Data packet scheduling method and device
A scheduling method and data packet technology, applied in the field of communications, can solve problems such as failure to avoid interference, failure to avoid co-channel interference, and failure to effectively avoid mutual interference between adjacent cells, and achieve the effect of avoiding severe interference and avoiding interference.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
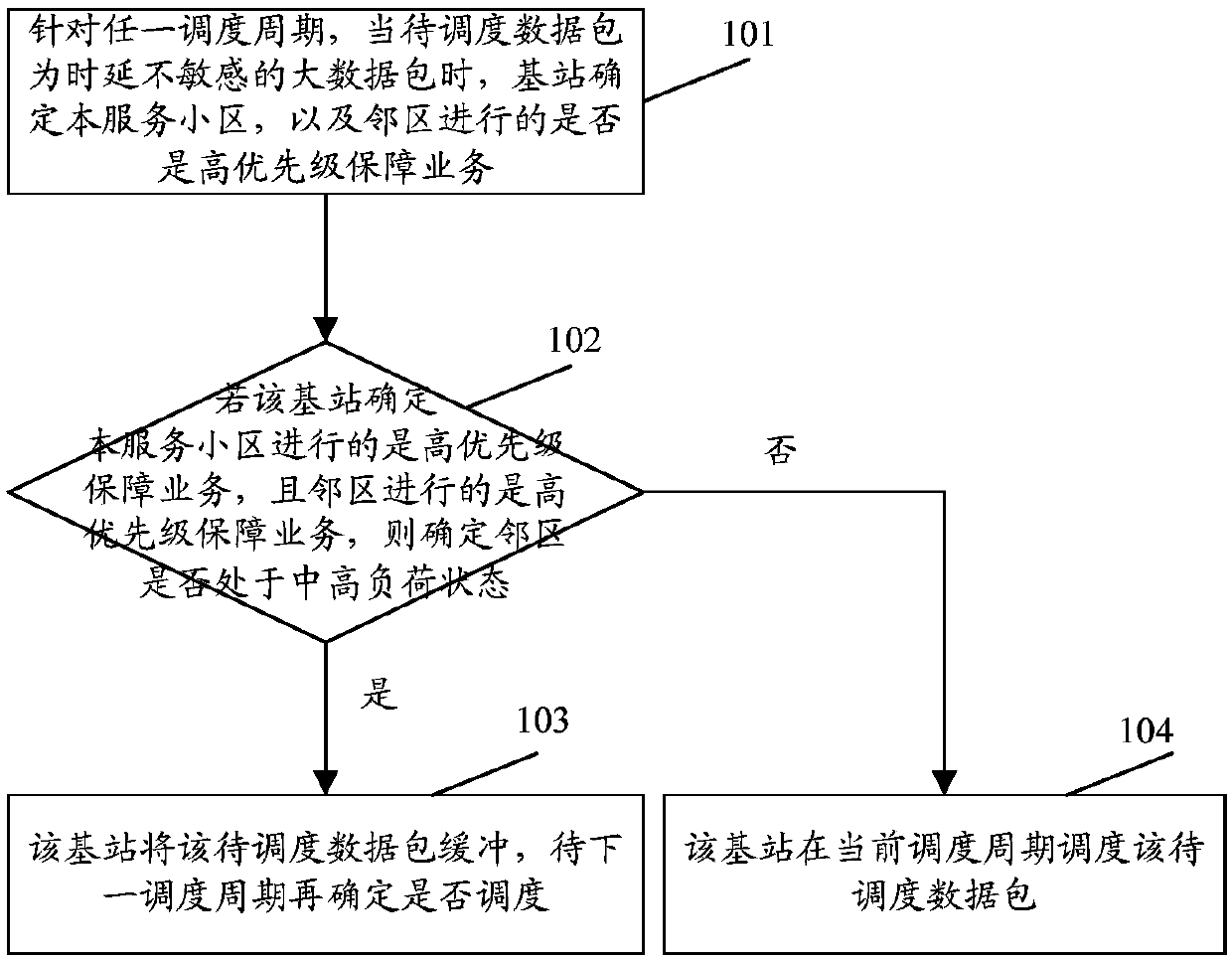
[0053] This embodiment describes in detail the process of scheduling large data packets that are not sensitive to delay when the service cell is performing high-priority guaranteed services and neighboring cells are performing high-priority guaranteed services.
[0054] see figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the data packet scheduling process in Embodiment 1 of the present application. The specific steps are:
[0055] Step 101 , for any scheduling period, when the data packet to be scheduled is a large data packet that is not sensitive to delay, the base station determines whether the serving cell and neighboring cells are performing high-priority guaranteed services.
[0056] Step 102, if the base station determines that the serving cell is performing a high-priority guaranteed service, and the neighboring cell is performing a high-priority guaranteed service, then determine whether the neighboring cell is in a medium-to-high load state, and if so, perform step ...
Embodiment 2
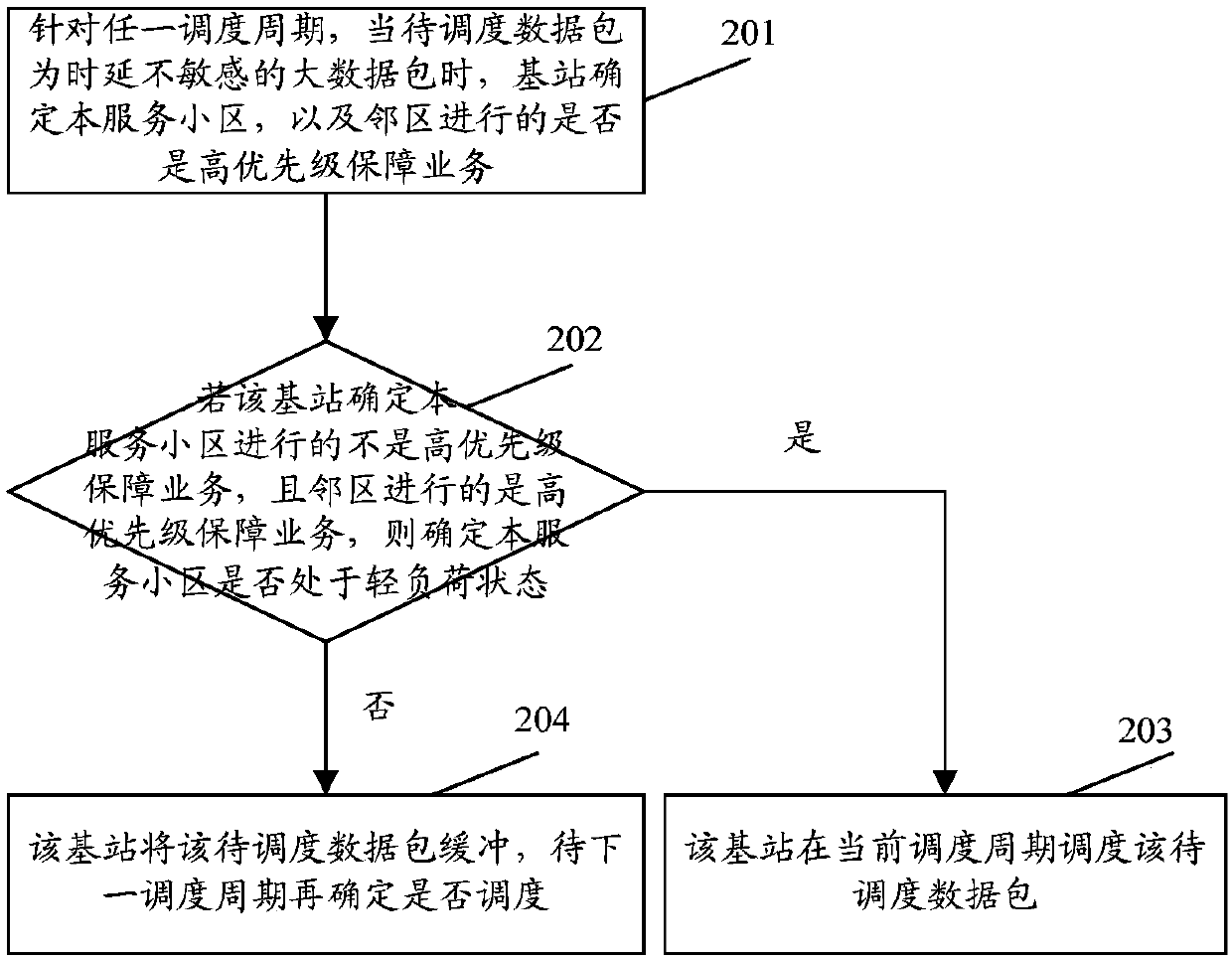
[0064] This embodiment describes in detail the process of scheduling a delay-insensitive large data packet when the serving cell does not perform high-priority guaranteed services, and the adjacent cells perform high-priority guaranteed services.
[0065] see figure 2 , figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the data packet scheduling process in Embodiment 2 of the present application. The specific steps are:
[0066] Step 201 , for any scheduling period, when the data packet to be scheduled is a large data packet that is not sensitive to delay, the base station determines whether the serving cell and neighboring cells are performing high-priority guaranteed services.
[0067] Step 202, if the base station determines that the serving cell is not performing high-priority guaranteed services, and the neighboring cells are performing high-priority guaranteed services, then determine whether the serving cell is in a light load state; if yes, execute step 203; otherwise , go to...
Embodiment 3
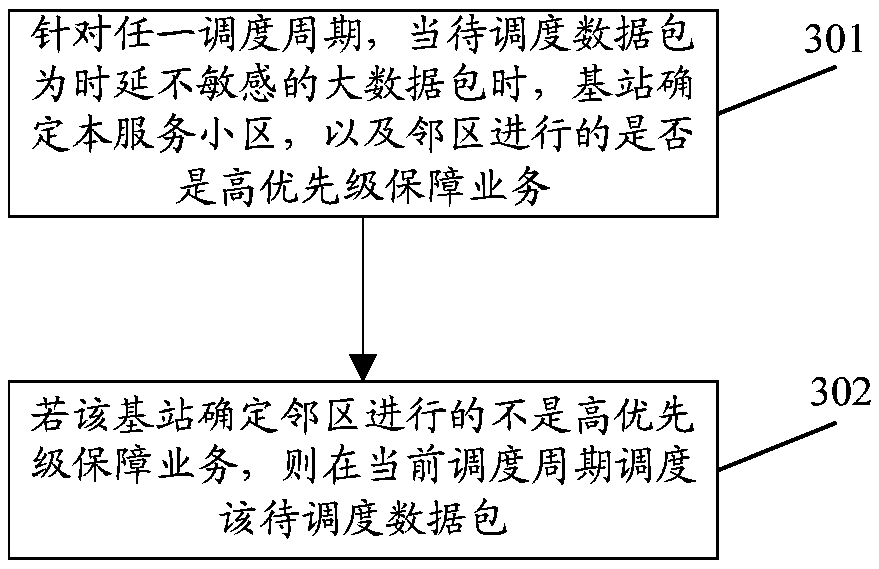
[0075] This embodiment describes in detail the process of scheduling large data packets that are not time-delay sensitive when the adjacent cells are not performing high-priority guaranteed services.
[0076] see image 3 , image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the data packet scheduling process in Embodiment 3 of the present application. The specific steps are:
[0077] Step 301 , for any scheduling period, when the data packet to be scheduled is a large data packet that is not sensitive to delay, the base station determines whether the serving cell and neighboring cells are performing high-priority guaranteed services.
[0078] Step 302, if the base station determines that the adjacent cell is not performing high-priority guaranteed services, schedule the data packet to be scheduled in the current scheduling period.
[0079] Based on the same inventive concept, the present application also proposes a data packet scheduling device, which is applied to medium and high load ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com