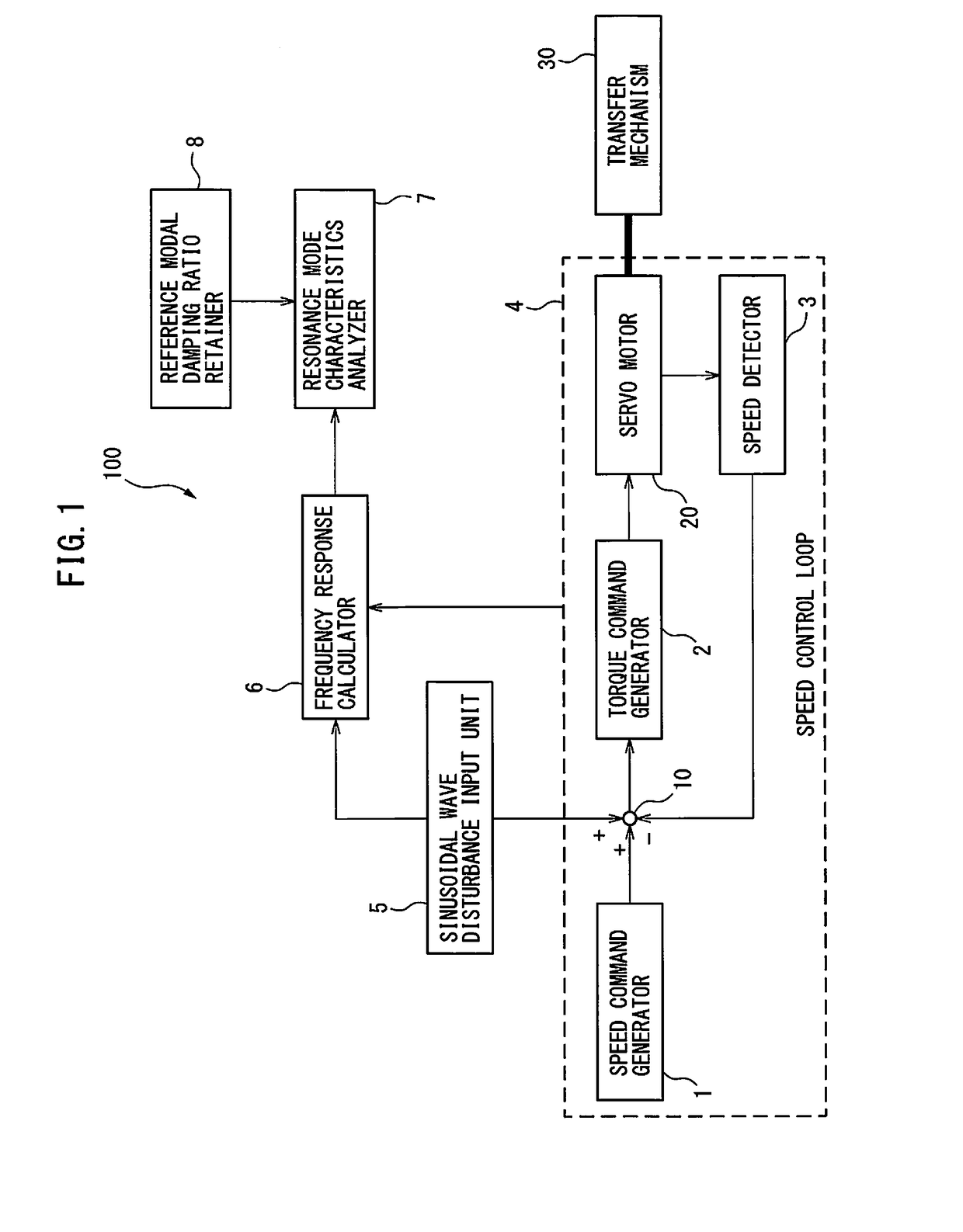
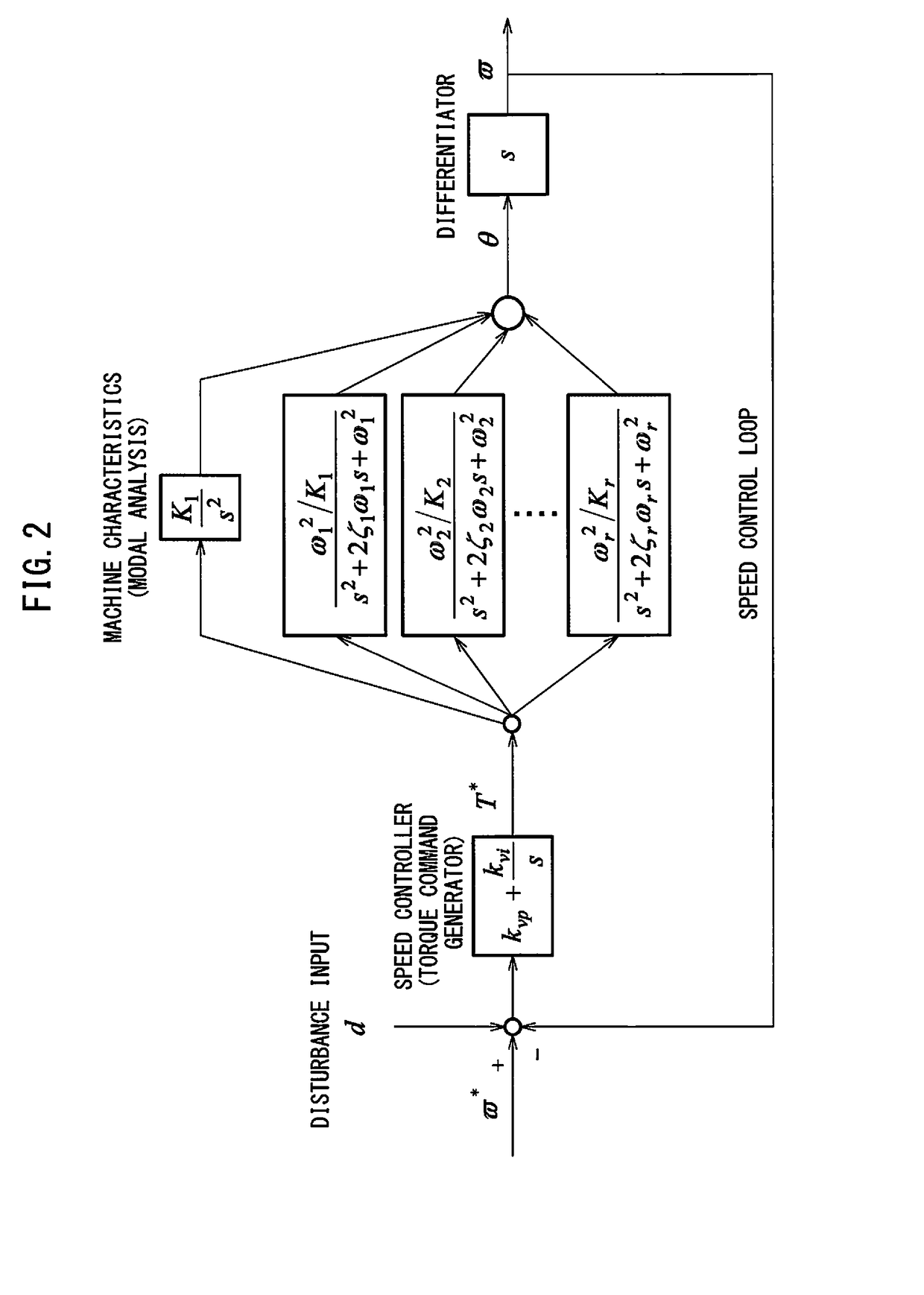
Servo controller for measuring lubrication characteristics of a machine by experimental modal analysis
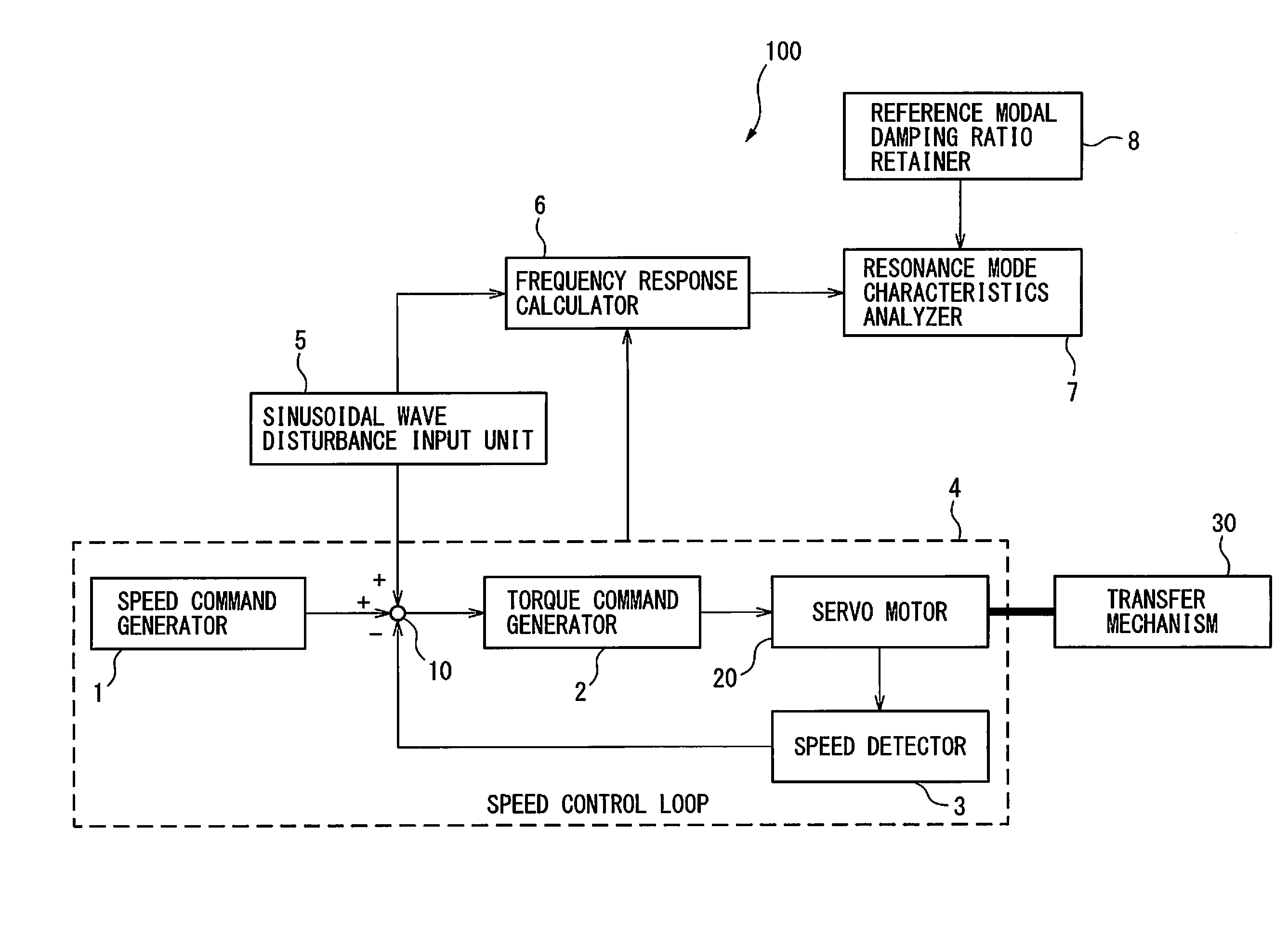
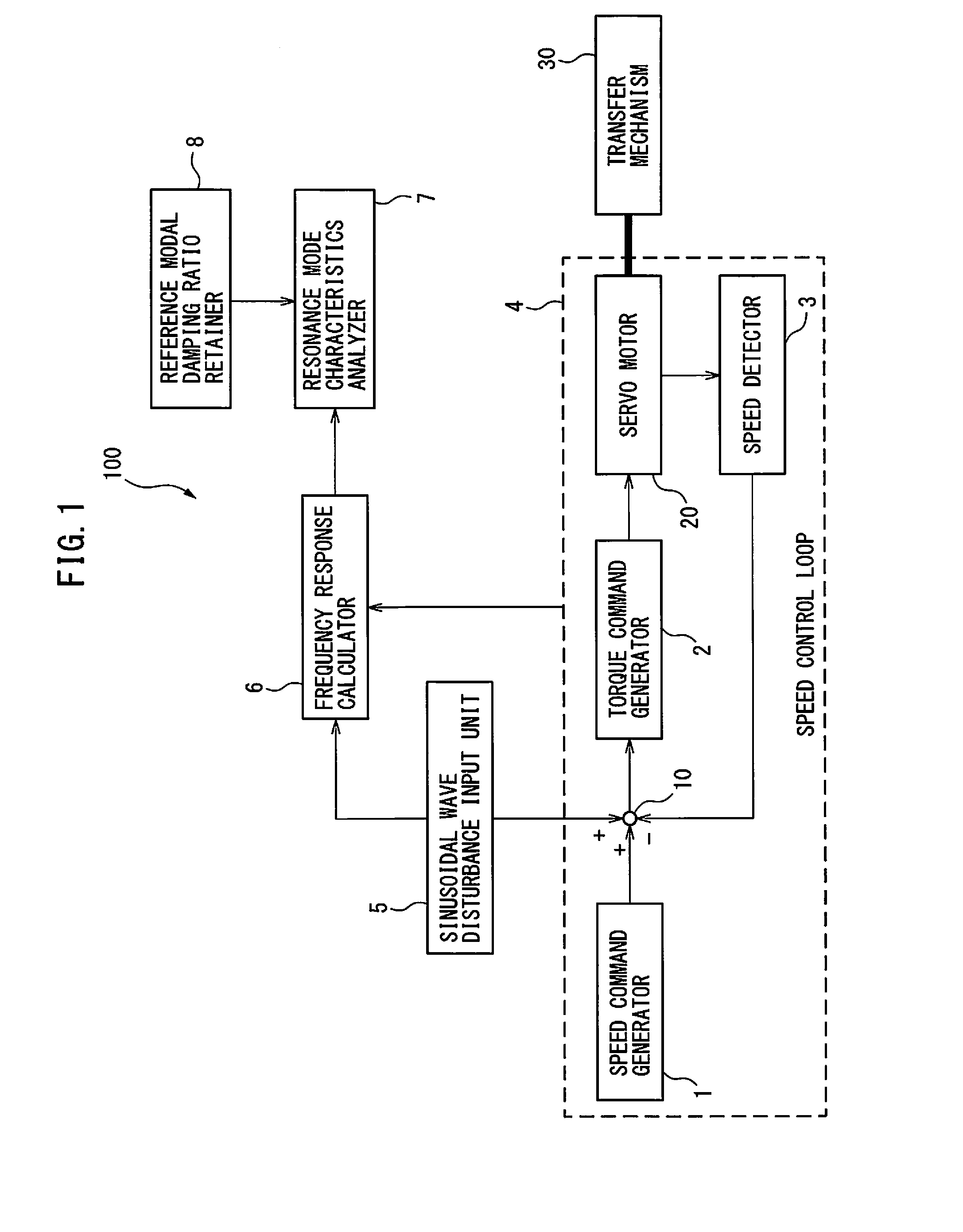
A servo controller includes: a sinusoidal wave disturbance input unit for supplying a sinusoidal wave disturbance to a speed control loop including a speed command generator, a torque command generator and a speed detector; a frequency response calculator for estimating the gain and phase from the output of the speed control loop; a resonance frequency detector for detecting resonance frequencies at which the gain becomes maximum; a resonance mode characteristics analyzer for estimating resonance characteristics from the frequency response; and, a reference modal damping ratio retainer for retaining a reference modal damping ratio as a resonance characteristic corresponding to the reference lubricating condition, and the resonance mode characteristics analyzer calculates lubrication characteristics on the basis of the reference modal damping ratio and the measured modal damping ratio at the resonance frequency corresponding to the reference modal damping ratio.
Owner:FANUC CORP
Stay cable vibration control method
ActiveCN102359067AImprove performanceImprove robustnessBridge structural detailsUltrasound attenuationVibration control
The invention belongs to the field of structural vibration control, and in particular relates to a semiactive stay cable control method of a variable damper based on non-linear friction type damping. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps that: according to displacement amplitude of a cable at a damper, a damping force is continuously regulated from high to low; and under the action of a corresponding damping force, displacement of the damper is always located in the previous period when the damper is locked, thus the obtained modal damping ratio is always high. A concrete semiactive control algorithm is that the modal damping ratio obtained in each period is equal to an attenuation curve of a stabilization system, wherein the attenuation curve is in exponential attenuation. The damping force provided by the invention is always dissipated, thus performance is stable and robustness is good. The system modal damping ratio obtained by the invention is higher and is much higher than a passive optimal modal damping ratio obtained by a linear viscous damper, thus a damping effect is good. The semiactive control method provided by the invention is simple and practical and is convenient to operate.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Turbine blade vibration test method and device
ActiveCN101122541BReasonable designReasonable matchVibration testingElasticity measurementResonance measurementData processing system
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD +1
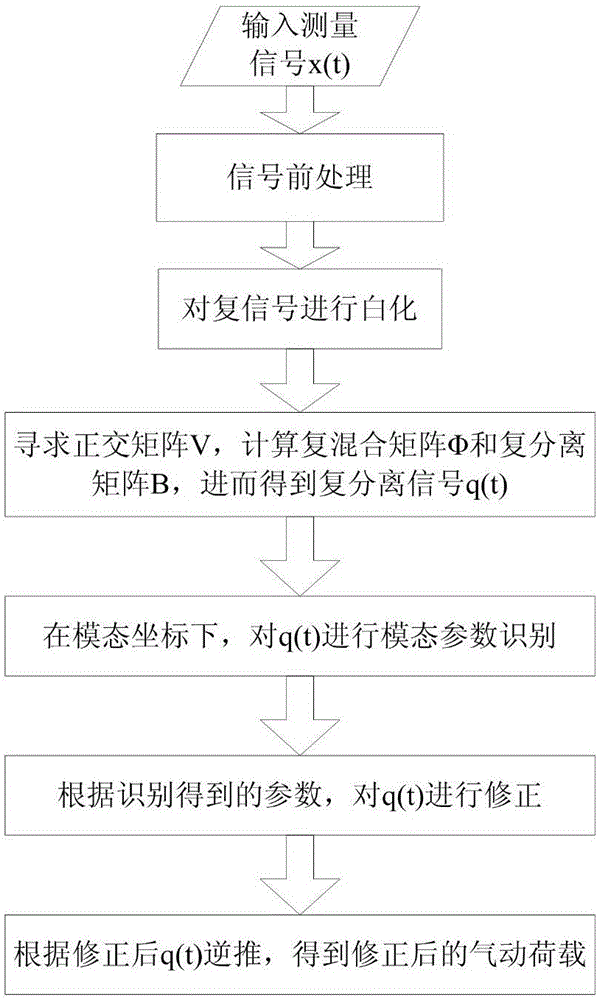
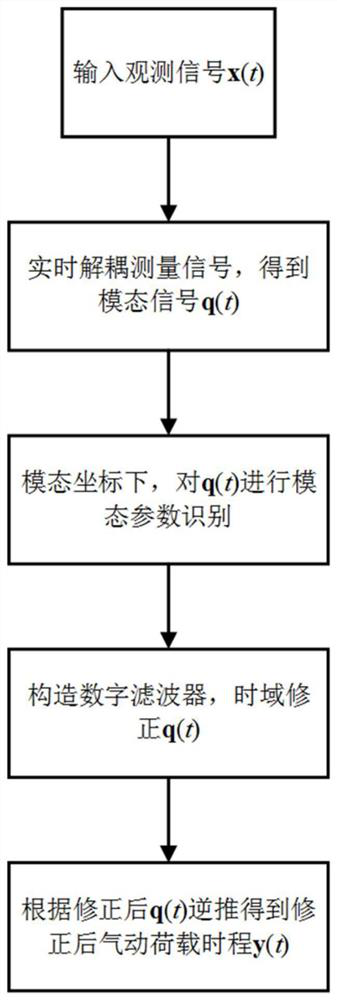
Time domain calibration method for high-frequency base force balance signal
ActiveCN112629637AFacilitate time history analysisFacilitates wind-induced response calculationsWeighing apparatus testing/calibrationTime domainEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of instrument calibration, and discloses a time domain calibration method for a high-frequency base force balance signal. The method comprises the following steps: 1, inputting an observation signal x(t); 2, decoupling the observation signal x(t) in real time to obtain a decoupled modal signal q(t); 3, performing modal parameter identification on the modal signal q(t) under the modal coordinates; 4, constructing a digital filter to correct the modal signal q(t) according to a modal parameter identification result; and 5, obtaining a corrected aerodynamic load time history y(t) through back-stepping according to the corrected modal signal. According to the invention, an adaptive blind source separation algorithm is adopted to carry out online decoupling on a measurement signal, natural vibration frequency and modal damping ratio identification is carried out on a modal signal obtained through decoupling, a corresponding digital filter is further constructed, a corrected real aerodynamic load time history is finally obtained, and further time history analysis is facilitated. The defects that an existing correction method can only decouple signals in an off-line mode and cannot obtain the corrected aerodynamic load time history are overcome.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
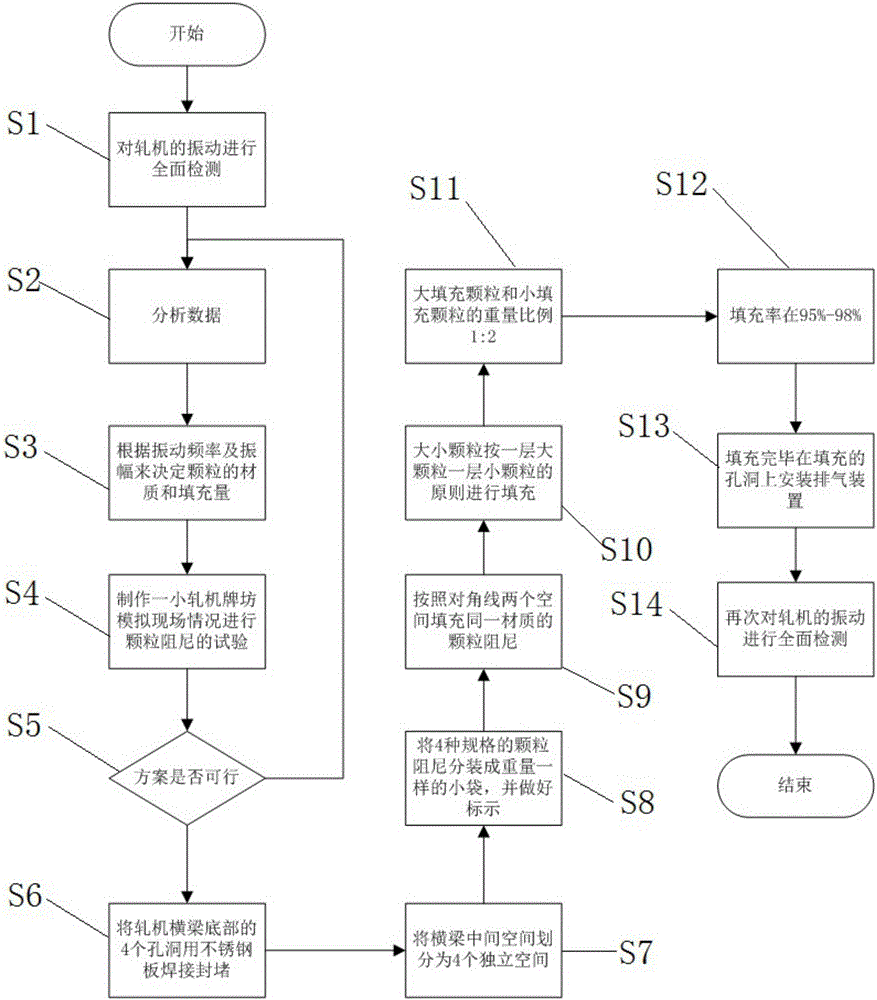
Thick plate rolling mill filled with particle damping and filling method of thick plate rolling mill
ActiveCN106269892AIncrease the modal damping ratioIncrease the attenuationNon-rotating vibration suppressionRolling safety devicesUltrasound attenuationThick plate
The invention discloses a thick plate rolling mill filled with particle damping and a filling method of the thick plate rolling mill. The rolling mill comprises rolling mill beams, a rolling mill house, an exhaust device, the particle damping and a blind plate. The rolling mill comprises the upper rolling mill beam and the lower rolling mill beam. A particle damping filling space is formed by the upper rolling mill beam, the lower rolling mill beam and the rolling mill house. The exhaust device is arranged on the upper rolling mill beam. The exhaust device communicates with the particle damping filling space. The lower rolling mill beam is provided with the blind plate. The blind plate is arranged in the particle damping filling space. By the adoption of the thick plate rolling mill filled with the particle damping and the filling method, the modal damping ratio of a rack in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction can be increased effectively, the attenuation amount of vibration energy on the transmission path of the rolling mill rack is increased greatly, the fatigue failure of related parts of the rolling mill is restrained effectively, the quality, accuracy and productivity of products are further improved, the downtime maintenance time is shortened greatly, and therefore huge economic benefits are generated.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
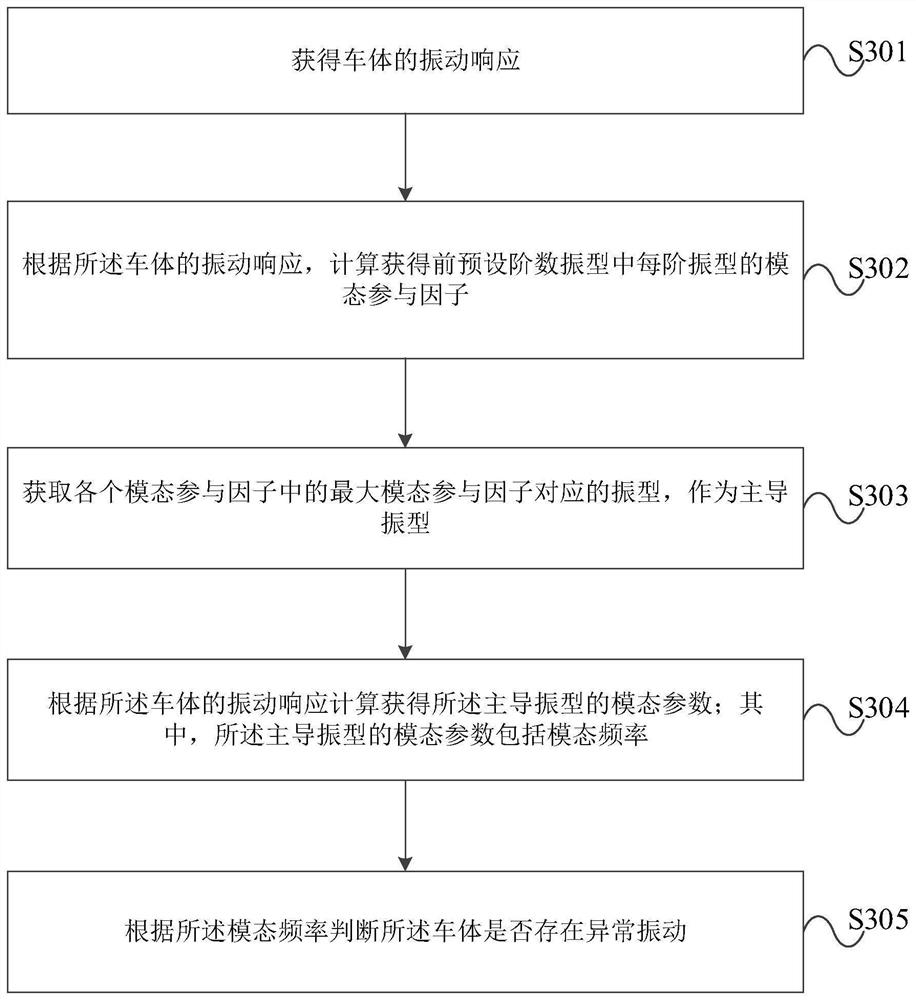
Abnormal vibration monitoring method and device for vehicle body
ActiveCN112834243AEffective identification of abnormal vibrationImprove recognition accuracyVehicle testingStructural engineeringModal damping ratio
The invention provides an abnormal vibration monitoring method and device for a vehicle body.The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring vibration response of the vehicle body; according to the vibration response of the vehicle body, calculating to obtain modal participation factors of each order of vibration modes of previous preset orders of vibration modes; acquiring a vibration mode corresponding to the maximum modal participation factor in the modal participation factors as a main vibration mode; performing calculation according to the vibration response of the vehicle body to obtain modal parameters of the main vibration mode which comprise a modal frequency and a modal damping ratio; judging whether the vehicle body has abnormal vibration or not according to the modal frequency; and according to the modal damping ratio, carrying out quantitative grading alarm on the severity of the abnormal vibration. The device is used for executing the method. According to the abnormal vibration monitoring method and device for the vehicle body, the abnormal vibration of the vehicle body can be effectively recognized, and the recognition precision of the abnormal vibration of the vehicle body is improved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF RAILWAY SCI CORP LTD +3
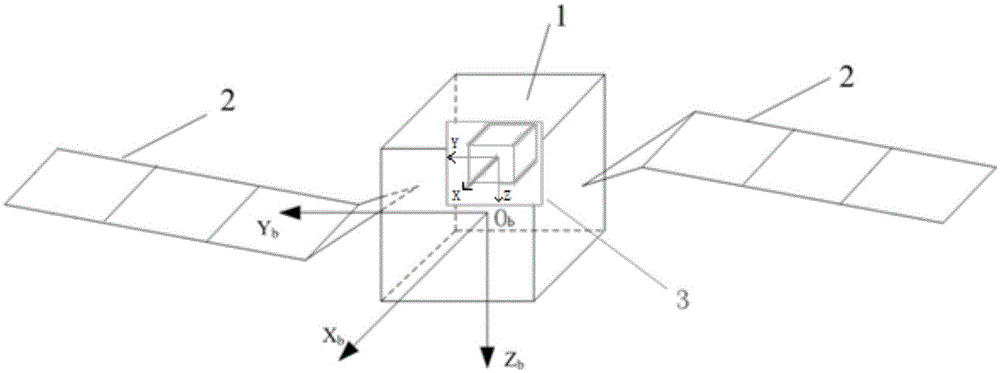
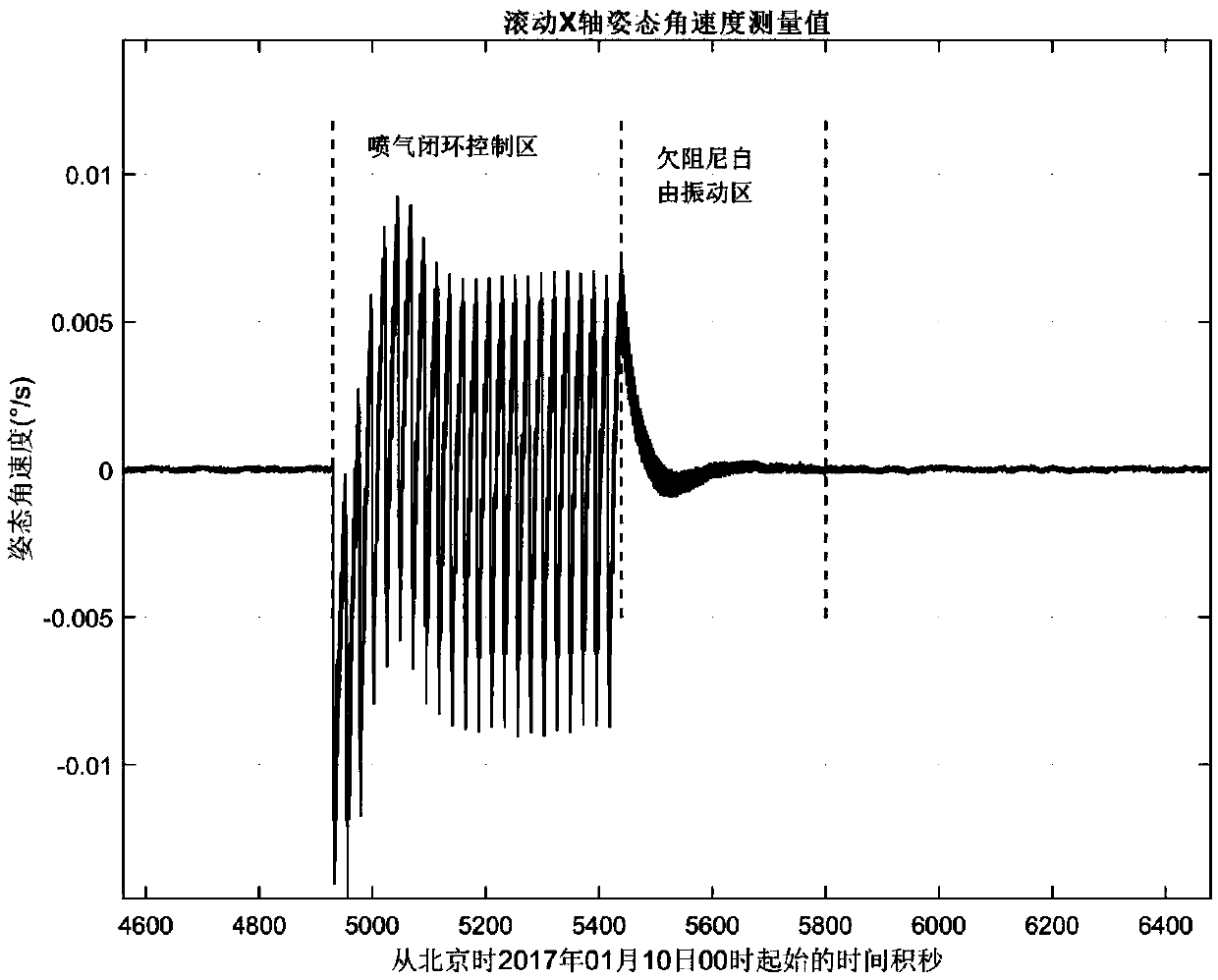
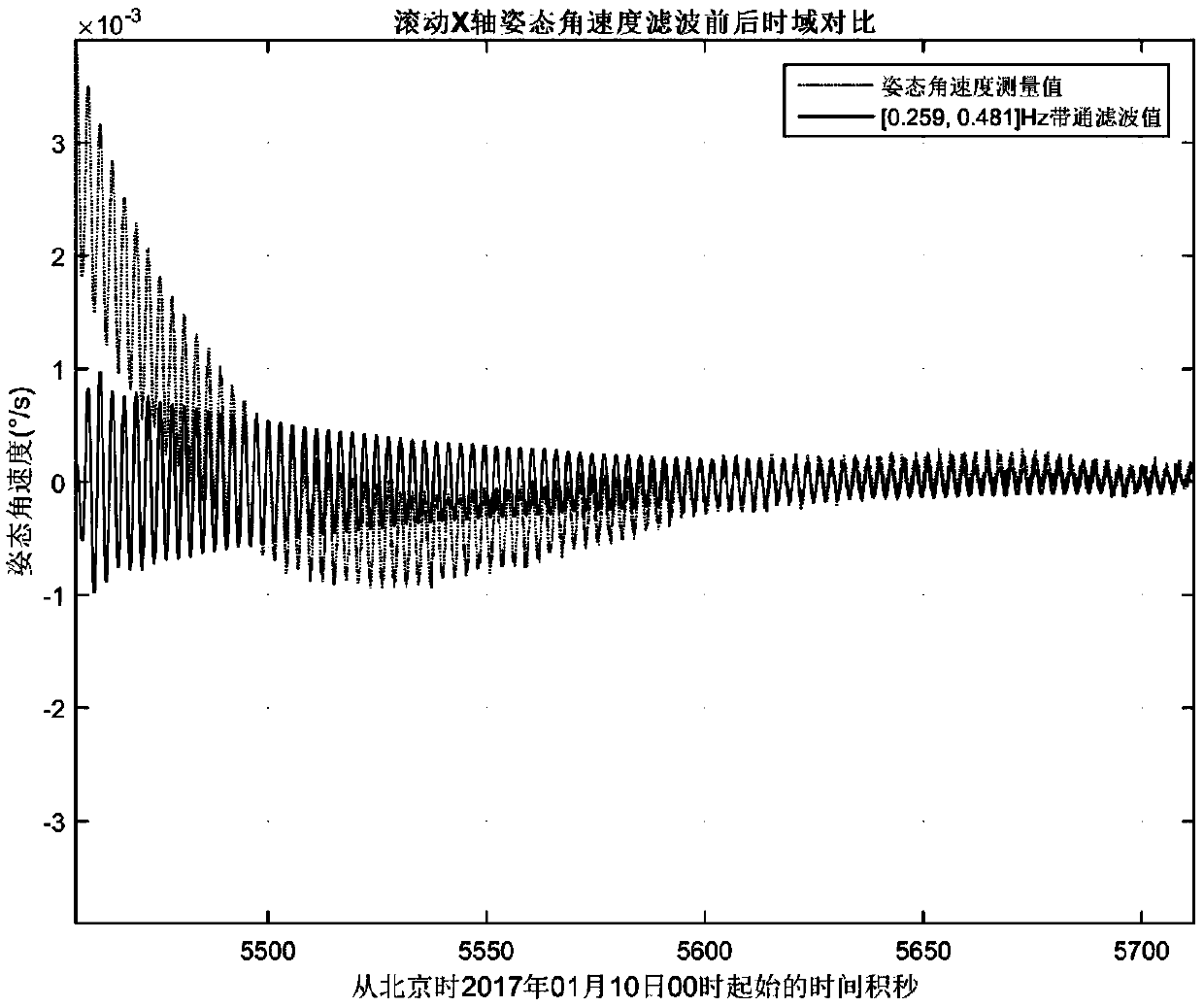
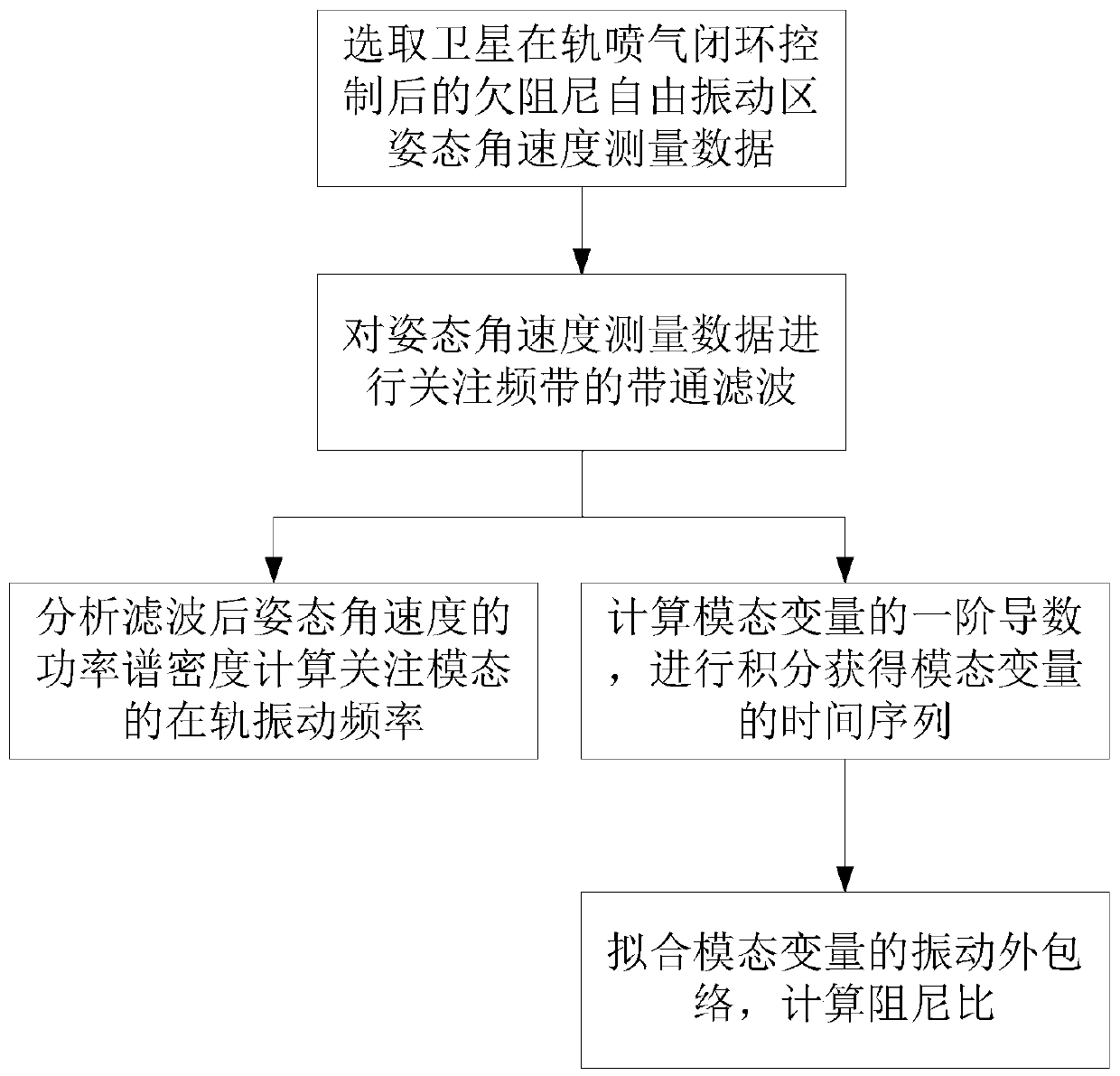
Method and system for identifying whole-spacecraft flexibility vibration modal parameters
ActiveCN109612665AMeet the needs of the identification of dynamic characteristics of on-orbit structuresIncrease manufacturing difficultyVibration testingLoop controlStructural dynamics
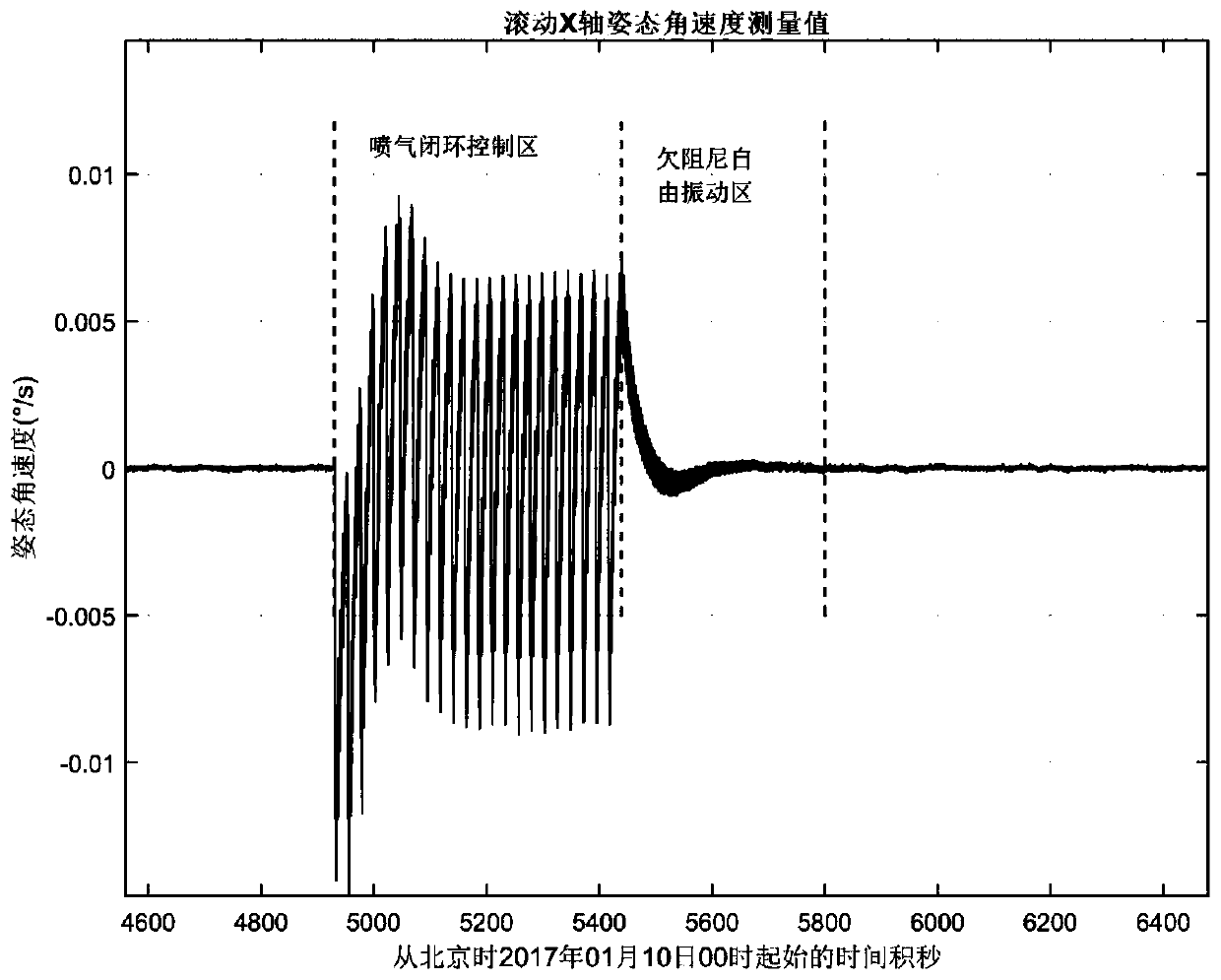
The invention provides a method for identifying whole-spacecraft flexibility vibration modal parameters. The method for identifying the whole-spacecraft flexibility vibration modal parameters comprises the following steps that pose angular speed is obtained, specifically, i-axis pose angular speed data omega' i (t) after filtering is obtained after pose angular speed measuring data omega i (t) corresponding to an i-axis of an underdamping free vibration area after satellite on-orbit air injection closed-loop control, wherein the i-axis is any one of an X-axis, a Y-axis and a Z-axis in a spacerectangular coordinate system; filtering is carried out, specifically, filtering is carried out on the omega i (t) to obtain the i-axis pose angular speed data omega' i (t) after filtering; on-orbit vibration frequency is calculated, specifically, the on-orbit vibration frequency fi is calculated and obtained according to the omega' i (t); time series is calculated, specifically, the time series eta i (t) of a modal variable is calculated and obtained according to the omega' i (t); and damping is calculated, specifically, the damping epsilon i of the i-axis vibration mode is obtained accordingto calculation. The method for identifying the whole-spacecraft flexibility vibration modal parameters meets the requirement of flexible satellite on-orbit structural dynamic characteristic identification, and on-orbit flexibility vibration modal frequency and modal damping ratio and other whole-spacecraft flexibility vibration modal parameters are extracted.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
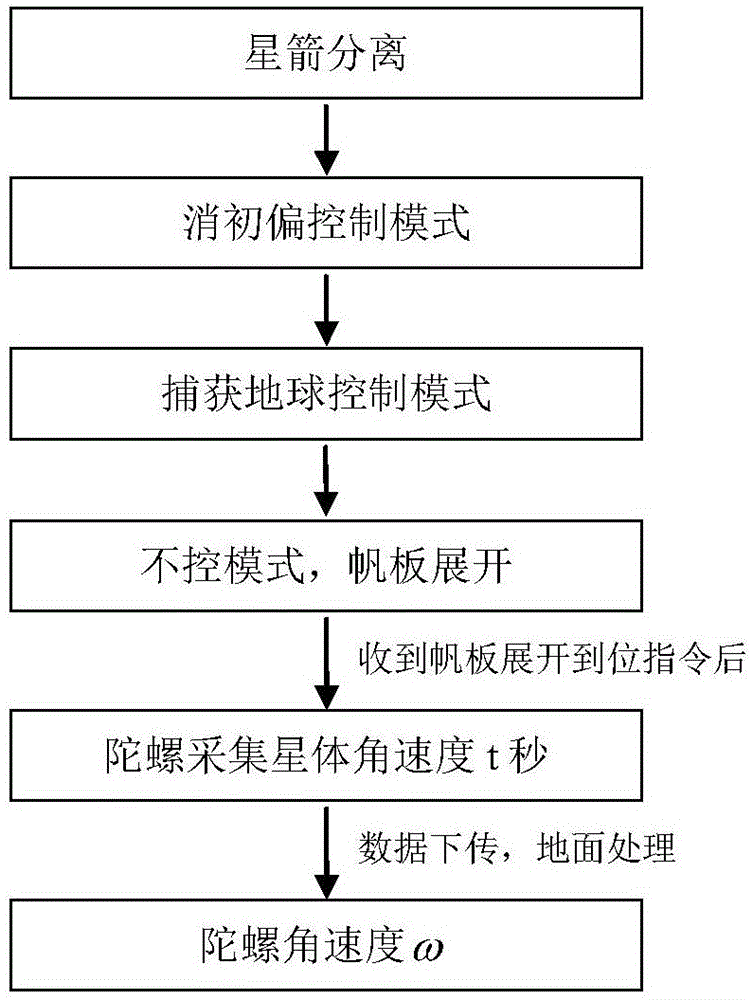
Method for identifying whole-satellite flexible vibration modal parameters by utilizing satellite gyroscope data
PendingCN110929386AIncrease design difficultyIncrease manufacturing difficultyMeasurement devicesDesign optimisation/simulationGyroscopeVibration control
The invention provides a method for identifying whole-satellite flexible vibration modal parameters by utilizing satellite gyroscope data. The whole-satellite flexible vibration modal parameters are identified by utilizing attitude angular velocity data measured by a gyroscope in an under-damping free vibration period after satellite on-orbit air injection control, wherein the whole-satellite flexible vibration modal parameters comprise an on-orbit flexible vibration modal frequency and a modal damping ratio. In the identification process, only gyro measurement data loaded on a satellite platform are used for analysis and processing, and displacement, speed and acceleration vibration sensors installed on flexible accessories are not used. According to the method, only measurement data of an existing inertial attitude sensor of a satellite platform are used for analysis and processing; the increased satellite design and manufacturing difficulty and the risk of on-orbit operation due tothe installation of other vibration sensors are avoided. The identified whole-satellite flexible vibration mode parameters can provide necessary support for application in the aspects of structural design, structural health monitoring, structural fault diagnosis, structural vibration control and the like of space flexible components.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Wind-induced vibration control method for high-pier long-span bridge during construction period
PendingCN112906260AImprove wind safetyReduce wind-induced vibration responseGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelVibration control
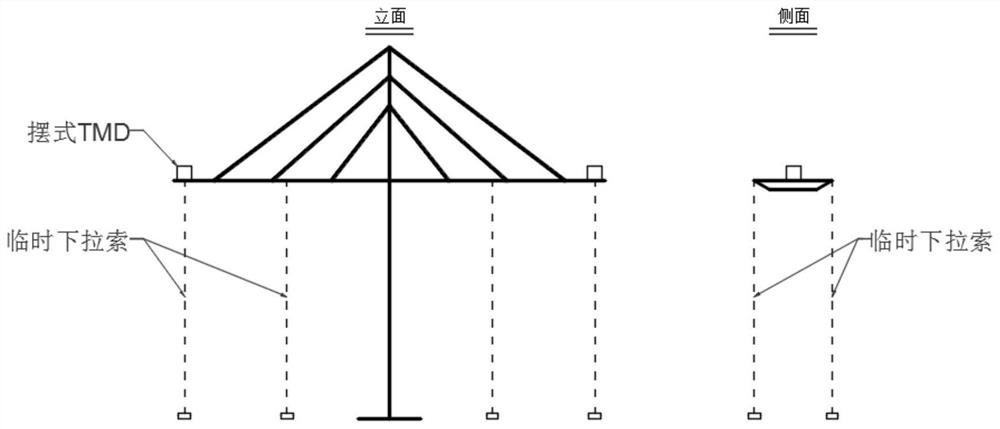
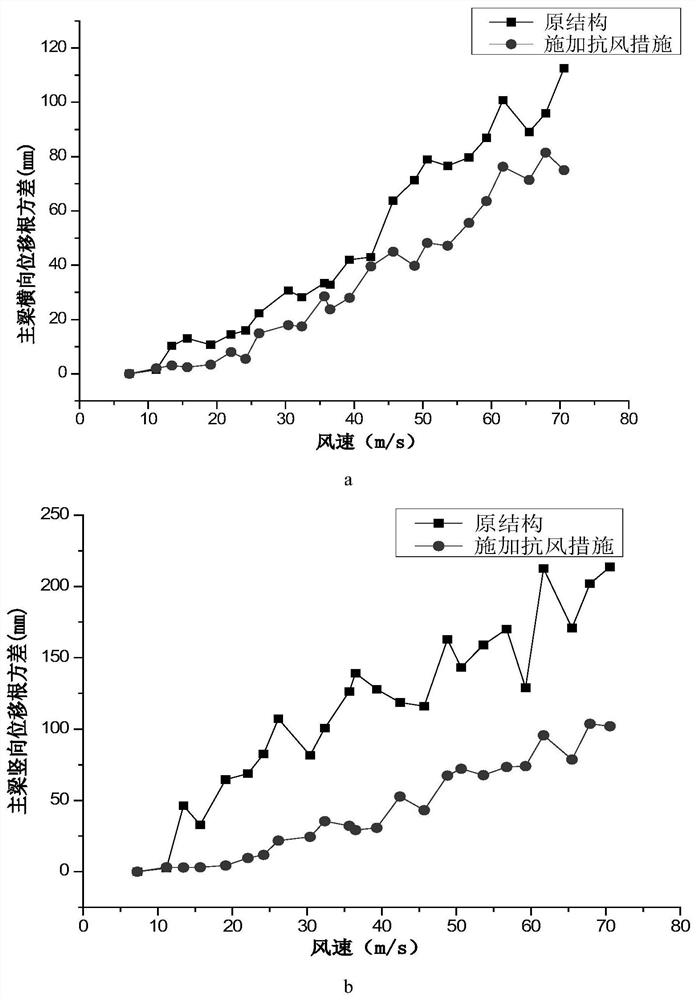
The invention discloses a wind-induced vibration control method for a high-pier long-span bridge during a construction period, and relates to the technical field of civil engineering, and the main points of the technical scheme are that the method comprises the following steps: analyzing and obtaining inherent frequency information of a main beam; establishing an original finite element model; establishing a wind-resistant finite element model; carrying out structural dynamic characteristic complex modal analysis; evaluating and analyzing the complex modal dynamic characteristic result from the structure frequency and the modal damping ratio to obtain a first vibration reduction effect; performing evaluating and analyzing according to the buffeting response calculation result to obtain a second damping effect; verifying the test result of the wind-induced vibration response to obtain verification data; and correcting the elastic modulus of the bridge tower and girder concrete of the original finite element model according to the verification data. According to the method, wind-induced vibration control in the construction period of the main beam is carried out by adopting a wind-resistant measure that the vertical lower inhaul cable is matched with the swing type TMD, the wind-induced vibration response and the wind-induced buffeting load in the construction period of the main beam of a bridge structure can be effectively reduced, and the wind-resistant safety in the construction period of a bridge and the comfort of constructors are improved.
Owner:湖南省潇振工程科技有限公司
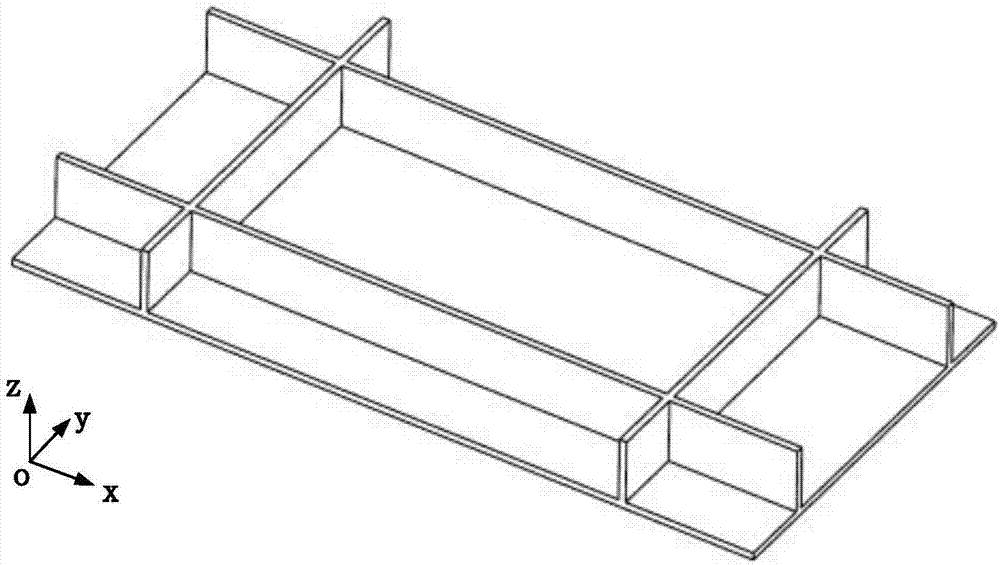
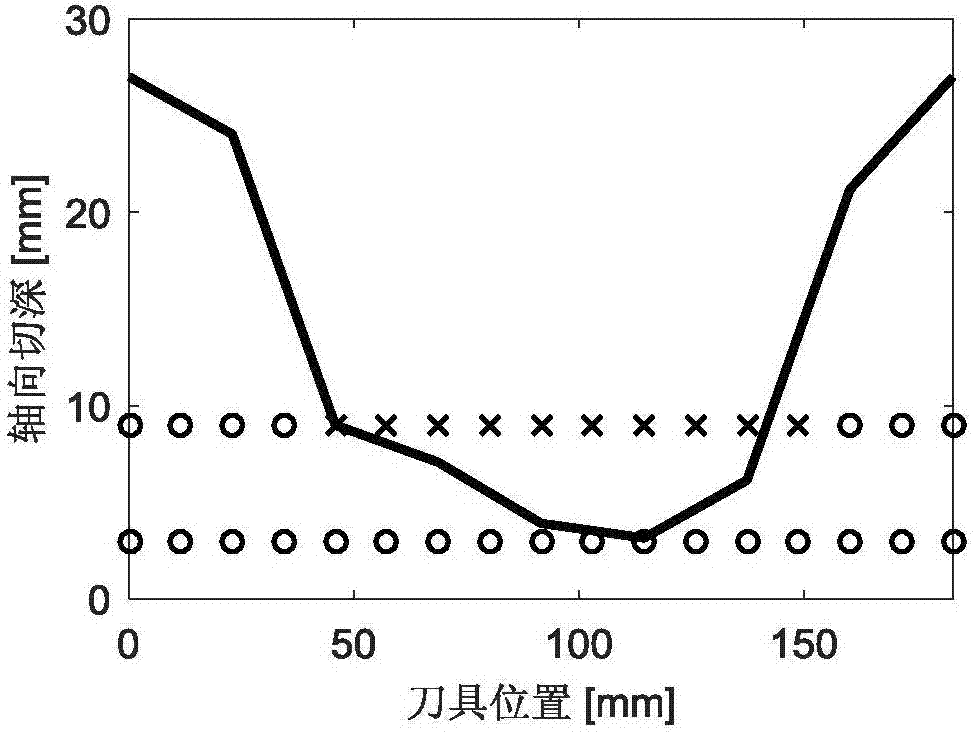
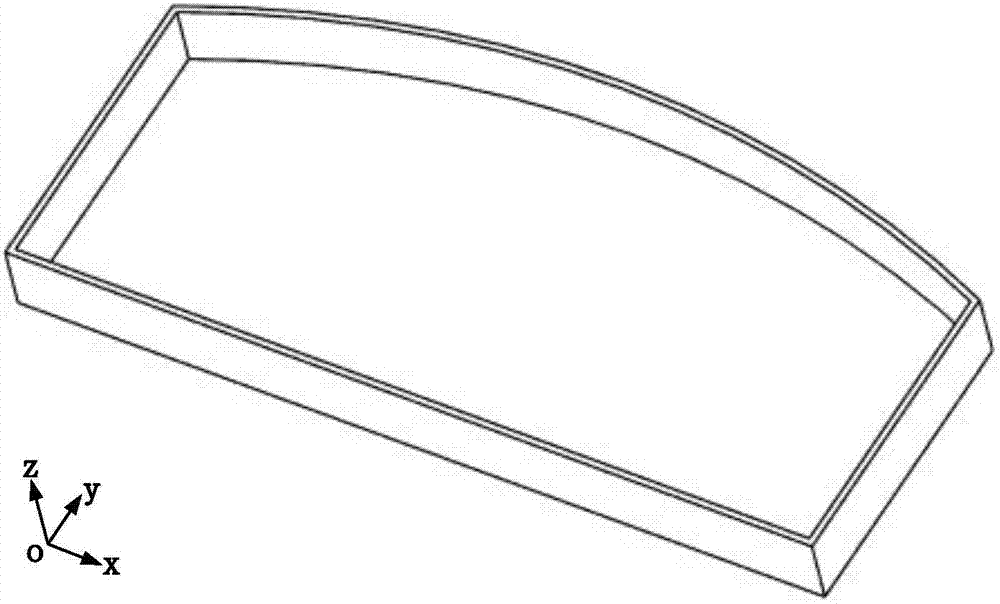
Box-type thin-walled part milling stability prediction method
ActiveCN107346356AHigh precisionGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationMaterial removalModal damping ratio
The invention discloses a box-type thin-walled part milling stability prediction method, used for solving the technical problem of lower prediction accuracy of an existing thin-walled part milling stability prediction method. The technical scheme is that the method comprises the steps of firstly using a modal hammer experiment to test a modal parameter of a tool and a modal damping ratio of a workpiece; then using a substructure modal synthesis method to calculate a workpiece dynamic characteristic with considering a material removal effect; afterwards, extracting dynamic displacements of the workpiece at different tool positions and different axial heights; finally establishing a multi-point contact milling dynamical model, substituting the previously obtained workpiece dynamic characteristic into the model, and solving reliability. Changes due to material removal, changes at different tool positions, and changes along the axial direction of the tool of the workpiece dynamic characteristic are considered at the same time, thus improving the prediction accuracy of box-type thin-walled part milling stability.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Material parameter testing method and testing device
PendingCN112611659AReduce the number of testsReduce test itemsMaterial thermal coefficient of expansionSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementThermal dilatationTest sample
The invention relates to the field of material testing, and discloses a material parameter testing method and a testing device. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining an inherent frequency test value and a modal damping ratio test value of a to-be-tested sample at a specific temperature t, determining an inherent frequency theoretical value of the to-be-tested sample according to the inherent frequency test value, and determining a modal damping ratio theoretical value of the to-be-tested sample according to the modal damping ratio test value, determining the elasticity modulus, Poisson's ratio and thermal expansion coefficient of the to-be-tested sample according to the inherent frequency theoretical value of the to-be-tested sample, and determining the loss factor of the to-be-tested sample according to the modal damping ratio theoretical value of the to-be-tested sample. The testing method is used for solving the problem that material parameters in a high-temperature environment cannot be effectively obtained in the prior art.
Owner:WEICHAI POWER CO LTD
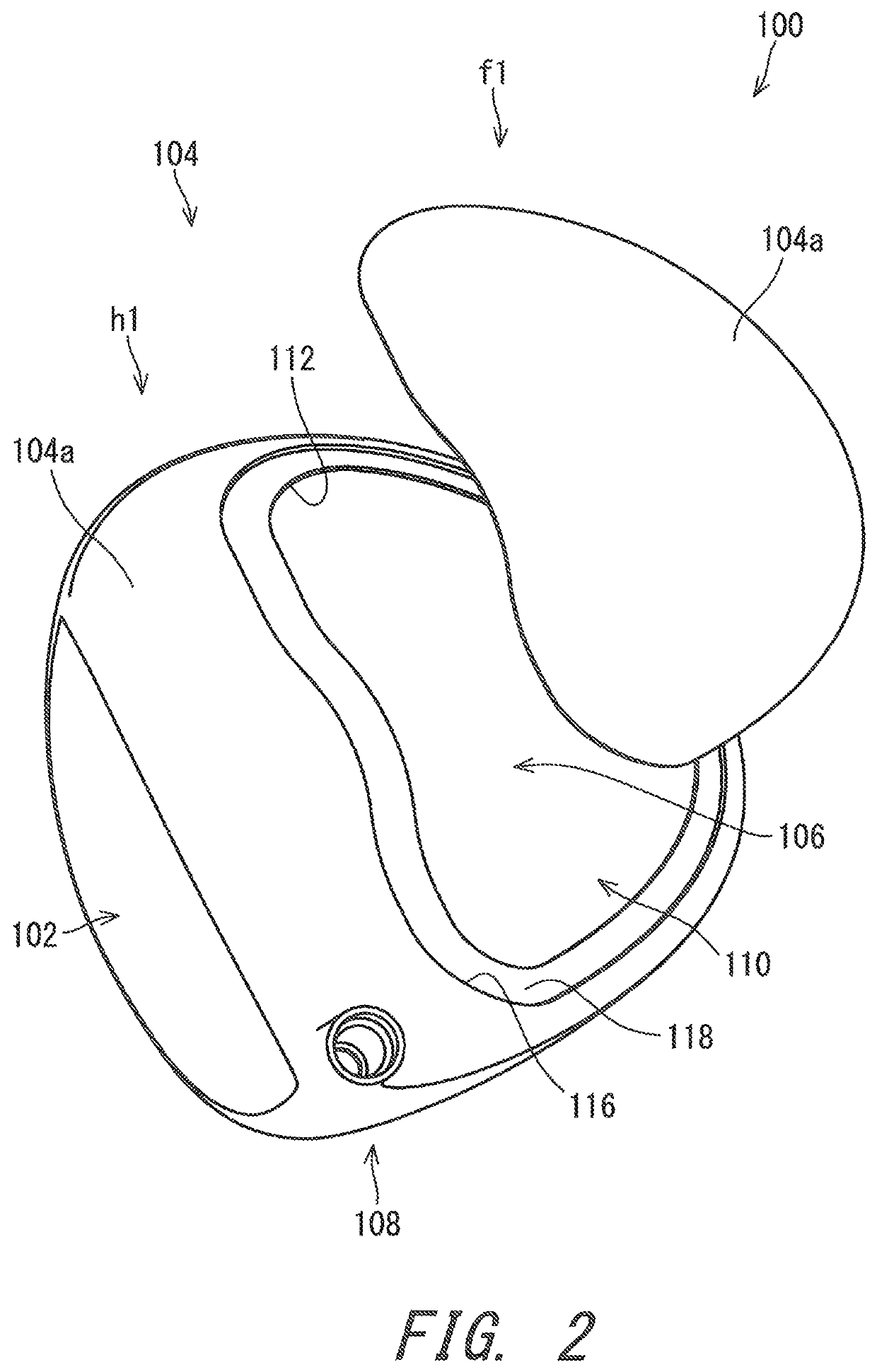
Golf club head
ActiveUS10828542B2Improve impactLong durationDomestic articlesGolf clubsStructural engineeringModal damping ratio
A golf club head includes a striking face, a crown and a sole. The crown and / or the sole includes an FRP member formed by a fiber reinforced plastic that contains a fiber and a matrix resin. The head has one or more characteristic mode shapes each having a natural frequency of 3000 Hz or greater and 5000 Hz or less. Of the one or more characteristic mode shapes, one characteristic mode shape that has a largest amplitude of a center of figure of the FRP member is defined as a specific characteristic mode shape, the specific characteristic mode shape has a frequency that is defined as a specific modal frequency, and the specific modal frequency has a modal damping ratio that is defined as a specific modal damping ratio. The specific modal damping ratio of the head is less than or equal to 0.6%.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Servo controller for measuring lubrication characteristics of a machine by experimental modal analysis
A servo controller includes: a sinusoidal wave disturbance input unit for supplying a sinusoidal wave disturbance to a speed control loop including a speed command generator, a torque command generator and a speed detector; a frequency response calculator for estimating the gain and phase from the output of the speed control loop; a resonance frequency detector for detecting resonance frequencies at which the gain becomes maximum; a resonance mode characteristics analyzer for estimating resonance characteristics from the frequency response; and, a reference modal damping ratio retainer for retaining a reference modal damping ratio as a resonance characteristic corresponding to the reference lubricating condition, and the resonance mode characteristics analyzer calculates lubrication characteristics on the basis of the reference modal damping ratio and the measured modal damping ratio at the resonance frequency corresponding to the reference modal damping ratio.
Owner:FANUC LTD
A passive vibration damping device for solar sail panels
ActiveCN104139873BPlay a role in dampingSimple working principleCosmonautic power supply systemsModal damping ratioFlange
The invention discloses a passive damping device for a solar panel. The passive damping device is arranged between a solar panel driving mechanism and a panel support. The passive damping device comprises a middle column, an upper flange, a lower flange and a damper. The upper flange and the lower flange are connected with the top end and the bottom end of the middle column. The upper flange is connected with the solar panel driving mechanism. The lower flange is connected with the panel support. The damper is arranged on the outer side of the middle column and is connected with the upper flange and the lower flange. High-damping-characteristic viscous-elastic materials are arranged between an inner shearing piece and an outer shearing piece. The passive damping device is high in reliability, long in service life and easy to mount, the passive damping device can be directly connected between the solar panel driving mechanism and the panel support, a panel structure does not need to be changed in a large-scale mode, the extra modal damping ratio is provided for each stage of vibration mode of a solar panel system, flexibility vibration of the solar panel can decline quickly, and the purpose that satellite platform control accuracy is improved is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com