Devices, systems and/or methods for myopia control
A technology of myopia and micro-lens, which is applied in glasses/protective glasses, glasses/goggles, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as the failure of emmetropization process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
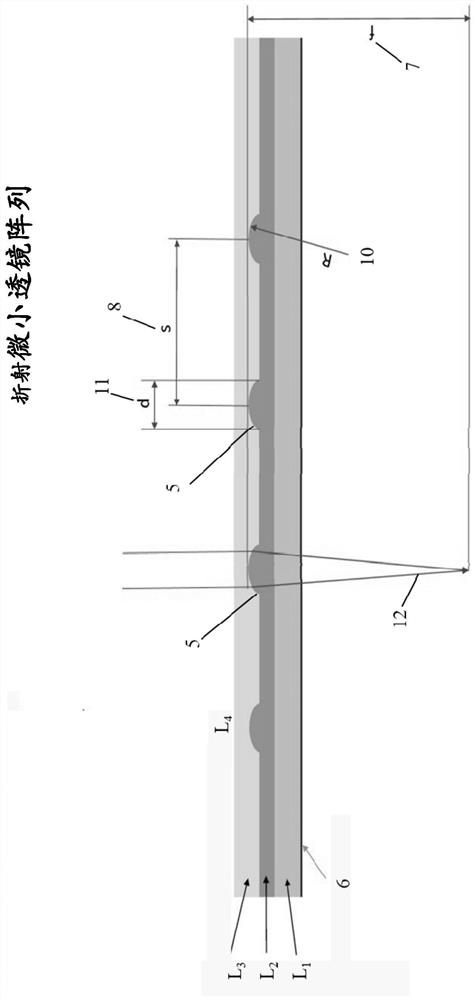
[0254] Example 1: Three-layer micro lens array
[0255] FIG. 1 shows an exemplary embodiment of a multilayer microlens array in a side view, not to scale. L 1 The layer is a transparent foil used as a substrate for the microlens array. The foil is a plastic polymer, however other suitable materials may also be used. In this example, L 2 The layer contains many microlenses, which are shown in side view in Fig. 1 as layer L 2 Small surface height 5 on the surface. In this embodiment, the diameter (d) or 11 is approximately 0.1 mm for each microlens. The focal path of light entering the microlens array is exemplified at 12 in FIG. 1 . L 2 The material used in the layers is another plastic polymer, however other suitable materials can also be used. In this example, L 2 The filling ratio in the layer is approximately 10%. L 3 layer is covered by L 2 layer of protection. L 3 The material used in the layers is plastic adhesive, however other suitable materials may als...
Embodiment 2
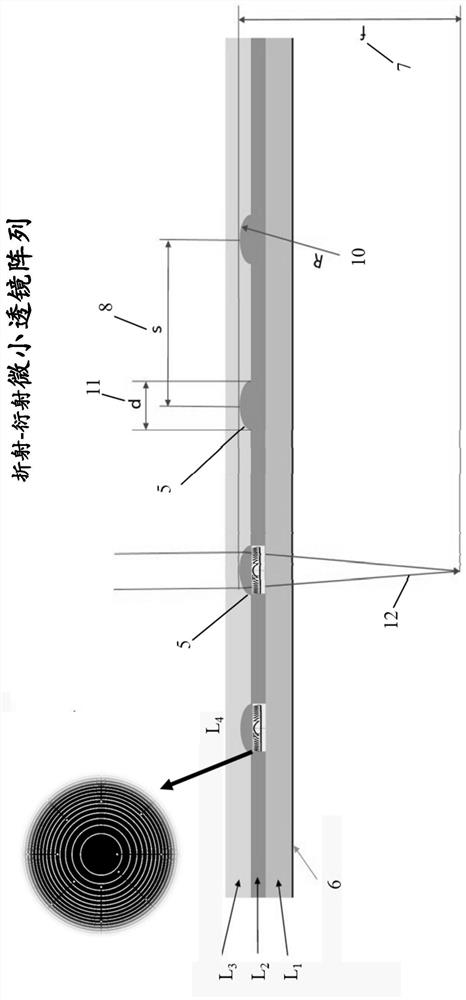
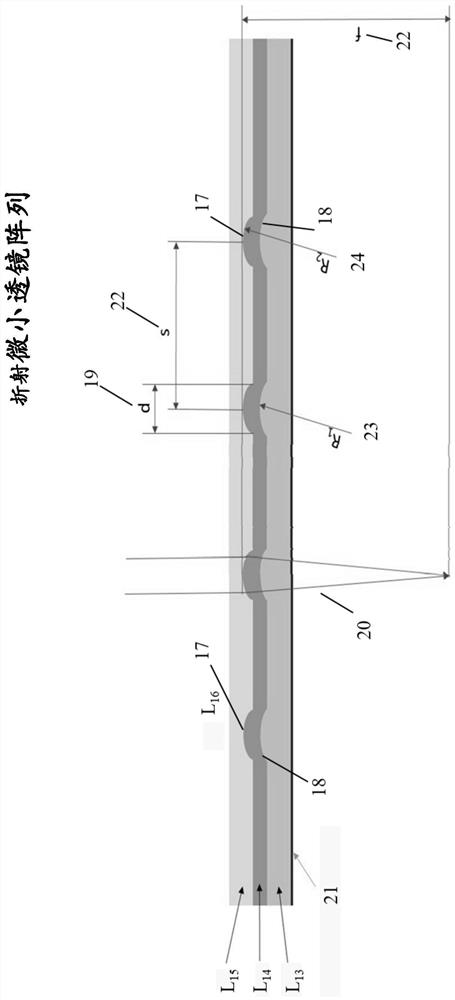
[0258] Example 2: Three-layer micro lens array
[0259] figure 2 An exemplary embodiment of a multilayer microlens array is shown in side view. In this example, the microlenses are found on the surfaces of two separate layers in the microlens array. L 13 layer is a transparent foil used as a substrate for the microlens array, and it also contains a part of the microlenses 18, which in this embodiment are in figure 2 The small surface height 18 is shown in side view. Foil is a plastic adhesive. In this example, L 14 The layer contains many microlenses 17 concentric with microlenses 18, and the microlenses 17 are in figure 2 shown in side view as layer L 14 Small bumps 17 on the surface. In this embodiment, the diameter (d) or 19 is approximately 0.1 mm for each lenslet. The focal path of light entering the microlens array is at figure 2 In 20 demonstrations. L 14 The material used in the layers is a plastic polymer, however other suitable materials may also be u...
Embodiment 3
[0261] Example 3: Two layers of tiny lens array
[0262] Figures 3A to 3E A non-limiting exemplary embodiment of a microlens array relative to a spectacle lens system is depicted in side view. There are many other suitable implementations of using tiny lenses on spectacle lenses, which are in Figures 3A to 3E not shown, but would be obvious to those skilled in the art. The geometry of the lenslets may depend on many factors including, but not limited to, the refractive index of the substrate layer, diameter, radius of curvature, effective focal length of individual lenslets, spacing between lenslets, or combinations thereof.
[0263] Figure 3A A spectacle lens system is depicted in which convex microlenses are molded directly into the spectacle lens, either on the front or back surface. Figure 3A A tiny lens 26 molded on the front of a spectacle lens 25 is depicted. The area closer to the eye is 27, while the area outside the spectacle lens is 28. exist Figure 3A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com