A xylose fermentation strain tolerant to inhibitors and its construction method and application
A fermentation strain and inhibitor technology, applied in the field of yeast, can solve the problems of complex construction steps and lack of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains, and achieve the effects of superior inhibitor tolerance, improved inhibitor tolerance, and good fermentation results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
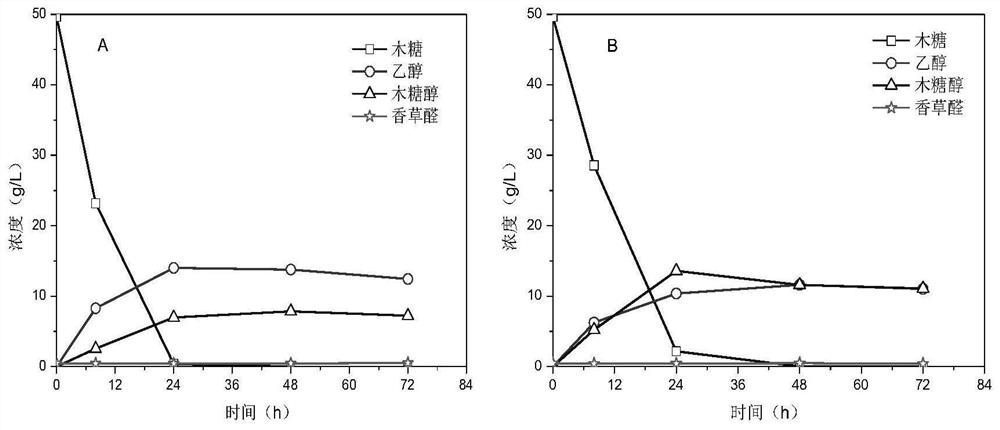
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] This embodiment is a method for constructing xylose fermentation strain SEB11 tolerant to inhibitors. The starting strain used in this embodiment is Saccharomyces cerevisiae SEB5 (CGMCC No.11325, General Microbiology Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms), which has Excellent performance of fermenting xylose to produce ethanol. The construction method includes the following steps:
[0041] (1) plasma mutagenesis treatment;
[0042]Select a loop of SEB5 strain into 2% YPD liquid medium, put it into a 30°C constant temperature shaker at 160rpm for pre-cultivation. After 16 hours of pre-cultivation, 1 mL of the bacterial liquid was taken, centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 3 minutes, the bacterial cells were collected, transferred to 2% YPD, and placed in a constant temperature shaker at 160 rpm at 30°C. When cultured for 8 hours, the starting yeast strain SEB5 was in the transition period between the logarithmic growth phase and the stationary ph...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The present embodiment is a fermentation experiment in which xylose is the sole carbon source under the condition of acetic acid (80mmol / L), which adopts the following steps:
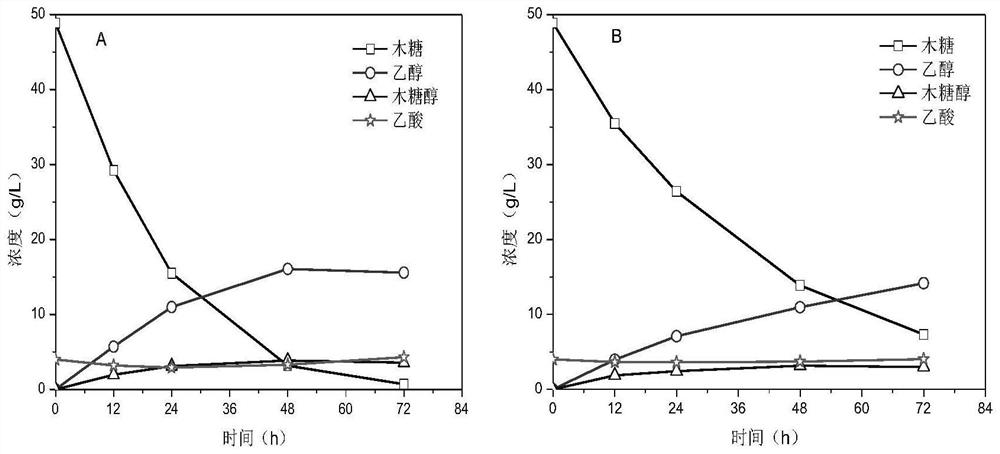
[0048] SEB11 was inoculated on 2% YPD solid plates and activated in a 30°C incubator for 24 hours. A ring of activated yeast was selected and inoculated into 100 mL of 5% YPD liquid medium, and incubated at a constant temperature for 16 hours (30° C., 160 rpm). The pre-cultured bacterial liquid was centrifuged to collect the thalline, inoculated 2.5g of wet thallus into 100mL of 5% YPX medium containing 80mmol / L acetic acid, and fermented in a constant temperature water bath (200rpm, 35°C). The results were as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0049] figure 1 Part A is the fermentation result of SEB11, figure 1 Part B of is the fermentation result of the starting strain SEB5. Compared with the original strain, the xylose consumption rate of SEB11 was significantly increased. The consumption rate of ...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The present embodiment is a fermentation experiment in which xylose is the only carbon source under the condition of the presence of 5-HMF (15mmol / L), and it adopts the following steps:
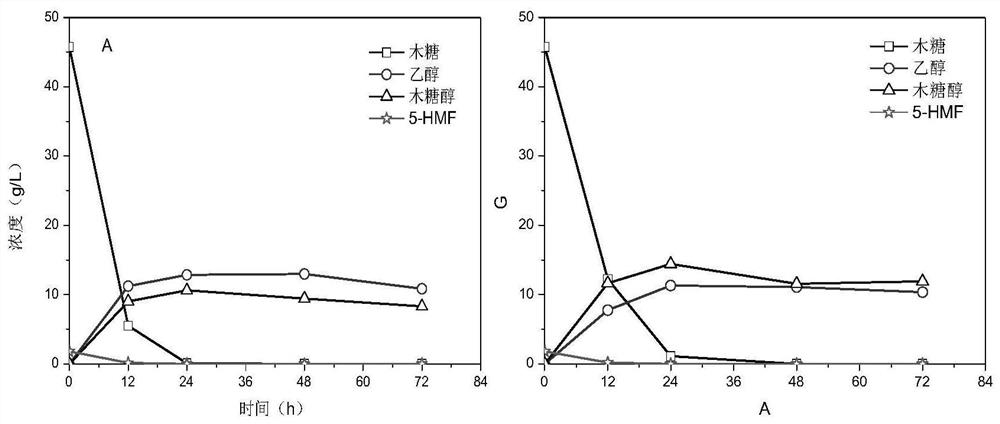
[0052] SEB11 was inoculated on 2% YPD solid plates and activated in a 30°C incubator for 24 hours. A ring of activated yeast was selected and inoculated into 100 mL of 5% YPD liquid medium, and incubated at a constant temperature for 16 hours (30° C., 160 rpm). The pre-cultured bacterial liquid was centrifuged to collect the bacterial cells, inoculated 2.5g of wet bacterial cells into 100mL of 5% YPX medium containing 15mmol / L 5-HMF, and fermented in a constant temperature water bath (200rpm, 35°C), the results Such as figure 2 shown.
[0053] figure 2 Part A is the fermentation result of SEB11 under this condition, figure 2 Part B is the fermentation result of the starting strain SEB5 under this condition. 15mmol / L 5-HMF had no obvious inhibitory effect on SEB11, showing bette...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com