Multi-user resource allocation method based on NOMA and SWIPT cognitive radio environment
A cognitive radio and resource allocation technology, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, advanced technologies, etc., can solve problems such as low reachable rate for weak users, decoding failures, neglect of user fairness, etc. Fairness, the effect of improving spectral efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
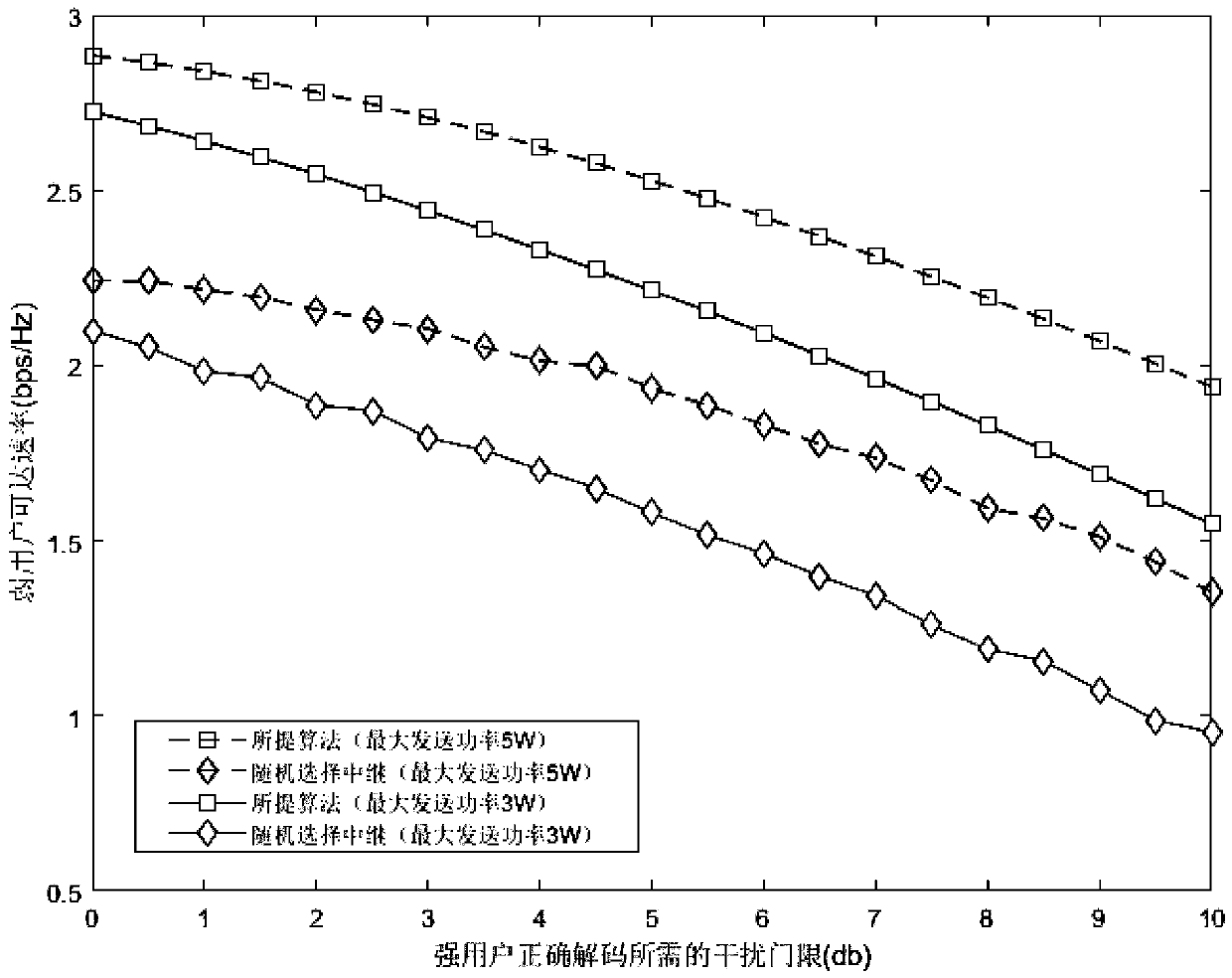
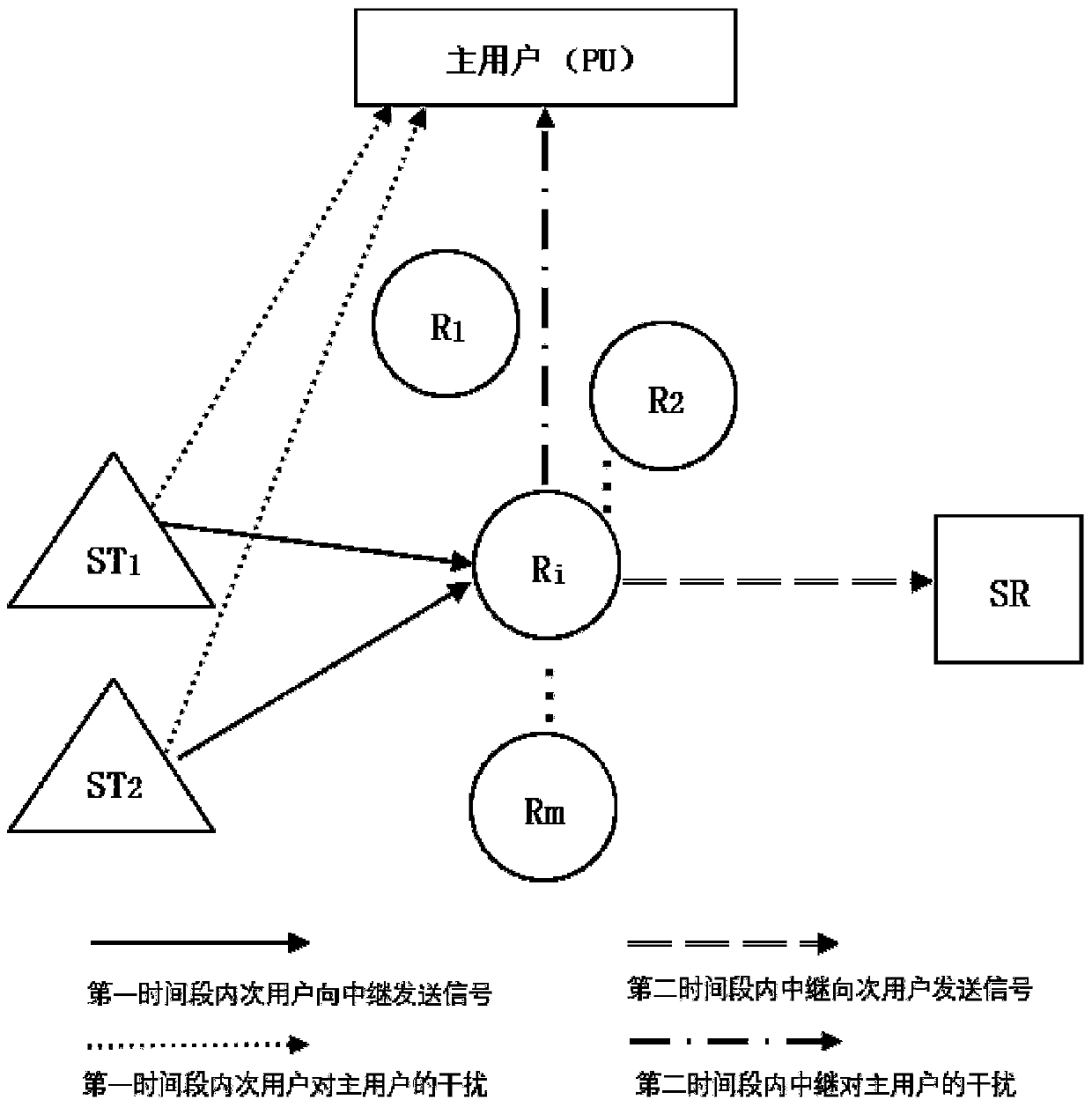
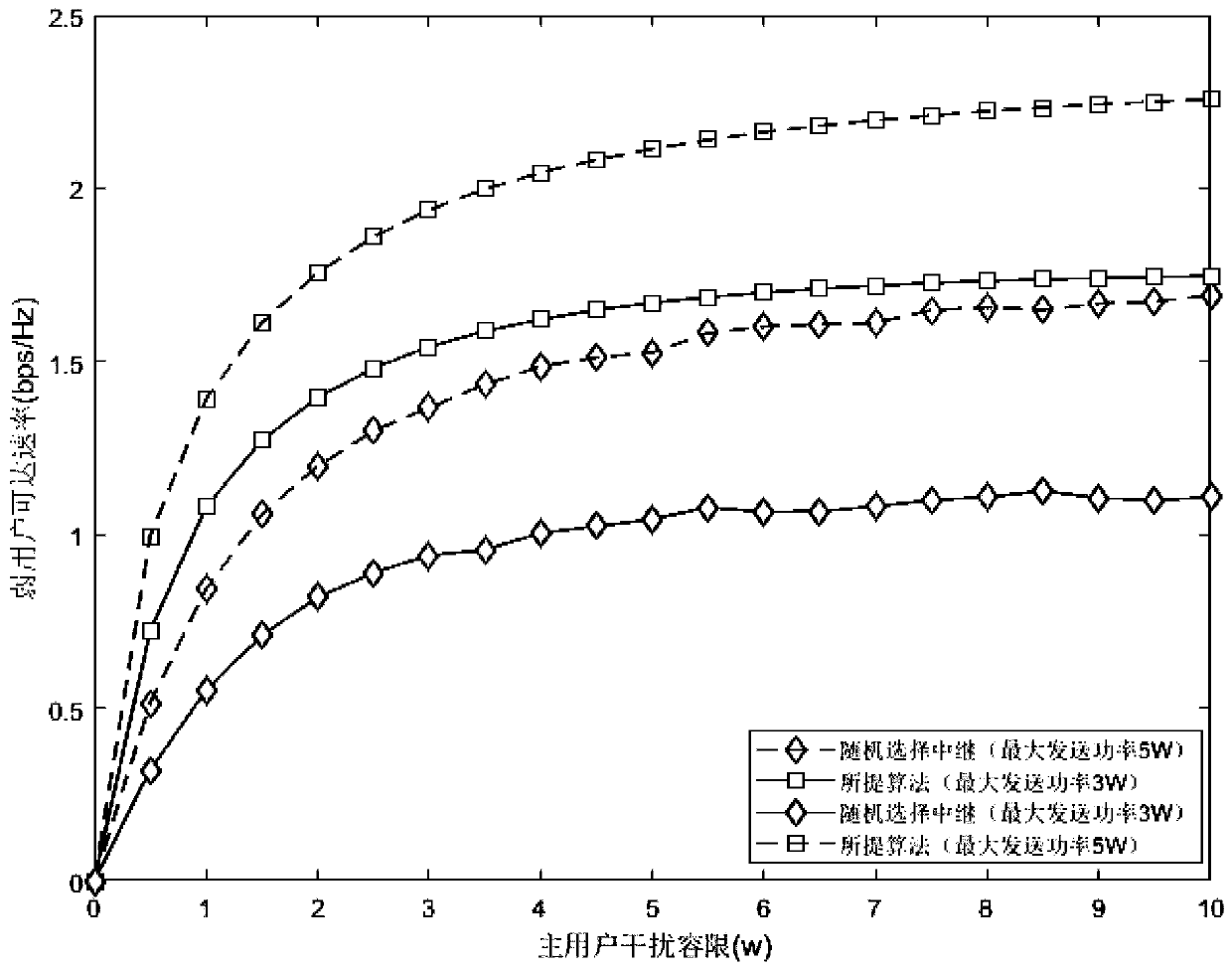
[0079] A multi-user resource allocation method based on NOMA and SWIPT cognitive radio environment, operating in a multi-user relay communication system based on NOMA and SWIPT cognitive radio environment, such as figure 1 As shown, including a primary user PU, m relays R 1 ~R m , two secondary user senders ST 1 and ST 2 , and a secondary user receiving end SR, the primary user PU is always in the communication state;
[0080] Since there is no direct connection path from the secondary user’s sending end to the secondary user’s receiving end, the signal of the secondary user needs to be amplified and forwarded (AF) through the relay. During this process, the relay will perform dynamic power down the forwarding signal service. In actual scenarios, the sending end and the receiving end often have a fixed energy source. However, due to the characteristics of large number, wide distribution, complex working environment, and difficulty in charging in time, it is assumed that th...
Embodiment 2
[0121] According to the multi-user resource allocation method based on NOMA and SWIPT cognitive radio environment described in Embodiment 1, the difference is that: within the first stage, two secondary user transmitting ends transmit radio frequency signals at the same time, and the relay receives radio frequency signals signal and perform energy harvesting; in the second stage, the relay forwards the remaining signal after energy harvesting in the first stage, and the energy used for forwarding is provided by the energy collected in the first stage; including Proceed as follows:
[0122] A. Transmission process: the first time period: in the first time period, the two secondary user senders ST 1 and ST 2 Simultaneously send signal, relay R i is activated and receives a signal, 1≤i≤m, which will cause interference to the PU during signal transmission. In order to highlight the main contradiction of the problem, we will simplify the problem appropriately. Ignore relay R us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com