Hydrophobic material surface modification method and application of material after modification
A surface modification, hydrophobic material technology, applied in analytical materials, instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of complex experimental conditions, multi-step process flow, unfavorable technical methods are widely used and popularized, and long-term effects cannot be guaranteed. Adhesion and cell culture effect, improvement of micron-scale cell manipulation and detection and analysis application, effect of good modification effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] This embodiment provides a modification method that can enhance the adhesion of nerve cells on the surface of PDMS hydrophobic materials, which specifically includes the following steps:
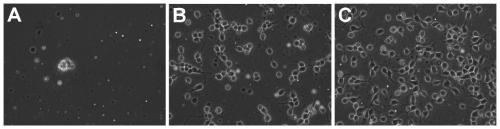
[0030] In this embodiment, in addition to the modification method involved in the present invention, two control groups (unmodified group and PDL modified group) were also set up to compare the cell adhesion effect.
[0031] Three pieces of PDMS membranes were placed in three regular 35mm cell culture dishes.
[0032] In Dish 1 (unmodified group), the PDMS membrane was washed for 3 min with fresh neuron cell basal culture medium (Gibco).
[0033] In dish 2 (PDL modification group), 100 μg / mL PDL solution was added to the surface of PDMS, 2 mL / dish, incubated at 20°C for 2 hours, and then washed with fresh cell culture medium for 3 minutes.
[0034] In Dish 3 (the present invention relates to a modification method), 100 μg / mL PDL-F127 solution was added to the surface of PDMS, 2 mL / di...
Embodiment 2
[0041] This embodiment provides the nerve cell patterning application of the PDMS hydrophobic material surface modification method in Example 1, which specifically includes the following steps:
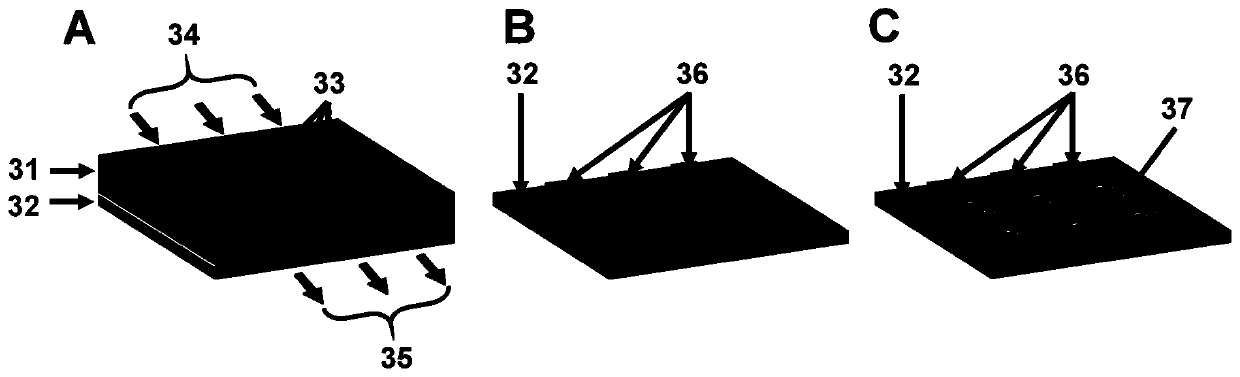
[0042] First, if image 3 As shown in A, the neuron patterning device that can be used for microfluidic pipelines is assembled, that is, the PDMS microchannel layer (31) is placed on a PDMS substrate layer (32), and the PDMS microchannel layer adopts conventional soft lithography technology In preparation, the micropipe layer comprises parallel micropipes (33), inlets (34), and outlets (35).
[0043] The device was placed in a conventional 35mm cell culture dish.
[0044] Pour 100 μg / mL PDL-F127 solution from the inlet of the microchannel layer (34) into the parallel microchannels (33), modify the inner surface of the microchannels, incubate at 20°C for 2 hours, and wash with fresh cell culture medium for 3 minutes.
[0045] Remove the PDMS micropipe layer (31), and keep the PDMS ba...
Embodiment 3
[0049] This example provides the long-term culture of nerve cells and the formation of neural networks in the microfluidic chip of the PDMS hydrophobic material surface modification method in Example 1, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0050] First, if Figure 5 As shown in A, the microfluidic chip used in this embodiment consists of a PDMS chip fluid layer (51) and a PDMS chip base layer (52) from top to bottom, wherein the chip fluid layer is prepared by conventional soft lithography technology, and the fluid layer It includes a micro-pipe network (53), a chip inlet (54), and a chip outlet (55).
[0051] The 100 μg / mL PDL-F127 solution is perfused into the micropipe network (53) from the chip inlet (54), the inner surface of the micropipe network is modified, incubated at 20° C. for 2 hours, and fresh nerve cell basal culture medium (Gibco Inc. ) for 3 minutes.
[0052] Such as Figure 5 As shown in B, the 2×10 6 Each / mL primary nerve cell (56) suspensi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com