Multi-focal structured illumination microscopy systems and methods
A microscope system, focal length technology, used in microscopy, fluorescence/phosphorescence, instrumentation, etc., to solve problems such as being unsuitable for thick or highly stained
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
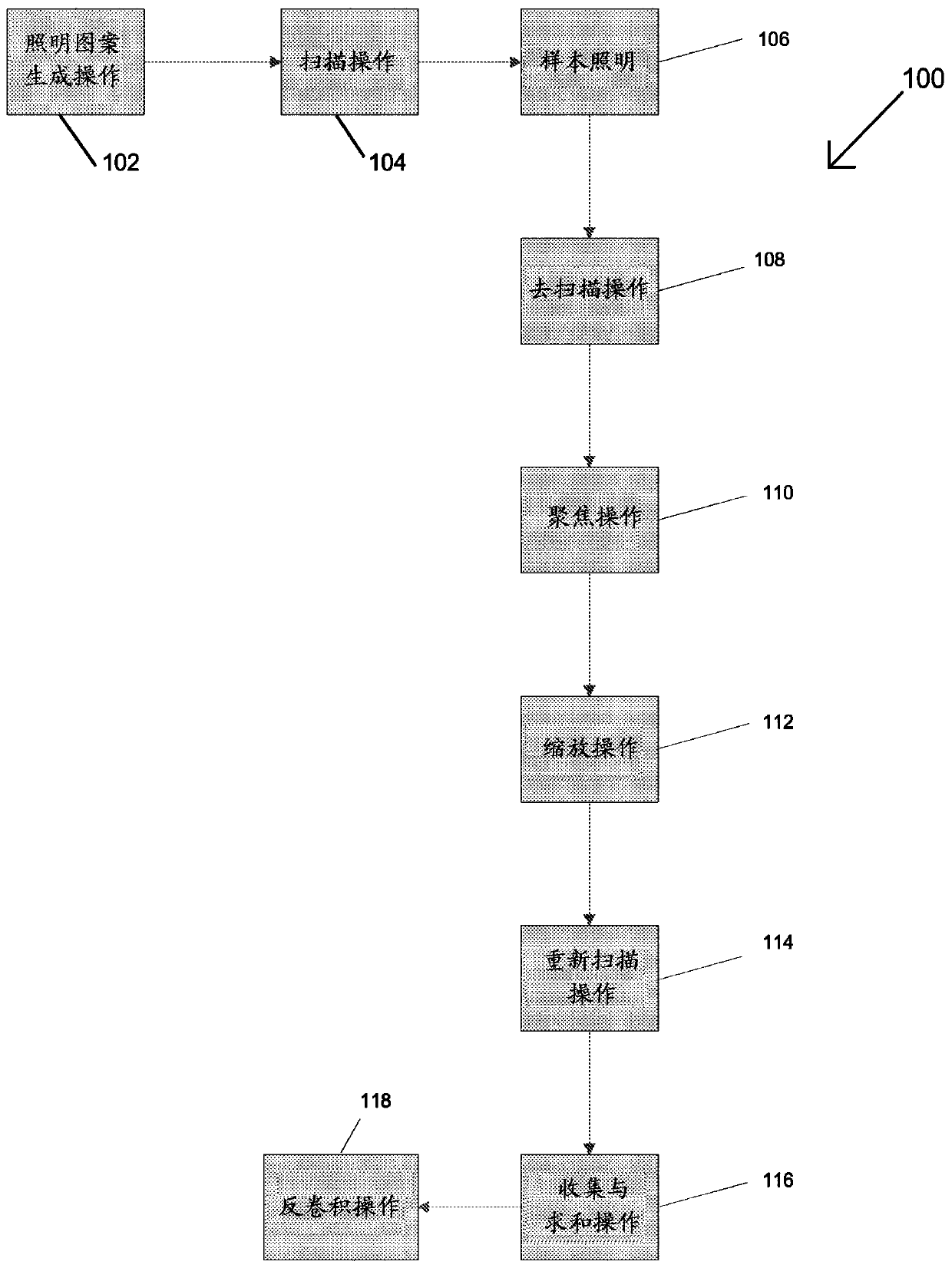
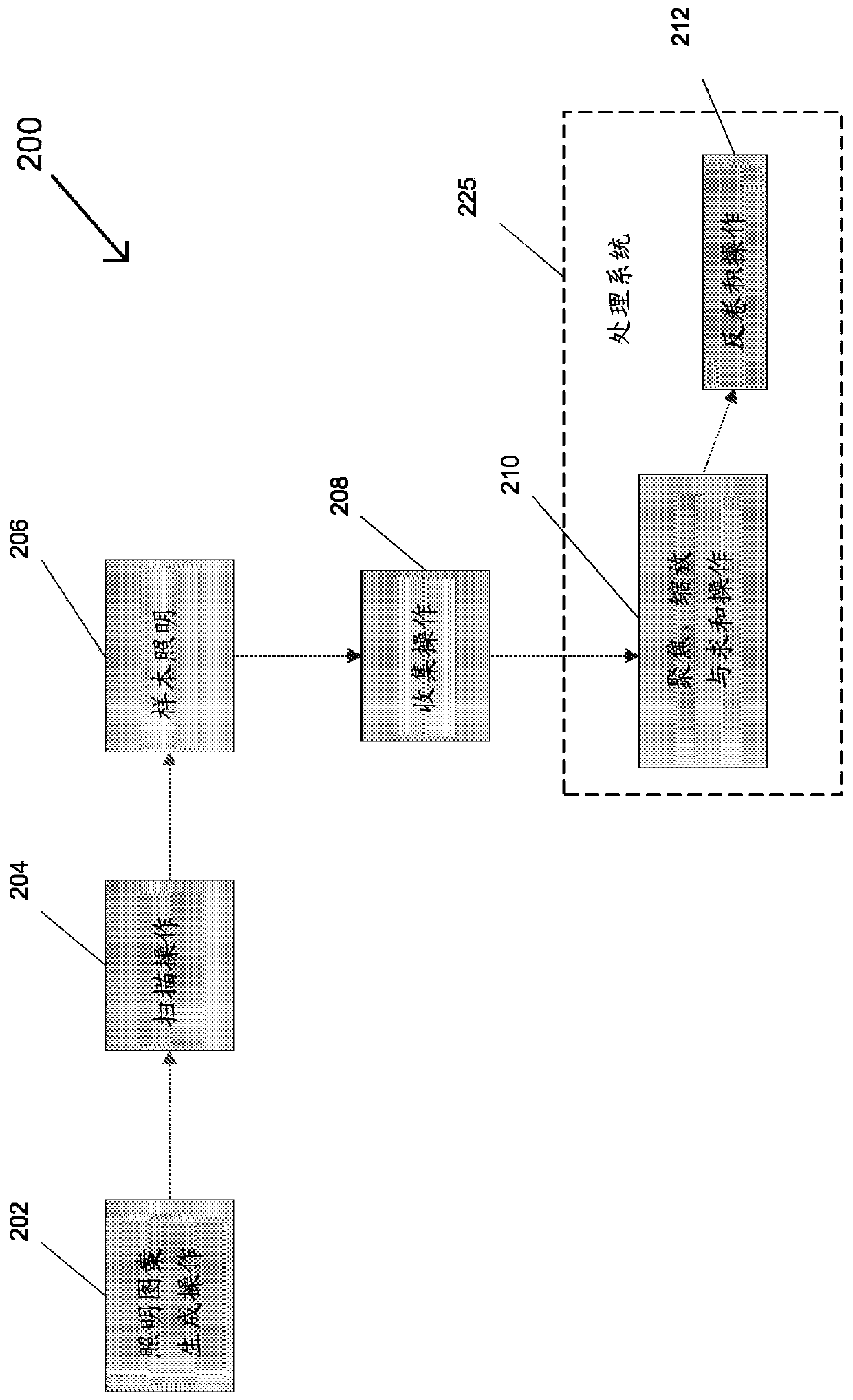
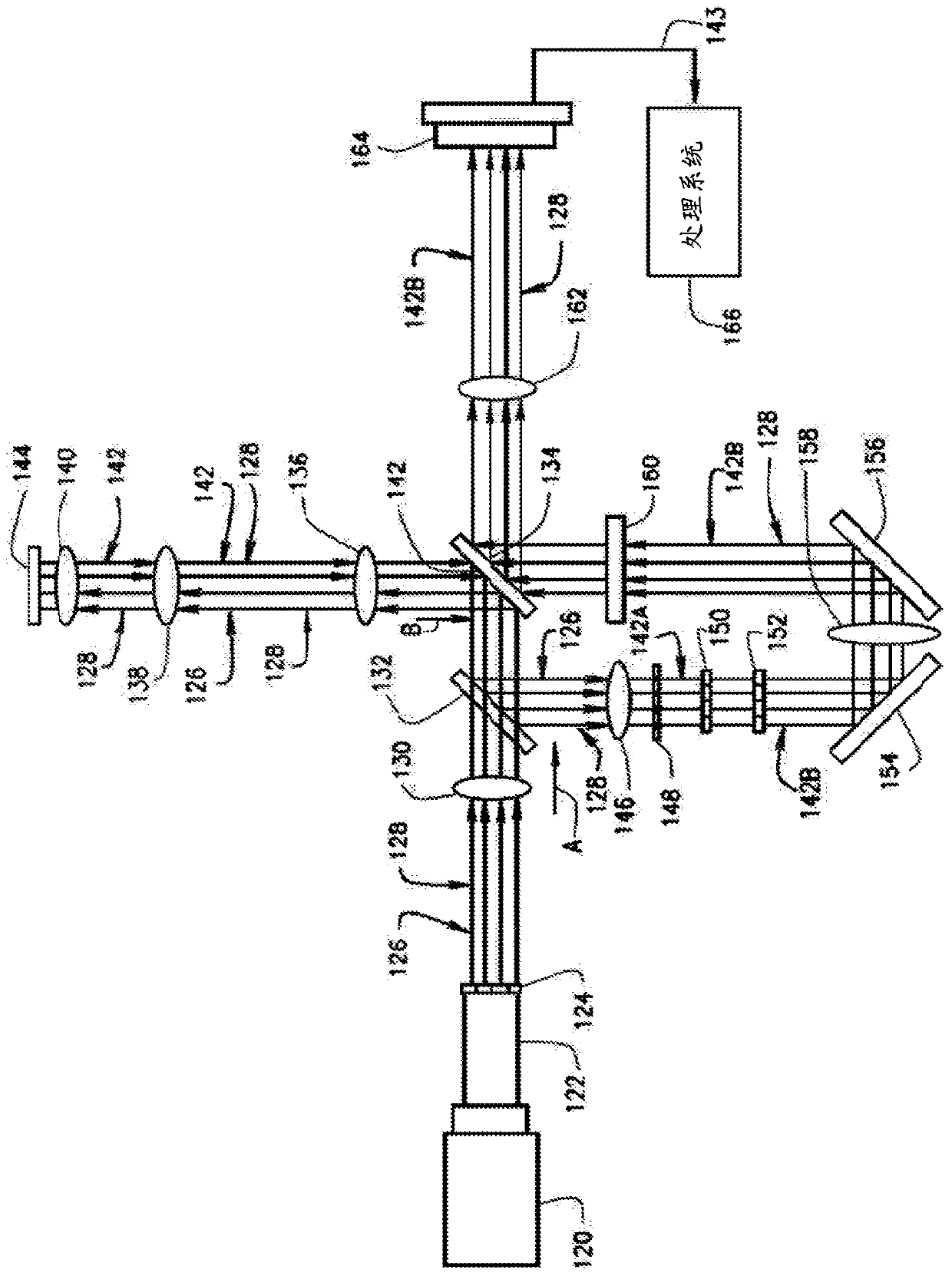
[0041] In modern microscopy, structured illumination microscopy (SIM) can be used to examine individual cells by using spatially patterned light to excite sample fluorescence to be detected later, and to process one or more images to yield resolution Super-resolution images that are twice the size of traditional wide-field microscopy images. However, the SIM system sacrifices speed (taking multiple raw images for each super-resolution image) for higher resolution. Furthermore, optical sectioning in SIM systems is performed computationally and thus prone to the shot noise inherent in the fluorescent background. This limits the thickness of samples that can be examined, requiring the use of other microscopic techniques when examining thicker samples. For example, confocal microscopy systems physically reject out-of-focus light using a pinhole arrangement that allows only light from a specific focal point of the emitted light emitted by the sample to be detected by the system, t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com