Time frequency domain time varying structure modal parameter identification method based on time varying common demominator model
A technology for structural modal and parameter identification, applied in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of differences in the results of the same algorithm, difficult to solve adaptability, difficult to use, etc., to suppress cross terms, Computationally efficient, simple to implement effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
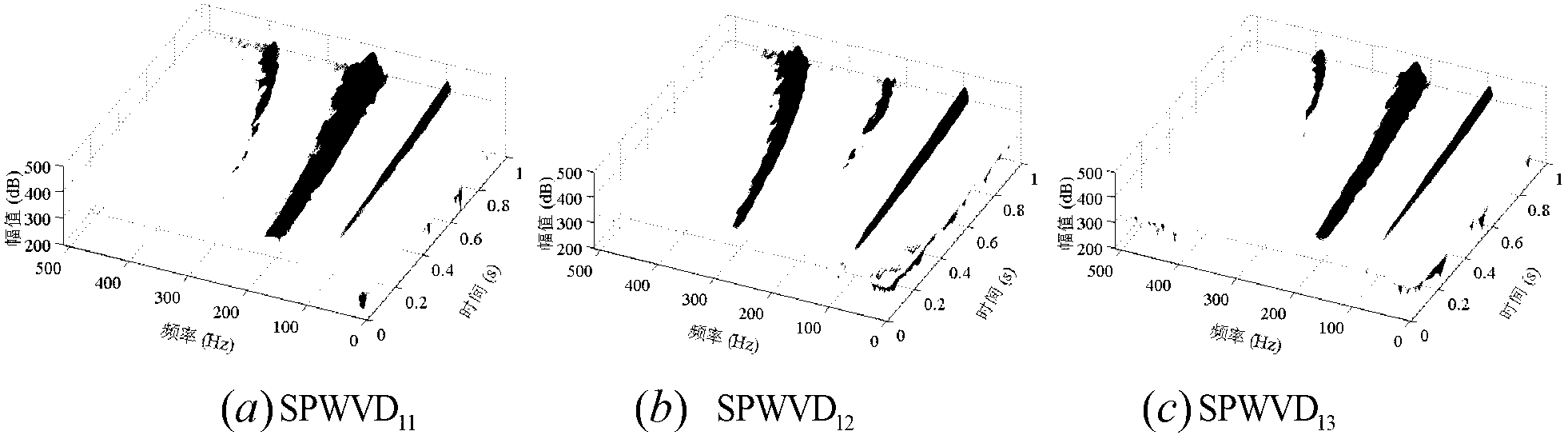
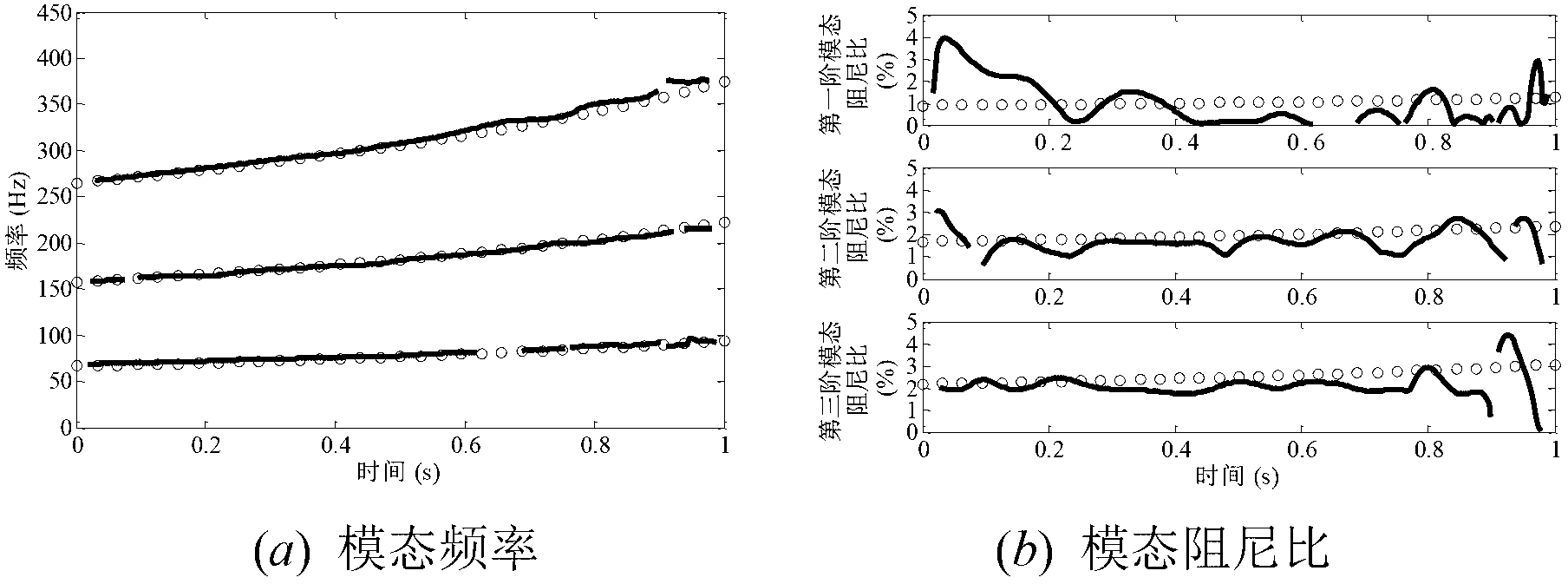
[0055] In order to better illustrate the purpose and advantages of the present invention, the present invention will be further described below by simulating the time-varying structure of aircraft and spacecraft under a working state through a three-degree-of-freedom time-varying structure example under random excitation.
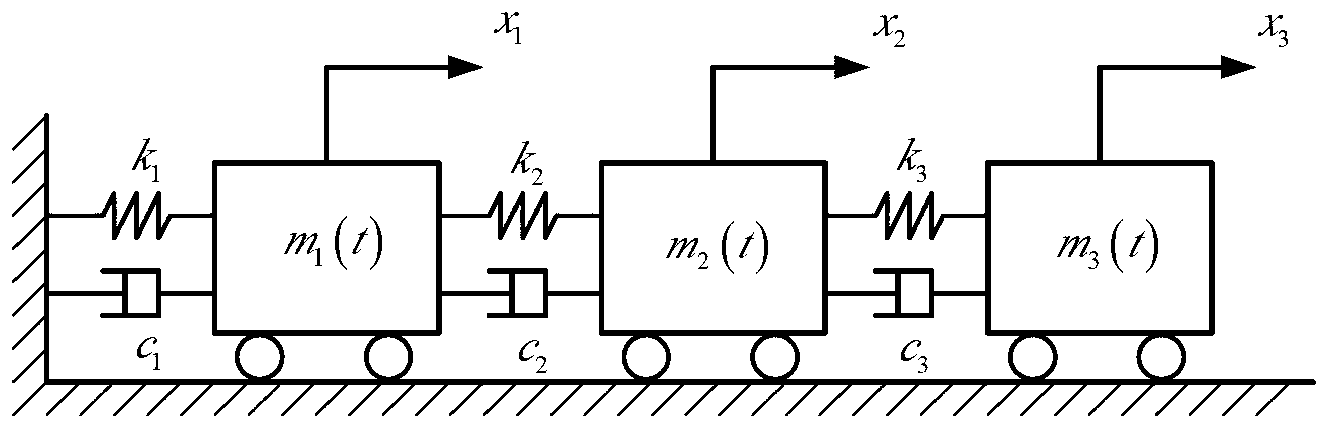
[0056] The three-degree-of-freedom spring-damper-mass system of the present embodiment, such as figure 1 shown.
[0057] The parameter of the three-degree-of-freedom system is k 1 =k 2 =k 3 =10 5 , c 1 =1.0,c 2 =0.5, c 3 =0.5, the initial mass is m 1 (0)=0.2, m 2 (0)=0.1, m 3 (0)=0.1. The dynamic governing equation of the system is:
[0058] M ( t ) x · · + C x · + Kx = f ( t ) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com