Pedestrian re-identification method based on multi-scale feature cutting and fusion
A pedestrian re-identification and multi-scale feature technology, applied in the field of pedestrian re-identification based on multi-scale feature cutting and fusion, can solve the problems of degraded re-identification performance, noisy image features, loss of significant information, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
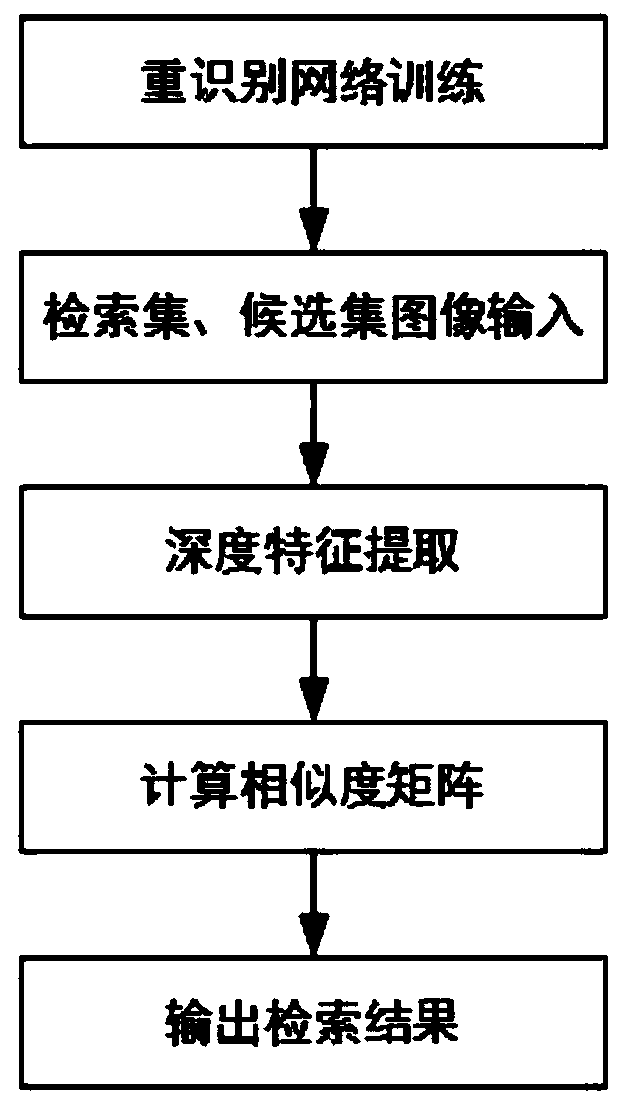
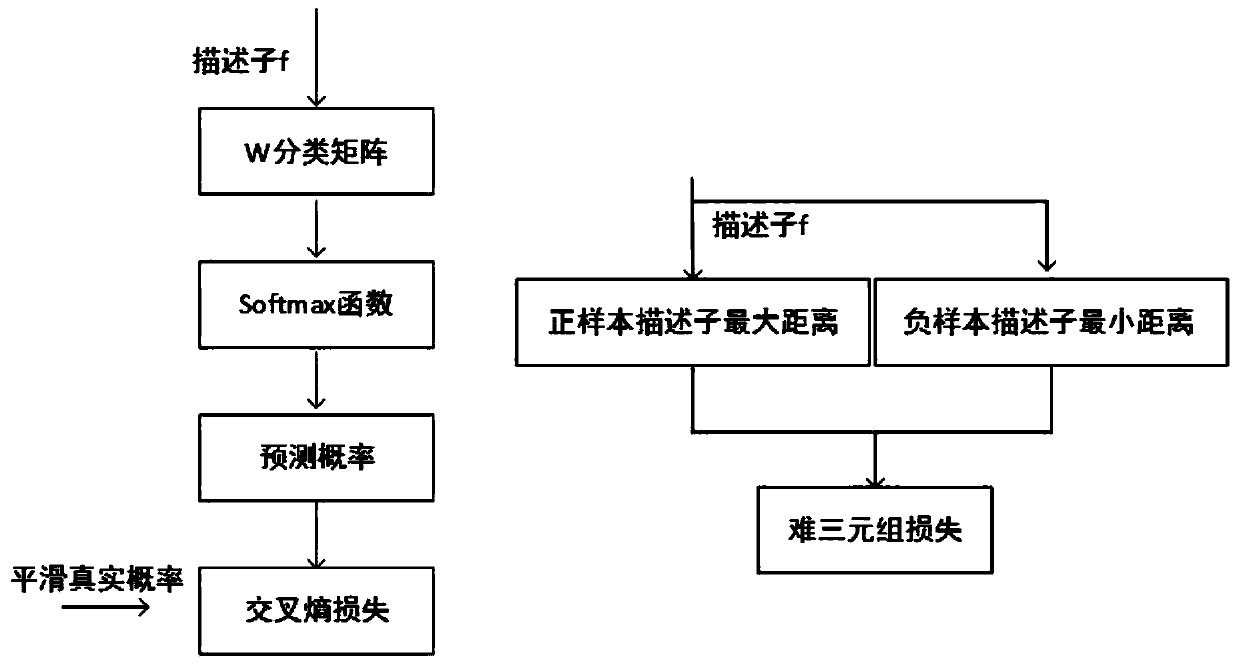
[0051] Such as figure 1 As shown, the implementation steps of a pedestrian re-identification method based on multi-scale deep feature cutting and fusion are disclosed. The implementation steps include: re-identification network training phase, retrieval set and candidate set descriptor extraction phase, similarity matrix calculation stage.
[0052] (1) Re-identification network training phase:
[0053] Training data preprocessing and data enhancement. For training data, RGB three-channel normalization and random horizontal flip are performed according to the mean value [0.485, 0.456, 0.406] and standard deviation [0.229, 0.224, 0.225];
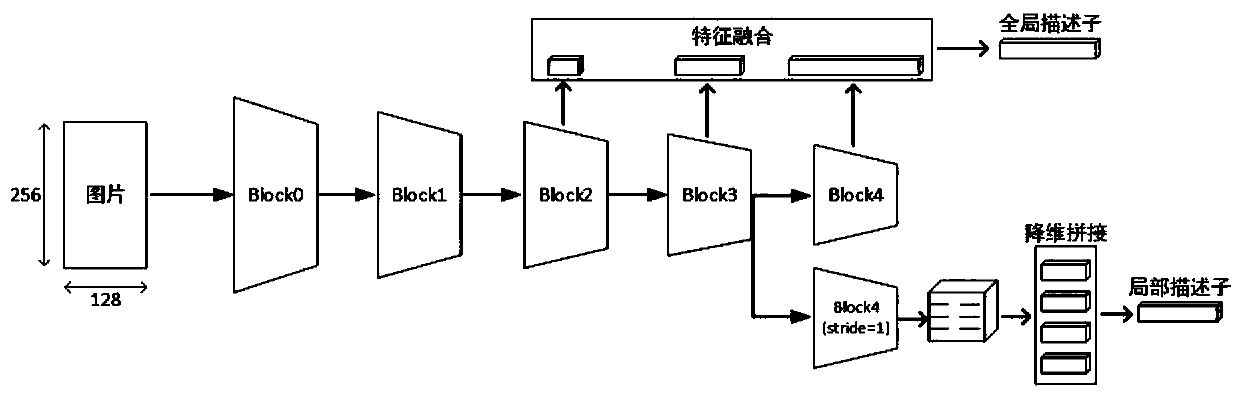
[0054] Such as figure 2 As shown, the global descriptor is extracted, and the information in the feature maps of different scales of the deep network is extracted, and then the feature fusion is performed to obtain the global descriptor:
[0055] The global branch adopts the ResNet50 structure, the input is an image of 256*128*3, and the f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com