Anti-tigit antibodies
An antibody and antigen technology, applied in the direction of antibodies, antibody medical components, anti-tumor drugs, etc., can solve problems such as low affinity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
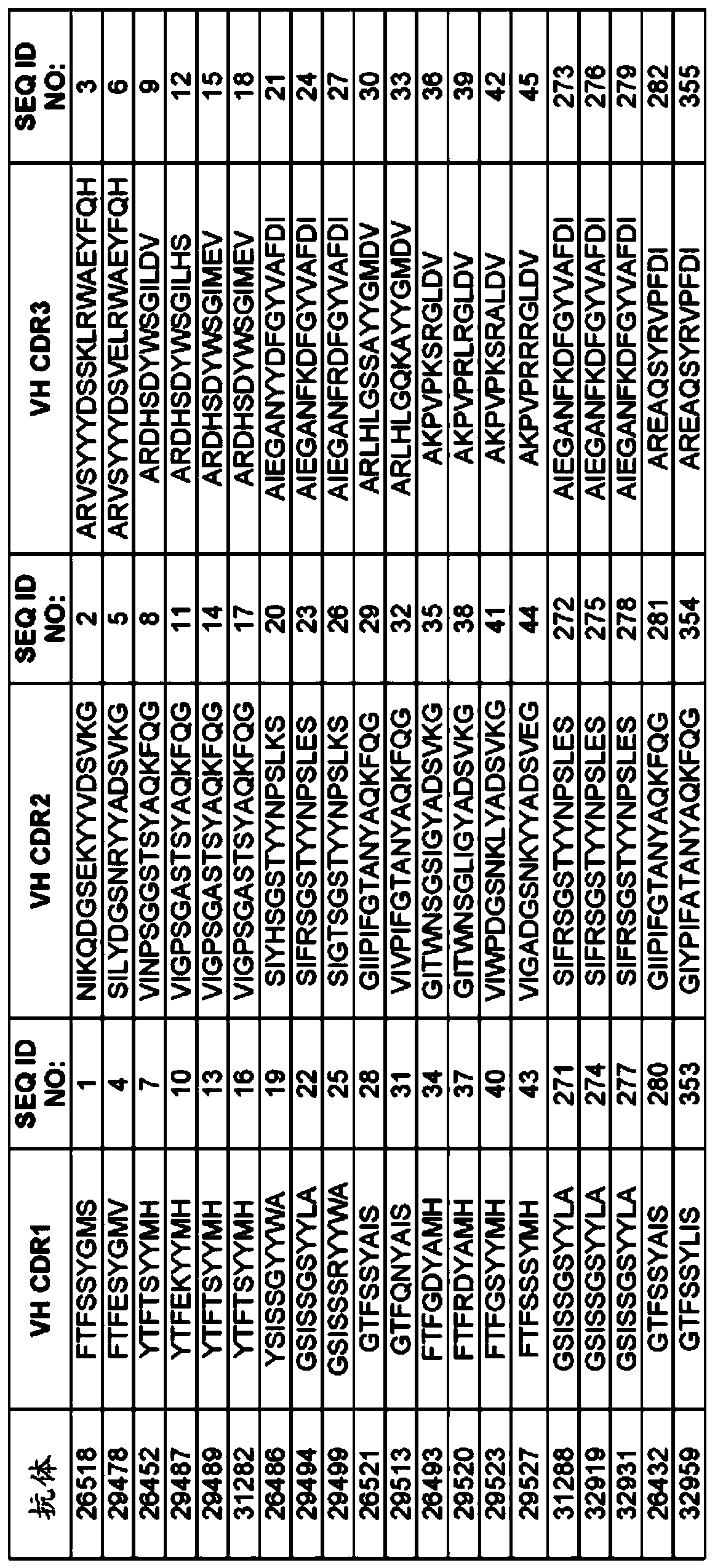
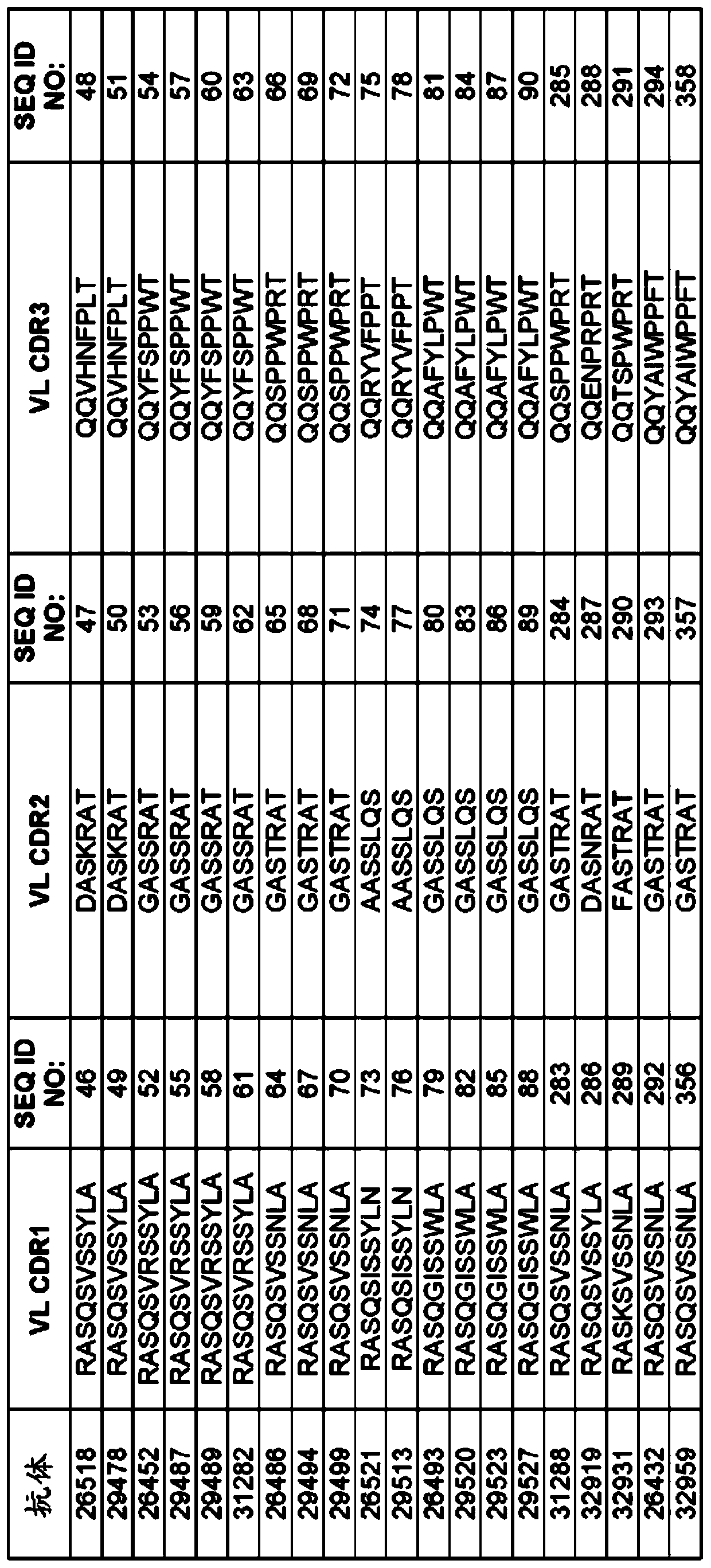
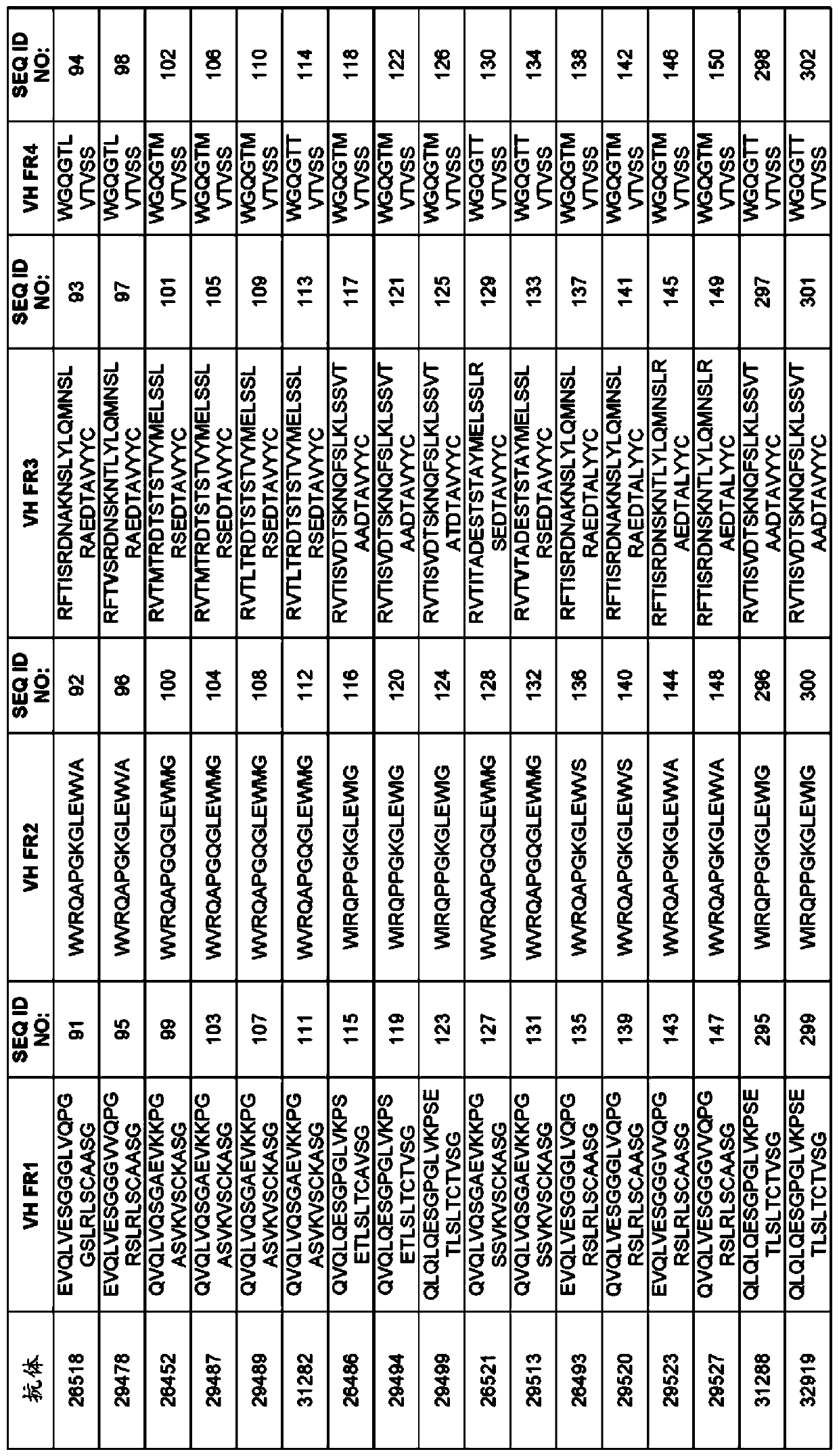
[0314] Example 1: Selection of TIGIT antigen binding protein
[0315] TIGIT ABP is selected from a synthetic library of human antibodies expressed and presented on the surface of yeast cells in the form of IgG, usually such as, for example, WO2009036379; WO2010105256; WO2012009568; and Xu et al., Protein Eng Des Sel., Vol. 26(10), No. 663 -As described on page 670 (2013), and more specifically as provided below. The sequence and characteristics of the ABP isolated from the recombinant library are provided in Figures 1 to 6.
[0316] As mentioned earlier, make eight each have ~10 9 Propagation of diverse primary human synthetic yeast libraries (see, for example, Xu et al., 2013; WO2009036379; WO2010105256 and WO2012009568). For the first two rounds of selection, as described (see, for example, Siegel et al., 2004), a magnetic bead sorting technique using the Miltenyi MACS system was performed. Simply put, the yeast cells (about ~ 10 10 Individual cells / library) were incubated with...
Embodiment 2
[0317] Example 2: Antibody optimization
[0318] Three maturation strategies were used to optimize the original clone: light chain diversification; HCDR1 and HCDR2 diversification; and HCDR3 diversification in the selected HCDR1 and HCDR2 diversity pool.
[0319] Light chain diversification: Extract the heavy chain variable region from the original output (as described above) and convert it to a diversity of 1 x 10 6 The light chain library. The selection was performed as described above, and one round of MACS sorting and three rounds of FACS sorting were performed, and 10 nM or 1 nM biotinylated TIGIT-HIS antigen (Creative Biomart) was used for each round.
[0320] HCDR1 and HCDR2 selection: Recombination of HCDR3 from clones selected from the light chain diversification program to have a diversity of 1 x 10 8 Pre-made libraries of HCDR1 and HCDR2 variants, and use monomeric HIS-TIGIT antigens for selection. Affinity pressure was applied by using decreasing concentrations of biot...
Embodiment 3
[0322] Example 3: Antibody production and purification
[0323] A. Produced in yeast
[0324] In order to generate a sufficient amount of optimized and non-optimized selected antibodies for further characterization, yeast clones were grown to saturation and then induced at 30°C for 48 hours with shaking. After induction, the yeast cells were pelleted, and the supernatant was harvested for purification. The IgG was purified using a protein A column and eluted with acetic acid at pH 2.0. Fab fragments are generated by papain digestion and purified in a two-step process of protein A (GE LifeSciences) and KappaSelect (GE Healthcare LifeSciences).
[0325] B. Produced in mammalian cells
[0326] In order to generate a sufficient amount of optimized and non-optimized selected antibodies for further characterization, a DNA vector encoding a specific antibody clone is generated and transduced into HEK cells. Order human codon-optimized synthetic DNA fragments of antibody variable domains a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com