Information hiding method and robot system based on big data and Fourier transform
A technology of Fourier transform and Fourier inverse transform, applied in the field of information, can solve the problems of information hiding, such as limited data volume and easy cracking, and achieve the effect of increasing the difficulty of detection and cracking, improving capacity and security, and improving security
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
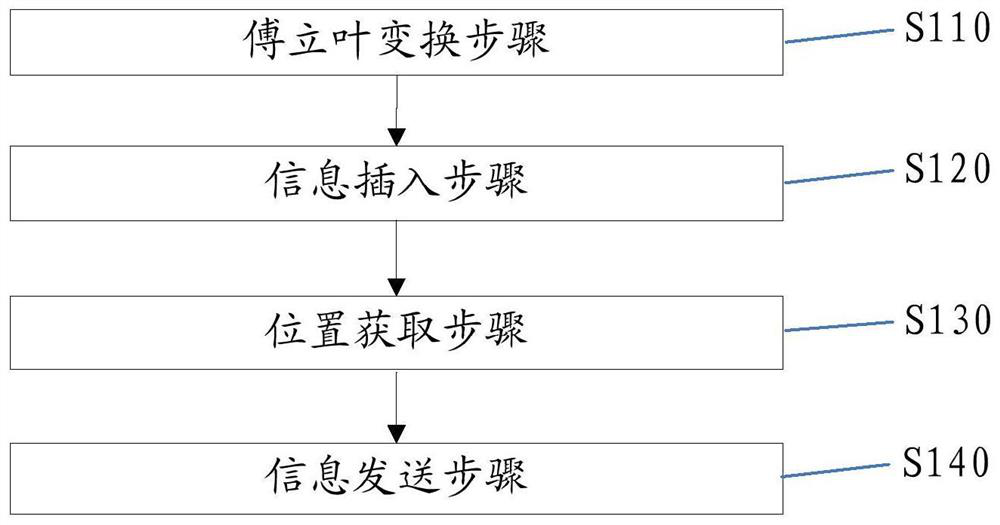
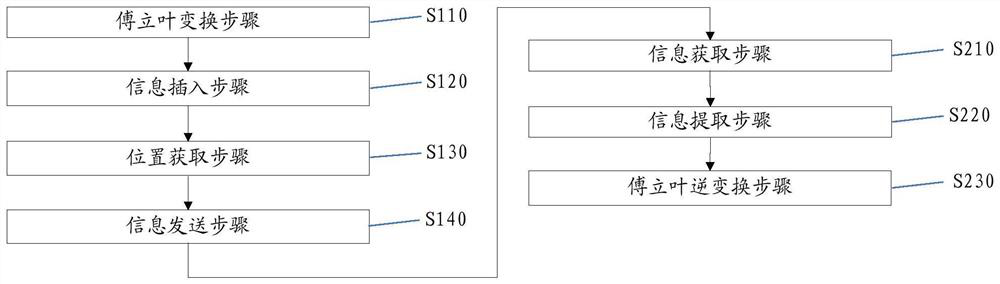
[0049] Embodiment 1 provides an information hiding method, such as figure 1 As shown, the method includes steps S110 to S140.
[0050] Fourier transform step S110: Convert the secret information x that needs to be hidden into data of the first function f(t), and perform Fourier transform with the first function f(t) as the original function The obtained image function is used as the second function F(w), and the data of the obtained second function F(w) is used as the first information. Secret information refers to the information to be hidden, which can be text, password, image, graphic or sound, etc. Preferably, the secret information x is obtained, the secret information is divided into a plurality of units (preferably, the division method includes dividing according to space, dividing according to time or dividing according to order), and taking the number of each unit as the number of t value (preferably, the numbering includes a spatial position or a time or a serial n...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2 provides a preferred information hiding method. According to the information hiding method described in Embodiment 1, combined with big data, the Fourier transform step S110 specifically includes step S111; the information insertion step S120 specifically includes step S121; the location acquisition step S130 specifically includes step S121. Step S131 is included.
[0056] Information segmentation step S111: segment the secret information x into multiple partial secret information x1, x2, . f(t2), . Take the image functions corresponding to the multiple first functions as multiple second functions F(w1), F(w2), ..., F(wm) respectively, and obtain the data of multiple second functions as multiple first functions. a message. Preferably, the secret information x is divided into m parts of equal length as a string to become x1, x2, . . . , xm. Preferably, the serial number of each part of the secret information after division is recorded, and the serial num...
Embodiment 3
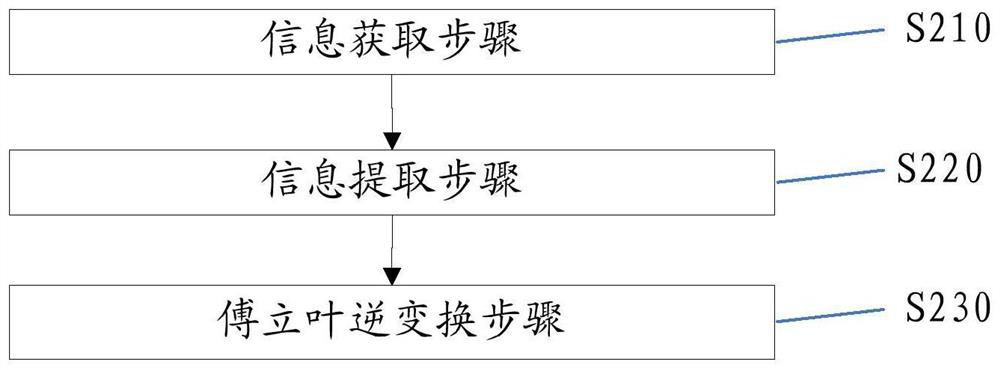
[0061] Embodiment 3 provides a kind of information extraction method, as figure 2 As shown, the method includes steps S210 to S230.
[0062] Information acquisition step S210 : accept the first position s input by the user.
[0063] Information extraction step S220 : extract the first information, that is, the data of the second function F(w), from the first position s in the big data. Preferably, the start number and the end number are obtained from the first position s in the big data. For example, the information at the first position s in the big data is "the data of the second function is the data of" F(w), "the starting position is" the starting position, and "the ending position is" The ending position, then according to the keywords "the data of the second function is", "the starting position is", and "the ending position is" to match, the corresponding content after these keywords can be located as the first The data of the two-function F(w), the start position, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com