Total protein measurement using whole blood refractometry
A protein, refractive index technology used in the field of clinical analyzers to solve problems such as reducing accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
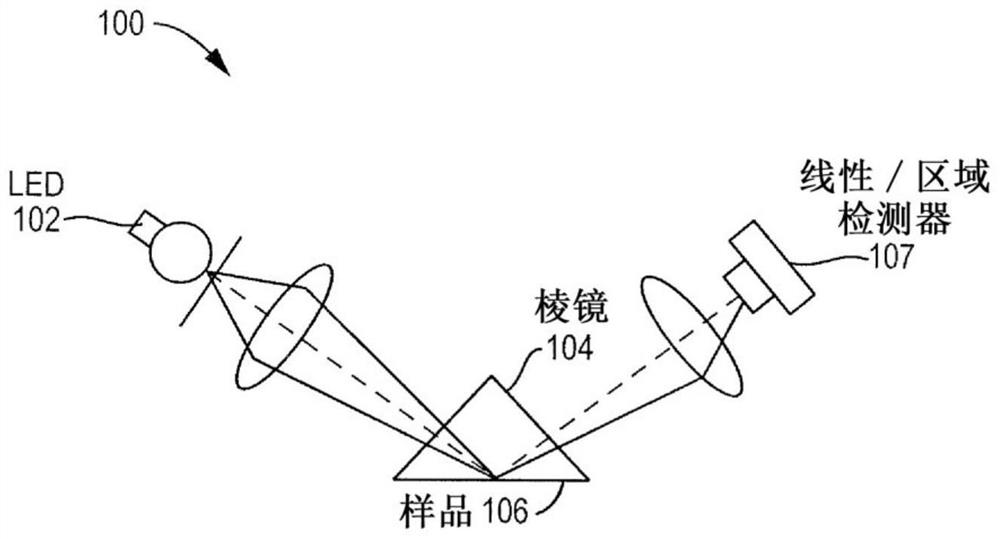
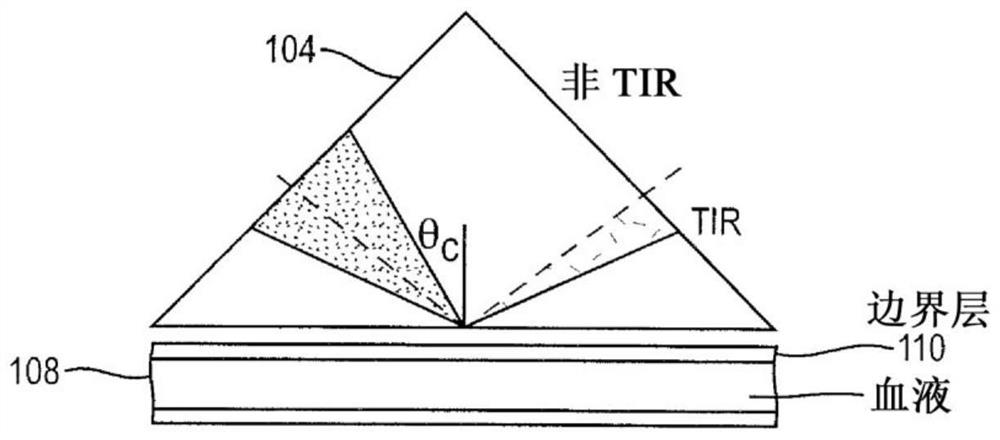
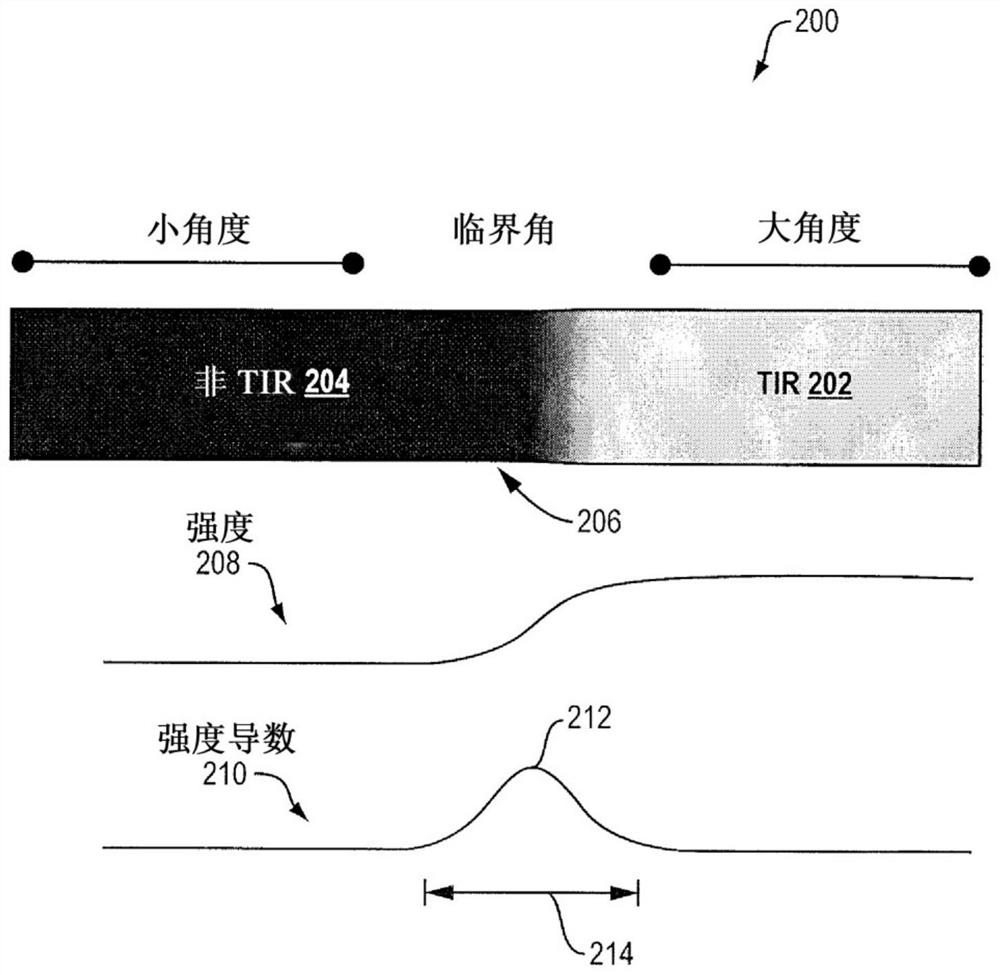
[0016] Aspects of the present disclosure include methods and apparatus for performing refractometry on a substantially cell-free plasma layer adjacent to a channel wall of a channel containing a flowing whole blood sample. This allows the measurement of the total protein content of the sample without the additional step of isolating plasma from whole blood samples.
[0017] When a whole blood sample flows through a channel with a small cross-sectional diameter, such as a blood vessel in the body or a capillary on a chip, for example, the sample appears as a flow with a substantially cell-free plasma membrane present at the edge of the channel. The substantially cell-free plasma membrane is a very thin layer with a thickness of less than 1 micron to several microns at the edges of the channels. It is believed that the presence of substantially cell-free plasma membranes in blood vessels, for example, helps prevent blockages and reduces fluid resistance in small blood vessels in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com