Shortest Path Planning Method Based on Turn Weight Constraints
A shortest path, weighted technology, applied in two-dimensional position/flight control and other directions, can solve the problems of occupying the opposite lane, congestion, delay in vehicle access, etc., and achieve the effect of avoiding turning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
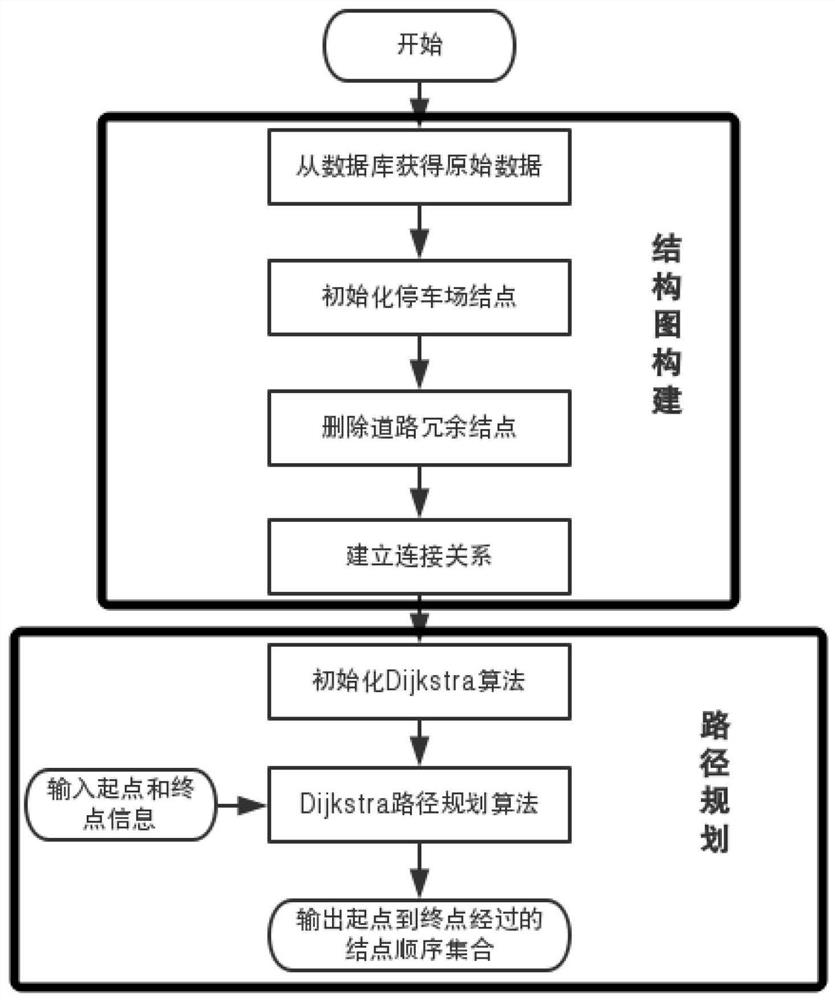
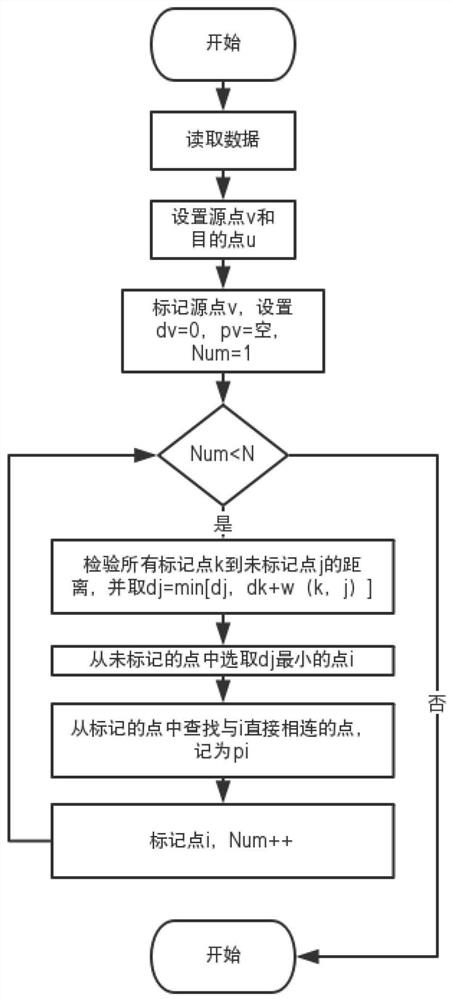
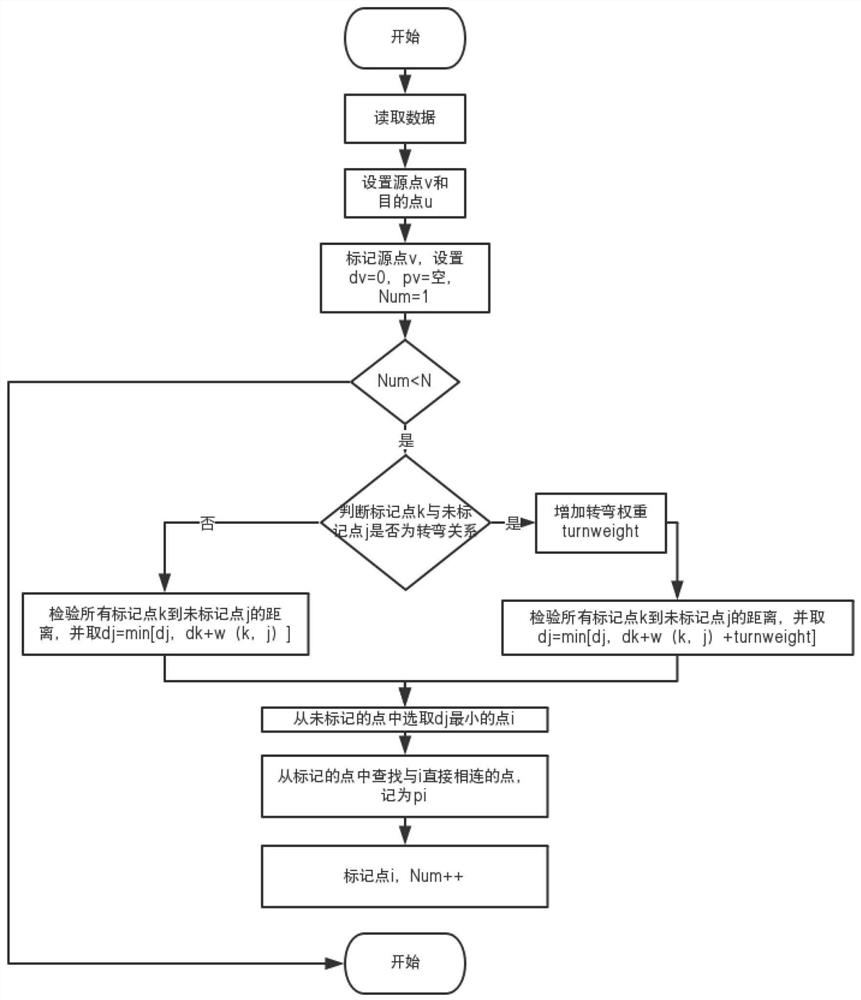
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0066] Figure 4 A schematic diagram of the application and implementation of a weight constraint-based omnidirectional wheel AGV shortest path planning method provided by the embodiment of the present invention, as shown in Figure 4 As shown, ① to ⑧ are graph nodes, and edge weights are given according to the length of the road. The AGV will drive from the starting node ① to the ending node ⑧, and find the shortest path.
[0067] According to the ordinary Dijstra algorithm, the path 1 is obtained as ①-②-④-⑤-⑥-⑧, and the path length is 45. Path 2 is ①-③-⑦-⑧, and the path length is 63. Finally choose path 1.
[0068] According to the improved Dijsktra algorithm proposed by the present invention, path 1 is ①-②-④-⑤-⑥-⑧, through 4 turns, so the final path length is 45+4*10=85; path 2 is ①-③ -⑦-⑧, after 2 turns, the final path length is 63+2*10=83, and path 2 is finally selected.
[0069] In multi-AGV path scheduling, the average usage time of path 2 is shorter than that of p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com