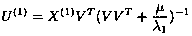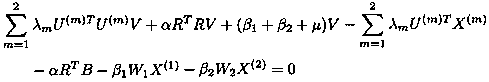Discrete supervised cross-media Hash retrieval method based on collaborative matrix decomposition
A matrix factorization, cross-media technology, applied in the field of discrete supervised cross-media hash retrieval, which can solve problems such as loss of category information, difficulty in directly solving the objective function of hashing methods, and complex semantic associations.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
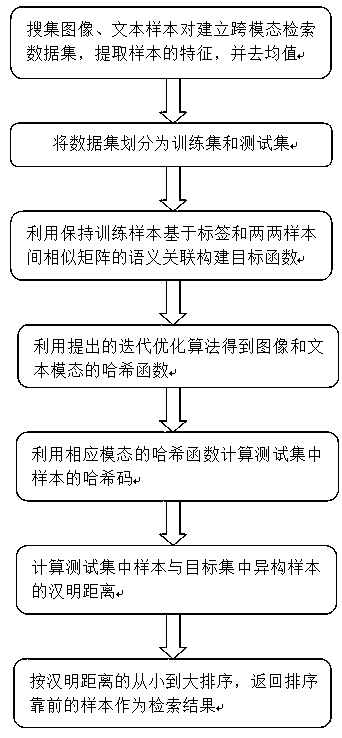
[0124]This embodiment takes the public dataset NUS-WIDE as an example, which contains 269,648 image and text sample pairs, and all sample pairs are distributed in 81 categories. In order to make each class have enough samples for training, the 21 classes with the most samples are selected, so 196,776 image and text sample pairs are reserved. The image and text samples in the data set were extracted with CaffeNet and BOW (BagOf Words) algorithms, respectively, with 4096-dimensional CNN features and 1000-dimensional BOW features, and the features were averaged. 99% of the sample pairs are randomly selected to form the training set, and the remaining 1% of the sample pairs form the test set. In order to objectively evaluate the performance of the method of the present invention, the average accuracy rate MPA@100 is used as the evaluation standard, and MPA@100 means that the MAP is calculated from the first 100 returned samples. On this dataset, the MAP@100 results are shown in T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com