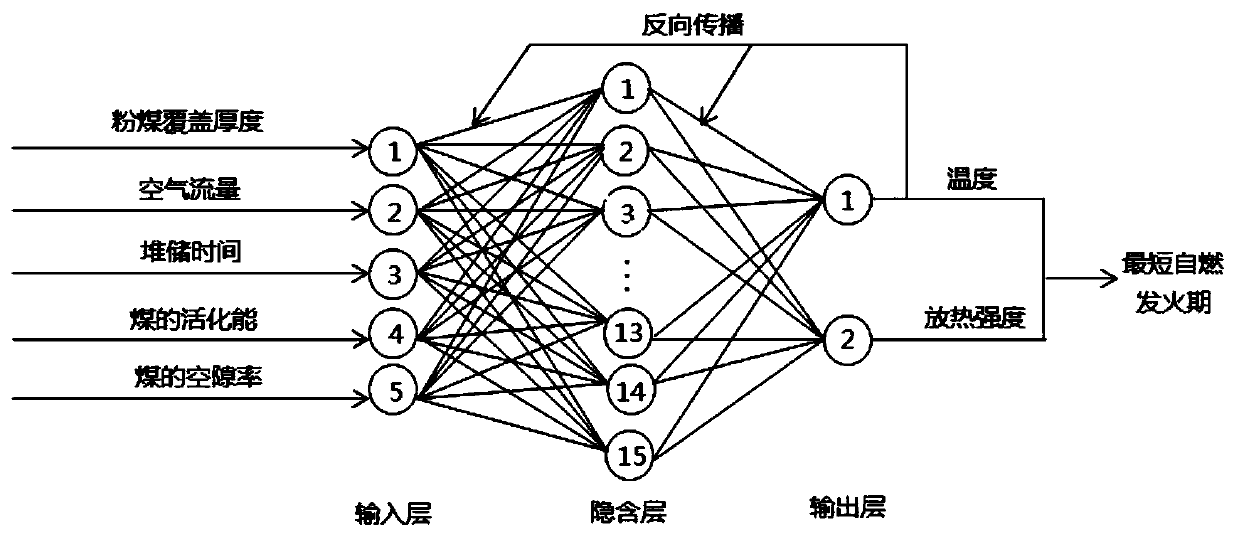
Method for predicting pulverized coal covered coal pile safe stacking and storing time by using neural network
A neural network and neural network model technology, applied in the field of coal spontaneous combustion prediction, can solve problems such as uncertainty and prediction lag, and achieve the effect of simple method and wide application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
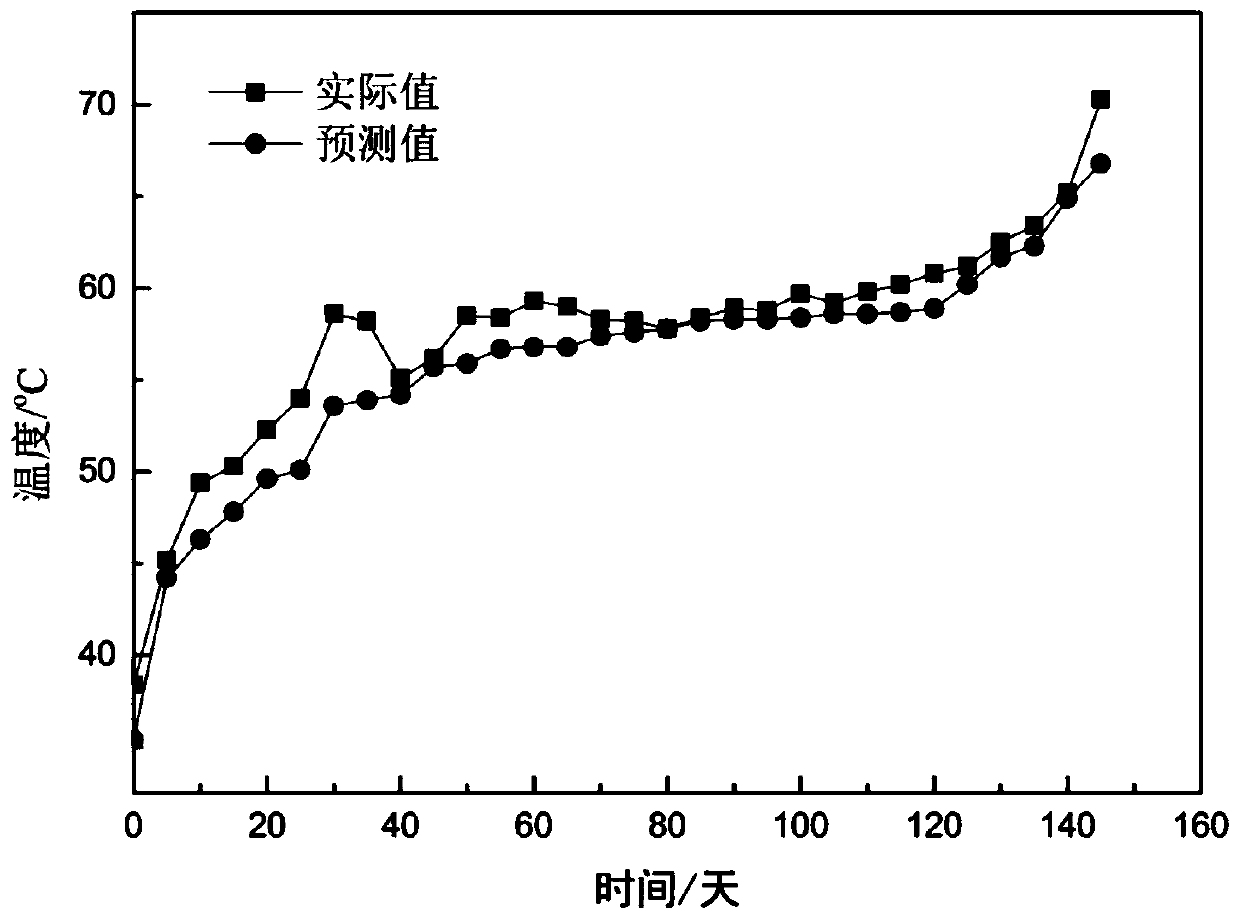
[0071] Select Shangwan coal with a diameter of 35m and a thickness of 70cm in the middle and lower part of the pulverized coal. The coal pile is stored in a fresh air flow (0.08cm / s) environment. The average porosity of the coal pile is 0.40, and the measuring point is selected at a distance of 2m from the ground. The coal oxide layer with a height and a depth of 1.5m is used as a measuring point for temperature and heat release intensity. The input data for the existing coal stockpile yields the output temperature and heat release intensity values. Table 1 is a comparison table of BP neural network prediction value and literature value of exothermic intensity. figure 2 It is a comparison chart of the predicted value of the BP neural network model of temperature and the measured value of the actual coal pile temperature. It can be seen from Table 1 that the value of the exothermic intensity predicted by the BP neural network fluctuates up and down from the average value of t...
Embodiment 2
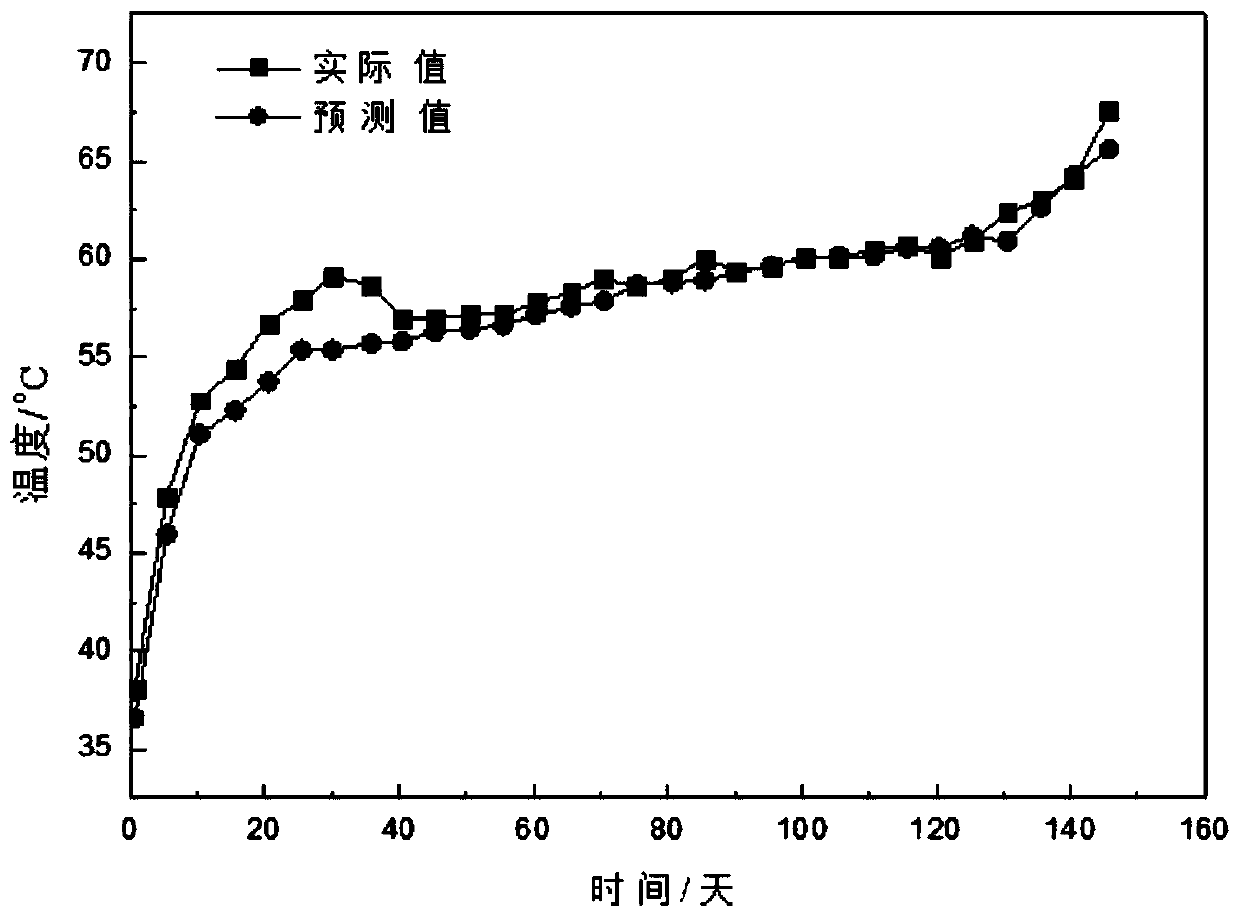
[0078] Select Yujialiang coal with a diameter of 35m and a thickness of 80cm in the middle and lower part of the pulverized coal. The coal pile is stored in a fresh air flow (0.08cm / s) environment. The average porosity of the coal pile is 0.45. The measuring point is selected at a distance from the ground The coal oxide layer with a height of 2m and a depth of 1.5m is used as a measuring point for temperature and heat release intensity. The input data for the existing coal stockpile yields the output temperature and heat release intensity values. Table 2 is a comparison table of the BP neural network prediction value and the literature value of the exothermic intensity. image 3 It is a comparison chart of the predicted value of the BP neural network model of temperature and the measured value of the actual coal pile temperature. It can be seen from Table 2 that the value of the exothermic intensity predicted by the BP neural network fluctuates up and down from the average va...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Ciyaowan coal with a diameter of 35m and a thickness of 90cm in the middle and lower part is selected. The coal pile is stored in a fresh air flow (0.08cm / s) environment. The average porosity of the coal pile is 0.48. The measuring point is selected at a distance of 2m from the ground. The coal oxide layer with a height and a depth of 1.5m is used as a measuring point for temperature and heat release intensity. The input data for the existing coal stockpile yields the output temperature and heat release intensity values. Table 3 is a comparison table of the BP neural network prediction value and the literature value of the exothermic intensity. Figure 4 It is a comparison chart of the predicted value of the BP neural network model of temperature and the measured value of the actual coal pile temperature. It can be seen from Table 3 that the value of the exothermic intensity predicted by the BP neural network fluctuates up and down from the average value of the exother...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com