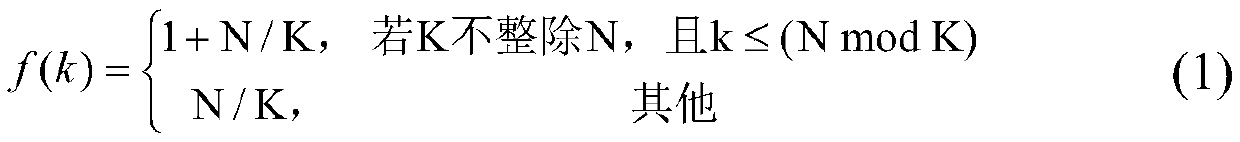Learning group grouping method based on difference
A grouping method and differentiated technology, applied in the grouping field of collaborative learning, can solve the problems of unfavorable students' academic performance, large differences, and failure to consider the balance of each group, and achieve the effect of improving academic performance, high efficiency and fast running speed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
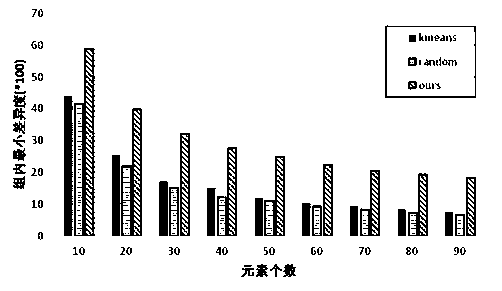
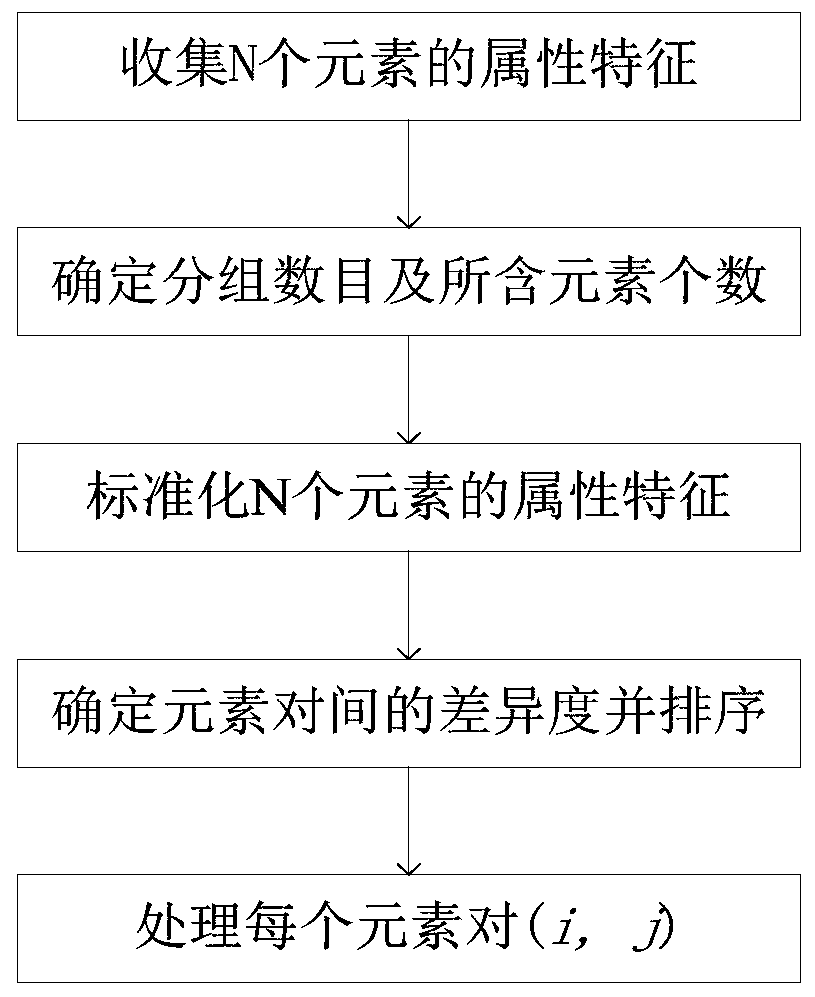
[0069] Taking the number of students N as 9, M as 4, and K as 3 as an example, the study group grouping method based on differences in this example consists of the following steps (see figure 1 ):
[0070] (1) Collect the attribute characteristics of N elements
[0071] The attribute feature v of the i-th element i Expressed as a vector as follows:
[0072] v i =(a i1 ,a i2 ,...,a im ,...,a iM )
[0073] Among them, each component a im Represents the quantized value of the element i corresponding to the mth attribute feature, a im is a real number, M represents the number of attribute features of the element, i∈{1,2,...,N}, m∈{1,2,...,M}, in this embodiment, N is 9, and M is 4, v i Values are:
[0074] v 1 =(a 11 ,...,a 14 )=(19,9,8,4)
[0075] v 2 =(a 21 ,...,a 24 )=(19,8,8,5)
[0076] v 3 =(a 31 ,...,a 34 )=(19,9,7,4)
[0077] v 4 =(a 41 ,...,a 44 )=(20,6,8,6)
[0078] v 5 =(a 51 ,...,a 54 )=(20,4,7,5)
[0079] v 6 =(a 61 ,...,a 64 )=(20,...
Embodiment 2
[0139] Taking the number of students N as 9, M as 4, and K as 3 as an example, the study group grouping method based on differences in this example consists of the following steps:
[0140] (1) Collect the attribute characteristics of N elements
[0141] This step is the same as in Example 1.
[0142] (2) Determine the number of groups and the number of elements contained
[0143] This step is the same as in Example 1.
[0144] (3) Standardize the attribute characteristics of N elements
[0145] This step is the same as in Example 1.
[0146] (4) Determine the degree of difference between element pairs and sort them
[0147] This step is the same as in Example 1.
[0148] (5) Process each element pair (i, j)
[0149] The difference-based grouping method of this embodiment is: processing each element pair (i, j) in step (5). The element pair (i, j) in this embodiment is: if both the i and j element pairs have been assigned to the group, the next element pair is processed...
Embodiment 3
[0151] Taking the number of students N as 9, M as 4, and K as 3 as an example, the study group grouping method based on differences in this example consists of the following steps:
[0152] (1) Collect the attribute characteristics of N elements
[0153] This step is the same as in Example 1.
[0154] (2) Determine the number of groups and the number of elements contained
[0155] This step is the same as in Example 1.
[0156] (3) Standardize the attribute characteristics of N elements
[0157] This step is the same as in Example 1.
[0158] (4) Determine the degree of difference between element pairs and sort them
[0159] This step is the same as in Example 1.
[0160] (5) Process each element pair (i, j)
[0161]The difference-based grouping method of this embodiment is: processing each element pair (i, j) in step (5). The element pair (i, j) in this embodiment is: one element in the element pair (i, j) has not been assigned to the group, one element has been assign...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com