Minimally invasive fixation device for tibial intercondylar spine fracture
A technology of fixation device and intercondylar spine, which is applied in the direction of fixator, internal fixator, internal bone synthesis, etc., can solve the problems that are not easy to carry out extensively, difficult to perform surgery, etc., achieve good promotion and use value, avoid large surgical trauma, and be clinically The effect of easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
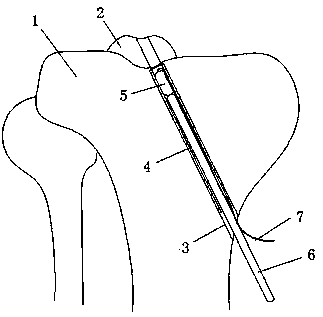
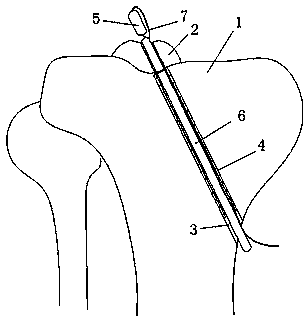
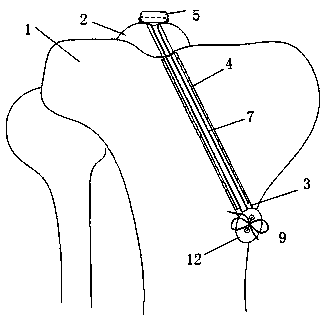
[0025] The present invention is made up of hollow sleeve 4, fixer, push rod 6, traction rope 7, and hollow sleeve 4 extends into tibial end face from the side of tibia 1, and fixer reaches tibia from hollow sleeve 4 under the push of push rod 6 On the end face, the fixing part passes through the intercondylar spinous fracture fragment 2 and reaches above the intercondylar spinous fracture fragment 2, pulls the traction rope 7 to press the fixing part above the intercondylar spinous fracture fragment 2, and tightens and fixes it from the bottom of the hollow sleeve 4 The traction rope 7 makes the fixing member fix the intercondylar spinous bone fragment 2 .
[0026] Shown in the figure, the present invention needs to punch on the tibia 1, the upper end of the fixed socket 3 of the tibia 1 is positioned at the tibial end surface below the intercondylar spinous fracture block 2 of the tibia 1, and the lower end of the fixed socket 3 is positioned at the tibial tuberosity below On...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com