Accelerated large-scale similarity calculation
A correlation and computer technology, applied in calculation, complex mathematical operations, instruments, etc., can solve calculation-intensive and time-consuming problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
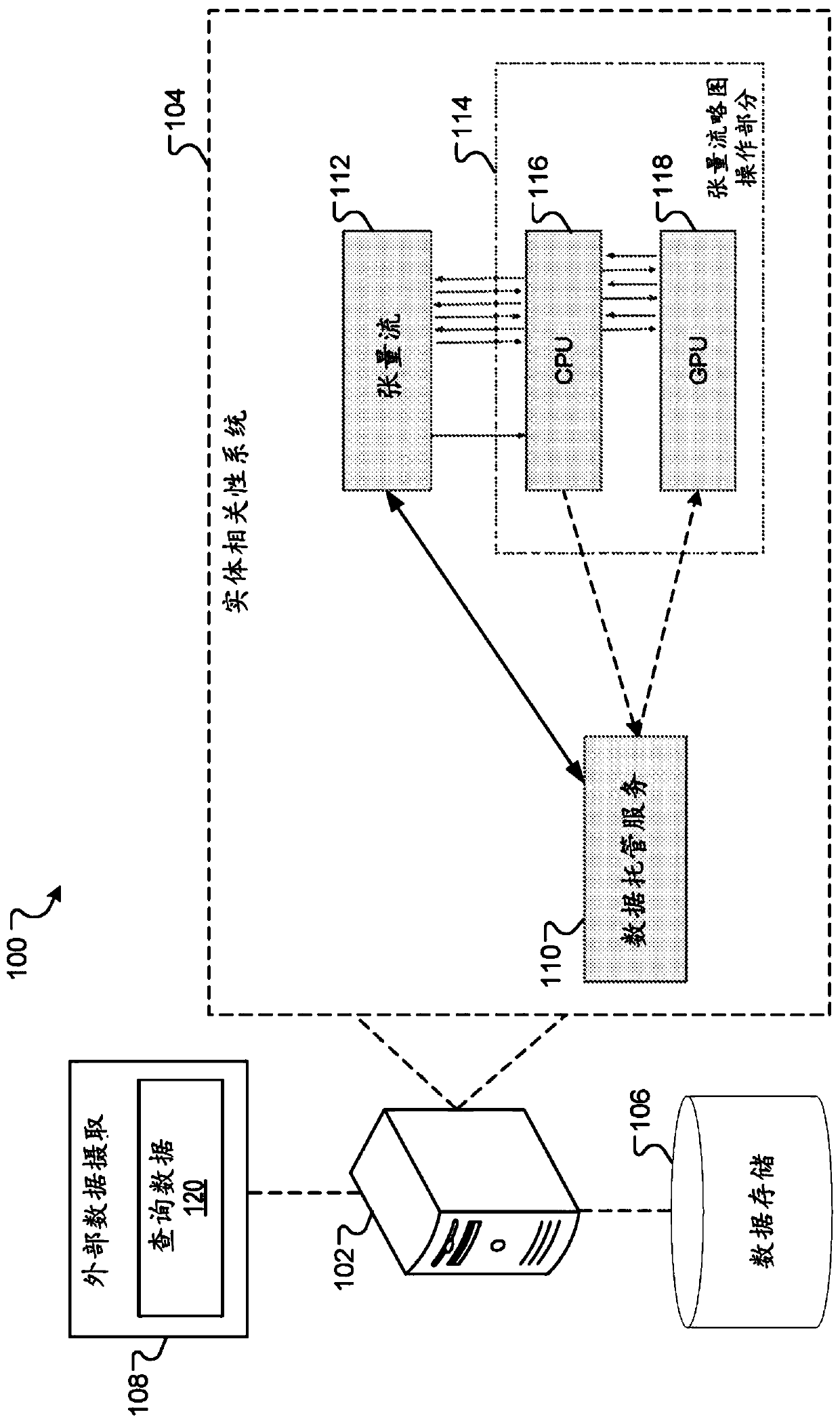
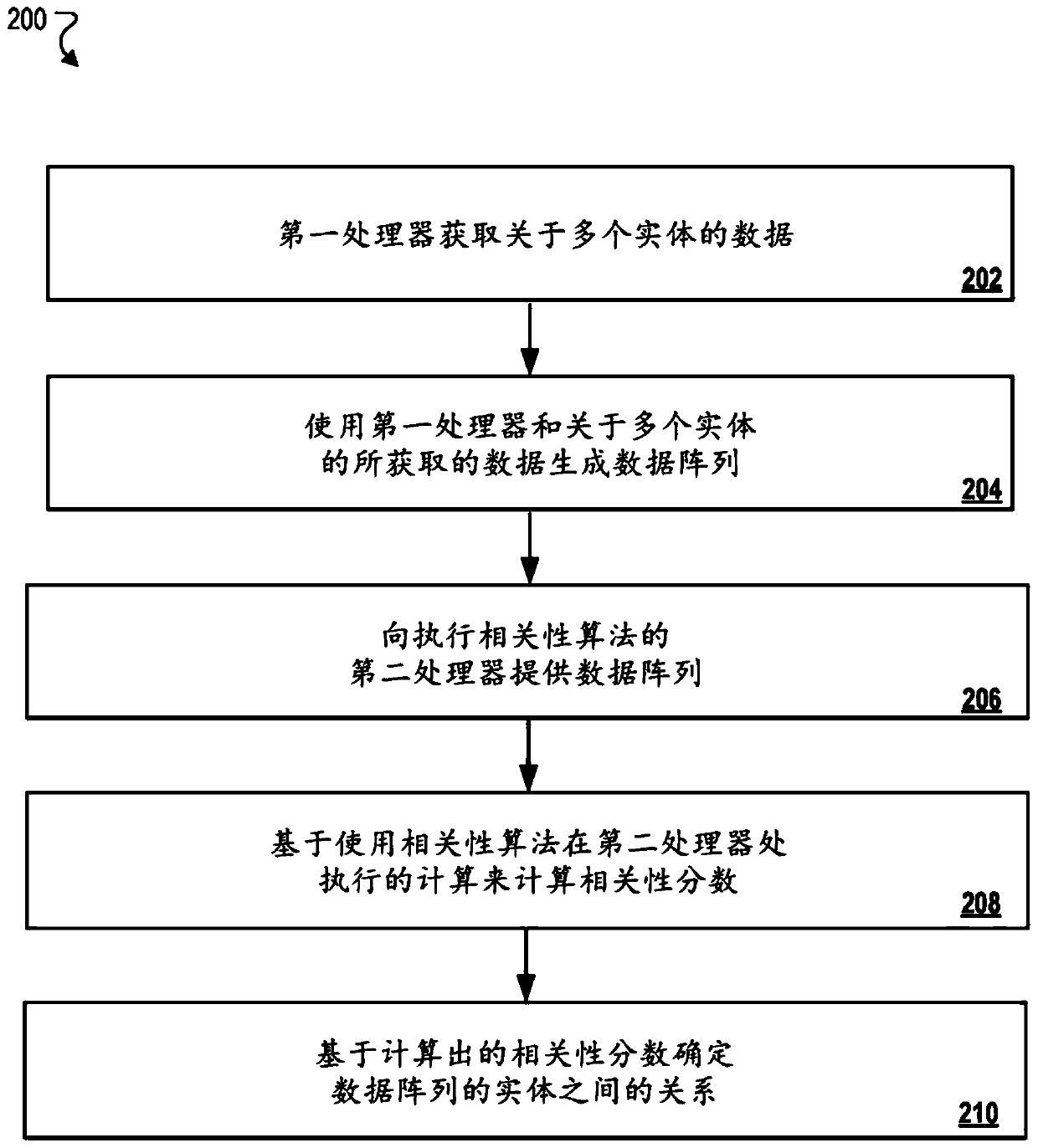
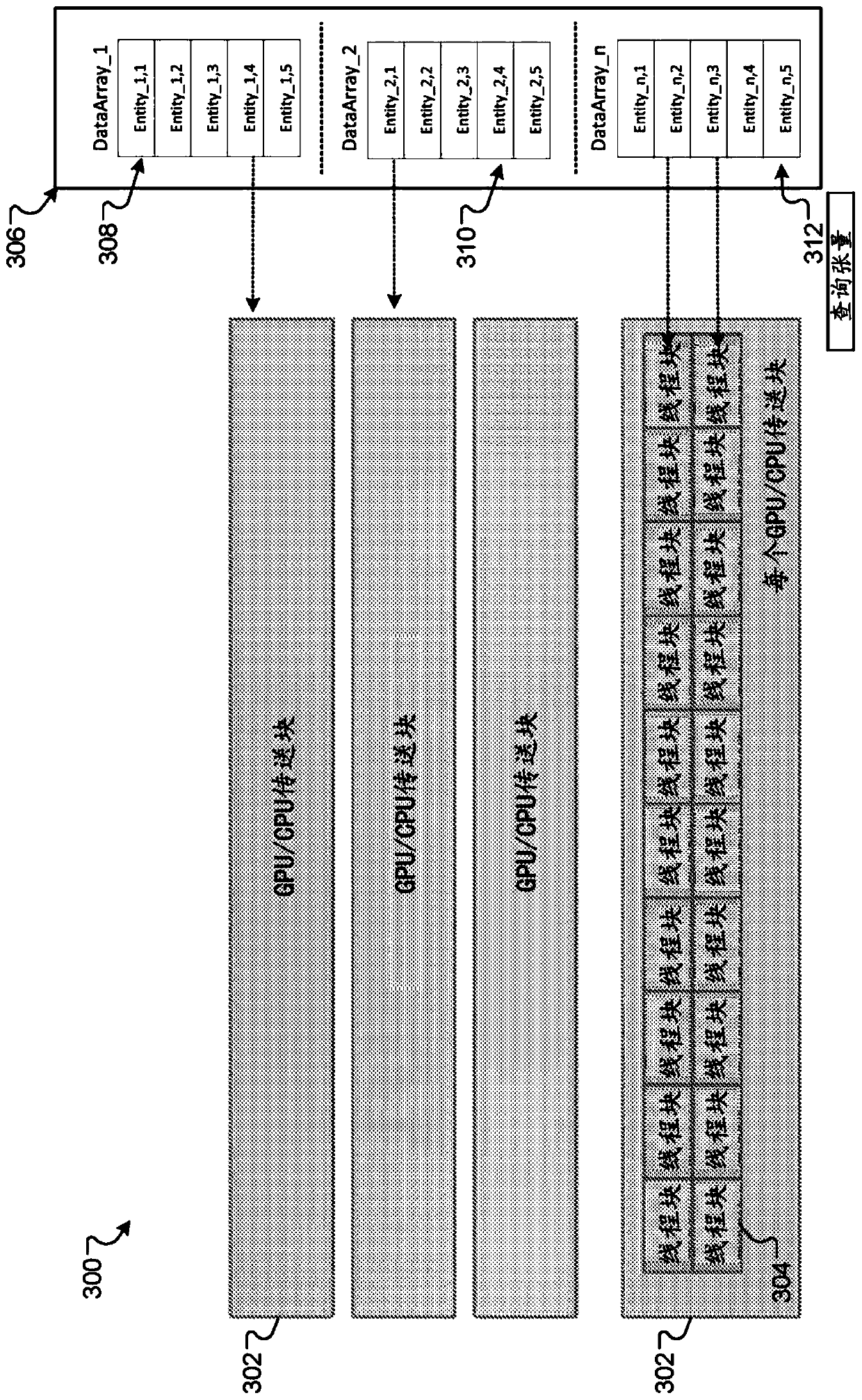
[0024] This document describes techniques for implementing a k-minimum hash or k-minimum value ("KMV") data processing algorithm to classify data preloaded at a graphics processing unit (GPU) to compute relationships between entities. Specifically, the described techniques can be used to accelerate data correlation calculations (e.g., for determining similarity between entities) by storing pre-sorted data on the GPU, so that the computing unit of the GPU can quickly determine the similarity between entities. relation. GPUs determine relationships by performing a specific type of correlation algorithm. Since the GPU is no longer required to pre-sort the data before performing the correlation algorithm, relationships can be computed or determined at the GPU at increased speed relative to current systems.
[0025] For example, entity correlation systems store large amounts of data including information describing different entities. The system may include a central processing u...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com